中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (2): 469-479.doi: 10.12307/2026.519
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
多重刺激响应性水凝胶在骨损伤修复中的应用:特殊响应能力及多样性功能
王 域,范民杰,郑朋飞
- 南京医科大学附属儿童医院,江苏省南京市 210000
-
收稿日期:2024-10-29接受日期:2025-01-06出版日期:2026-01-18发布日期:2025-07-02 -
通讯作者:郑朋飞,博士,主任医师,副教授,南京医科大学附属儿童医院,江苏省南京市 210000 -
作者简介:王域,男,2003年生,福建省宁德市人,汉族,主要从事骨与软骨组织工程研究。
Application of multistimuli-responsive hydrogels in bone damage repair: special responsiveness and diverse functions
Wang Yu, Fan Minjie, Zheng Pengfei
- Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-29Accepted:2025-01-06Online:2026-01-18Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Zheng Pengfei, MD, Chief physician, Associate professor, Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wang Yu, Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
多重刺激响应性水凝胶:水凝胶材料是一种具有三维网状结构的聚合材料,能够吸收并保留大量的水分,在此基础上科学家通过添加化学基团、复合其他种类材料等多种改良方式使水凝胶能够响应骨损伤环境中的内源性刺激,或者人为施加外源性刺激,以可控地发挥水凝胶性能。
骨损伤修复:多种原因可导致骨骼结构的破坏和功能丧失,在生理状态下,人体会通过炎症、机化、成骨、重塑过程重新恢复为与原来结构功能相近的骨组织,但是在感染、软骨退行性病变、骨质疏松等病理状态下则需要医学干预,以部分恢复骨骼功能。
背景:多重刺激响应性水凝胶因特殊的响应能力以及多样性功能在骨组织工程领域受到了广泛关注。
目的:综述多重刺激响应性水凝胶在骨损伤修复中的应用,探讨其研发思路和未来发展方向。
方法:检索PubMed、Web of Science、万方数据库收录的相关文献,英文检索词为“hydrogels,bone defect,bone repair,bone healing,bone tissue engineering,Degenerative joint diseases,osteoarthritis,Cartilage”等,中文检索词为“多响应性水凝胶,智能水凝胶,骨损伤修复,骨组织工程”,文献检索时限为各数据库建库到2024年8月,最终纳入83篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:多重刺激响应性水凝胶能够对物理、化学和生物等多个层面的刺激做出反应,同时发挥溶胀、形变、降解等固有功能以及其他材料赋予的特殊功能,使它们在解决骨损伤修复的临床问题中具有巨大的潜力。但在实际应用中,如何确保这些材料在复杂的生物体内环境中保持稳定性和持久性,在需要时能够可控无害地降解,是一个亟待解决的问题。
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-4045-6039(王域)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
王 域, 范民杰, 郑朋飞. 多重刺激响应性水凝胶在骨损伤修复中的应用:特殊响应能力及多样性功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 469-479.
Wang Yu, Fan Minjie, Zheng Pengfei. Application of multistimuli-responsive hydrogels in bone damage repair: special responsiveness and diverse functions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 469-479.
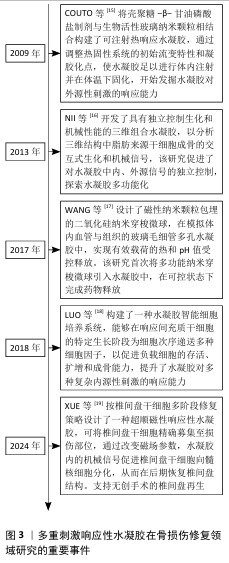
2.2 多重刺激响应性水凝胶基础
2.2.1 水凝胶的一般特性 水凝胶是一种能够吸收并保持大量水分而不溶解的交联聚合物网络,具有独特的三维结构和优异的生物相容性,在骨损伤修复领域展现出了广阔的应用前景。临床试验证明,相较于使用自体骨、软骨移植修复骨损伤,水凝胶在修复结构完整性和增强骨承重能力上均有优势。
可塑性:水凝胶具有优秀的可塑性,可以根据需要设计成不同的形状、尺寸和孔隙率,以模拟骨组织的微环境,为细胞生长、血管形成和营养物质传输提供理想的平台[20]。这种可塑性使水凝胶能够紧密贴合复杂的骨缺损表面,减少移植物与宿主骨之间的间隙,从而改善移植物的血供和营养状况,降低感染风险[21]。更重要的是,部分水凝胶具有剪切稀化的特性,其黏度随着剪切率的增加而降低,保护封装物质在注射时不被剪切应力破坏,赋予水凝胶可注射性[22];同时,水凝胶还具有一定的力学强度,能够在一定程度上支撑和保护修复部位的骨组织,直至其自然愈合[23]。
溶胀:水凝胶具有溶胀特性,多孔的特性使它在水中能够迅速吸水膨胀,并在溶胀状态下保留大量体积的水而不溶解,这种特性源于水凝胶内部的交联网络结构[24]。当外部环境发生变化时,水凝胶的溶胀状态也相应改变,这意味着水凝胶可以发生微观、宏观层面形变,微观层面的形变导致水凝胶网络结构的收缩或展开,影响药物分子在凝胶内部的扩散速率和释放行为,在骨组织中这种形变可以被骨细胞所感应,从而调节细胞行为和细胞信号转导[25];宏观层面的形变可以对组织产生牵拉或挤压,使其能够吸收渗出液,保持创面湿润环境,已被应用于治疗皮肤缺损、细菌感染、烧伤[26]、糖尿病足等复杂创面[27]。
降解:水凝胶具有溶解的能力。在水凝胶中掺入生长因子、药物或干细胞等生物活性因子,在环境发生变化时,水凝胶的聚合物网络三维结构会发生破坏,进而缓释这些生物活性因子并持续作用于损伤部位,进一步促进骨组织的再生和修复过程[28],这种特性成为了水凝胶响应控释的基础。如果使用水凝胶代替金属内固定物用于骨缺损的修补,则不需要再次手术以取出固定支架。

2.2.2 现有水凝胶材料的不足之处以及改进方法 现有的水凝胶材料通常使用体外成型植入、自然降解释放药物的设计策略。自然降解无法响应环境的变化;释放药物模式单一且释放速率不可控,无法和骨损伤修复过程相匹配,在降解末期水凝胶的强度不足以支撑未完全修复的承重骨,体外成型后植入未发挥出水凝胶可塑性的优势。在未来需要针对特定的应用环境,集不同材料之长,通过对骨损伤修复机制的研究,采用化学基团修饰、添加无机材料或细胞等方法,为水凝胶赋予响应复杂刺激的能力,将“单调的填充物”改造成“培育新生细胞的摇篮”。
2.2.3 刺激响应分类 给予水凝胶的刺激分为内源性来源和外源性来源。内源性刺激多为生物化学因子,包括酶、活性氧、pH值变化等;外源性刺激包括力、声、光、电、磁、热等物理刺激因子。水凝胶发生的响应可分为形变、溶胀、降解等固有性质响应,以及通过外源性材料赋予的产热、电刺激、活性氧消除、灭菌、改善细胞功能等额外附加性能(图4)。
如同生物一样,多重刺激响应性水凝胶不仅对多种刺激敏感,还能够根据不同水平的刺激发生多种可控的响应,将外源性刺激转化为骨损伤修复的治疗因素,从而适应临床治疗中的复杂需求。
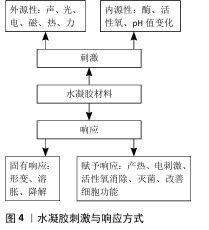
2.3 不同响应方式水凝胶材料在骨损伤修复中的应用
2.3.1 声响应水凝胶 超声波是一种频率高于人类听觉上限(约20 kHz)的声波,常被应用于促进水凝胶交联、颗粒物质在水凝胶中分散以及水凝胶的物理或化学性状改良。超声波作为一种可控且对软组织穿透能力强的能量波,能够充分地刺激深部骨组织中的水凝胶植入物,是一种具有潜力的响应性水凝胶触发因素。
(1)基于压电材料的声敏水凝胶:压电材料将超声能量转换为电能,驱动活性氧的生成,用于杀灭耐药性细菌。LIU等[29]将钛酸钡纳米压电材料负载于柔性可注射水凝胶中,实现了对耐药性细菌的杀灭;研究还发现,超声刺激和电刺激不仅对细菌有直接杀灭作用,还可以改善损伤部位的微环境,促进间充质干细胞的迁移分化,从而间接促进骨组织再生。
植入人体的声学响应材料应有良好的生物相容性。VINIKOOR等[30]使用可生物降解的有机压电材料聚L-乳酸代替传统压电材料钛酸钡制备了一种胶原水凝胶,在保持声电转换能力的同时保留了胶原水凝胶剪切稀化和可降解的特性;体外间充质干细胞实验显示,电刺激通过诱导间充质干细胞迁移和转化生长因子β1的释放加速其分化为软骨细胞。
为了进一步探究生物电信号对缺损处组织细胞增殖和分化的影响机制,ZHOU等[31]开发了一种更加适应于骨损伤修复的钛酸钡纳米压电材料明胶水凝胶,通过超声驱动产生的可控电刺激对不同来源间充质干细胞进行干预,提出在超声空化过程中对压电水凝胶产生的电刺激可导致细胞膜去极化,有利于Ca2+通过开放的钙通道流入;作为第二信使,Ca2+可以激活磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/细胞外信号调节激酶信号通路,使下游基因Runx2的表达上调,促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化。
(2)基于声学液滴汽化的声敏水凝胶:利用声学液滴汽化技术将药物水溶液封装于全氟化碳气泡中,通过超声激发气泡气化实现药物的精准释放[32]。ALIABOUZAR等[33]研发了一种声学响应支架,通过设计不同的超声汽化阈值以实现多种药物互不干扰的控释,发现液滴汽化产生的连续孔促进了细胞迁移和血管生成[34]。
(3)基于酶促反应的声敏水凝胶:利用酶促反应,通过超声刺激释放药物或激活细胞因子,促进骨组织再生。ZHAO等[35]将载有钙、凝血酶原和促血管生成因子磷脂酰肌醇3激酶的脂质体与和纤维蛋白原、谷氨酰胺转氨酶前体溶液混合,通过超声触发脂质体释放凝血酶,凝血酶在钙离子和谷氨酰胺转氨酶的催化下水解纤维蛋白原,形成纤维蛋白固体水凝胶网络,使磷脂酰肌醇3激酶分散,从而促进组织内微血管网络的形成,这种水凝胶系统可以在30 s内穿透猪小腿胫骨并稳定交联,在临床骨缺损血管重建中具有应用潜能。
