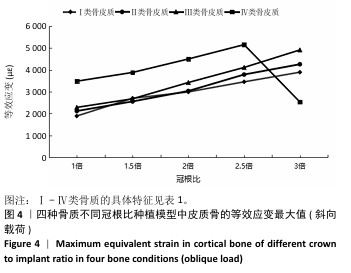
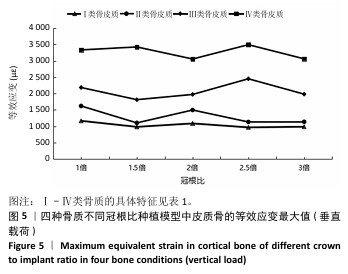
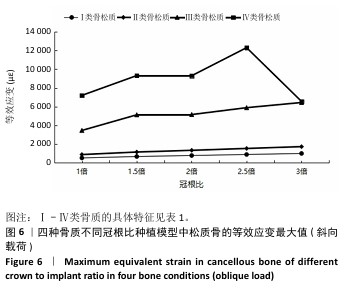
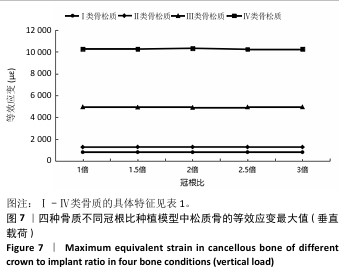
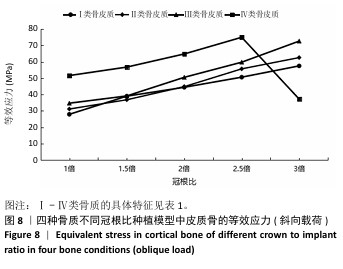
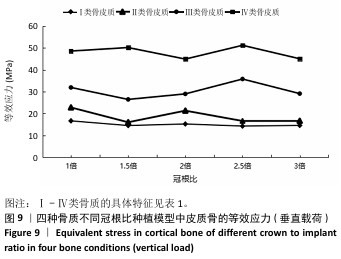
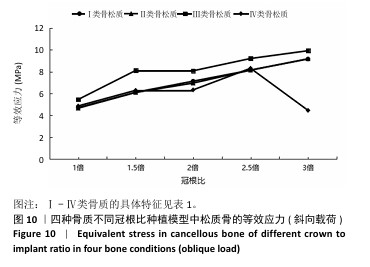
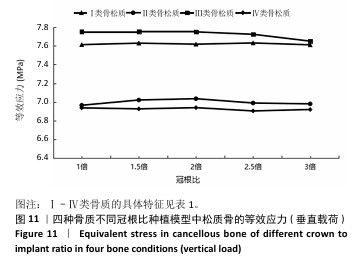
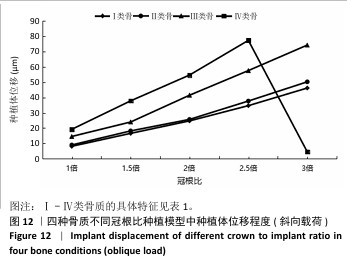
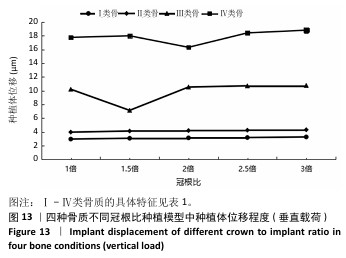
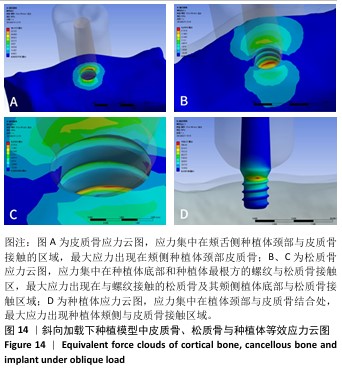
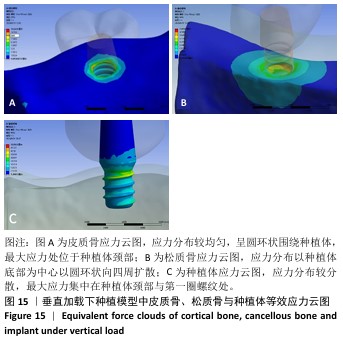
[1] 路泊遥,杨大维,刘蔚晴,等.超短种植体临床应用效果的影响因素[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2021,48(3):329-333.
