[1] GUGLIELMOTTI MB, OLMEDO DG, CABRINI RL. Research on implants and osseointegration. Periodontol 2000. 2019; 79(1):178-189.
[2] BLANCO C, LIñARES A, DOPICO J, et al. Peri-implantitis, systemic inflammation, and dyslipidemia: a cross-sectional biochemical study. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2021;51(5):342-351.
[3] DIAZ P, GONZALO E, VILLAGRA LJG, et al. What is the prevalence of peri-implantitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):449.
[4] CATON JG, ARMITAGE G, BERGLUNDH T, et al. A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri‐implant diseases and conditions – Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;89(S1):S1-S8.
[5] NG E, TAY JRH, BALAN P, et al. Metagenomic sequencing provides new insights into the subgingival bacteriome and aetiopathology of periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2021; 56(2):205-218.
[6] BANU RAZA F, VIJAYARAGHAVALU S, KANDASAMY R, et al. Microbiome and the inflammatory pathway in peri-implant health and disease with an updated review on treatment strategies. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023;13(2):84-91.
[7] SHI Y, TONG Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Microbial profiles of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: Submucosal microbial dysbiosis correlates with disease severity. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2022;33(2):172-183.
[8] LI Y, LI X, GUO D, et al. Immune dysregulation and macrophage polarization in peri-implantitis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1291880.
[9] 刘官娟,宋娜,安哲庆,等.宏基因组学与种植体周围炎[J].中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(34):5511-5516.
[10] TSUKASAKI M, TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: evolving concepts in bone-immune interactions in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(10):626-642.
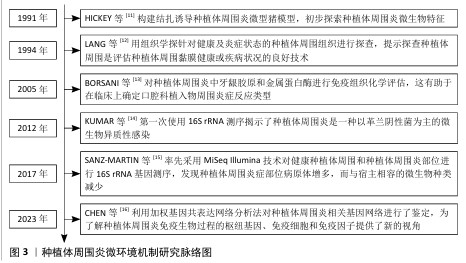
[11] HICKEY JS, O’NEAL RB, SCHEIDT MJ, et al. Microbiologic characterization of ligature-induced peri-implantitis in the microswine model. J Periodontol. 1991;62(9):548-553.
[12] LANG NP, WETZEL AC, STICH H, et al. Histologic probe penetration in healthy and inflamed peri-implant tissues. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994;5(4):191-201.
[13] BORSANI E, SALGARELLO S, MENSI M, et al. Histochemical and immunohistochemical evaluation of gingival collagen and metalloproteinases in peri-implantitis. Acta Histochem. 2005;107(3):231-240.
[14] KUMAR PS, MASON MR, BROOKER MR,
et al. Pyrosequencing reveals unique microbial signatures associated with healthy and failing dental implants. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(5):425-433.
[15] SANZ-MARTIN I, DOOLITTLE-HALL J, TELES RP, et al. Exploring the microbiome of healthy and diseased peri-implant sites using Illumina sequencing. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44(12):1274-1284.
[16] CHEN LW, JIN SH, LU Q, et al. Identification of immunological bioprocesses involved in peri-implantitis using weighted gene co-expression network analysis. J Periodontol. 2023;94(9):1078-1089.
[17] JAKUBOVICS NS, GOODMAN SD, MASHBURN-WARREN L, et al. The dental plaque biofilm matrix. Periodontol 2000. 2021;86(1):32-56.
[18] 文言,王宇蓝.菌斑生物膜与种植体周围炎相关研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2024, 32(9):730-736.
[19] DE MELO F, MILANESI FC, ANGST PDM, et al. A systematic review of the microbiota composition in various peri-implant conditions: data from 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Arch Oral Biol. 2020; 117:104776.
[20] ALVES CH, RUSSI KL, ROCHA NC, et al. Host-microbiome interactions regarding peri-implantitis and dental implant loss. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):425.
