中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 459-468.doi: 10.12307/2025.979
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
壳聚糖在口腔软硬组织修复与再生中的应用
王 卓,孙盼盼,程焕芝,曹婷婷
- 济宁医学院口腔医学院,山东省济宁市 272067
-
收稿日期:2024-10-14接受日期:2024-12-03出版日期:2026-01-18发布日期:2025-07-02 -
通讯作者:曹婷婷,硕士,讲师,济宁医学院口腔医学院,山东省济宁市 272067 -
作者简介:王卓,女,2003年生,黑龙江省鹤岗市人,汉族,济宁医学院口腔医学院在读本科,主要从事口腔医学研究。 -
基金资助:济宁医学院大学生创新训练计划项目(cx2024441py),项目负责人:王卓;2023年度济宁医学院本科教学改革研究项目(yb202322),项目负责人:孙盼盼
Application of chitosan in repair and regeneration of oral hard and soft tissues
Wang Zhuo, Sun Panpan, Cheng Huanzhi, Cao Tingting
- School of Stomatology, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-14Accepted:2024-12-03Online:2026-01-18Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Wang Zhuo, School of Stomatology, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Cao Tingting, MS, Lecturer, School of Stomatology, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:College Students Innovation Training Program Project of Jining Medical University, No. cx2024441py (to WZ); 2023 Annual School-level Undergraduate Teaching Reform Research Project of Jining Medical University, No. yb202322 (to SPP)
摘要:
文题释义:
壳聚糖:一种衍生自甲壳素的天然聚合物,是自然界中唯一含游离氨基的阳离子碱性多糖,具有生物相容性、生物降解性、抗氧化性、抗炎活性等特点,在组织修复再生领域展现出广阔的应用前景。
口腔软硬组织:主要包括牙体组织、牙周组织、口腔黏膜、唾液腺、颞下颌关节和颌骨等。其中,牙体组织包括牙釉质、牙本质、牙髓和牙骨质,牙周组织包括牙龈、牙周膜、牙槽骨和牙骨质。
背景:壳聚糖因良好的生物学性能和独特的物理化学性质在生物医学领域占有一席之地,尤其是在组织工程学和药物递送方面有着良好的应用前景。
目的:总结壳聚糖在口腔软硬组织修复再生中作用的研究进展。
方法:应用计算机检索中国知网、PubMed等数据库,以“壳聚糖,口腔黏膜病,牙周病,组织再生,抑菌,药物载体,伤口愈合”为中文检索词,以“chitosan,oral mucosal diseases,periodontal diseases,tissue regeneration,bacteriostatic,drug carrier, wound healing”为英文检索词,文献检索时限限定为2010-2024年,根据纳入和排除标准进行筛选,最终纳入88篇文献进行汇总分析。
结果与结论:壳聚糖具有刺激成骨祖细胞和牙髓干细胞募集和黏附等作用,是骨和牙髓再生中一种很有前途的生物材料。壳聚糖通过抑制口腔中的变形链球菌、牙龈卟啉单胞菌和念珠菌,从而预防龋病、牙周病和念珠菌病的发生。壳聚糖纳米复合材料具有更高的稳定性、更好的生物相容性和药物的缓释特性,并且可以通过与其他化学试剂结合来增强材料的抗癌性能。壳聚糖具有药物输送、抗菌活性、止血和促创面愈合等功能,能够阻断唾液和口腔菌群对创面的侵蚀,缓解疼痛,修复和促进创面愈合。壳聚糖可促进钙化物的沉积,有利于牙釉质和牙本质的再矿化。
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-5886-8383(王卓);https://orcid.org/0009-0009-0478-1696(曹婷婷)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
王 卓, 孙盼盼, 程焕芝, 曹婷婷. 壳聚糖在口腔软硬组织修复与再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 459-468.
Wang Zhuo, Sun Panpan, Cheng Huanzhi, Cao Tingting. Application of chitosan in repair and regeneration of oral hard and soft tissues[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 459-468.
2.1.1 壳聚糖的来源与结构 甲壳素主要存在于甲壳类动物和软体动物的壳、昆虫的外骨骼以及真菌、藻类的细胞壁中[2-4],是世界上第二丰富的天然聚合物,也是海洋中含量最丰富的天然多糖。甲壳素可以通过强碱性环境下的化学水解或采用特定酶水解的方法完成去乙酰化得到壳聚糖,通过精确地调节壳聚糖的去乙酰化程度,可定制更符合生物医学、制药等各个领域应用的壳聚糖参数。
壳聚糖是一种线性半结晶多糖生物聚合物,由(1/4)-2-乙酰氨基-2脱氧-b-d-葡聚糖(n-乙酰d-氨基葡萄糖)和(1/4)-2-氨基-脱氧-b-d-葡聚糖(d-氨基葡萄糖)组成[5-6],有3个提供反应性的主要官能团:氨基、羟基和n-乙酰胺基团,分别位于C2、C6和C3[7]。因结构中存在氨基基团,壳聚糖是唯一被认为是阳离子聚电解质的天然多糖,它还含有一个羟基基团,有助于促进环境内的静电吸引[8],并且基团在聚合物主链中可以进行结构修饰,进而调整壳聚糖的特性[9]。通过改变n-乙酰-d-氨基葡萄糖和d-氨基葡萄糖的模式和比例可以改变壳聚糖的溶解度,并根据所需的机械性能、降解率和释放特性进行定制。研究表明,壳聚糖易于被转化为多种衍生物,特定的结构可能会诱导不同的生物学效应[10]。
2.1.2 壳聚糖的性质与功能 相比甲壳素,壳聚糖具有更好的溶解性、生物相容性和可降解性。作为一种来源广泛、易于化学修饰的高分子材料,壳聚糖的特性与其纯度、分子质量、脱乙酰程度以及乙酰氨基和氨基的排列等因素有关。可以通过交联、微乳均质、溶液浇注和静电纺丝等先进技术将壳聚糖转化为多功能水凝胶、纳米颗粒和超薄膜,独特的生物相容性、降解性和活性基团使壳聚糖在药物控释和组织修复等生物医学领域成为研究热点。其中,壳聚糖水凝胶受益于壳聚糖带正电荷的氨基与微生物细胞膜之间的相互作用而具有良好的吸附和抗菌性能,因此被广泛用于组织工程、创面愈合、细胞培养和药物递送。壳聚糖薄膜可以通过提供润湿的环境、防止细菌感染和刺激组织再生来加速创面愈合。与鞣酸交联的多巴胺修饰的壳聚糖水凝胶已被证明可以提高细胞的存活率,促进大鼠受伤脊髓中轴突的再生[11]。使用环糊精和羧甲基氯改性的壳聚糖,克服了水溶性低的特点,成为组织再生领域的新宠儿。静电纺丝壳聚糖基纳米纤维垫由于固有的纳米孔隙率、更高的表面积体积比、药物递送、可生物降解、生物相容性、止血和抗菌特性而具有巨大应用潜力[12]。

2.2 壳聚糖在口腔组织修复中的应用
2.2.1 龋病的预防与治疗 龋病是一种由口腔内多种细菌引起的慢性感染性疾病,始于牙菌斑中细菌代谢产生的酸,引发龋病的细菌又被称为致龋菌,越来越多的研究关注到细菌在龋病发生中的作用。研究显示,变形链球菌在酸性环境中可以生存并持续产酸,引起口腔pH值降低,导致牙釉质脱矿与龋病的发生[13],被认为是导致龋病产生最有力的致病菌。
众所周知氟化物可以预防龋病的发生,通常被用于口腔护理产品如牙膏和漱口水中,但不恰当地应用氟化物也可能对人群产生不利后果[14-15]。传统修复龋病的方法无法从根本上抑制口腔内细菌的生长和生物膜的形成,因此,开发一种能够抑制细菌和生物膜形成的新型抗菌药物成为预防龋病发生的迫切需要[16]。大量研究表明壳聚糖可以抑制牙菌斑生物膜的形成和黏附,其正电位基团还可以破坏细胞膜,从而有效抑制细菌生长,被广泛应用于水凝胶、敷料、牙膏、漱口水和纳米系统等中,具有良好的抗菌和保护牙釉质的作用[17]。
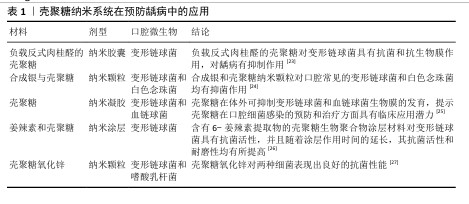