声响应水凝胶为骨损伤修复提供了一种新的治疗策略,具有精准释放药物、改善微环境、促进细胞增殖和分化的特点。未来研究方向可以侧重于开发新型声敏水凝胶材料、系统化治疗策略、进行临床试验等。

2.3.2 光响应水凝胶 近红外光波长长于可见光(750 nm)而短于中红外光(2 500 nm),被广泛应用于水凝胶的光化学交联和光热疗法之中,但是随着研究的进行也暴露出现一些问题:光化学交联中,光敏剂通过产生活性氧启动水凝胶的聚合反应,而过高水平活性氧对负载的骨髓间充质干细胞有损伤作用;在光热疗法中,过高温度会导致水凝胶降解损毁。科学家将这些缺点转化为特性,通过控制活性氧释放水平和控制水凝胶降解速度来开发新型的光响应水凝胶。
(1)光动力疗法水凝胶:光动力疗法利用光敏剂在近红外光下产生活性氧来杀灭肿瘤细胞和细菌。WANG等[36]使用壳聚糖、明胶和β-谷氨酰胺制备了一种温敏水凝胶,负载骨诱导剂骨形态发生蛋白2和光敏剂T8IC+H2O2,在45℃左右水凝胶会转变成溶胶,释放出负载药物的同时抑制温度进一步上升,在温和的光疗条件下实现了对牙周炎细菌的杀灭和骨形态发生蛋白2的释放,促进了牙槽骨修复。
相对于治疗细菌感染,治疗骨肉瘤需要更高水平的活性氧,近红外光刺激难以赋予光敏剂产生足量的活性氧,如果增大辐照强度或者增加光敏剂浓度可能对周围组织造成更大的损伤。XIAO等[37]将压电刺激引入光热疗法,使用Bi/SrTiO3纳米异质结增强光敏剂的活性氧生成能力,制备了具有优异活性氧生成能力的光动力疗法水凝胶,为骨肉瘤和骨缺损的治疗提供了新的思路。
(2)光控制水凝胶固化和降解:光引发剂可以控制水凝胶的固化和降解过程,从而实现药物的精准释放和细胞网络的构建。GEHRE等[38]使用光引发剂P2CK固化聚甲基丙烯酸酯水凝胶,这种特殊的引发剂对激光更加敏感,不仅可以减少引发固化的光照剂量,并且可通过双光子激光烧蚀促进孔道内的水凝胶降解,有利于减少对负载细胞的损伤,在体外创建骨组织模型,这项技术对于骨缺损修复缓慢的高龄患者尤其有益,如果能够在水凝胶中提前构造出细胞网络将有助于缩短骨折愈合时间。
光响应水凝胶通过对引发剂进行特化改良,赋予水凝胶活性氧产生和引发降解的功能,但一些关于水凝胶光热疗法的研究表明高水平的活性氧反而会降低细胞存活率,未来仍然需要进一步探究水凝胶光疗法中活性氧和温度对组织细胞的共同作用。另外,使用X射线可以进一步提升光对深部组织的穿透性[39],应用X射线开展的光动力疗法也值得研究。

2.3.3 电响应水凝胶 外源性电信号可以模拟生物体内的自然电信号,刺激成骨细胞和软骨细胞的增殖与分化,促进钙和磷等矿物质在骨骼中的沉积,从而加强新骨的形成。电刺激疗法已被广泛应用于骨损伤治疗中,同时骨修复过程会产生多种电化学电位及内源性的电学性质变化,开发监测性水凝胶材料有助于对骨修复的原理进行进一步解析。电刺激的持续性、可控性可以进行长时间的药物调控释放。
(1)基于骨细胞监测的多功能导电水凝胶:电响应水凝胶可以用于监测骨细胞信号和促进骨组织再生。HUANG等[40]将碳纳米管整合到羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶中制备了复合导电水凝胶,这种水凝胶可通过电极电位监测成骨细胞标志物的碱性磷酸酶水平,实验证明该水凝胶可通过碳纳米管的作用持续增强干细胞成骨分化和新骨组织的形成,证明了碳纳米管/羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶在监测早期成骨分化方面具有良好的灵敏度,他们还将骨形态发生蛋白2加入水凝胶中协同诱导新骨形成,这项研究为再生医学中新形成骨组织的长期无创连续监测奠定了基础。
ARAMBULA-MALDONADO等[41]使用生物活性玻璃作为中间介质,通过反应性表面活性剂在明胶-聚甲基丙烯酸酯中均匀分散多壁碳纳米管来创建纳米复合水凝胶,该水凝胶能够精确模仿不同骨骼的有机-无机组成及其导电性能,支持多能间充质祖细胞的生长分化,为骨细胞的电刺激响应机制的探究做出铺垫。在此基础上,科学家继续探究负载碳纳米管聚甲基丙烯酸酯水凝胶的细胞黏附能力提升方法,通过添加纤连蛋白包被水凝胶及使用预分化的间充质干细胞作为负载细胞,克服了碳纳米管水凝胶表面粗糙和疏水等不利于细胞黏附的因素,经过改良的水凝胶能够使共培养间充质干细胞进一步增殖分化为更加成熟的成骨谱系[42]。
(2)基于电响应的药物控释水凝胶:电响应水凝胶可以用于控制小分子药物的释放。RESINA等[43]利用聚丙烯酸载药微球制备了pH值和电刺激双响应水凝胶,用于控制氯霉素的释放,在高pH值体外环境下,聚丙烯酸载药微球发生电离且聚合物膨胀完全溶剂化,形成膨胀水凝胶从而负载氯霉素;在体内炎症环境下,随着pH值下降,聚丙烯酸载药微球以紧凑型球状构象形成收缩的收缩水凝胶,电刺激能够促进氯霉素更快地释放。这种载药体系具有多种药物控释以及联合用药的可能性,在骨肿瘤和骨炎的深部酸性环境下具有应用潜力。
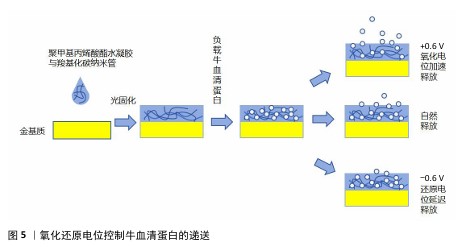
为了进一步改善电响应水凝胶对大分子肽及蛋白质的靶向稳定递送,CHEAH等[44]在碳纳米管水凝胶的基础上进行改良,使用生物相容性更好的电极涂层材料聚乙烯二氧噻吩代替碳纳米管,使用电化学沉积法将其沉积于负载大分子蛋白质的聚甲基丙烯酸酯水凝胶中,通过施加恒定氧化还原电位、静电相互作用使大分子蛋白质从聚甲基丙烯酸酯水凝胶被吸引到聚乙烯二氧噻吩上实现受控释放,这种水凝胶可以在24 d内稳定控制牛血清蛋白的递送,显著降低大剂量蛋白质药物泄漏和失活的风险,在重组生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白2等蛋白质药物的靶向递送上是一项开创性研究。图5展示了氧化还原电位控制牛血清蛋白的递送。
电刺激可控、持续性强,使电响应水凝胶在骨组织工程中具有广泛的应用潜力,但是现有的碳纤维材料不利于骨细胞生长分化且降解产物的毒性未知,未来需要进一步开发可无害降解的导电材料,或者进一步提升碳纤维材料水凝胶的生物相容性。
2.3.4 磁响应水凝胶 交变磁场是一种随时间变化的磁场,其方向和强度都不断变化。在磁响应水凝胶的应用中,交变磁场可以用于控制磁性纳米颗粒的运动,在复杂人体组织环境中实现药物向多种组织精准靶向递送[45]。交变磁场通过水凝胶中铁微粒产生感应电流,将电能转化为热能以杀死肿瘤细胞,通过药物协同作用进一步增强肿瘤灭活效果[46]。科学家利用水凝胶将磁性纳米颗粒植入损伤骨组织中,使交变磁场控制磁性纳米颗粒发挥骨组织修复功能。
(1)强化磁性热疗的水凝胶:为了解决磁性热疗时磁性纳米颗粒扩散的问题,KASI?SKI等[47]合成了一种生物相容且可生物降解的三嵌段共聚物水凝胶,负载了磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒和化疗药物紫杉醇,合成的共聚物能够在室温下形成透明、自由流动的溶胶,而当温度升高到37 ℃时产物变为白色、不透明的半固体凝胶,这意味着此水凝胶可以在低温下被注射,并且在热疗时限制氧化铁纳米颗粒的扩散;获得的磁性氧化铁颗粒磁滞回线几乎为S型,代表着合成的磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒为超顺磁性,在产热过程中以涡流损耗为主,磁滞损耗较小,可以使温度快速可控地到达预定值,并且颗粒间不会因为磁化磁吸形成团聚体,具有令人满意的加热性能;此外,水凝胶中紫杉醇释放曲线接近零级动力学,不随着热疗温度上升而发生变化,在骨肉瘤的磁性热疗中具有应用潜能。
(2)磁场引导的药物递送水凝胶:ZHOU等[48]受到巨噬细胞吞噬并通过活性氧杀灭细菌的启发,用聚多巴胺包被明胶微球,然后将抗菌纳米颗粒和磁性纳米颗粒修饰到这些聚多巴胺包被的明胶微球上,构建功能化微球,使它能够响应磁场的调控在未凝固的水凝胶中定向迁移,抗菌纳米颗粒涂层上的反应性儿茶酚基团可以捕获细菌,通过IR780碘化物在近红外光照射下产生活性氧从而杀死细菌。这项技术不仅利用磁场精确输送功能化微球到达牙颈表面和植入材料的外表面,而且在杀菌的同时使活性氧产生区域远离骨再生中心,最大限度地减少活性氧对骨修复的影响。
在复杂的骨组织中,使用交变磁场控制水凝胶磁性微球的载体运送药物,需要克服微球群体移速不一致发生扩散的问题,实现对微球流的精确控制[49]。针对一种预后较差的骨肉瘤,TAO等[50]将基因特异性抑制剂Ro-3306和阿奇霉素分别包裹在明胶水凝胶磁性微球中,通过交变磁场驱动微球定向运动,遥控载药微球克服流体阻力和布朗运动进入肿瘤细胞团,着重解决了在交变磁场频率过快时微球磁矩在高频磁场作用下不能及时跟随磁场变化的现象,构建了可控的运动模式。
实际应用中,磁性颗粒可以进行异位注射而缓慢向靶区域引导释放,减少反复关节内注射药物引起的不适,同时维持治疗区域内局部药物浓度。IBRAHIEM等[51]在胆盐表面活性剂构成的脂质双层内部同时负载了磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒及抗炎药氯诺昔康,制备了一种磁性微球,将磁性微球负载在热敏水凝胶中,再将水凝胶注射到骨关节炎大鼠大腿肌肉中原位固化,通过膝盖的外部磁铁将颗粒引导至关节处,实现了氯诺昔康的长时间缓释,成功缓解了大鼠关节肿胀。
磁响应水凝胶在精确靶向递送药物方面相较于磁性热疗展现出更大的发展潜力,未来的研究应致力于增强水凝胶在正常组织中的相容性与稳定性,减少微球异位释放,同时提高其运动能力,确保水凝胶微球能深入到靶区域;此外,还需提升药物释放的靶向性,为磁性水凝胶微球打造更精确的导航系统和更高效的药物触发释放机制。

2.3.5 热响应水凝胶 除了应用于光动力疗法和光固化,近红外光表现出卓越的深层组织穿透能力,光热疗法利用光热转化剂将红外光转换为热量导致局部温度快速升高,对周围骨组织产生显著热疗效应;水凝胶中掺杂的温敏材料也会使水凝胶发生温和相变,从而调控药物释放,两者协同应用还能改变水凝胶的溶胀性能,使水凝胶发生微观层面的形变。
(1)基于光热转换剂的热响应水凝胶:水凝胶被注射进入骨肿瘤组织后,如果未能及时固化容易发生扩散泄漏,在后续的光热、药物治疗中损伤周围健康组织,因此,开发对骨肿瘤靶向性高的响应性固化水凝胶至关重要。ZHAO等[52]通过将CuS纳米颗粒和阿霉素掺入由N-异丙基丙烯酰胺和尿嘧啶双键共聚物形成的水凝胶网络中,制备了pH值/近红外双响应纳米可注射智能水凝胶,将液态溶胶注射到肿瘤周围后进行近红外光照射,CuS纳米颗粒能够将近红外光转换为局部热量,实现快速原位凝胶形成以及对肿瘤细胞的热杀伤,尿嘧啶双键共聚物中的氨基则在水凝胶形成过程中限制非肿瘤酸性微环境的阿霉素爆发释放,从而减少对周围组织的损伤。
