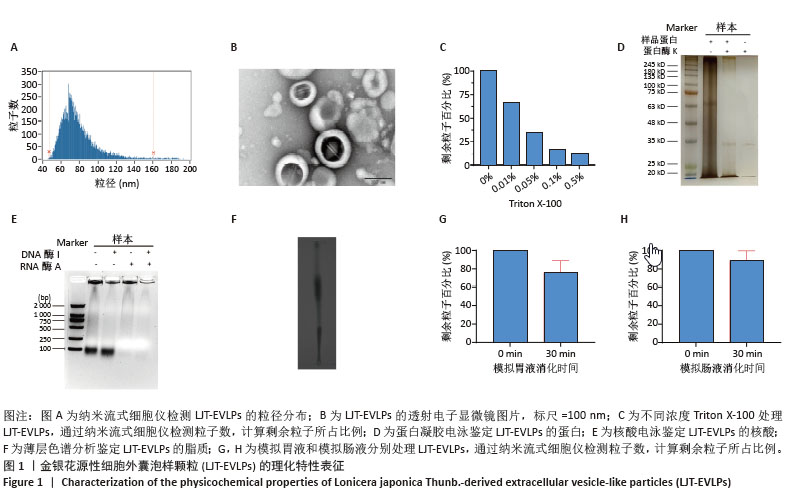
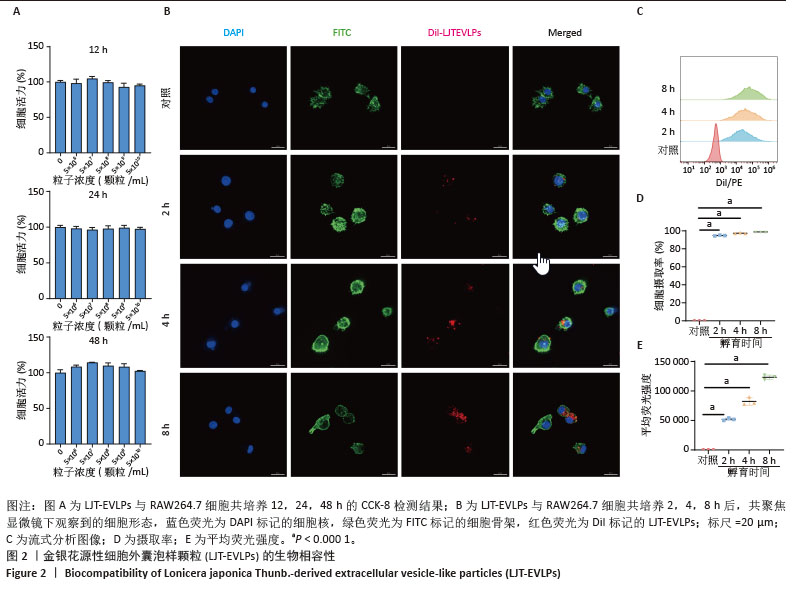
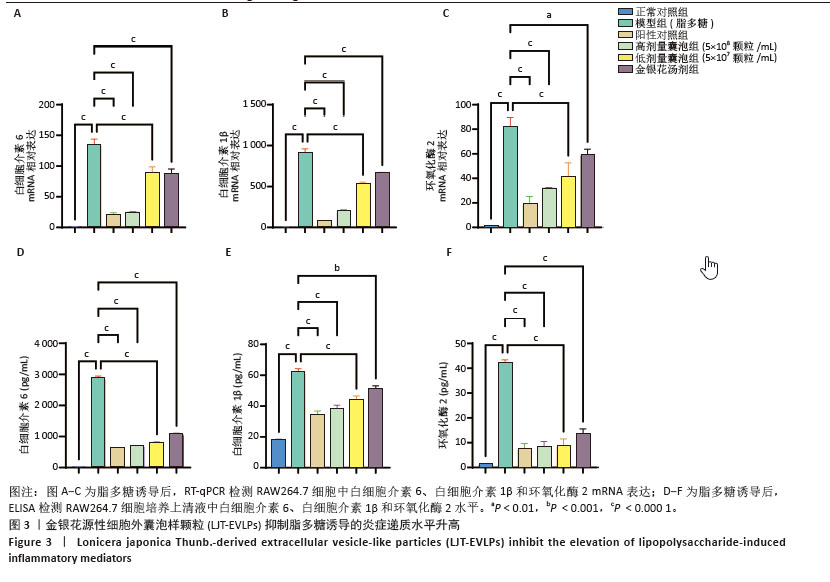
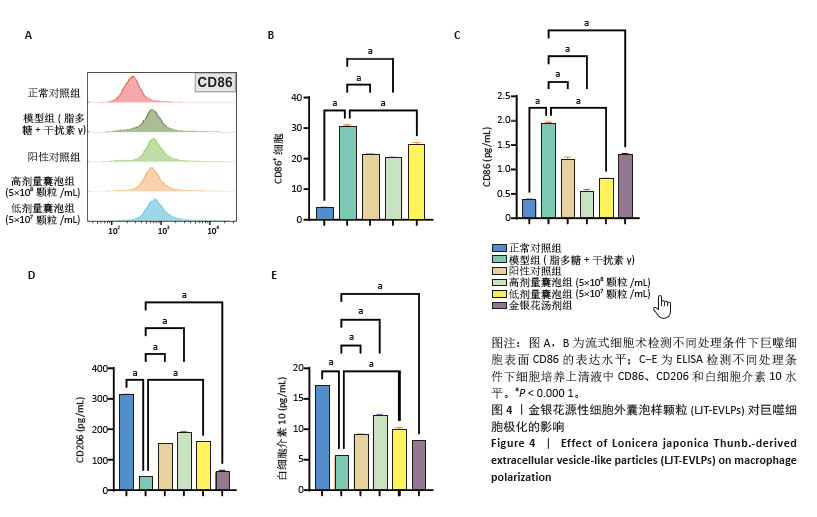
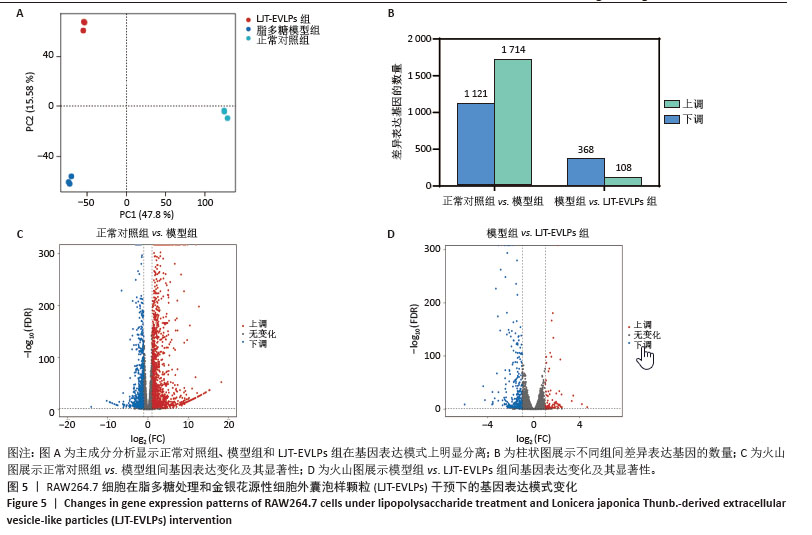