FLORES-ESPINOZA等[18]使用傅里叶变换红外光谱对明胶-壳聚糖水凝胶进行分析,采用琼脂扩散法和微量稀释法评估了其对变形链球菌的抑菌效果,发现该水凝胶具有良好的降解能力和溶胀能力,对变形链球菌的抗菌作用显著。SURBAMANIYAN等[19]在对比低浓度壳聚糖与较高浓度庆大霉素在抑制变形链球菌方面的作用后,发现两者均具有抑制作用,但低浓度壳聚糖表现出更好的抑制效果。CAMPUS等[20]通过采用国际龋齿检测与评估系统对龈上菌斑进行取样分析,发现含有壳聚糖的牙膏对变形链球菌的抑制作用显著,从而判断其具有预防龋齿的功效。DURAISAMY等[21]使用含有维生素K2、羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒和壳聚糖涂层纳米复合材料种植体进行变形链球菌的抗菌潜力研究,结果显示该复合材料能够有效抑制变形链球菌的作用。一项将氟化壳聚糖聚合物配制成漱口水的实验显示,氟化壳聚糖聚合物不仅可以保护牙齿免受酸脱矿,而且还具有抗菌的能力[22]。上述这些研究展现出壳聚糖在抑制变形链球菌方面的优势,然而由于壳聚糖机械性能低和水溶性差等特点,目前壳聚糖的抗菌性能在实际应用中受到限制,因此,通过化学修饰、枝接等方式对壳聚糖进行改性成为提高其抗菌活性的研究热点之一。壳聚糖纳米系统在龋病的预防中有较为广泛的应用,见表1。
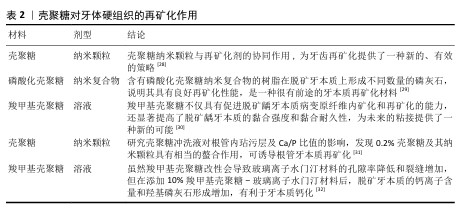
此外,在酸的作用下,牙齿矿物质发生溶解,钙和磷酸盐等无机离子由牙中脱出称为脱矿。牙齿硬组织质脱矿是最常见的牙齿问题之一,如果不及时采取有效的干预措施,最终也可引发龋洞形成。再矿化是治疗龋病的一种常用方法,研究显示壳聚糖对于牙本质有一定的再矿化作用,见表2。目前基于壳聚糖载体性能和再矿化作用开发仿生矿化药物,是该领域研究的热点。
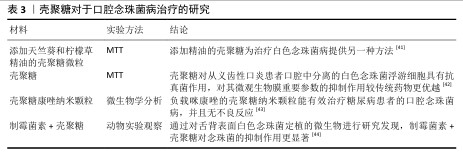
2.2.3 口腔黏膜病的治疗 口腔念珠菌病是由念珠菌属感染所引起的口腔黏膜疾病,是人类最常见的口腔真菌感染,临床常因所在部位与分型不同而表现各异。随着抗生素、糖皮质激素及免疫抑制剂等药物的广泛应用,口腔念珠菌病呈明显上升趋势,其危害性逐渐引起人们重视。口腔念珠菌病的治疗原则为去除诱发因素、积极治疗基础病,必要时辅以支持治疗,通常分为局部及全身抗真菌治疗。近年来,一些学者发现壳聚糖具有抑制真菌的作用,壳聚糖对于口腔念珠菌病的治疗研究见表3。
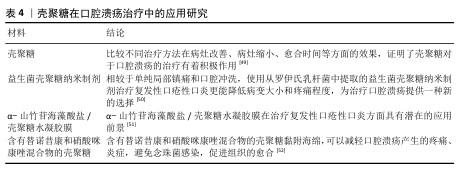
口腔溃疡是口腔黏膜常见的病损之一,其复发性、周期性发作引发的疼痛给人们的日常生活带来极大的不便。口腔溃疡的病因可能涉及许多因素,如遗传、创伤、全身性疾病、压力、维生素和微量元素缺乏以及感染等。目前,口腔溃疡最常见的治疗方法包括口服药物、外用凝胶或薄膜及喷雾等。其中,口服药物具有首关消除效应,显著降低了药物的生物利用度,而喷雾制剂在使用过程中容易被摄入[45-46],外用的凝胶或薄膜材料因含有大量的水对人体软组织具有一定的亲和性,还可以阻断口腔唾液和菌群对溃疡创面的侵蚀,缓解疼痛,修复和促进溃疡创面的愈合,隔离患处,从而成为口腔溃疡最常用和最有效的治疗方法之一[47-48]。见表4。
综上所述,口腔常见疾病与微生物的感染和入侵息息相关,壳聚糖对细菌和真菌具有广泛的抗菌活性,其安全性及化学结构易于被化学修饰改性等特点,在口腔疾病的预防和治疗中展现出广阔的应用前景。
2.2.4 口腔创面愈合 口腔手术中的创面愈合是一个连续而又复杂的动态过程,包括局部止血、炎症组织增殖(主要是成纤维细胞、上皮细胞和内皮细胞)、新血管生成、上皮化、合成、胶原纤维的结合和排列、肉芽组织的形成,到最终恢复组织的完整性[53]。口腔是一个特殊的微环境,因此接受口腔手术的患者在创面愈合过程中发生并发症的风险会增加,如何尽量减少口腔手术后创面愈合并发症的发生,是目前口腔临床研究面临的严峻课题。
BAGHERI等[54]采用壳聚糖纳米纤维结合氧化锌纳米颗粒支架材料进行创面愈合实验,结果显示该材料具有良好的血液相容性,有利于创面边缘成纤维细胞迁移和增殖,显示出作为有效创面敷料的潜力。POURSEIF等[55]研究了盐酸四环素包裹壳聚糖的抗菌活性和药物释放率,发现盐酸四环素包裹壳聚糖对大肠埃希菌、铜绿假单胞菌和金黄色葡萄球菌可产生抑制作用,并且在高温条件下更有利于药物的释放,进而揭示了该递药系统在皮肤创面、牙种植体和导尿管细菌感染治疗中的应用潜力。LIU等[56]成功制备了壳聚糖-高岭土纳米纤维膜,当高岭土比例为10%时,纳米纤维膜在全血凝固时间实验中表现出显著的止血效果;动物实验结果显示,该纳米纤维膜能够在14 d内有效促进大鼠背部创面的愈合,未观察到明显的炎症反应,表明壳聚糖-高岭土纳米纤维膜在止血和促进创面愈合方面具有良好的应用潜力。CHEN等[57]使用N-琥珀酰化壳聚糖处理功能失调的血管内皮细胞,发现白细胞介素1β转化酶和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达降低,而血小板-内皮细胞黏附分子、血管内皮生长因子和白细胞介素10的表达显著上调,表明N-琥珀酰化壳聚糖可以促进血管的再生、加速创面愈合。壳聚糖/聚乙烯吡咯烷酮/二氢槲皮素纳米复合膜导可有效清除中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞中的过量活性氧,阻止创口氧化应激的形成,创口愈合率达到 95%[58]。
KUMAR等[59]将浸渍洗必泰的纳米壳聚糖用作颌面部软组织创面的手术敷料,发现与传统洗必泰敷料材料相比,浸渍洗必泰的纳米壳聚糖能够更好地促进创面愈合。一项从组织病理学角度研究壳聚对糖尿病大鼠口腔黏膜伤口愈合影响的实验显示,壳聚糖在促进创面愈合的同时还可以减少口腔黏膜组织纤维化的发生[60]。NAMDAR等[61]研究比较亚叶酸壳聚糖水凝胶和肉毒杆菌毒素A对大鼠动物模型唇裂手术创面修复的影响,发现亚叶酸壳聚糖水凝胶可诱导更快的黏膜初始愈合。JESUS等[62]通过评估壳聚糖对8例患者口腔黏膜愈合的影响探究口腔黏膜创口愈合过程,发现壳聚糖可募集并激活中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞,刺激血管生成,加快创面愈合,并且并发症较少。
综上所述,壳聚糖作为一种天然带正电荷的多糖,通过结合带负电的红细胞及静电作用增加血液黏度,激活血小板的黏附和聚集,进而达到创口止血的目的;又通过活化成纤维细胞、激活胶原蛋白合成,促进释放生长因子和巨噬细胞迁移,在创口愈合等方面表现出优良的性能,在阻断唾液和口腔菌群对创面的侵蚀、缓解疼痛等方面均为临床上提供了新思路。

2.2.5 口腔颌面部肿瘤的治疗 癌症的特征在于体内大量细胞的异常增殖和生长[63]。口腔鳞状细胞癌是人类最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,每年有大量患者受到口腔癌症的困扰,严重影响患者的生活质量。尽管手术、化疗和放疗等癌症治疗方法取得了一定进展,但由于早期检测不足,这些方法的疗效仍然有限,远期效果相对较差。因此,开发能够选择性靶向给药的新技术显得尤为重要[64]。壳聚糖是自然界中唯一的阳离子多糖,能够与阴离子药物形成聚电解质复合物,作为药物输送载体具有诸多优势,可提高药物的递送效率。壳聚糖纳米复合材料不仅具有更高的稳定性和良好的生物相容性,在肿瘤治疗中还有利于抗癌药物的缓释特性,从而进一步增强抗癌性能。
WANG等[65]采用壳聚糖纳米结合5-氨基乙酰丙酸作为药物载体,利用光动力疗法递送光敏剂,通过观察其对口腔鳞状细胞癌疗效得出,壳聚糖纳米搭载5-氨基乙酰丙酸具有显著抗口腔肿瘤发生的作用。 MAJ等[66]探究壳聚糖搭载多酚作为抗癌剂在改善口腔健康和癌症预防中的潜在优势,结果显示二者协同作用可以提高癌细胞凋亡的效率,减少不良反应。MUSTAFA等[67]探讨搭载硫代秋水仙碱苷和月桂酸的壳聚糖基纳米凝胶对口腔癌细胞的影响,发现该凝胶具有良好的抗癌作用且细胞毒性小,使其成为癌症治疗中无毒化疗的潜在候选者;此外,较强的调节促凋亡基因表达能力也显示其在靶向癌症治疗的潜力。LI等[68]通过构建用巨噬细胞膜伪装的壳聚糖纳米颗粒药物载体实现miR-144/451a协同用于口腔鳞状细胞癌治疗,结果显示该仿生纳米系统可以发挥协同递送作用,有效提高miR-144/451a对口腔鳞状细胞癌的抑制作用。
综上所述,壳聚糖可以通过搭载不同的化学物质并充分发挥不同物质的作用,从而促进癌细胞的死亡,最后达到预防和治疗癌症的目的。

2.3 壳聚糖在口腔组织再生中的应用 牙髓病、牙周病、颌骨创伤及肿瘤、颞下颌关节损害是口腔颌面部常见的疾病,传统的治疗手段和方法很难恢复受损组织的结构与功能,组织工程的出现给这一问题带来了希望。组织工程成功的关键是在可降解的支架材料上形成再生组织,作为细胞附着、增殖和分化的过渡结构,支架材料必须具有良好的生物相容性、可降解性,而且能够模仿天然细胞外基质的生物学和理化性质。壳聚糖作为一种天然的生物材料不仅能满足上述要求,还容易被制成微球、海绵状、丝状等三维多孔结构,有利于携带生长因子,被视为组织工程支架的理想材料。