构建在人体中无害且稳定的光热转换系统,提升水凝胶材料的强度,是将水凝胶推广于光热疗法的关键。LI等[53]构建了一种由甲基丙烯酸酯改性明胶和甲基丙烯酸酯改性透明质酸组成的双组分水凝胶骨支架;作为保护外壳,热pH值双响应的沸石咪唑酸盐框架8利用表面电荷在无害的光热转换剂黑磷纳米片表面原位结晶形成光热转换系统,将其导入双组分水凝胶骨支架中形成了一种全新的复合水凝胶,这种复合水凝胶保留了双组分良好的注射性和紫外光原位固化特性,更通过双交联网络提升了机械强度,在长期红外光热疗中沸石咪唑酸盐框架8能保护黑磷纳米片免受氧化并增强光热性能,体外实验更是了证明其抗菌、抗炎、促进成骨的优异性能。这项研究为基于水凝胶的疗法铺平了道路,为大规模骨缺损、细菌感染和炎症控制提供了一种比传统治疗侵入性更小但更有效的解决方案。
在糖尿病病理环境下,骨缺损通常更加难以愈合,其中感染、炎症、高糖、缺氧的微环境导致成骨细胞更加难以定植。WU等[54]设计了一种软、硬质双组分的水凝胶系统,在软质水凝胶框架的基础上引入3D打印的聚(ε-己内酯)支架,作为支撑以及骨细胞定植组分;聚多巴胺作为光热转换剂赋予了水凝胶系统光热响应能力;沸石咪唑啉框架8能够同时响应糖尿病骨缺损的酸性微环境和近红外光热治疗,释放Zn2+,Zn2+在释放过程中能够清除活性氧并促进巨噬细胞向M2型分化,释放的Zn2+对环境中的细菌有杀伤作用,导致细菌细胞膜渗漏,同时Zn2+也是成骨、血管形成过程中的催化剂。M2型巨噬细胞能够减弱炎症反应,募集内源性间充质干细胞和内皮细胞,促进新生血管形成和新骨形成。
生物陶瓷在受热后释放离子抑制炎症和细菌生长并促进牙周骨整合,水凝胶的优异负载能力使开发生物陶瓷光热转换剂治疗牙种植体周围病变成为了可能。XIA等[55]开发出了一种利用光热效应的生物陶瓷-海藻酸钙水凝胶,其中负载含铜的硅酸钙生物陶瓷和含锌的硅酸钙生物陶瓷,钙离子使其能够与海藻酸钠交联形成Cu-Zn复合水凝胶,这两种生物陶瓷能够在近红外激光照射下释放铜离子、锌离子和硅酸根离子,在热刺激作用下产生热离子效应,最大限度地破坏细菌细胞;Cu-Zn复合水凝胶还可激活骨髓来源间充质干细胞并促进其成骨分化,并且在不添加额外交联剂的条件下获得较理想的交联效果,产生良好的可注射性能,这为以后的海藻酸盐水凝胶研发提供了一种全新思路。
(2)基于温敏材料的药物释放水凝胶:耐药性也是癌症治疗中的挑战,其产生的原因之一就是化疗药物不能长时间在肿瘤内维持高水平彻底杀灭肿瘤干细胞。将温敏固化功能和药物递送功能集成于水凝胶,使水凝胶能够渗入肿瘤细胞外基质中充分接触肿瘤细胞。SCALZONE等[56]开发了一种由(聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物)-聚乙二醇-(聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物)热敏感水凝胶三嵌段共聚物混合Ⅰ型胶原酶/吡格列酮、多柔比星聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物微球组成的顺序药物递送系统,水凝胶三嵌段共聚物能在室温时保持溶液状态,在体温下发生相变形成药物储存库,水凝胶基质中封装的Ⅰ型胶原酶在固化过程中优先释放以降解肿瘤周围的细胞外基质,之后由储存库中的药物微球缓慢释放吡格列酮、多柔比星,逆转了由药物转运蛋白P-gp介导的多柔比星耐药性,使肿瘤干细胞能够被更好地被多柔比星杀灭。
骨缺损常常伴随着周围组织感染和炎症反应,热疗法和药物治疗往往能对骨缺损的修复产生协同作用。LIU等[57]利用甲状旁腺素、生物玻璃纳米颗粒、单体N-异丙基丙烯酰胺和亲水性N-羟甲基丙烯酰胺研发了一种新型近红外活化水凝胶,在红外光照射下该水凝胶温度升高发生可逆相变,调控生物玻璃纳米颗粒孔径以调节甲状旁腺素的释放,结果显示该复合水凝胶可以产生定周期的脉冲释放和稳定释放两种释放模式,能够有效促进间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,对人脐静脉内皮细胞表现出强烈的促血管生成作用。
(3)基于热形变的水凝胶:机械信号(刚度、黏弹性和附着处的形貌)可以诱导间充质干细胞的分化,目前已有的动态力施加系统能够可控产生宏观机械刺激,但是基质刚度较高无法精确可控地模拟体内细胞分化微环境的机械刺激,通过热刺激控制溶胀产生的微形变和刚度变化是一种可行的解决方案。
CASTRO NAVA等[58]研发了一种热响应性低刚度N-乙基丙烯酰胺/N-异丙基丙烯酰胺水凝胶,该水凝胶掺杂了能够将近红外光转化为热量的金纳米棒,可通过调节脉冲频率产生生理频率下的机械刺激,定时用近红外激光光脉冲机械刺激间充质干细胞后细胞质和细胞核面积都显著增加,通过免疫荧光发现暴露于循环机械力的间充质干细胞前成骨细胞标志物 Runx2和转录激活因子YAP的核输入增加。这意味着低刚度动态基质的机械驱动成功引导人类间充质干细胞分化朝着成骨方向发展,未来可以在此基础上进一步研究生化信号是否可能对间充质干细胞的成骨产生协同效应。
YANG等[59]通过集成单层碳化铌(Nb2C)于聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)制备了一种近红外触发的变形水凝胶,与骨髓间充质干细胞体外共培养产生精确的微运动,微运动诱导骨髓间充质干细胞伸长并向成骨分化,骨折部位的可调微运动激活了肥大软骨细胞的功能和分化,加速了血管内皮生长因子的分泌和新生血管形成,这种效应在骨折边缘处因水凝胶和骨组织的紧密黏合所导致的低应变而减弱;动物体内骨缺损修复实验显示,该水凝胶可调节的微运动通过顺序激活软骨内成骨、促进新生血管形成、启动矿物质沉积和联合加速全层骨再生来加强骨折自然愈合过程。
温敏水凝胶已被广泛研究,而热致形变的水凝胶材料以及相关细胞分化基质仍然是一个新兴领域,未来的热响应水凝胶需更加注重提升机械强度和热稳定性。

2.3.6 pH值响应水凝胶
(1)基于pH响应的活性氧清除载药水凝胶:在骨损伤微环境中,pH值的降低与活性氧的积累密切相关,在炎症细胞浸润过程中尤为显著[60]。活性氧不仅加剧炎症反应,还干扰细胞代谢、促进乳酸积累,导致微环境进一步酸化[61]。pH值作为一种反映骨组织氧化损伤灵敏且方便的指标,科学家采用多种策略使水凝胶能够响应微环境中pH值的变化,进而调节活性氧平衡。
QI等[62]通过在聚甲基丙烯酸酯水凝胶中引入3-丙烯酰胺基苯硼酸,并成功负载了抗氧化剂原花青素和阿米卡星,这种水凝胶在低pH值和高活性氧环境下释放药物,有效杀灭细菌并促进M2型巨噬细胞活化。LUO团队[63]使用4-甲酰基苯硼酸作为交联剂融合羧甲基壳聚糖和葡聚糖构建了双交联网络水凝胶,这种水凝胶具有可注射性,能深入牙周袋,负载的镁-没食子酸在酸性环境下快速降解与清除活性氧,同时促进骨修复和免疫微环境改善。LU等[64]采用CaCO3微球负载骨形态发生蛋白2,并与过氧化氢酶共同添加到聚甲基丙烯酸酯水凝胶中,过氧化氢酶在水凝胶植入后被快速释放以消除活性氧并产生氧气,改善骨损伤的缺氧环境;而载药微球在酸性环境下缓慢降解,诱导间充质干细胞的募集和分化,从而促进成骨,更重要的是,CaCO3微球的降解产物本身就是骨修复的原料,能够在晚期钙质累积时促进骨愈合过程。这种水凝胶实现了过氧化氢酶和骨形态发生蛋白2的差异性释放,有效改善骨损伤微环境,促进成骨。
(2)多功能pH值响应介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒水凝胶:介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒具有特殊结构和功能,其多孔的结构、较高的比表面积能够负载多种药物[65],可通过表面功能化修饰响应多种内外源性刺激,已被广泛地应用于肿瘤、抗感染治疗等[66],但在骨组织工程中的应用潜力尚未充分挖掘。
二氧化硅纳米颗粒在体内通常由肝、肾等部位的巨噬细胞吞噬清除[67]。GONG等[68]创新性地使用二氧化硅纳米颗粒负载柚皮苷,并通过壳聚糖包被纳米颗粒,将其分散在聚甲基丙烯酸酯水凝胶中,在酸性溶酶体环境中释放柚皮苷来抑制破骨细胞活性,促进骨再生。
2.3.7 基质金属蛋白酶响应水凝胶 骨关节炎是一种慢性关节疾病,特征在于软骨退变和关节炎症[69]。基质金属蛋白酶在骨关节炎病理过程中扮演着关键角色,它们由软骨、破骨、巨噬细胞等向关节滑液中分泌,能够降解细胞外基质的胶原蛋白和蛋白多糖等成分,推动骨关节炎的发展[70]。针对基质金属蛋白酶的响应性水凝胶在治疗骨关节炎方面显示出巨大潜力,通过程序性响应释放药物的水凝胶,可以同时完成关节保护、关节润滑、药物治疗的功能[71]。
ZHOU等[72]以甲基丙烯酸酯修饰的磺化偶氮杂环烯、甲基丙烯酸酯透明质酸、二巯基端基质金属蛋白酶13为敏感肽,通过主-客相互作用将抗炎药羟氯喹包封,采用微流控装置和光交联技术制备了一种针对缺氧炎症关节的可注射水凝胶微球系统(HAM-SA@HCQ),由于甲基丙烯酸酯修饰磺化偶氮杂环烯的疏水深腔、酚基和偶氮键,水凝胶微球具有较强的载药能力、较强的活性氧清除能力和特定的缺氧反应药物释放能力,在骨关节炎组织微环境中,水凝胶微球被过量的基质金属蛋白酶13降解,在缺氧条件下释放羟氯喹,与清除活性氧的杯芳烃协同作用,抑制巨噬细胞的炎症反应;HAM-SA@HCQ注射于骨关节炎症关节后可显著减弱氧化应激,下调缺氧诱导因子1α和炎症因子的表达,防止软骨被破坏。
类风湿性关节炎常常反复发作,为了解决患者长期服药、多次关节内注射的问题,SINGH等[73]设计了酶反应性甲氨蝶呤封装的微米级聚合物-脂质杂化水凝胶微球,水凝胶优秀的黏弹性和可塑性使其能在关节腔内长时间保存而不影响关节活动,当关节滑液中基质金属蛋白酶水平升高时加速药物释放,为类风湿性关节炎的长期治疗提供了便利。
对于范围更大且形态不确定的的骨缺损,基质金属蛋白酶可以实时反映局部修复状况。ZHANG等[74]采用注射后反应成胶策略开发了基于四臂聚乙二醇的基质金属蛋白酶敏感水凝胶,利用活性酯基团和胺基在温和条件下发生氨解反应的原理将水凝胶分为2个组分,其一为胺基化的四臂聚乙二醇封装基质金属蛋白酶可裂解肽(pp)形成聚乙二醇-pp-NH2,其二为聚乙二醇封装磷脂酰丝氨酸形成聚乙二醇-磷脂酰丝氨酸,使用双注射器同时注射两种组分使其在缺损骨部位快速成胶,通过基质金属蛋白酶2在骨缺损修复过程中的波动表达实现按需释放磷脂酰丝氨酸,从而抑制巨噬细胞向M1型转化,发挥抗炎作用。
LI等[75]对白细胞介素10细胞外囊泡进行基因工程改造并将其负载在自组装肽水凝胶中,SOX9细胞外囊泡则被负载于聚乙二醇/聚甲基丙烯酸酯复合水凝胶微球中,前者在基质金属蛋白酶13的作用下可快速降解,释放白细胞介素10细胞外囊泡抗炎,后者在自组装肽水凝胶完全降解后才开始在基质金属蛋白酶13作用下分解聚甲基丙烯酸酯缓慢释放细胞外囊泡,起到促进软骨修复作用。这种敏化水凝胶仅一次注射就可以完成抗炎、促进软骨修复的序贯治疗。