[2] 秦思琪,王岚,高志.短种植体的临床研究进展[J].现代医药卫生, 2022,38(20):3493-3498.
[3] YUAN X, LIU Y, YANG Y, et al. Effect of short implant crown-to-implant ratio on stress distribution in anisotropic bone with different osseointegration rates. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):683.
[4] GOMES JML, LIMÍRIO JPJO, LEMOS CAA, et al. Response to the “Letter to the Editor” regarding the article: Pellizzer EP, et al. The influence of crown-to-implant ratio in single crowns on clinical outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prosthet Dent 2021;126:497-502. J Prosthet Dent. 2022;127(3):524-525.
[5] PICCININI M, CUGNONI J, BOTSIS J, et al. Numerical prediction of peri-implant bone adaptation: Comparison of mechanical stimuli and sensitivity to modeling parameters. Med Eng Phys. 2016;38(11): 1348-1359.
[6] MEIJER HJA, BOVEN C, DELLI K, et al. Is there an effect of crown-to-implant ratio on implant treatment outcomes? A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29 Suppl 18(Suppl Suppl 18):243-252.
[7] HAUSMANN DW, HAHMANN M, MOGK M, et al. Influence of Crown-to-Implant Ratio on Crestal Bone Loss at Implants with Single Crowns and Bridges: A 5- to 20-Year Long-Term Cohort Study in Patients with Periodontal Disease. Int J Prosthodont. 2024;(3):245-252.
[8] YE Z, YE H, WU Y, et al. Effect of bone mass density and alveolar bone resorption on stress in implant restoration of free-end edentulous posterior mandible: Finite element analysis of double-factor sensitivity. Ann Anat. 2024;253:152210.
[9] WANG SH, SHEN YW, FUH LJ, et al. Relationship between Cortical Bone Thickness and Cancellous Bone Density at Dental Implant Sites in the Jawbone. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(9):710.
[10] OLIVEIRA MR, GONÇALVES A, GABRIELLI MAC, et al. Evaluation of Alveolar Bone Quality: Correlation Between Histomorphometric Analysis and Lekholm and Zarb Classification. J Craniofac Surg. 2021; 32(6):2114-2118.
[11] DE MATOS JDM, LOPES G, NAKANO LJN, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of 3-unit fixed partial dentures on monotype and two-piece zirconia dental implants. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2022;25(3):239-246.
[12] 孙江伟,王俊祥,白布加甫·叶力思,等.不同光滑颈圈种植体修复时应力分布的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(7):1004-1011.
[13] 徐远志,张富强,徐钦,等.上颌窦底不同位置冲顶对上颌窦内提升术影响的三维有限元分析[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2008, 29(5):71-75.
[14] LIU C, XING Y, LI Y, et al. Bone quality effect on short implants in the edentulous mandible: a finite element study. BMC Oral Health. 2022; 22(1):139.
[15] 热依拉·库尔班,霞黑达·依拉尔江,陈欣,等.超短种植体不同修复方式的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(30): 4824-4829.
[16] QIN S, GAO Z. Comparative evaluation of short or standard implants with different prosthetic designs in the posterior mandibular region: a three-dimensional finite element analysis study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2023;26(12):1499-1509.
[17] PANMEI G, KUMAR A, BASAK S, et al. Evaluation and Comparison of Stress in Divergent and Convergent Collar Designs of Implants With Different Bone Densities: A Finite Element Study. Cureus. 2023;15(3): e36550.