2.3.1 牙髓组织再生 牙髓是来源于外间充质的疏松结缔组织,位于牙体硬组织所形成的髓腔内,牙髓具有形成牙本质、营养、感觉和防御外来刺激的功能。因自身条件所限,牙髓在受到外界伤害时很难恢复正常,将导致牙髓坏死和根尖周炎的发生,最终的治疗方法是进行根管治疗及全冠修复。其实在牙髓中含有能够自我修复和再生功能的细胞,即牙髓干细胞,在对牙髓坏死的年轻恒牙进行牙髓再生手术时,组织工程的核心原理是通过选择合适的支架来搭载牙髓干细胞,在生长因子的作用下实现牙髓的再生,见图3。理想的牙髓血运重建支架应同时具备抗菌、免疫调节和再生特性。
GON?ALVES DA COSTA SOUSA等[69]在牙髓血运重建过程中使用含有环丙沙星和先天防御调节剂1002的壳聚糖纳米纤维支架,发现该支架具有抗炎活性并可促进牙髓状组织形成,还可抑制粪肠球菌、金黄色葡萄球菌生物膜的活性。LOUKELIS等[70]通过冷冻干燥法制备了含有牙髓干细胞的壳聚糖支架,体外细胞实验显示该支架增强了牙髓干细胞的成牙潜力并支持牙本质-牙髓再生。ZAMORA等[71]研究显示,壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石/磷酸三钙复合材料不仅具有生物相容性,还可以恢复受感染或炎症影响的组织,植入皮下后可形成由Ⅲ型胶原纤维、血管和炎症细胞组成的结缔组织,说明该复合材料有利于牙髓组织的再生。由此可见,壳聚糖对牙髓血运重建、牙髓干细胞分化与增殖及结缔组织的形成有着重要作用;此外,壳聚糖还具有诱导细胞归巢的潜力,为实现临床上牙髓组织再生提供了有力支持。

2.3.2 牙周组织再生 牙周组织受到损害会导致牙槽骨、牙周膜和牙骨质的破坏,虽然通过去除病因可以阻止局部破坏,但对于缺损组织的再生仍需通过外科手术进行修复。近年来,利用壳聚糖进行牙周再生的技术取得了显著进展,从最初利用壳聚糖的抗菌特性控制感染和炎症,到后来通过牙周组织中的干细胞实现组织再生,相关研究不断深入。
HSIEH等[72]的研究表明,壳聚糖能够诱导牙周膜成纤维细胞形成球状体,这些球状体在初始附着后逐渐聚集并导致球体体积增加,进而促进牙周膜的生成。BASIR等[73]研究证实壳聚糖材料可一定程度地增加牙周韧带宽度。刘莉[74]研究发现,负载牙龈间充质干细胞和转化生长因子β1的壳聚糖水凝胶能够促进牙骨质表面牙周膜组织的再生。有研究显示,协同负载骨形成蛋白7和奥硝唑的壳聚糖β-甘油磷酸水凝胶可显著减少犬根分叉缺损中的破骨细胞数量,增加成骨细胞数量,促进牙骨质-牙周膜-牙槽骨复合体的再生[75]。胡通等[76]研究负载骨形态发生蛋白的壳聚糖水凝胶在鼠脱位牙再植愈合中的效果,发现该水凝胶能够有效促进大鼠脱位牙再植后的牙周缺损修复。
综上所述,壳聚糖通过与其他化学药物的结合能够有效促进牙周组织的再生,尤其是在缺失的牙周膜和牙骨质的再生方面展现出良好的潜力。

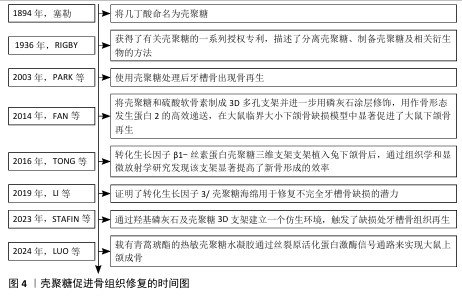
2.3.3 骨组织再生 颌骨由上颌骨和下颌骨组成,其边缘嵌有牙根的部分称为牙槽骨。骨髓炎、放射性骨坏死和药物相关性颌骨坏死是公共医疗保健中的重大挑战。细菌感染在颌骨损伤中起着关键作用[77],其中最常见的致病微生物是专性或兼性厌氧菌,如草绿色链球菌和葡萄球菌,通常需要手术干预和长期(数周至数月)的抗生素治疗,然而这些方法往往只能控制细菌感染,无法有效促进骨组织再生。具有双重抗菌活性和成骨效力的生物材料,有望成为治疗颌骨感染的新方法。壳聚糖具有良好的生物相容性、生物降解性和抗菌性,能够刺激成骨祖细胞的募集和黏附,在口腔组织工程领域展现出广阔的应用前景。壳聚糖促进骨组织修复时间图,如图4。
LóPEZ-VALVERDE等[78]通过显微计算机断层扫描法对种植体周围的骨整合和骨形成进行评估,发现相比较传统的表面蚀刻种植体,壳聚糖涂层更有助于改善种植体表面周围区域的骨愈合和骨形成。SUN等[79]探讨壳聚糖-甘油磷酸钠-海藻酸钠水凝胶在感染性颌骨缺损修复和治疗中的可行性,发现该系统有助于颌骨缺损的修复,为探索感染性颌骨缺损管理的新策略提供思路。有研究证实,使用改性壳聚糖凝胶可消除区域临界大小的骨缺损,促进骨再生,可作为颌骨重建中一种有潜力的生物材料[80]。XU等[81]采用冷冻干燥法设计了一种搭载二甲双胍的复合支架,该支架由磷酸β三钙、壳聚糖和介孔二氧化硅组成,将该复合支架植入牙周炎大鼠的牙槽骨缺损区域,发现该支架可促进牙周炎环境中牙槽骨缺损的修复,该支架或将成为治疗牙周炎环境中牙槽骨缺损有前途的候选者。LUO等[82]探讨载有青蒿琥酯的热敏壳聚糖水凝胶对大鼠上颌牙拔除的成骨作用发现该水凝胶可通过丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路来促进颌骨的再生。壳聚糖对牙槽骨的修复同样具有积极作用,见表5。
综上所述,壳聚糖具有良好的生物相容性、可加工性、可改性机械性能和功能化潜力,使其成为有价值的组织再生支架;此外,壳聚糖基支架可以促进组织结构内新生血管的形成,通过刺激内皮细胞的增殖和迁移以及增加血管生成因子的分泌来促进血管生成,这对组织再生也至关重要。

| [1] SONG H, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Hydroxyapatite/NELL-1 Nanoparticles Electrospun Fibers for Osteoinduction in Bone Tissue Engineering Application. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:4321-4332. [2] COHEN E, POVERENOV E. Hydrophilic Chitosan Derivatives: Synthesis and Applications. Chemistry. 2022;28(67): e202202156 [3] JUNCEDA-MENA I, GARCÍA-JUNCEDA E, REVUELTA J. From the problem to the solution: Chitosan valorization cycle. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;309:120674. [4] SABERI RISEH R, VATANKHAH M, HASSANISAADI M, et al. Chitosan-based nanocomposites as coatings and packaging materials for the postharvest improvement of agricultural product: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;309:120666. [5] MENG Q, ZHONG S, WANG J, et al. Advances in chitosan-based microcapsules and their applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;300: 120265. [6] MENG W, SUN H, MU T, et al. Chitosan-based Pickering emulsion: A comprehensive review on their stabilizers, bioavailability, applications and regulations. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;304:120491. [7] GAL MR, RAHMANINIA M, HUBBE MA. A comprehensive review of chitosan applications in paper science and technologies. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;309: 120665. [8] SZULC M, LEWANDOWSKA K. Biomaterials Based on Chitosan and Its Derivatives and Their Potential in Tissue Engineering and Other Biomedical Applications-A Review. Molecules. 2022;28(1):247. [9] SAHEED IO, OH WD, SUAH FBM. Chitosan modifications for adsorption of pollutants - A review. J Hazard Mater. 2021;408:124889. [10] PETRONI S, TAGLIARO I, ANTONINI C, et al. Chitosan-Based Biomaterials: Insights into Chemistry, Properties, Devices, and Their Biomedical Applications. Mar Drugs. 