2.3.8 活性氧响应水凝胶 活性氧在骨损伤微环境中不仅导致酸化,还通过氧化应激对内源性或外源性干细胞造成严重损害,这种损害表现为抑制干细胞的能量供应、诱导炎症反应、阻碍干细胞的增殖改变方向分化,进而抑制骨损伤的正常修复过程。尽管干细胞疗法在治疗骨关节炎方面展现出显著潜力,能够缓解疼痛、促进软骨和骨细胞分化、修复关节软骨、减少炎症、调节免疫反应、降低细胞凋亡率以及刺激血管生成,改善骨关节炎微环境,但活性氧的存在对移植的干细胞同样构成威胁[76-79]。因此,为保护这些干细胞并确保其功能最大化,研究人员开发出了能够响应活性氧的水凝胶。
MA等[80]开发了可注射活性氧响应水凝胶封装牙髓干细胞,用于治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎,水凝胶中的聚乙二醇二丙烯酸赋予了水凝胶光固化能力,而硫酮醛结构通过氧化还原消耗活性氧,保护牙髓干细胞并促进其向纤维软骨分化,这种水凝胶能显著改善关节微环境,同时作为屏障保护牙髓干细胞,提升牙髓干细胞对酸、碱和蛋白酶降解的抵抗力,减少细胞的死亡率。
间充质干细胞分泌的微泡可以更加针对地促进骨关节炎软骨修复,避免干细胞移植导致的致癌风险,但是微泡的分泌物受到微环境干扰较大且半衰期短,需要进行精确调控释放。LIU等[81]利用苯硼酸、丝素蛋白与聚乙烯醇制备了活性氧响应性水凝胶,负载间充质干细胞分泌的微泡,活性氧在水凝胶体系中作为药物的释放开关:当活性氧水平升高时,苯硼酸的共价键断裂,开关打开,微泡释放,同时活性氧在反应过程中被消耗,开关关闭,微泡停止释放;此外,实数蛋白与聚乙烯醇形成的动态共价键不仅能快速成胶,同时使其在注入关节后承受运动而不过快降解。
为了在外泌体治疗骨关节炎中提升对早期炎症的干预,LU等[82]构建了一种双层水凝胶,水凝胶的上层为负载双氯芬酸苯硼酸交联聚乙烯醇,在活性氧水平升高时苯硼酸降解并释放出双氯芬酸,从而消耗活性氧减轻氧化应激,促进巨噬细胞向M2型分化,抑制炎症;上层水凝胶降解完毕后,下层水凝胶随后暴露,外泌体从由透明质酸组成的下层水凝胶中通过胶原酶降解缓慢释放到微环境中,刺激软骨生成,这种设计紧密衔接了炎症缓解和软骨修复2个阶段,缩短了治疗时间。
苯硼酸作为活性氧响应材料,可以通过动态化学键对负载药物进行控释,消除过量的活性氧,但当活性氧水平过高时水凝胶结构会发生破坏,使负载药物短暂出现爆发性释放。WANG等[83]将活性氧响应和药物释放的水凝胶组分分离并构建双交联网络,解决了这一问题,这种水凝胶可以承受频繁关节活动造成的结构损伤,有效和持久治疗骨关节炎。

| [1] BARBOSA M, JABS EW, HUSTON S. Treacher Collins Syndrome. 2004 Jul 20 [updated 2024 Jun 20]. //ADAM MP, FELDMAN J, MIRZAA GM, PAGON RA, WALLACE SE, BEAN LJH, GRIPP KW, AMEMIYA A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2024. [2] GALINDO ZAVALA R, NÚÑEZ CUADROS E, DÍAZ CORDOVÉS-REGO G, et al. Avances en el tratamiento de la osteoporosis secundaria [Advances in the treatment of secondary osteoporosis]. An Pediatr (Barc). 2014;81(6):399.e1-7. [3] 李峰,尤炯鸣,王锋,等.浙江省温州地区老年脑卒中后患者髋部骨折发病率调查及危险因素分析[J]. 中国基层医药, 2024,31(5):675-680. [4] 熊竹,曾帅丹,韩帅,等.儿童肱骨髁上骨折区域性流行病学调查研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2021,10(3):210-214. [5] SCHADE AT, KHATRI C, NWANKWO H, et al. The economic burden of open tibia fractures: A systematic review. Injury. 2021; 52(6):1251-1259. [6] VAN BERGEN SH, MAHABIER KC, VAN LIESHOUT EMM, et al. Humeral shaft fracture: systematic review of non-operative and operative treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(8):5035-5054. [7] CANCIO-BELLO AM, BARLOW JD. Avascular Necrosis and Posttraumatic Arthritis After Proximal Humerus Fracture Internal Fixation: Evaluation and Management. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2023;16(2):66-74. [8] BHOGAL SS, D’AURIA JL, GEHRMANN SV, et al. Poymethyl Methacrylate for Elbow Arthroplasty: Is There Another Way? J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2024;6(2):233-235. [9] CALLAGHAN JJ, FOREST EE, OLEJNICZAK JP, et al. Charnley total hip arthroplasty in patients less than fifty years old. A twenty to twenty-five-year follow-up note. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(5):704-714. [10] AL-TAMIMI AA, QUENTAL C, FOLGADO J, et al. Stress analysis in a bone fracture fixed with topology-optimised plates. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2020;19(2):693-699. [11] LEGG PI, MALIK-TABASSUM K, IBRAHIM YH, et al. Post-Operative Outcomes of Circular External Fixation in the Definitive Treatment of Tibial Plafond Fractures: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2022;14(4):e24204. [12] PEPELASSI E, PERREA D, DONTAS I, et al. Porous Titanium Granules in comparison with Autogenous Bone Graft in Femoral Osseous Defects: A Histomorphometric Study of Bone Regeneration and Osseointegration in Rabbits. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:8105351. [13] KLEIN A, BAKHSHAI Y, ROEDER F, et al. Technique and results after immediate orthotopic replantation of extracorporeally irradiated tumor bone autografts with and without fibular augmentation in extremity tumors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021; 22(1):750. [14] 郑健茂,毛学理,凌均棨.镁基支架及其在动物骨缺损修复中的应用[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2015(6):720-723. [15] COUTO DS, HONG Z, MANO JF. Development of bioactive and biodegradable chitosan-based injectable systems containing bioactive glass nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(1):115-123. [16] NII M, LAI JH, KEENEY M, et al. The effects of interactive mechanical and biochemical niche signaling on osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells using combinatorial hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(3):5475-5483. [17] WANG L, JANG G, BAN DK, et al. Multifunctional stimuli responsive polymer-gated iron and gold-embedded silica nano golf balls: Nanoshuttles for targeted on-demand theranostics. Bone Res. 2017;5: 17051. [18] LUO Z, ZHANG S, PAN J, et al. Time-responsive osteogenic niche of stem cells: A sequentially triggered, dual-peptide loaded, alginate hybrid system for promoting cell activity and osteo-differentiation. Biomaterials. 