中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (4): 582-586.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0094
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
减体积肝移植在大鼠脂肪肝供肝肝移植模型中的应用
赵英鹏,李 立,陈 刚,白建华,刘其雨
- 昆明市第一人民医院暨昆明医科大学附属甘美医院肝胆胰外科,云南省昆明市 650011
Reduced-size liver transplantation with fatty liver donors in a rat model
Zhao Ying-peng, Li Li, Chen Gang, Bai Jian-hua, Liu Qi-yu
- Department of Hepatobiliary and Transplantation Surgery, the First Hospital of Kunming & Affiliated Ganmei Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
摘要:
.jpg)
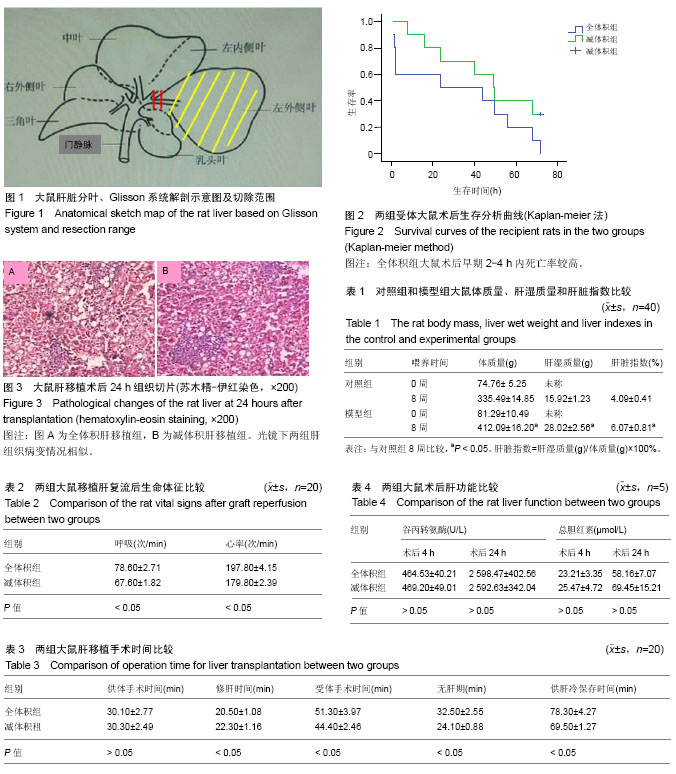
摘要 背景:肝移植供体缺乏,脂肪肝在人群中发病率高,中度以上脂肪肝作为边缘供体,肝移植后移植物丢失风险高,为提高这类供体利用率,需要建立稳定的大鼠模型作为研究对象。 目的:建立适合脂肪肝供肝的稳定大鼠减体积肝移植模型。 方法:随机各选取20对SD-SD脂肪肝供肝肝移植大鼠,全体积组行全体积原位肝移植术,减体积组行减体积肝移植术。供肝恢复灌流后,观察记录两组大鼠呼吸动度、呼吸频率、心跳及大血管充盈情况,术后观察大鼠恢复情况,解剖死亡大鼠了解死因;记录两组手术时间并作比较;两组大鼠术后进行生存分析;比较两组大鼠术后肝功能及病理组织学改变,评估差异性。 结果与结论:①供肝恢复灌注后,全体积组肝移植受体大鼠呼吸频率、心率快于减体积肝移植组受体大鼠 (P < 0.05),下腔静脉充盈情况相对较差;②减体积组受体大鼠术后一般情况恢复好于全体积组大鼠;③全体积组修肝时间短于减体积组,但受体手术时间明显长于减体积组(P < 0.05);全体积组受体大鼠术后早期死亡率明显高于减体积组,主要死亡原因是腹腔出血、空气栓塞和低血容量性休克;两组受体大鼠后续存活时间比较差异无显著性意义;④两组受体大鼠术后肝功能肝酶学和总胆红素总体差异无显著性意义,病理组织学表现相似;⑤综上,脂肪肝供肝大鼠减体积肝移植模型稳定可靠,解决了脂肪肝供肝全体积肝移植术中术野暴露不清、术后易致受体大鼠循环失稳的问题,是研究脂肪肝供肝肝移植的理想动物模型之一。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0002-4126-282X(赵英鹏)
中图分类号:
.jpg)