2023; 21(3):147. [11] LIU K, DONG X, WANG Y, et al. Dopamine-modified chitosan hydrogel for spinal cord injury. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;298:120047. [12] WANG W, XUE C, MAO X. Chitosan: Structural modification, biological activity and application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020; 164:4532-4546. [13] RÓNA V, BENCZE B, KELEMEN K, et al. Effect of Chitosan on the Number of Streptococcus mutans in Saliva: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(20):15270. [14] 张文倩,朱佳珂,张雯宇,等.2022年内蒙古自治区饮用水中氟化物监测及健康风险评估[J].中国公共卫生,2024,40(11): 1341-1346. [15] BURGETTE JM, DAHL ZT, YI JS,et al. Mothers’ Sources of Child Fluoride Information and Misinformation From Social Connections. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(4):e226414. [16] RASHKI S, ASGARPOUR K, TARRAHIMOFRAD H,et al. Chitosan-based nanoparticles against bacterial infections. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;251:117108. [17] ZHANG C, HUI D, DU C,et al. Preparation and application of chitosan biomaterials in dentistry. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;167: 1198-1210. [18] FLORES-ESPINOZA AI, GARCIA-CONTRERAS R, GUZMAN-ROCHA DA, et al. Gelatin-Chitosan Hydrogel Biological, Antimicrobial and Mechanical Properties for Dental Applications. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023; 8(8):575. [19] SUBRAMANIYAN K, KEMPARAJ U, CHAVAN S, et al. Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity of Cotton Balls Incorporated With Musa paradisiaca and Chitosan: An In Vitro Study. Cureus. 2022;14(8):e27553. [20] CAMPUS G, COCCO F, WIERICHS RJ, et al. Effects of Hydroxyapatite-Containing Toothpastes on Some Caries-Related Variables: A Randomised Clinical Trial. Int Dent J. 2024;74(4):754-761. [21] DURAISAMY R, GANAPATHY D, SHANMUGAM R, et al. Assessment of Antimicrobial Activity of Nanocomposites Based on Nano-Hydroxyapatite (HAP), Chitosan, and Vitamin K2. Cureus. 2024; 16(1):e53339. [22] RAHAYU DP, DRAHEIM R, LALATSA A, et al. Harnessing the Antibacterial Properties of Fluoridated Chitosan Polymers against Oral Biofilms. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(3):488. [23] MU R, ZHANG H, ZHANG Z, et al. Trans-cinnamaldehyde loaded chitosan based nanocapsules display antibacterial and antibiofilm effects against cavity-causing Streptococcus mutans. J Oral Microbiol. 2023;15(1):2243067. [24] PARAMESWARI BD, DHEVISHRI S,RANJITH R, et al. Nanoparticles in Prosthetic Materials: A Literature Review. J Pharm Bioallied Sci.2021;13(Suppl 2):S917-S920. [25] HANIASTUTI T, PUSPASARI TA, HAKIM ER, et al. Potential Effect of Giant Freshwater Prawn Shell Nano Chitosan in Inhibiting the Development of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguinis Biofilm In Vitro. Int J Dent. 2023;2023:8890750. [26] VAS NV, JAIN RK, RAMACHANDRAN SK. Gingerol and Chitosan-Based Coating of Thermoformed Orthodontic Aligners: Characterization, Assessment of Anti-Microbial Activity, and Scratch Resistance: An In Vitro Study. Cureus. 2023;15(8):e42933. [27] MOHAMMADIPOUR HS, TAJZADEH P, ATASHPARVAR M, et al. Formulation and antibacterial properties of lollipops containing of chitosan- zinc oxide nano particles on planktonic and biofilm forms of Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):957. [28] NANDHINI G, SASIDHARAN NAIR R, MANO CHRISTIANE ANGELO JB, et al. Comparative Analysis of the Effectiveness of Four Distinct Remineralizing Agents in Artificial White Spot Lesions Following Chitosan Nanoparticle Pretreatment: An In Vitro Study. Cureus. 2024;16(5):e59924. [29] NIU J, LI D, ZHOU Z, et al. The incorporation of phosphorylated chitosan/amorphous calcium phosphate nanocomplex into an experimental composite resin. Dent Mater J. 2021;40(2):422-430. [30] ZHANG Q, GUO J, HUANG Z, et al. Promotion Effect of Carboxymethyl Chitosan on Dental Caries via Intrafibrillar Mineralization of Collagen and Dentin Remineralization. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(14):4835. [31] ABDELKAFY H, ELSHEIKH HM, KATAIA MM, et al. Efficacy of using chitosan and chitosan nanoparticles as final irrigating solutions on smear layer removal and mineral content of intraradicular dentin. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2023;41(2):170-177. [32] PUTRANTO AW, MEIDYAWATI R, DWISEPTYOGA S, et al. Evaluation of Physical Properties in Carboxymethyl Chitosan Modified Glass Ionomer Cements and the Effect for Dentin Remineralization: SEM/EDX, Compressive Strength, and Ca/P Ratio. Eur J Dent. 2024. doi: 10.1055/s-0044-1786864. [33] KWON T, LAMSTER IB, LEVIN L. Current Concepts in the Management of Periodontitis. Int Dent J. 2021;71(6): 462-476. [34] ALGHAMDI B, JEON HH, NI J, et al. Osteoimmunology in Periodontitis and Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023;21(2):128-146. [35] JAVADKHANI A, SHOKOUHI B, MOSAYEBZADEH A, et al. Nano-Catechin Gel as a Sustained Release Antimicrobial Agent against Clinically Isolated Porphyromonas gingivalis for Promising Treatment of Periodontal Diseases. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1932. [36] HUANG H, HAN R, HUANG PP, et al. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of a Zinc Oxide-Graphene Oxideloaded Chitosan-Based Thermosensitive Gel. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024;34(6): 1229-1238. [37] LAZAREVIC M, PETROVIC S, PIERFELICE TV, et al. Antimicrobial and Osteogenic Effects of Collagen Membrane Decorated with Chitosan-Nano-Hydroxyapatite. Biomolecules. 2023;13(4):579. [38] JALALUDDIN M, KULKARNI A, RAJ K, et al. Assessment of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Chitosan-Based Tetracycline Gel on Periodontal Pathogens: An In vitro Study. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2023;15(Suppl 1): S438-S441. [39] ANGGANI HS, PERDANA RG, SIREGAR E, et al. The effect of coating chitosan on Porphyromonas gingivalis biofilm formation in the surface of orthodontic mini-implant. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2021;12(1): 84-88. [40] THANGAVELU A, STELIN KS, VANNALA V, et al . An Overview of Chitosan and Its Role in Periodontics. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021; 13(Suppl 1):S15-S18. [41] GARCIA LGS, ROCHA MGD, FREIRE RS, et al. Chitosan microparticles loaded with essential oils inhibit duo-biofilms of Candida albicans and Streptococcus mutans. J Appl Oral Sci. 2023;31:e20230146. [42] ARAUJO HC, RAMÍREZ CARMONA W, SATO C, et al. In vitro antimicrobial effects of chitosan on microcosm biofilms of oral candidiasis. J Dent. 2022;125:104246. [43] GAMIL Y, HAMED MG, ELSAYED M, et al. The anti-fungal effect of miconazole and miconazole-loaded chitosan nanoparticles gels in diabetic patients with Oral candidiasis-randomized control clinical trial and microbiological analysis. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):196. [44] PÉREZ-SAYÁNS M, BEIRO-FUENTES R, OTERO-REY EM, et al. Efficacy of different formulations of nystatin in an experimental model of oral candidiasis in sialoadenectomized rats. J Dent Sci. 2021; 16(1):123-130. [45] NALBANTOĞLU B, NALBANTOĞLU A. Vitamin D Levels in Children With Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2020;99(7):460-463. [46] GASMI BENAHMED A, NOOR S, MENZEL A, et al. Oral Aphthous: Pathophysiology, Clinical Aspects and Medical Treatment. Arch Razi Inst. 2021;76(5):1155-1163. [47] ZHANG Z, ZHANG Q, GAO S, et al. Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and wet-adhesive poly(ionic liquid)-based oral patch for the treatment of oral ulcers with bacterial infection. Acta Biomater. 2023;166:254-265. [48] ZHANG W, BAO B, JIANG F, et al. Promoting Oral Mucosal Wound Healing with a Hydrogel Adhesive Based on a Phototriggered S-Nitrosylation Coupling Reaction. Adv Mater. 