[21] CHOUDHARY P, SINGH S, AGARWAL V. Microbial Biofilms. 2020. doi:10.5772/intechopen.90790.
[22] WANG CW, ASHNAGAR S, GIANFILIPPO RD, et al. Laser-assisted regenerative surgical therapy for peri-implantitis: A randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2021; 9(23):378-388.
[23] SILVA-BOGHOSSIAN CM, DUARTE PT, SILVA DGD, et al. Colonization dynamics of subgingival microbiota in recently installed dental implants compared to healthy teeth in the same individual: a 6-month prospective observational study. J Appl Oral Sci. 2023;31:e20230134.
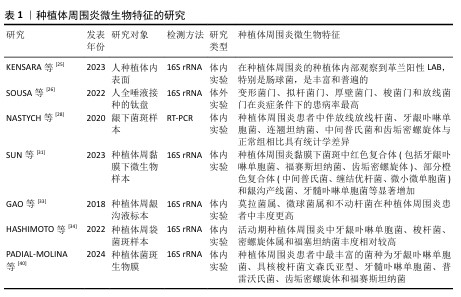
[24] KENSARA A, HEFNI E, WILLIAMS MA, et al. Microbiological Profile and Human Immune Response Associated with Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J Prosthodont. 2021; 30(3):210-234.
[25] KENSARA A, SAITO H, MONGODIN EF, et al. Microbiological profile of peri-implantitis: Analyses of microbiome within dental implants. J Prosthodont. 2023;32(9): 783-792.
[26] SOUSA V, SPRATT D, DAVRANDI M, et al. Oral Microcosm Biofilms Grown under Conditions Progressing from Peri-Implant Health, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(21):14088.
[27] BERGLUNDH T, ARMITAGE G, ARAUJO MG, et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45 Suppl 20:S286-s291.
[28] NASTYCH O, GONCHARUK-KHOMYN M, FOROS A, et al. Comparison of Bacterial Load Parameters in Subgingival Plaque during Peri-implantitis and Periodontitis Using the RT-PCR Method. Acta Stomatol Croat. 2020;54(1):32-43.
[29] GAZIL V, BANDIAKY ON, RENARD E, et al.
Current Data on Oral Peri-Implant and Periodontal Microbiota and Its Pathological Changes: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms. 2022;10(12):2466.
[30] DI SPIRITO F, GIORDANO F, DI PALO MP, et al. Microbiota of Peri-Implant Healthy Tissues, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis: A Comprehensive Review. Microorganisms. 2024;12(6):1137.
[31] SUN F, LIU J, LI SQ, et al. [Profiles and differences of submucosal microbial in peri-implantitis and health implants: A cross-sectional study]. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023;55(1):30-37.
[32] HEREKAR M, SETHI M, PRITHVIRAJ DR, et al. A Clinical Study Evaluating Changes in the Microbial Flora Around Dental Implants During Various Stages of Implant Restoration. Implant Dent. 2015;24(5): 527-532.
[33] GAO X, ZHOU J, SUN X, et al. Diversity analysis of subgingival microbial bacteria in peri-implantitis in Uygur population. Medicine Baltimore). 2018;97(5):e9774.
[34] HASHIMOTO Y, OKADA S, YASUDA K, et al.
Microbial differences between active and remission peri-implantitis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):5284.
[35] BANU RAZA F, VIJAYARAGAVALU S, KANDASAMY R, et al. Microbiome and the inflammatory pathway in peri-implant health and disease with an updated review on treatment strategies. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023;13(2):84-91.
[36] DE ANDRADE KQ, ALMEIDA-DA-SILVA CLC, COUTINHO-SILVA R. Immunological Pathways Triggered by Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum: Therapeutic Possibilities? Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:7241312.
[37] BRENNAN CA, GARRETT WS. Fusobacterium nucleatum - symbiont, opportunist and oncobacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2019; 17(3):156-166.