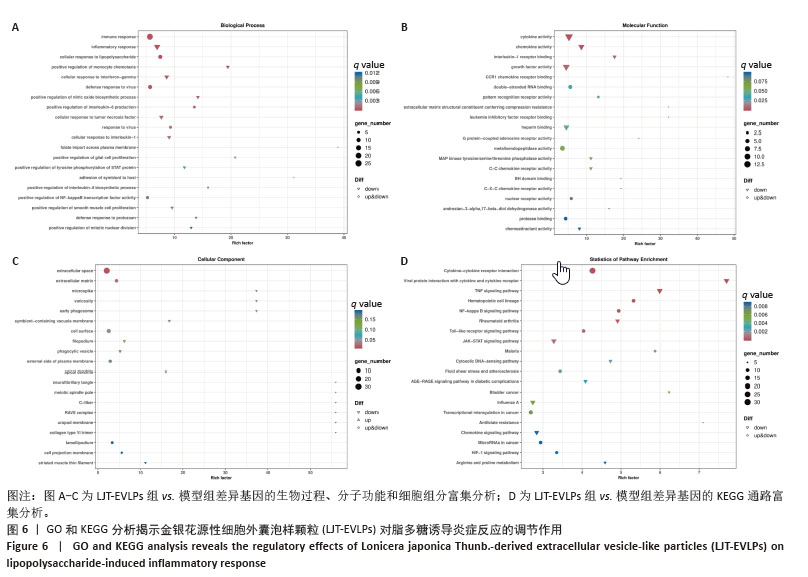
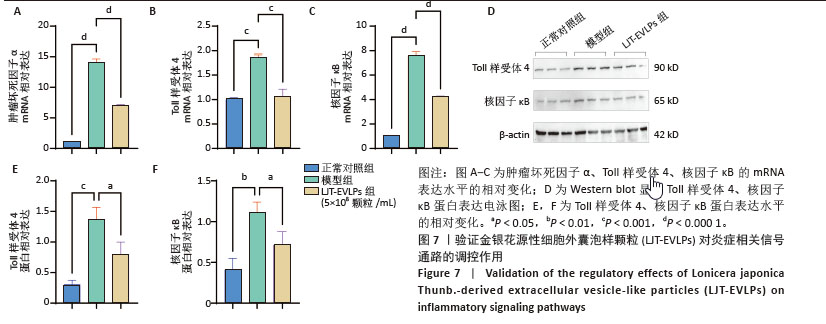
[1] SEMENZA GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and cardiovascular disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 2014;76:39-56.