2018;163:25-42. [19] XUE B, PENG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. A Novel Superparamagnetic-Responsive Hydrogel Facilitates Disc Regeneration by Orchestrating Cell Recruitment, Proliferation, and Differentiation within Hostile Inflammatory Niche. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(44):e2408093. [20] LI Q, YU H, ZHAO F, et al. 3D Printing of Microenvironment-Specific Bioinspired and Exosome-Reinforced Hydrogel Scaffolds for Efficient Cartilage and Subchondral Bone Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(26): e2303650. [21] AGARWAL R, GARCÍA AJ. Biomaterial strategies for engineering implants for enhanced osseointegration and bone repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:53-62. [22] ZANDI N, SANI ES, MOSTAFAVI E, et al. Nanoengineered shear-thinning and bioprintable hydrogel as a versatile platform for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2021;267:120476. [23] JIANG Z, LI Y, SHEN Y, et al. Robust Hydrogel Adhesive with Dual Hydrogen Bond Networks. Molecules. 2021;26(9):2688. [24] ROCKWELL PN, MANEVAL JE, VOGEL BM, et al. Water Diffusion and Uptake in Injectable ETTMP/PEGDA Hydrogels. J Phys Chem B. 2023;127(22):5055-5061. [25] CAO H, DUAN L, ZHANG Y, et al. Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):426. [26] LIU W, GAO R, YANG C, et al. ECM-mimetic immunomodulatory hydrogel for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected chronic skin wound healing. Sci Adv. 2022;8(27):eabn7006. [27] CHEN Y, WANG X, TAO S, et al. Research advances in smart responsive-hydrogel dressings with potential clinical diabetic wound healing properties. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):37. [28] KASS LE, NGUYEN J. Nanocarrier-hydrogel composite delivery systems for precision drug release. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022;14(2): e1756. [29] LIU D, LI L, SHI BL, et al. Ultrasound-triggered piezocatalytic composite hydrogels for promoting bacterial-infected wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2022;24:96-111. [30] VINIKOOR T, DZIDOTOR GK, LE TT, et al. Injectable and biodegradable piezoelectric hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):6257. [31] ZHOU S, XIAO C, FAN L, et al. Injectable ultrasound-powered bone-adhesive nanocomposite hydrogel for electrically accelerated irregular bone defect healing. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):54. [32] ALIABOUZAR M, KRIPFGANS OD, WANG WY, et al. Stable and transient bubble formation in acoustically-responsive scaffolds by acoustic droplet vaporization: theory and application in sequential release. Ultrason Sonochem. 2021;72:105430. [33] ALIABOUZAR M, DAVIDSON CD, WANG WY, et al. Spatiotemporal control of micromechanics and microstructure in acoustically-responsive scaffolds using acoustic droplet vaporization. Soft Matter. 2020;16(28):6501-6513. [34] HUANG L, QUESADA C, ALIABOUZAR M, et al. Spatially-directed angiogenesis using ultrasound-controlled release of basic fibroblast growth factor from acoustically-responsive scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2021; 129:73-83. [35] ZHAO Z, ZHANG Y, MENG C, et al. Tissue-Penetrating Ultrasound-Triggered Hydrogel for Promoting Microvascular Network Reconstruction. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(23):e2401368. [36] WANG W, ZHANG G, WANG Y, et al. An injectable and thermosensitive hydrogel with nano-aided NIR-II phototherapeutic and chemical effects for periodontal antibacteria and bone regeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):367. [37] XIAO C, WANG R, FU R, et al. Piezo-enhanced near infrared photocatalytic nanoheterojunction integrated injectable biopolymer hydrogel for anti-osteosarcoma and osteogenesis combination therapy. Bioact Mater. 2024;34:381-400. [38] GEHRE C, QIU W, KLAUS JÄGER P, et al. Guiding bone cell network formation in 3D via photosensitized two-photon ablation. Acta Biomater. 2024;174:141-152. [39] GADZHIMAGOMEDOVA Z, ZOLOTUKHIN P, KIT O, et al. Nanocomposites for X-Ray Photodynamic Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(11):4004. [40] HUANG Y, ZHANG L, JI Y, et al. A non-invasive smart scaffold for bone repair and monitoring. Bioact Mater. 2022;19:499-510. [41] ARAMBULA-MALDONADO R, LIU Y, XING M, et al. Bioactive and electrically conductive GelMA-BG-MWCNT nanocomposite hydrogel bone biomaterials. Biomater Adv. 2023;154:213616. [42] ARAMBULA-MALDONADO R, MEQUANINT K. Osteogenic Differentiation Potential of iMSCs on GelMA-BG-MWCNT Nanocomposite Hydrogels. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024;9(6):338. [43] RESINA L, EL HAUADI K, SANS J, et al. Electroresponsive and pH-Sensitive Hydrogel as Carrier for Controlled Chloramphenicol Release. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(3): 1432-1444. [44] CHEAH E, BANSAL M, NGUYEN L, et al. Electrically responsive release of proteins from conducting polymer hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2023;158:87-100. [45] SONG W, LI L, LIU X, et al. Hydrogel microrobots for biomedical applications. Front Chem. 2024;12:1416314. [46] DIAS AMM, COURTEAU A, BELLAYE PS, et al. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Immunotherapy of Cancers through Macrophages and Magnetic Hyperthermia. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(11):2388. [47] KASIŃSKI A, ŚWIERCZEK A, ZIELIŃSKA-PISKLAK M, et al. Dual-Stimuli-Sensitive Smart Hydrogels Containing Magnetic Nanoparticles as Antitumor Local Drug Delivery Systems-Synthesis and Characterization. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(8):6906. [48] ZHOU Q, LIU J, YAN J, et al. Magnetic microspheres mimicking certain functions of macrophages: Towards precise antibacterial potency for bone defect healing. Mater Today Bio. 2023;20:100651. [49] CHEN W, WEN Y, FAN X, et al. Magnetically actuated intelligent hydrogel-based child-parent microrobots for targeted drug delivery. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(4): 1030-1039. [50] TAO Y, LI L, YANG X, et al. Magnetic-driven hydrogel microrobots for promoting osteosarcoma chemo-therapy with synthetic lethality strategy. Front Chem. 2024;12:1386076. [51] IBRAHIEM B, SHAMMA R, SALAMA A, et al. Magnetic targeting of lornoxicam/SPION bilosomes loaded in a thermosensitive in situ hydrogel system for the management of osteoarthritis: Optimization, in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo studies in rat model via modulation of RANKL/OPG. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024;14(7):1982-2002. [52] ZHAO Q, YUE X, MIAOMIAO L, et al. Nano-injectable pH/NIR-responsive hydrogel for chemo-photothermal synergistic drug delivery. J Biomater Appl. 2023;38(5): 614-628. [53] LI Q, WANG R, XUE J, et al. ZIF-8-Modified Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Incorporated into Injectable Dual-Component Hydrogels for Enhanced Photothermal Antibacterial and Osteogenic Activities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(25):32058-32077. [54] WU M, LIU H, ZHU Y, et al. Bioinspired soft-hard combined system with mild photothermal therapeutic activity promotes diabetic bone defect healing via synergetic effects of immune activation and angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2024;14(10): 4014-4057. [55] XIA Y, ZHANG Z, ZHOU K, et al. Cuprorivaite/hardystonite/alginate composite hydrogel with thermionic effect for the treatment of peri-implant lesion. Regen Biomater. 2024;11:rbae028. [56] SCALZONE A, BONIFACIO MA, COMETA S, et al. pH-Triggered Adhesiveness and Cohesiveness of Chondroitin Sulfate-Catechol Biopolymer for Biomedical Applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:712. [57] LIU S, HAN Z, HAO JN, et al. Engineering of a NIR-activable hydrogel-coated mesoporous bioactive glass scaffold with dual-mode parathyroid hormone derivative release property for angiogenesis and bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:1-13. [58] CASTRO NAVA A, DOOLAAR IC, LABUDE-WEBER N, et al. Actuation of Soft Thermoresponsive Hydrogels Mechanically Stimulates Osteogenesis in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells without Biochemical Factors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(1):30-43. [59] YANG Q, XU M, FANG H, et al. Targeting micromotion for mimicking natural bone healing by using NIPAM/NbC hydrogel. Bioact Mater. 2024;39:41-58. [60] CHEN QX, LI JY, HAN F, et al. A Multifunctional Composite Hydrogel That Rescues the ROS Microenvironment and Guides the Immune Response for Repair of Osteoporotic Bone Defects. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(27).doi:10.1002/adfm. 202201067 [61] LI JY, HAN FX, MA JJ, et al. Targeting Endogenous Hydrogen Peroxide at Bone Defects Promotes Bone Repair. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(10). doi:10.1002/adfm.202111208 [62] QI H, WANG B, WANG M, et al. A pH/ROS-responsive antioxidative and antimicrobial GelMA hydrogel for on-demand drug delivery and enhanced osteogenic differentiation in vitro. Int J Pharm. 