2021;33(48): e2105667. [49] PARRA-MORENO FJ, EGIDO-MORENO S, SCHEMEL-SUÁREZ M, et al. Treatment of recurrent aphtous stomatitis: A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2023; 28(1):e87-e98. [50] SAMIRANINEZHAD N, KAZEMI H, REZAEE M, et al. Effect of lactobacillus reuteri-derived probiotic nano-formulation on recurrent aphthous stomatitis: a double-blinded randomized clinical trial. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):1019. [51] MILANDA T, CINDANA MO’O FR, MOHAMMED AFA, et al. Alginate/Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Film Containing α-Mangostin for Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis Therapy in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(8):1709. [52] OSSAMA M, LAMIE C, TAREK M, et al. Management of recurrent aphthous ulcers exploiting polymer-based Muco-adhesive sponges: in-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):87-99. [53] ROMERO-OLID MN, BUCATARU E, RAMOS-GARCÍA P, et al. Efficacy of Chlorhexidine after Oral Surgery Procedures on Wound Healing: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023; 12(10):1552. [54] BAGHERI M, VALIDI M, GHOLIPOUR A, et al. Chitosan nanofiber biocomposites for potential wound healing applications: Antioxidant activity with synergic antibacterial effect. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021;7(1):e10254. [55] POURSEIF T, GHAFELEHBASHI R, ABDIHAJI M, et al. Chitosan -based nanoniosome for potential wound healing applications: Synergy of controlled drug release and antibacterial activity. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;230:123185. [56] LIU T, ZHANG Z, LIU J, et al. Electrospun kaolin-loaded chitosan/PEO nanofibers for rapid hemostasis and accelerated wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;217: 998-1011. [57] CHEN Z, YUAN M, LI H, et al. Succinylated chitosan derivative restore HUVEC cells function damaged by TNF-α and high glucose in vitro and enhanced wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;265(Pt 2):130825. [58] ZHANG J, CHEN K, DING C, et al. Fabrication of chitosan/PVP/dihydroquercetin nanocomposite film for in vitro and in vivo evaluation of wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;206:591-604. [59] KUMAR NH, SAMUEL S, MATHEW S, et al. Maxillofacial Soft-tissue Healing Efficacy between Nano-chitosan and Collagen-Chitosan Membrane - A Comparative Study. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2023;13(2):144-148. [60] GÜR R, BÜYÜKAKYÜZ N, AYDIL BA, et al. Histopathological investigation of the effect of chitosan on oral mucous wound healing in experimentally established diabetic rats. Deneysel olarak oluşturulmuş diyabetik sıçanlarda kitosanın oral mukozada yara iyileşmesine etkisinin histopatolojik araştırılması. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2023;29(2):140-148. [61] NAMDAR P, MOADDABI A, YAZDIAN R, et al. Histologic Evaluation of the Effects of Folinic Acid Chitosan Hydrogel and Botulinum Toxin A on Wound Repair of Cleft Lip Surgery in Rats. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(3):142. [62] DE JESUS G, MARQUES L, VALE N, et al. The Effects of Chitosan on the Healing Process of Oral Mucosa: An Observational Cohort Feasibility Split-Mouth Study. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023;13(4):706. [63] PEI J, NATARAJAN PM, UMAPATHY VR, et al. Advancements in the Synthesis and Functionalization of Zinc Oxide-Based Nanomaterials for Enhanced Oral Cancer Therapy. Molecules. 2024;29(11):2706. [64] SINGH SK, SINGH R. Nanotherapy: targeting the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(5):258. [65] WANG J, WANG K, LIANG J, et al. Chitosan-tripolyphosphate nanoparticles-mediated co-delivery of MTHFD1L shRNA and 5-aminolevulinic acid for combination photodynamic-gene therapy in oral cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021;36: 102581. [66] MAJ M, TYLKOWSKI B, KONOPKA P, et al. Advancing oral health: Harnessing the potential of chitosan and polyphenols in innovative mouthwash formulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;175:116654. [67] MUSTAFA A, INDIRAN MA, RAMALINGAM K, et al. Anticancer potential of thiocolchicoside and lauric acid loaded chitosan nanogel against oral cancer cell lines: a comprehensive study. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):9270. [68] LI K, QIU Y, LIU X,et al. Biomimetic Nanosystems for the Synergistic Delivery of miR-144/451a for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Balkan Med J. 2022;39(3):178-186. [69] GONÇALVES DA COSTA SOUSA M, CONCEIÇÃO DE ALMEIDA G, MARTINS MOTA DC, et al. Antibiofilm and immunomodulatory resorbable nanofibrous filing for dental pulp regenerative procedures. Bioact Mater. 2022;16:173-186. [70] LOUKELIS K, MACHLA F, BAKOPOULOU A, et al. Kappa-Carrageenan/Chitosan/Gelatin Scaffolds Provide a Biomimetic Microenvironment for Dentin-Pulp Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7): 6465. [71] ZAMORA I, ALFONSO MORALES G, CASTRO JI, et al. Chitosan (CS)/Hydroxyapatite (HA)/Tricalcium Phosphate (β-TCP)-Based Composites as a Potential Material for Pulp Tissue Regeneration. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(15):3213. [72] HSIEH HY, YAO CC, HSU LF, et al. Biological properties of human periodontal ligament cell spheroids cultivated on chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol membranes. J Formos Med Assoc. 2022;121(11):2191-2202. [73] BASIR L, BABASHAHI E, RAZAVI SM, et al. Effects of Chitosan as a Novel Obturation Material for Pulpectomized Teeth on Periapical Inflammation, Periodontal Ligament Widening, and Hard Tissue Resorption: A Preliminary Exploratory Study on Dogs. Front Dent. 2024;21:22. [74] 刘莉.负载GMSCs和TGF-β1的壳聚糖水凝胶促进牙周膜再生的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2022. [75] 王宇洁,邹杰林,蔡明轩,等.壳聚糖基水凝胶在口腔组织工程中的应用[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2023,48(1):138-147. [76] 胡通,张珏,朱秀安,等.负载BMP-2壳聚糖水凝胶在大鼠完全脱位牙再植愈合中的研究[J].皖南医学院学报,2024,43(4):361-364. [77] SHIBAHARA T. Antiresorptive Agent-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ARONJ): A Twist of Fate in the Bone. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2019; 247(2):75-86. [78] LÓPEZ-VALVERDE N, LÓPEZ-VALVERDE A, CORTÉS MP, et al. Bone Quantification Around Chitosan-Coated Titanium Dental Implants: A Preliminary Study by Micro-CT Analysis in Jaw of a Canine Model. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:858786. [79] SUN M, CHENG L, XU Z, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Vancomycin Hydrochloride-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Composite Hydrogels. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:826971. [80] PATLATAYA NN, BOLSHAKOV IN, LEVENETS AA, et al. Experimental Early Stimulation of Bone Tissue Neo-Formation for Critical Size Elimination Defects in the Maxillofacial Region. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(21):4232. [81] XU W, TAN W, LI C, et al. Metformin-loaded β-TCP/CTS/SBA-15 composite scaffolds promote alveolar bone regeneration in a rat model of periodontitis. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(12):145. [82] LUO J, LIANG C, CHEN K, et al. Artesunate-loaded thermosensitive chitosan hydrogel promotes osteogenesis of maxillary tooth extraction through regulating T lymphocytes in type 2 diabetic rats. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):356. [83] YU F, GENG D, KUANG Z, et al. Sequentially releasing self-healing hydrogel fabricated with TGFβ3-microspheres and bFGF to facilitate rat alveolar bone defect repair. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(3):425-434. [84] STAFIN K, ŚLIWA P, PIĄTKOWSKI M. Towards Polycaprolactone-Based Scaffolds for Alveolar Bone Tissue Engineering: A Biomimetic Approach in a 3D Printing Technique. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(22):16180. [85] LUO Q, YANG Y, HO C, et al. Dynamic hydrogel-metal-organic framework system promotes bone regeneration in periodontitis through controlled drug delivery. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):287. [86] HUANG CL, HUANG HY, LU YC, et al. Development of a flexible film made of polyvinyl alcohol with chitosan based thermosensitive hydrogel. J Dent Sci. 2023; 18(2):822-832. [87] GU Z, QIU C, CHEN L, et al. Injectable thermosensitive hydrogel loading erythropoietin and FK506 alleviates gingival inflammation and promotes periodontal tissue regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;11:1323554. [88] WEI XY, XIA W, ZHOU T. Antibacterial activity and action mechanism of a novel chitosan oligosaccharide derivative against dominant spoilage bacteria isolated from shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2022;74(2):268-276. |
| [1] | 白相宇, 霍 峰, 郝 妍, 王泽成, 郭晓宇. 负载血小板衍生生长因子BB的壳聚糖/还原氧化石墨烯支架修复牙槽骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 329-337. |
| [2] | 闫启全, 杨立斌, 李梦君, 倪亚卓, 陈科颖, 许 博, 李耀扬, 马士卿, 李 睿, 李建文. 负载抗菌肽KR-12-a5猪小肠黏膜下层复合纳米羟基磷灰石生物支架的制备及抗菌性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 384-394. |
| [3] | 刘晓红, 赵 天, 穆云萍, 冯文金, 吕存声, 张智永, 赵子建, 李芳红. 脱细胞真皮基质水凝胶促进大鼠皮肤创面的愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [4] | 袁 茜, 张 昊, 庞 杰. 负载柚皮苷壳聚糖/β-磷酸三钙支架的表征及生物学性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| [5] | 张其娅, 童伊翔, 杨世姣, 张宇梦, 邓 凌, 吴 玮, 解 瑶, 廖 健, 毛 岭. 梯度玻璃分级超透氧化锆的体外生物相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 443-450. |
目前临床上对口腔组织修复的方法仍然存在一定局限性,比如治疗成年人牙髓病和根尖周病最为常用的方法根管治疗术,仅能恢复患牙咀嚼功能、保存牙齿,并不能实现真正意义上的牙髓组织再生和血运重建,而牙髓组织是牙齿维持各项生理功能的关键因素。由炎症、创伤、肿瘤和先天性畸形等因素导致的颌骨缺损,传统的治疗方法主要是自体骨移植、同种异体骨移植和牵张成骨等,然而,由于继发性损伤、可塑性差、免疫排斥和成骨能力有限等,使这些方法的应用存在一定的局限性[1]。而口腔自身结构及内环境的复杂性,也给颌面部软硬组织损伤的修复与再生带来巨大的挑战。
组织工程的发展为口腔颌面部疾病的修复与再生带来了前所未有的希望和可能。生物材料是促进机体自我修复与再生,或构建出新的组织与器官的一类天然或人工合成的特殊功能材料,又称为生物医用材料,在组织工程中发挥着重要作用。近年来,壳聚糖作为天然生物材料在组织修复和再生等生物医学领域的应用一直备受关注。壳聚糖显著的作用主要体现在以下几个方面:发挥自身作用促进组织的修复、凝血和矿化;具有三维多孔结构,能够模仿细胞外基质,在酸性环境中可完全溶解,是一种天然的组织工程支架材料;起负载作用,如协同负载抗炎药物和生物活性因子,促进炎症消退;可与其他材料制备成复合物,能够显著改善壳聚糖的理化性质及生物学功能。以往关于壳聚糖应用在组织工程、药物递送和生物传感器等方面的报道较多,该文对近年来壳聚糖在口腔软硬组织修复与再生中的研究进展作一综述,并在此基础上探讨壳聚糖在此领域所面临的机遇与挑战,为进一步推动壳聚糖在口腔医学中的应用提供参考依据。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及时间 由第一作者在2024年8月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 2010年1月至2024年8月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网、PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“壳聚糖,口腔黏膜病,牙周病,组织再生,抑菌,药物载体,伤口愈合”为中文检索词,以“chitosan,oral mucosal diseases,periodontal diseases,tissue regeneration,bacteriostatic,drug carrier, wound healing ”为英文检索词。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述。
1.1.6 手工检索策略 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例的检索策略,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 共检索564篇文献,其中中文文献53篇、英文文献511篇。
1.2 入选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与壳聚糖相关的文献;②与口腔黏膜病相关的文献;③与牙周组织病有关文献;④与骨组织相关的文献:⑤影响因子高、具有新颖性和代表性的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①内容相关性小、陈旧性、重复性文献;②逻辑不严谨,可信度差的文献;③论据不充分、论点不明晰的文献。
1.3 质量评估和数据的处理 共检索到564篇文献,通过阅读文献后删除与该综述主旨不符合、重复的文献,实际纳入88篇文献,其中中文文献4篇、英文文献84篇。文献筛选流程见图2。
3.2 该综述区别他人他篇的特点 该文从壳聚糖的来源与结构出发,阐述其性质与功能在生物医学领域应用的潜能,结合口腔软硬组织的特点及目前口腔常见病多发病的临床诊治情况,分析其在口腔组织修复与再生中的应用前景。以往文献大多仅涉及壳聚糖在组织工程中的应用,鲜有将其与临床上口腔组织修复紧密结合,该文分别探究壳聚糖的特性对于口腔组织的修复与再生的影响,为壳聚糖今后用于口腔疾病治疗和组织修复提供新的思路。
3.3 该综述的局限性 该文对壳聚糖在口腔组织的修复与再生的应用进行了综述,重点关注到壳聚糖在口腔常见病如龋病、牙周病、口腔黏膜病、颌骨肿瘤中的应用,但对唾液腺和颞下颌关节疾病的相关研究较少。壳聚糖具有促进组织再生、抑菌、药物载体和促进伤口愈合的能力已经确立,但其治疗机制的复杂性和可实施性仍不清楚。
3.4 该综述的意义与展望 壳聚糖作为具有广泛来源的天然生物材料,在口腔组织修复与再生中具有广阔的应用前景。该文总结壳聚糖在龋齿预防、牙体硬组织矿化、牙周病和口腔黏膜病治疗以及口腔组织再生中的作用,详细阐述其抗菌、促矿化、药物递送、促愈合、止血、促进细胞黏附、增殖及血管生成和组织再生的能力,帮助学者快速掌握壳聚糖在口腔组织修复与再生的研究进展,推动壳聚糖向口腔临床医学方面发展,为口腔组织修复与再生与修复提供了理论依据。
该文基于壳聚糖的生物学特性,系统阐述了壳聚糖的来源、结构、性质及功能,为后续探讨壳聚糖在口腔疾病治疗中的应用奠定理论基础,并帮助读者全面了解壳聚糖的特性,激发阅读兴趣。文章重点聚焦于壳聚糖在口腔组织修复与再生领域的应用,详细分析了其在治疗口腔常见疾病(如龋病、牙周病、口腔黏膜病、颌骨肿瘤等)以及促进创面愈合方面的作用。同时,文章对壳聚糖在牙髓、牙周及骨组织再生中的潜力进行了总结与归纳。该文从壳聚糖单独应用及其与其他化学物质结合两方面,深入探讨了壳聚糖在口腔软硬组织修复与再生中的作用机制,为壳聚糖在未来口腔医学领域的应用提供了新的研究思路与方向。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||