[2] LIN A, MIANO JM, FISHER EA, et al. Chronic inflammation and vascular cell plasticity in atherosclerosis. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024;3(12):1408-1423.
[3] YAN Y, LI S, LIU Y, et al. Temporal relationship between inflammation and insulin resistance and their joint effect on hyperglycemia: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(1):109.
[4] COHEN J, MATHEW A, DOURVETAKIS KD, et al. Recent Research Trends in Neuroinflammatory and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells. 2024;13(6):511.
[5] HAJISHENGALLIS G, NETEA MG, CHAVAKIS T. Trained immunity in chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025; 25(7):497-514.
[6] SONG H, XIA M, ZHAO P, et al. Overexpression of TGFBR3 Aggravates Cognitive Impairment and Neuroinflammation by Promoting Microglia M1 Polarization in the APP/PS1 Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2025;62(6):7706-7722.
[7] SALIS Z, SAINSBURY A. Association of long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with knee osteoarthritis: a prospective multi-cohort study over 4-to-5 years. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):6593.
[8] CHO JH, SUH S. Glucocorticoid-Induced Hyperglycemia: A Neglected Problem. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024;39(2):222-238.
[9] CHI CC, WANG SH. Efficacy and cost-efficacy of biologic therapies for moderate to severe psoriasis: a meta-analysis and cost-efficacy analysis using the intention-to-treat principle. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:862851.
[10] DAI C, LIU Y, LV F, et al. An alternative approach to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria: new insights into traditional Chinese medicine monomers combined with antibiotics. Adv Biotechnol (Singap). 2025; 3(1):6.
[11] SHI Z, WANG Q, JIA F, et al. Pharmacological and toxicological effects of Jiangfangbaoxin and determination of its components in the blood of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):4934.
[12] 宋亚玲,王红梅,倪付勇,等.金银花中酚酸类成分及其抗炎活性研究[J].中草药,2015,46(4):490-495.
[13] 雷玲,李兴平,白筱璐,等.金银花抗内毒素、解热、抗炎作用研究[J].中药药理与临床,2012,28(1):115-117.
[14] 李康宁,宋志领,贾利龙,等.金银花提取物对LPS诱导的急性前部葡萄膜炎小鼠的抗炎作用及其机制 [J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2021,47(4):978-983.
[15] HUANG J, XIE M, HE L, et al. Chlorogenic acid: a review on its mechanisms of anti-inflammation, disease treatment, and related delivery systems. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1218015.
[16] MUKKAVILLI R, YANG C, SINGH TANWAR R, et al. Absorption, Metabolic Stability, and Pharmacokinetics of Ginger Phytochemicals. Molecules. 2017;22(4):553.
[17] 李坤艳.含绿原酸的清热解毒类中药注射剂不良反应及其机理探讨[J].中国卫生产业,2014,11(8):87-88.
[18] ZHAO Q, WANG T, WANG H, et al. Consensus statement on research and application of Chinese herbal medicine derived extracellular vesicles-like particles (2023 edition). Chin Herb Med. 2023;16(1):3-12.
[19] MU N, LI J, ZENG L, et al. Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles: Current Progress and Prospects. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18: 4987-5009.
[20] WANG X, XIN C, ZHOU Y, et al. Plant-Derived Vesicle-like Nanoparticles: The Next-Generation Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(5):588.
[21] MENG Y, GAO J, HUANG X, et al. Molecular Trojan Based on Membrane-Mimicking Conjugated Electrolyte for Stimuli-Responsive Drug Release. Adv Mater. 2025;37(12):e2415705.
[22] 王若宁,张迎洁,王笑红,等.不同来源细胞外囊泡在中药组分高效递送领域中应用的研究进展[J].中草药,2023,54(14):4672-4681.
[23] 吕品,李晓天.基于体外试验和网络药理学研究金银花抗炎抗菌活性及分子机制[J].中国现代应用药学,2021,38(14):1678-1685.
[24] KUMAR P, GOEL A, DASH B, et al. Innovations in Drug Delivery Systems for Biologics: Enhancing Stability and Targeted Delivery for Next-Generation Therapeutics. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2025;41:e20250001.
[25] MOHITE P, SULE S, PAWAR A, et al. Development and characterization of a self-nano emulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) for Ornidazole to improve solubility and oral bioavailability of BCS class II drugs. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):27724.
