| [1] 彭昊,陈森,郑慧锋,等.生物型假体全髋关节置换术治疗成人髋关节发育不良继发骨关节炎的疗效评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013,21(15):1502-1507.[2] 杨育晖,左建林,高忠礼.成人髋关节发育不良髋臼侧影像学评估的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(15):1390-1394.[3] 原林,高梁斌.髋关节的解剖和生物力学[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2001,3(2):146-147.[4] 许猛.CroweⅠ型发育不良髋臼月状面三维形态学分型及髋臼周围截骨术的有限元研究[J].长春:吉林大学,2017.[5] 傅明,张志奇,向珊珊,等.髋臼旋转截骨术及Chiari截骨术对发育性髋关节发育不良生物力学影响的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(6):641-644.[6] 赵明光,胡志刚,赵伟民.人体髋关节受力的建模与动力学仿真[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(33):332-333.[7] 张小兆,陈继营.全髋关节置换治疗成人发育性髋关节发育不良[J].实用骨科杂志,2017,23(8):720-723.[8] Brand RA. Hip Osteotomies: A biomechanical consideration. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1997;5(5):282-291.[9] Wenger DR, Bomar JD. Human hip dysplasia: evolution of current treatment concepts. J Orthop Sci. 2003;8(2):264-271.[10] Herman S, Jaklic A, Herman S, et al. Hip stress reduction after Chiari osteotomy. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2002;40(4):369-375.[11] Hipp JA, Sugano N, Millis MB, et al. Planning acetabular redirection osteotomies based on joint contact pressures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(364):134-143.[12] Santore R, Nelson FR, Muldoon M. Iliac crest bone-muscle transfer in periacetabular osteotomy. Orthopedics. 2000;23(3): 207-209.[13] Sanchez-Sotelo J, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ, et al. Surgical treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults: I. Nonarthroplasty options. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2002;10(5): 321-333.[14] Ganz R, Klaue K, Vinh TS, et al. A new periacetabular osteotomy for the treatment of hip dysplasias. Technique and preliminary results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;(232):26-36.[15] 杨建鑫,马超,张春林.生物力学测量与传统测量的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(24):4503-4506.[16] Keyak JH, Rossi SA, Jones KA, et al. Prediction of femoral fracture load using automated finite element modeling. J Biomech. 1998;31(2):125-133.[17] Brekelmans WA, Poort HW, Slooff TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317.[18] Vasu R, Carter DR, Harris WH. Stress distributions in the acetabular region--I. Before and after total joint replacement. J Biomech. 1982;15(3):155-164.[19] Koeneman JB, Hansen TM, Beris K. Three dimentional finite elements analysis of the hip joint. Trans ORS. 1989;14:223. [20] 汪金平,杨天府,钟凤林,等.股骨生物力学特性的有限元分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(10):931-934.[21] 马文辉,张学敏,王继芳.髋臼缺损有限元模型的建立及力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(43):8004-8007.[22] 崔旭,赵德伟,古长江.股骨头缺血性坏死塌陷预测的生物力学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2005,23(2):82-87.[23] 韩树洋,葛世荣.股骨头形状对人工髋关节力学行为影响的有限元分析[J].航天医学与医学工程,2010,23(5):367-370.[24] 李永奖,张力成,杨国敬,等.人工髋关节假体三维有限元模型构建及其生物力学意义[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2007,22(9):711-713.[25] 黄敏,廖广姗,周海,等.人工髋关节断柄失效的力学分析与推理(附专家点评)[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(2):171-177.[26] 张玉朵,张伟,王玉林,等.人工髋关节置换前后股骨及假体的生物力学分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(5):579-582.[27] 董方亮,付志厚.先天性髋关节脱位髋臼造盖术的研究现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(11):839-841.[28] 宋远征,赵建宁.应用特征性几何参数研究髋关节发育不良导致骨性关节炎的生物力学机制[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2012,17(1):77-79.[29] Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint. Acta Orthop Scand.1939(Suppl 58):131-132.[30] 赵德伟,田丰德.单纯髋臼前后缘发育不良的解剖学与临床研究.中国临床解剖学杂志,2008,26(1):101-104.[31] Lubovsky O, Peleg E, Joskowicz L, et al. Acetabular orientation variability and symmetry based on CT scans of adults. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2010;5(5):449-454 |
.jpg)
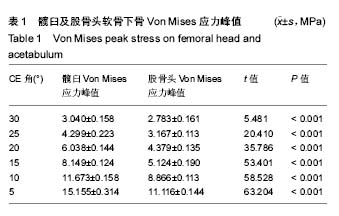
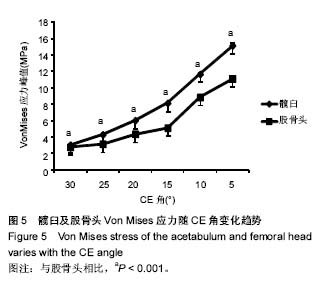
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)