[38] KRöGER A, HüLSMANN C, FICKL S, et al. The severity of human peri-implantitis lesions correlates with the level of submucosal microbial dysbiosis. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(12):1498-1509.
[39] BELIBASAKIS GN, MANOIL D. Microbial Community-Driven Etiopathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis. J Dent Res. 2021;100(1): 21-28.
[40] PADIAL-MOLINA M, MONTALVO-ACOSTA S, MARTíN-MORALES N, et al. Correlation between Inflammasomes and Microbiota in Peri-Implantitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(2):961.
[41] ALBREKTSSON T, WENNERBERG A. On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019; 21 Suppl 1:4-7.
[42] SARTORETTO SC, CALASANS-MAIA J, RESENDE R, et al. The Influence of Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite Surface in the Early Stages of Osseointegration: A Multiparameter Animal Study in Low-Density Bone. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15: 8803-8817.
[43] MARIANI E, LISIGNOLI G, BORZì RM, et al.
Biomaterials: Foreign Bodies or Tuners for the Immune Response? Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):636.
[44] CHEN X, ZHAO Y. Genetic Involvement in Dental Implant Failure: Association With Polymorphisms of Genes Modulating Inflammatory Responses and Bone Metabolism. J Oral Implantol. 2019;45(4): 318-326.
[45] 尹昭懿,李效宇,王子璇,等.免疫反应在种植体周围炎中的作用研究进展[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2022,36(1):46-50.
[46] SARAVIA J, CHAPMAN NM, CHI H. Helper T cell differentiation. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019;16(7):634-643.
[47] MANSOORI MN, SHUKLA P, KAKAJI M, et al.
IL-18BP is decreased in osteoporotic women: Prevents Inflammasome mediated IL-18 activation and reduces Th17 differentiation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33680.
[48] YOU L, CHEN L, PAN L, et al. SOST Gene Inhibits Osteogenesis from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Inducing Th17 Cell Differentiation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(3):1030-1040.
[49] ZHU L, HUA F, DING W, et al. The correlation between the Th17/Treg cell balance and bone health. Immun Ageing. 2020;17:30.
[50] 吴东潮,何东宁,余飞燕,等.种植体周围炎免疫应答机制的研究进展[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2024,25(5):371-377,388.
[51] 钱治,仲泽远,崔元斌,等.T细胞与骨代谢[J].中国免疫学杂志,2021,37(11):7.
[52] SUN L, FU J, ZHOU Y. Metabolism Controls the Balance of Th17/T-Regulatory Cells. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1632.
[53] CAFFERATA EA, CASTRO-SAAVEDRA S, FUENTES-BARROS G, et al. Boldine inhibits the alveolar bone resorption during ligature-induced periodontitis by modulating the Th17/Treg imbalance. J Periodontol. 2021; 92(1):123-136.
[54] 廖安琪,杨仁丽,杨醒眉.种植体周围炎的免疫应答机制及其影响因素的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2021,41(12):1143-1147.
[55] TSAI DY, HUNG KH, CHANG CW, et al. Regulatory mechanisms of B cell responses and the implication in B cell-related diseases. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26(1):64.
[56] HAN Y, JIN Y, MIAO Y, et al. Improved RANKL expression and osteoclastogenesis induction of CD27+CD38- memory B cells: A link between B cells and alveolar bone damage in periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2019;54(1):73-80.
[57] FUJIWARA Y, PIEMONTESE M, LIU Y, et al. RANKL Receptor Activator of NFκB Ligand) Produced by Osteocytes Is Required for the Increase in B Cells and Bone Loss Caused by Estrogen Deficiency in Mice. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(48):24838-24850.
[58] 林晓萍,韩亚琨.B细胞骨免疫在牙周炎中的作用[J].口腔疾病防治,2020,28(4): 205-213.
[59] 韦雨杏,董皓,韦惠平,等.种植体周围炎炎性组织差异表达基因的筛选及验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30): 4844-4849.