[18] YUAN JC, SUKOTJO C. Occlusion for implant-supported fixed dental prostheses in partially edentulous patients: a literature review and current concepts. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2013;43(2):51-57.
[19] WEINBERG LA. Reduction of implant loading using a modified centric occlusal anatomy. Int J Prosthodont. 1998;11(1):55-69.
[20] 陈佳文,罗思阳,刘印,等.骨质对右上第一磨牙种植修复体咬合调整影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(16): 2579-2586.
[21] FROST HM. Bone’s mechanostat: a 2003 update. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2003;275(2):1081-1101.
[22] FROST HM. A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians. Angle Orthod. 2004;74(1):3-15.
[23] 徐大鹏,景捷,马璐,等.基于种植牙愈合过程模拟上颌后牙种植体选择的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(25): 3942-3948.
[24] SáENZ-RAVELLO G, OSSANDÓN-ZÚÑIGA B, MUÑOZ-MEZA V, et al. Short implants compared to regular dental implants after bone augmentation in the atrophic posterior mandible: umbrella review and meta-analysis of success outcomes. Int J Implant Dent. 2023;9(1):18.
[25] MISCH CE. Consideration of biomechanical stress in treatment with dental implants. Dent Today. 2006;25(5):80,82,84-85;quiz 85.
[26] PELLIZZER EP, MARCELA DE LUNA GOMES J, ARAÚJO LEMOS CA, et al. The influence of crown-to-implant ratio in single crowns on clinical outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(4):497-502.
[27] 崔惠文.不同冠根比种植单冠修复体对口腔种植患者治疗效果的影响[J].中国实用医药,2024,19(6):56-59.
[28] SCHNEIDER D, WITT L, HÄMMERLE CHF. Influence of the crown-to-implant length ratio on the clinical performance of implants supporting single crown restorations: a cross-sectional retrospective 5-year investigation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(2):169-174.
[29] PAKZAD P, MOSAVAR A. A new look toward crown-to-implant ratio. Am J Dent. 2022;35(1):43-48.
[30] LEE H, JO M, SAILER I, et al. Effects of implant diameter, implant-abutment connection type, and bone density on the biomechanical stability of implant components and bone: A finite element analysis study. J Prosthet Dent. 2022;128(4):716-728.
[31] CHANG M, CHRONOPOULOS V, MATTHEOS N. Impact of excessive occlusal load on successfully-osseointegrated dental implants: a literature review. J Investig Clin Dent .2013;4(3):142-150.
[32] GUGLIELMOTTI MB, OLMEDO DG, CABRINI RL. Research on implants and osseointegration. Periodontol 2000. 2019;79(1):178-189.
[33] OVERMANN AL, APARICIO C, RICHARDS JT, et al.Orthopaedic osseointegration: Implantology and future directions. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(7):1445-1454.
[34] 赖春花,徐淑兰,许言,等.颌骨不同骨质区域对种植体表面的接触成骨的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2021,37(8):1008-1013.
[35] PAMMER D. Evaluation of postoperative dental implant primary stability using 3D finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(3):280-287.
[36] LI J, YIN X, HUANG L, et al. Relationships among Bone Quality, Implant Osseointegration, and Wnt Signaling. J Dent Res. 2017;96(7):822-831.
[37] ORLANDO F, AROSIO F, AROSIO P, et al. Bone Density and Implant Primary Stability. A Study on Equine Bone Blocks. Dent J (Basel). 2019; 7(3):73.
[38] 孜拉来·居来提,马吾兰江·阿不都仁木,艾克丽亚·艾尼瓦尔,等.不同骨质条件下超短种植体应用于下颌后牙区的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(22):4679-4686.
[39] BRUNSKI JB. Avoid pitfalls of overloading and micromotion of intraosseous implants. Dent Implantol Update. 1993;4(10):77-81. |