[26] PEINKOFER G, MAASS M, PFANNKUCHE K, et al. Persistence of intramyocardially transplanted murine induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes from different developmental stages. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):46.
[27] HUNTER AC. Molecular hurdles in polyfectin design and mechanistic background to polycation induced cytotoxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58(14):1523-1531.
[28] MOGHIMI SM, SYMONDS P, MURRAY JC, et al. A two-stage poly(ethylenimine)-mediated cytotoxicity: implications for gene transfer/therapy. Mol Ther. 2005;11(6):990-995.
[29] WANG Y, WANG Z, XIE K, et al. High-Efficiency Cellular Reprogramming by Nanoscale Puncturing. Nano Lett. 2020;20(7):5473-5481.
[30] BOKKA R, RAMOS AP, FIUME I, et al. Biomanufacturing of Tomato-Derived Nanovesicles. Foods. 2020;9(12):1852.
[31] BRUNO SP, PAOLINI A, D’ORIA V, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Citrus sinensis Modulate Inflammatory Genes and Tight Junctions in a Human Model of Intestinal Epithelium. Front Nutr. 2021;8:778998.
[32] POCSFALVI G, TURIÁK L, AMBROSONE A, et al. Protein biocargo of citrus fruit-derived vesicles reveals heterogeneous transport and extracellular vesicle populations. J Plant Physiol. 2018;229:111-121.
[33] JU S, MU J, DOKLAND T, et al. Grape exosome-like nanoparticles induce intestinal stem cells and protect mice from DSS-induced colitis. Mol Ther. 2013;21(7):1345-1357.
[34] XIAO Q, ZHAO W, WU C, et al. Lemon-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Nanodrugs Enable to Efficiently Overcome Cancer Multidrug Resistance by Endocytosis-Triggered Energy Dissipation and Energy Production Reduction. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(20):e2105274.
[35] ZHANG Z, YU Y, ZHU G, et al. The Emerging Role of Plant-Derived Exosomes-Like Nanoparticles in Immune Regulation and Periodontitis Treatment. Front Immunol. 2022;13:896745.
[36] CUI Y, GAO J, HE Y, et al. Plant extracellular vesicles. Protoplasma. 2020;257(1):3-12.
[37] FENG J, XIU Q, HUANG Y, et al. Plant-Derived Vesicle-Like Nanoparticles as Promising Biotherapeutic Tools: Present and Future. Adv Mater. 2023;35(24):e2207826.
[38] CONG M, TAN S, LI S, et al. Technology insight: Plant-derived vesicles-How far from the clinical biotherapeutics and therapeutic drug carriers? Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;182:114108.
[39] DAD HA, GU TW, ZHU AQ, et al. Plant Exosome-like Nanovesicles: Emerging Therapeutics and Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms. Mol Ther. 2021;29(1):13-31.
[40] PINEDO M, DE LA CANAL L, DE MARCOS LOUSA C. A call for Rigor and standardization in plant extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(6):e12048.
[41] ZHANG M, VIENNOIS E, PRASAD M, et al. Edible ginger-derived nanoparticles: A novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Biomaterials. 2016;101:321-340.
[42] ZHUANG X, DENG ZB, MU J, et al. Ginger-derived nanoparticles protect against alcohol-induced liver damage. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:28713.
[43] LIU C, YAN X, ZHANG Y, et al. Oral administration of turmeric-derived exosome-like nanovesicles with anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving bioactions for murine colitis therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):206.
[44] GAO C, ZHOU Y, CHEN Z, et al. Turmeric-derived nanovesicles as novel nanobiologics for targeted therapy of ulcerative colitis. Theranostics. 2022;12(12):5596-5614.
[45] ZHENG S, LIU S, HOU A, et al. Systematic review of Lonicerae Japonicae Flos: A significant food and traditional Chinese medicine. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1013992.
[46] MA P, YUAN L, JIA S, et al. Lonicerae Japonicae Flos with the homology of medicine and food: a review of active ingredients, anticancer mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, quality control, toxicity and applications. Front Oncol. 2024;14:1446328.
[47] KWEON B, OH J, LIM Y, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Honeysuckle Leaf Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation on BV2 Microglia. Nutrients. 2024;16(22):3954.
[48] CHAI M, GAO B, WANG S, et al. Leveraging plant-derived nanovesicles for advanced nucleic acid-based gene therapy. Theranostics. 2025; 15(1):324-339.
[49] YOU JY, KANG SJ, RHEE WJ. Isolation of cabbage exosome-like nanovesicles and investigation of their biological activities in human cells. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(12):4321-4332.
[50] MAJUMDER J, TARATULA O, MINKO T. Nanocarrier-based systems for targeted and site specific therapeutic delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;144:57-77. |