[60] TOBEIHA M, MOGHADASIAN MH, AMIN N, et al. RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway: A Mechanism Involved in Exercise-Induced Bone Remodeling. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:6910312.
[61] GALARRAGA-VINUEZA ME, OBREJA K, RAMANAUSKAITE A, et al. Macrophage polarization in peri-implantitis lesions. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(4):2335-2344.
[62] CHENG X, ZHOU X, LIU C, et al. Oral Osteomicrobiology: The Role of Oral Microbiota in Alveolar Bone Homeostasis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:751503.
[63] THEODORIDIS C, DOULKERIDOU C, MENEXES G, et al. Comparison of RANKL and OPG levels in peri-implant crevicular fluid between healthy and diseased peri-implant tissues. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. 2022; 26(1):823-836.
[64] CALLEJAS JA, GIL J, BRIZUELA A, et al. Effect of the Size of Titanium Particles Released from Dental Implants on Immunological Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7333.
[65] ZHOU F, ZHANG G, WU Y, et al. Inflammasome Complexes: Crucial mediators in osteoimmunology and bone diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022; 110:109072.
[66] BASERI M, RADMAND F, HAMEDI R, et al.
Immunological Aspects of Dental Implant Rejection. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020: 7279509.
[67] SUGISAKI R, MIYAMOTO Y, YOSHIMURA K, et al. Possible involvement of elastase in enhanced osteoclast differentiation by neutrophils through degradation of osteoprotegerin. Bone. 2020;132:115216.
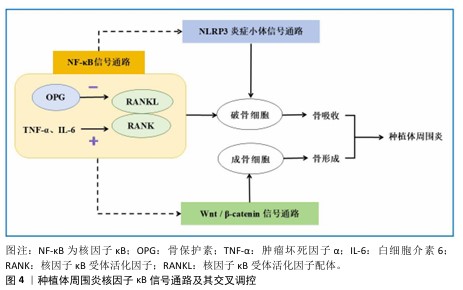
[68] 霍花,宋斌,廖健.种植体周病的相关信号通路机制及其交互调控作用[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2024,4(5):310-314.
[69] HU L, CHEN W, QIAN A, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling components and mechanisms in bone formation, homeostasis, and disease. Bone Res. 2024;12(3):469-501.
[70] APPELMAN-DIJKSTRA NM, PAPAPOULOS SE. Clinical advantages and disadvantages of anabolic bone therapies targeting the WNT pathway. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(10):605-623.
[71] ZHANG Q, LIU J, MA L, et al. Wnt5a is involved in LOX-1 and TLR4 induced host inflammatory response in peri-implantitis. J Periodontal Res. 2020;55(2):199-208.
[72] SUI X, DENG S, LIU M, et al. Constitutive Activation of β-Catenin in Differentiated Osteoclasts Induces Bone Loss in Mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):2091-2102.
[73] AMIN N, BOCCARDI V, TAGHIZADEH M, et al. Probiotics and bone disorders: the role of RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(3):363-371.
[74] ARAL K, BERDELI E, COOPER P, et al. Differential expression of inflammasome regulatory transcripts in periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 2019;91:606-616.
[75] 李碧榕,孟维艳.NLRP3炎症小体在种植体周围炎中的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2022,38(12):1119-1123.
[76] 李小红,郝志军,许应宏,等.牙种植修复术后感染对NLRP3信号通路及炎症细胞因子水平的影响[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2022,32(8):1185-1188.
[77] GALINDO-MORENO P, MONTALVO-ACOSTA S, MARTíN-MORALES N, et al. Inflammasomes NLRP3 and AIM2 in peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2023;34(12):1342-1353.
[78] XU W, LU Y, YUE J, et al. Occlusal trauma inhibits osteoblast differentiation and bone formation through IKK-NF-κB signaling. J Periodontol. 2020;91(5):683-692.
[79] YAO L, HUANG C, DAI J. Staphylococcus aureus enhances osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by stimulating the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(11):9395-9403. |