2024; 657:124134. [63] LUO Q, YANG Y, HO C, et al. Dynamic hydrogel-metal-organic framework system promotes bone regeneration in periodontitis through controlled drug delivery. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024; 22(1):287. [64] LU K, WANG D, ZOU G, et al. A multifunctional composite hydrogel that sequentially modulates the process of bone healing and guides the repair of bone defects. Biomed Mater. 2024;19(3). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ad2ed1. [65] DING Y, HAO Y, YUAN Z, et al. A dual-functional implant with an enzyme-responsive effect for bacterial infection therapy and tissue regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(7):1840-1854. [66] MAO Y, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. A multifunctional nanocomposite hydrogel with controllable release behavior enhances bone regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbad046. [67] ZHANG Y, LIN X, CHEN X, et al. Strategies to Regulate the Degradation and Clearance of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Review. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:5859-5878. [68] GONG S, LANG S, WANG Y, et al. pH-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Naringin for Targeted Osteoclast Inhibition and Bone Regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024; 19:6337-6358. [69] WU Y, LIN Z, YAN Z, et al. Sinomenine contributes to the inhibition of the inflammatory response and the improvement of osteoarthritis in mouse-cartilage cells by acting on the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105715. [70] LI Z, LIU B, ZHAO D, et al. Protective effects of Nebivolol against interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-induced type II collagen destruction mediated by matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13). Cell Stress Chaperones. 2017; 22(6):767-774. [71] LI D, CHEN K, TANG H, et al. A Logic-Based Diagnostic and Therapeutic Hydrogel with Multistimuli Responsiveness to Orchestrate Diabetic Bone Regeneration. Adv Mater. 2022;34(11):e2108430. [72] ZHOU T, XIONG H, YAO SY, et al. Hypoxia and Matrix Metalloproteinase 13-Responsive Hydrogel Microspheres Alleviate Osteoarthritis Progression In Vivo. Small. 2024;20(19):e2308599. [73] SINGH R, JADHAV K, KAMBOJ R, et al. Self-actuating inflammation responsive hydrogel microsphere formulation for controlled drug release in rheumatoid arthritis (RA): Animal trials and study in human fibroblast like synoviocytes (hFLS) of RA patients. Biomater Adv. 2024;160:213853. [74] ZHANG M, YU T, LI J, et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase-Responsive Hydrogel with On-Demand Release of Phosphatidylserine Promotes Bone Regeneration Through Immunomodulation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(20):e2306924. [75] LI S, ZHENG W, DENG W, et al. Logic-Based Strategy for Spatiotemporal Release of Dual Extracellular Vesicles in Osteoarthritis Treatment. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(26):e2403227. [76] KYRIAKIDIS T, PITSILOS C, IOSIFIDOU M, et al. Stem cells for the treatment of early to moderate osteoarthritis of the knee: a systematic review. J Exp Orthop. 2023;10(1):102. [77] VEGA A, MARTÍN-FERRERO MA, DEL CANTO F, et al. Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis With Allogeneic Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Transplantation. 2015; 99(8):1681-1690. [78] HE L, HE T, FARRAR S, et al. Antioxidants Maintain Cellular Redox Homeostasis by Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(2):532-553. [79] ATASHI F, MODARRESSI A, PEPPER MS. The role of reactive oxygen species in mesenchymal stem cell adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation: a review. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(10):1150-1163. [80] MA J, LI J, WEI S, et al. Delivery of dental pulp stem cells by an injectable ROS-responsive hydrogel promotes temporomandibular joint cartilage repair via enhancing anti-apoptosis and regulating microenvironment. J Tissue Eng. 2024;15:20417314241260436. [81] LIU S, CHENG S, CHEN B, et al. Microvesicles-hydrogel breaks the cycle of cellular senescence by improving mitochondrial function to treat osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023; 21(1):429. [82] LU X, DAI S, HUANG B, et al. Exosomes loaded a smart bilayer-hydrogel scaffold with ROS-scavenging and macrophage-reprogramming properties for repairing cartilage defect. Bioact Mater. 2024;38: 137-153. [83] WANG T, HUANG C, FANG Z, et al. A dual dynamically cross-linked hydrogel promotes rheumatoid arthritis repair through ROS initiative regulation and microenvironment modulation-independent triptolide release. Mater Today Bio. 2024;26:101042. |
