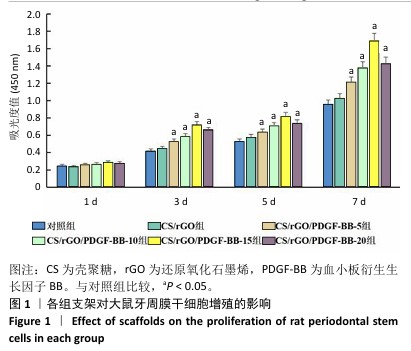
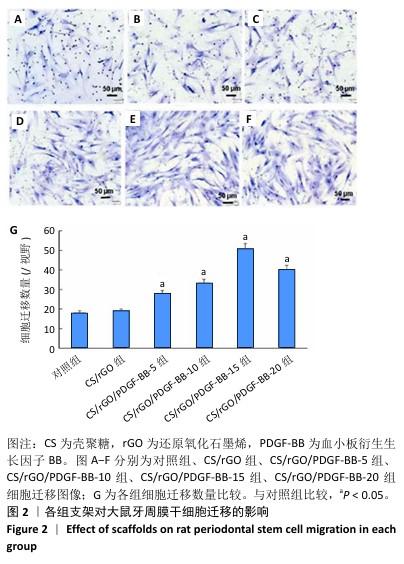
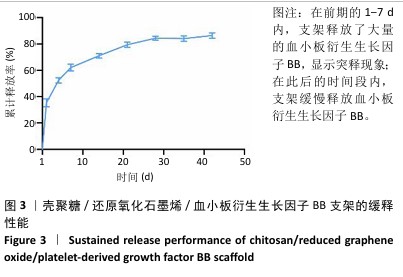
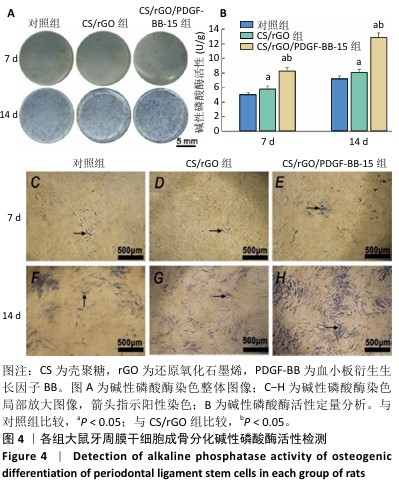
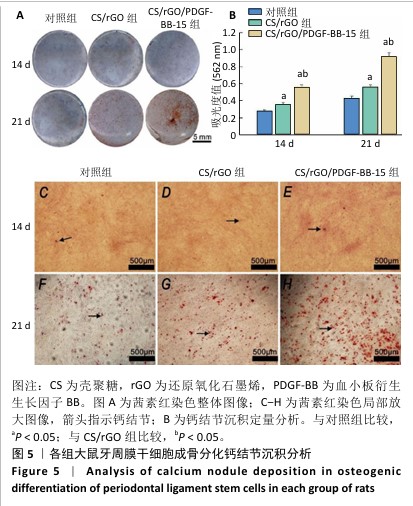
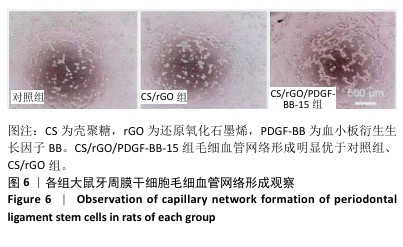
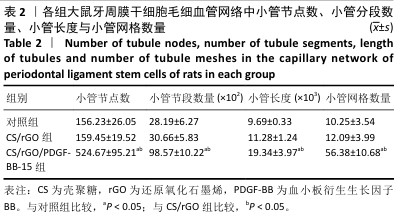
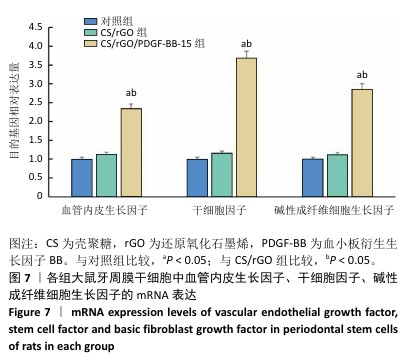
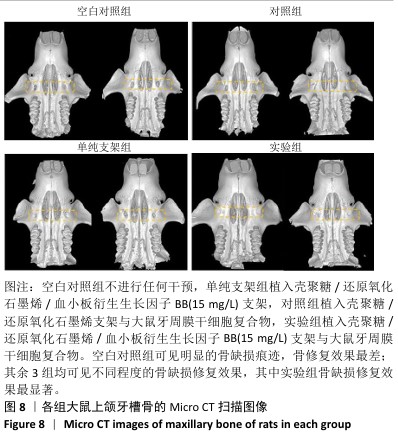
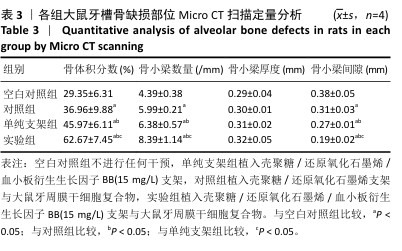
[1] FAN Y, CUI C, ROSEN CJ, et al. Klotho in Osx(+)-mesenchymal progenitors exerts pro-osteogenic and anti-inflammatory effects during mandibular alveolar bone formation and repair. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):155.
[2] LU J, WANG Z, ZHANG H, et al. Bone Graft Materials for Alveolar Bone Defects in Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022;28(1):35-51.
