中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (4): 576-581.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0093
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
针刺“足三里”穴对脾虚证模型大鼠肠系膜淋巴结T淋巴细胞亚群的影响
曾荣华,周 露,欧阳厚淦,彭 珊,高书亮,汪建民,吴慧婷,欧阳彦楚,崔田田
- 江西中医药大学,江西省南昌市 330004
Effect of acupuncture at Zusanli on T lymphocyte subsets in mesenteric lymph nodes of spleen deficiency syndrome rats
Zeng Rong-hua, Zhou Lu, Ouyang Hou-gan, Peng Shan, Gao Shu-liang, Wang Jian-min, Wu Hui-ting, Ouyang Yan-chu, Cui Tian-tian
- Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
.jpg)
文题释义:
D-木糖:是一种戊糖, D-木糖口服后在小肠吸收后不被肝脏利用,不能在体内代谢,迅速从肾经尿液排出。在肝肾功能正常的情况下测定尿D-木糖排泄率,可反映机体对碳水化合物的吸收能力,故口服木糖后尿中排出量即反映小肠相对吸收量。
T淋巴细胞:是机体免疫系统内功能最重要的一大细胞群,在正常机体内各个T淋巴细胞亚群相互使用,维持着机体正常的免疫功能。T淋巴细胞亚群的分类方法最常用的是根据细胞表面标志,利用单克隆抗体将其分为不同功能亚群。抗CD3单抗与CD3抗原分子的ε链结合,是总T细胞的标志,抗CD4单抗与辅助/诱导功能T细胞反应,抗CD8单抗与抑制/细胞毒功能T细胞反应。T淋巴细胞表面有特异性标志,即T细胞分化抗原。用这种抗原已制备了近20种单克隆抗体。CD4细胞代表T辅助细胞(TH)CD8细胞是T抑制细胞(Ts)等。应用免疫组化染色,在显微镜下计数,计算某种亚群的百分数。
摘要
背景:肠道及相关淋巴组织是构成肠道免疫的重要组成部分,在以脾虚水液代谢障碍为主要消化道症状中肠道免疫起到了重要的调节作用。
目的:观察针刺对脾虚症大鼠淋巴结组织T淋巴细胞亚群的影响,探讨脾虚与肠道黏膜免疫之间相关性及针刺治疗脾虚证的作用机制。
方法:选用36只雌性SD大鼠随机分为3组,模型组,针刺组,空白组。通过劳倦伤脾加饮食失节多因素复合法建立脾虚大鼠模型,造模31 d;造模成功后针刺组针刺大鼠双侧“足三里”穴;模型组自然恢复;空白组不予干预。造模期间及治疗期间检测各组大鼠尿D-木糖排泄率检测,治疗结束后,摘取小肠肠系膜淋巴结,免疫组织化学法观察大鼠肠系膜淋巴结T淋巴细胞亚群的变化。
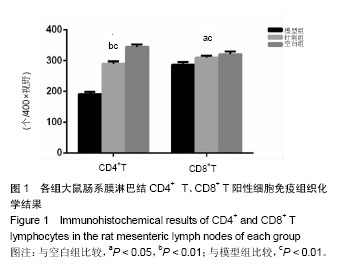
结果与结论:①在脾虚状态下模型组、针刺组相比空白组大鼠尿D-木糖排泄率明显降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),针刺治疗后针刺组尿D-木糖排泄率与模型组相比明显升高(P < 0.01),稍低于空白组(P < 0.05);②模型组、针刺组CD4+T淋巴细胞计数均低于空白组(P < 0.01);针刺组CD4+T巴细胞计数高于模型组(P < 0.01);③模型组CD8+T淋巴细胞计数明显低于空白组(P < 0.01);针刺组CD8+T淋巴细胞计略数低于空白组(P < 0.05),高于模型组(P < 0.01);④模型组和针刺组CD4+/CD8+T淋巴细胞比值明显低于空白组(P < 0.05),针刺组高于模型组(P < 0.01);⑤结果表明,针刺“足三里”穴能够提高脾虚证大鼠尿D-木糖排泄率,提高小肠的消化吸收能力,明显改善改善脾虚证大鼠纳差、便溏、泄泻等消化系统症状;调节脾虚证大鼠肠系膜淋巴结T淋巴细胞亚群的平衡,提高其肠道免疫功能,调整肠道消化功能紊乱状态,维持机体免疫耐受,调节机体免疫稳态。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-5263-4564(曾荣华)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)