| [1] | 王 卓, 孙盼盼, 程焕芝, 曹婷婷. 壳聚糖在口腔软硬组织修复与再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 459-468. |
| [2] | 周世博, 俞 兴, 陈海龙, 熊 洋. 纳米晶胶原基骨联合补肾壮筋汤修复骨质疏松大鼠骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 354-361. |
| [3] | 闫启全, 杨立斌, 李梦君, 倪亚卓, 陈科颖, 许 博, 李耀扬, 马士卿, 李 睿, 李建文. 负载抗菌肽KR-12-a5猪小肠黏膜下层复合纳米羟基磷灰石生物支架的制备及抗菌性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 384-394. |
| [4] | 袁 茜, 张 昊, 庞 杰. 负载柚皮苷壳聚糖/β-磷酸三钙支架的表征及生物学性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| [5] | 张峻玮, 陈玲玲, 马振元, 聂伟志, 李朝辉, 王海涛, 段来宝, 侯金永, 毕宏政. 钛制弹性髓内钉治疗锁骨中段骨折断端三维移位及危险因素分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 269-277. |
| [6] | 刘 博, 吾湖孜·吾拉木, 朱光兆, 郭晓斌, 宋子悦, 孟兴补, 胡俊杰, 张晓岗. 贻贝源性抗菌肽涂层改性假体预防早期假体周围感染和调节骨转入[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 278-287. |
| [7] | 郭敬文, 王庆伟, 何子俊, 胡梓航, 陈 志, 朱 荣, 王煜明, 刘文菲, 罗庆禄. 不同浓度硅基生物陶瓷关节腔内注射治疗大鼠膝骨关节炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 288-295. |
一项关于温州市老年人脑卒中后髋关节骨折的流行病学调查指出,偏瘫容易导致老年人行走时跌倒而发生髋关节骨折,在4 500例研究对象中,第1年内发生髋关节骨折176例(发生率为3.91%),第2年内发生髋关节骨折120例(发生率为2.67%)[3]。另一项关于儿童肘部损伤的回顾性分析显示,在2 913例肱骨髁上骨折患儿中,同平面摔伤是最常见的致伤原因(96.0%),其次为低处坠落伤(1.6%)和运动损伤(1.1%),修复这些骨损伤不仅关乎患者身体完整性的恢复,更是他们重返正常生活、重拾日常功能的关键所在[4]。在一项对胫骨骨折的系统性评价中,骨折带给患者高昂的治疗费用、长达56 d的平均住院时间和平均4次手术[5]。其中,感染、骨不连和骨筋膜室综合征等各种并发症不仅增加治疗费用,还会延长住院时间,截肢虽然能够减少并发症的产生,但是将导致40%的患者无法胜任原来的工作,产生了更大的间接经济损失。另一项对肱骨干骨折的系统性研究发现,不论是选择手术治疗还是保守治疗,并发症均会导致长时间的疼痛和活动受限,严重降低患者的生活质量[6]。现有骨损伤修复的方法及不足之处,见表1。
基于以上背景,临床急需一种能够减少炎症、对骨损伤小、性质稳定、能够促进成骨的材料。水凝胶作为一种新兴的骨修复材料有响应环境刺激的能力,正逐渐受到关注,越来越多的科学家将多种响应能力赋予水凝胶以发挥其优势。该文首先描述水凝胶的一般特性,然后阐述科学家如何对水凝胶进行改良,使其拥有多重响应能力,以解决实际骨损伤修复的复杂问题,最后总结多重刺激响应性水凝胶在不同骨损伤中的应用多重刺激响应性水凝胶的未来发展方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者于2024年8月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据建库至2024年8月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Web of Science、万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“hydrogels,acoustic response hydrogel,sound sensitivity hydrogel,ultrasonic hydrogel,photosensitive hydrogel,electric response hydrogel,magnetic sensitivity hydrogel,thermosensitive hydrogel,infrared hydrogel,Deformation responsive hydrogel,enzyme responsive hydrogel,pH response hydrogel,bio actuation hydrogel,dual response hydrogel,Triple responsive hydrogel,Intelligent response,Multiple responsive hydrogel,bone defect,bone repair,bone healing,bone tissue engineering,Degenerative joint diseases,osteoarthritis,Cartilage”,中文检索词为“多响应性水凝胶,智能水凝胶,骨损伤修复,骨组织工程”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 包括论文、实验研究。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed 数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检索共获得8 978篇文献。
1.2 入选标准
纳入标准:①水凝胶应用在骨损伤修复中的相关文献;②水凝胶具有多种功能或者能够响应多种刺激的文献;③原创性高且结论明确的研究。
排除标准:①重复性研究;②综述、荟萃分析、会议论文;③水凝胶功能和响应能力单一的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 初步检索共获得8 978篇文献,首先进行摘要通读,排除内容关联不大、内容质量不高的文献,选取与该文研究方向一致且数据齐全的文章进行分析,最终纳入83篇相关文献进行综述,见图2。
3.2 该综述区别于他人他篇的特点 先前的综述大多以不同材料进行分类,但随着研究和临床的结合,不同类型水凝胶材料逐渐按照临床需求表现出了类似的刺激响应模式。该综述按照主要响应方式进行分类,聚焦于临床需求,全面分析水凝胶响应物理、生物化学刺激因素在骨损伤修复中的应用,阐述了其优缺点,强调可控性与自适应性,从而推动了材料科学与生物医学领域的交叉融合,为骨损伤修复材料的研究和应用提供了新的视角和思路。
3.3 既往他人在该领域研究的贡献 大部分科学家通过在已有的光固化、温敏固化水凝胶负载具有刺激响应能力的生物运输材料(微球、外泌体等)、换能材料(光热剂、磁性材料、电热材料)赋予水凝胶新的响应能力;一部分科学家则使用两种不同响应性的水凝胶通过交联剂构建双重水凝胶网络,这种方式会赋予水凝胶更好的力学性能以及顺序降解的能力,但是交联剂可能对细胞有害;还有少部分科学家在其他应用场景下研发全新的多功能水凝胶支架,并且探索性地将其应用于骨损伤修复。
3.4 该领域研究存在的问题 正如任何新兴技术一样,多重刺激响应性水凝胶也面临着一些挑战,在实际应用中如何确保这些材料在复杂的生物体内环境中保持稳定性和持久性,在需要时能够可控无害地降解,是一个亟待解决的问题。虽然有大量文献支持机械力、形变、水凝胶基质刚度联合其他因素对负载于其中的间充质干细胞软骨分化具有影响的理论,但是研究者通常使用牵引器械产生宏观的力和形变开展研究,这种刺激方式在植入体内后显然和骨折治疗的复位固定原则相冲突。目前仍然缺乏技术产生可控的形变和其他刺激因素共响应水凝胶,将这些理论转化为实际应用,通过现有的4D打印技术可以研发具有微小可逆形变能力的水凝胶材料,并引入电、磁响应系统控制形变,可能是一种可行的解决方案。
3.5 该综述的局限性 该综述检索到的文献虽然都是以临床问题为导向,但是大多实验只进行到动物模型实验和骨细胞共培养阶段,需要进一步检索临床试验文献来验证水凝胶材料的实用性。
3.6 未来展望 展望未来,多重刺激响应性水凝胶的研究和应用将更加广泛和深入。随着材料科学和生物技术的不断进步,会有更多具有新颖响应机制和优异性能的新型水凝胶被开发出来,以满足不同疾病治疗和组织修复的需求:在磁响应水凝胶中,水凝胶可以作为优良的载体和工作介质,负载多功能微型纳米机器人,参与局部骨损伤的修复;在电响应水凝胶中,将骨损伤恢复速度以及修复程度,通过水凝胶传感器量化为康复指标,能够更有效地促进骨折患者的康复训练;此外,可以将针对不同刺激的多种功能水凝胶设计成独立模块,在实际治疗根据需要中进行组合,产生更高效、更全面的治疗效果。
随着跨学科合作的加强,智能响应性水凝胶的研究和应用将不仅局限于实验室,而是更多地走向临床,在临床问题中进行研发转化,期待着这些材料在临床试验中展现出其实际的治疗效果和安全性,为临床治疗提供更多选择。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
该文综述了多重刺激响应性水凝胶在骨损伤修复领域的应用,并探讨了其研发思路和未来发展方向。文章分析了现有骨损伤修复方法的不足,提出了开发新型骨修复材料的必要性,介绍了水凝胶材料的优点,包括可塑性、溶胀性和降解性等,是一种具有潜力的新型骨修复材料,以及现有水凝胶材料成为一种成熟骨修复材料仍需改进之处,如缺乏响应环境变化的能力、降解速率不可控等。文章按照刺激来源(内源性/外源性)和响应类型(固有性质/附加性能)对多重刺激响应性水凝胶进行了分类,并详细介绍了声响应、光响应、电响应、磁响应、热响应、pH值响应、金属基质蛋白酶响应和活性氧响应等不同类型水凝胶在骨损伤修复中的应用。文章总结多重刺激响应性水凝胶的研发思路,包括将多种响应能力赋予水凝胶,构建双重水凝胶网络,以及开发全新的多功能水凝胶支架等。最后提出了多重刺激响应性水凝胶面临的挑战,如材料稳定性、可控降解和体内应用等,并展望了未来发展方向,包括开发新型水凝胶材料、构建模块化设计。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||