[3] HOLLÝ D, KLEIN M, MAZREKU M, et al. Stem Cells and Their Derivatives-Implications for Alveolar Bone Regeneration: A Comprehensive Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11746.
[4] KOUSHIK TM, MILLER CM, ANTUNES E. Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: Function of Multi-Material Hierarchically Structured Scaffolds. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(9):e2202766.
[5] LEKHAVADHANI S, SHANMUGAVADIVU A, SELVAMURUGAN N. Role and architectural significance of porous chitosan-based scaffolds in bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;251:126238.
[6] WANG S, ZHANG Y, SHI Y, et al. Rhubarb charcoal-crosslinked chitosan/silk fibroin sponge scaffold with efficient hemostasis, inflammation, and angiogenesis for promoting diabetic wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 2):126796.
[7] ZHAO Y, PENG X, XU X, et al. Chitosan based photothermal scaffold fighting against bone tumor-related complications: Recurrence, infection, and defects. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;300:120264.
[8] MANIKANDAN V, LEE NY. Reduced graphene oxide: Biofabrication and environmental applications. Chemosphere. 2023;311(Pt 1):136934.
[9] UMEKAR MS, BHUSARI GS, POTBHARE AK, et al. Bioinspired Reduced Graphene Oxide Based Nanohybrids for Photocatalysis and Antibacterial Applications. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(13):
1759-1781.
[10] 魏小翠,穆睿,毕博,等.氧化石墨烯修饰三维氧化锆骨组织工程支架的制备及细胞相容性研究[J].医学研究生学报,2019,32(8): 797-802.
[11] 毕博.还原氧化石墨烯修饰壳聚糖骨组织工程支架的制备和表征[D].广州:南方医科大学,2021.
[12] CAO J, ZHANG Q, YANG Q, et al. Epigenetic regulation of osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells in periodontitis. Oral Dis. 2023;29(7):2529-2537.
[13] MAO B, WANG M, WAN S. Platelet derived growth factor and its receptor in intracerebral hemorrhage. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022;51(5):634-639.
[14] 陈佳娜,聂敏海,胡馨月,等.血小板衍生生长因子BB促进人牙周膜干细胞的增殖和成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(10): 1534-1540
[15] 魏琴,张雪,马磊,等.血小板衍生生长因子BB诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19): 2953-2957
[16] KAWABATA T, TOKUDA H, KUROYANAGI G, et al. Incretin accelerates platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced osteoblast migration via protein kinase A: The upregulation of p38 MAP kinase. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):2341.
[17] PAN J, DENG J, LUO Y, et al. Thermosensitive Hydrogel Delivery of Human Periodontal Stem Cells Overexpressing Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Enhances Alveolar Bone Defect Repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2019; 28(24):1620-1631.
[18] 姜涛,马磊,李志强,等.血小板衍生生长因子BB诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向血管内皮细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(25): 3937-3942.
[19] 毕博,臧圣奇,何懋典,等.还原氧化石墨烯修饰壳聚糖骨组织工程支架的制备及表征[J].医学研究生学报,2021,34(4):350-356.
[20] LIU FD, DUAN HM, HAO F, et al. Biomimetic chitosan scaffolds with long-term controlled release of nerve growth factor repairs 20-mm-long sciatic nerve defects in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(5): 1146-1155.
[21] ZHOU M, LOZANO N, WYCHOWANIEC JK, et al. Graphene oxide: A growth factor delivery carrier to enhance chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in 3D hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2019;96:271-280.
[22] SANMUGAM A, ABBISHEK S, KUMAR SL, et al. Synthesis of chitosan based reduced graphene oxide-CeO(2) nanocomposites for drug delivery and antibacterial applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023;145:106033.
[23] 赵金龙,刘继超,于洋.聚己内酯和β-磷酸三钙复合支架经血小板衍生生长因子BB修饰后的促血管生成作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(21):3300-3306.
[24] 邓佳佳,潘杰,於丽明,等.血小板衍生生长因子BB对牙周膜干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2020,29(4):343-349.
[25] DONOS N, AKCALI A, PADHYE N, et al. Bone regeneration in implant dentistry: Which are the factors affecting the clinical outcome? Periodontol 2000. 2023;93(1):26-55.
[26] KIM DY, PARK G, HONG HS, et al. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Priming Enhances Vasculogenic Capacity of Bone Marrow-Derived Endothelial Precursor Like Cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(5):695-704.
[27] Su W, Liu G, Liu X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development. JCI Insight. 2020;5(8):e135446.
[28] GUO X, LI MX, BAYER C, et al. [Effect of platelet-derived growth factor-BB on pulmonary vascular remodeling in neonatal rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and its mechanism]. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2023;25(4): 407-414.
[29] LI X, QUAN H, HE J, et al. The role of platelet-derived growth factor BB signaling pathway in the regulation of stem and progenitor Leydig cell proliferation and steroidogenesis in male rats. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2023;233:106344.
[30] ZHANG JM, FENG FE, WANG QM, et al. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Protects Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Derived From Immune Thrombocytopenia Patients Against Apoptosis and Senescence and Maintains MSC-Mediated Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(12):1631-1643.
[31] REN F, FANG Q, XI H, et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB and epidermal growth factor promote dairy goat spermatogonial stem cells proliferation via Ras/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Theriogenology. 2020;155:205-212.
[32] DENG J, PAN J, LUO Y, et al. The platelet derived growth factor BB promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;129:105162.
[33] ZHANG M, YU W, NIIBE K, et al. The Effects of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB on Bone Marrow Stromal Cell-Mediated Vascularized Bone Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:3272098. |