[1] AHMAD K, SHAIKH S, CHUN HJ, et al. Extracellular matrix: the critical contributor to skeletal muscle regeneration-a comprehensive review. Inflamm Regen. 2023;43(1):58.
[2] 孔健达,穆玉晶,朱磊,等.骨骼肌再生过程中卫星细胞调控机制及其生态位信号的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(7):1105-1111.
[3] CARECCIA G, MANGIAVINI L, CIRILLO F. Regulation of Satellite Cells Functions during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration: A Critical Step in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;25(1):512.
[4] SNIJDERS T, NEDERVEEN JP, MCKAY BR, et al. Satellite cells in human skeletal muscle plasticity. Front Physiol. 2015;6:283.
[5] KACZMAREK A, KACZMAREK M, CIAŁOWICZ M, et al. The Role of Satellite Cells in Skeletal Muscle Regeneration-The Effect of Exercise and Age. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(10):1056.
[6] ALVES J, MAGALHÃES R, MACHADO A, et al. Non-pharmacological cognitive intervention for aging and dementia: Current perspectives. World J Clin Cases. 2013;1(8):233-241.
[7] 解瑛傲,孔健达,陈芸,等.骨骼肌中卫星细胞衰老生物学机制及潜在的应对策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(25):4094-4100.
[8] DUMONT NA, WANG YX, RUDNICKI MA. Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms regulating satellite cell function. Development. 2015;142(9):1572-1581.
[9] RODRIGUEZ-OUTEIRIÑO L, HERNANDEZ-TORRES F, RAMÍREZ-DE ACUÑA F, et al. Muscle Satellite Cell Heterogeneity: Does Embryonic Origin Matter? Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:750534.
[10] GUGLIUZZA MV, CRIST C. Muscle stem cell adaptations to cellular and environmental stress. Skelet Muscle. 2022;12(1):5.
[11] HEKMATNEJAD B, RUDNICKI MA. Transplantation to study satellite cell heterogeneity in skeletal muscle. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:902225.
[12] ARPKE RW, SHAMS AS, COLLINS BC, et al. Preservation of satellite cell number and regenerative potential with age reveals locomotory muscle bias. Skelet Muscle. 2021;11(1):22.
[13] KOIKE H, MANABE I, OISHI Y. Mechanisms of cooperative cell-cell interactions in skeletal muscle regeneration. Inflamm Regen. 2022; 42(1):48.
[14] LAUMONIER T, MENETREY J. Muscle injuries and strategies for improving their repair. J Exp Orthop. 2016;3(1):15.
[15] DILWORTH FJ, BLAIS A. Epigenetic regulation of satellite cell activation during muscle regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011;2(2):18.
[16] ZAMMIT PS, GOLDING JP, NAGATA Y, et al. Muscle satellite cells adopt divergent fates: a mechanism for self-renewal? J Cell Biol. 2004;166(3):347-357.
[17] CHEN YF, LEE CW, WU HH, et al. Immunometabolism of macrophages regulates skeletal muscle regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10: 948819.
[18] SONG T, SADAYAPPAN S. Featured characteristics and pivotal roles of satellite cells in skeletal muscle regeneration. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2020;41(4):341-353.
[19] WITT R, WEIGAND A, BOOS AM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and myoblast differentiation under HGF and IGF-1 stimulation for 3D skeletal muscle tissue engineering. BMC Cell Biol. 2017;18(1):15.
[20] MARSHALL E, COSTA LM, GUTIERREZ-MARCOS J. Cysteine-rich peptides (CRPs) mediate diverse aspects of cell-cell communication in plant reproduction and development. J Exp Bot. 2011;62(5):1677-1686.
[21] XIAO T, YAN Z, XIAO S, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines regulate epidermal stem cells in wound epithelialization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):232.
[22] MORRONI J, BENEDETTI A, ESPOSITO L, et al. Injury-experienced satellite cells retain long-term enhanced regenerative capacity. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):246.
[23] JOHNSON AL, KAMAL M, PARISE G. The Role of Supporting Cell Populations in Satellite Cell Mediated Muscle Repair. Cells. 2023; 12(15):1968.
[24] BELIZÁRIO JE, FONTES-OLIVEIRA CC, BORGES JP, et al. Skeletal muscle wasting and renewal: a pivotal role of myokine IL-6. Springerplus. 2016;5:619.
[25] ISESELE PO, MAZURAK VC. Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cell Differentiation by Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: A Critical Review. Front Physiol. 2021;12: 682091.
[26] KAGAN P, SULTAN M, TACHLYTSKI I, et al. Both MAPK and STAT3 signal transduction pathways are necessary for IL-6-dependent hepatic stellate cells activation. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0176173.
[27] BURKS TN, COHN RD. Role of TGF-β signaling in inherited and acquired myopathies. Skelet Muscle. 2011;1(1):19.
[28] 孔健达,解瑛傲,陈世娟,等.血流限制训练干预老年肌少症:生物学机制和应用方案建议[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(23): 3743-3750.
[29] 王震,蔺海旗,何霏,等.运动激活骨骼肌卫星细胞:增龄性肌衰减症及肌肉损伤修复的运动预防和治疗[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(23):3752-3759.
[30] CHEN B, SHAN T. The role of satellite and other functional cell types in muscle repair and regeneration. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2019;40(1): 1-8.
[31] SHAMIM B, HAWLEY JA, CAMERA DM. Protein Availability and Satellite Cell Dynamics in Skeletal Muscle. Sports Med. 2018;48(6):1329-1343.
[32] MASSCHELEIN E, D’HULST G, ZVICK J, et al. Exercise promotes satellite cell contribution to myofibers in a load-dependent manner. Skelet Muscle. 2020;10(1):21.
[33] HAWKE TJ. Expanding Roles for Muscle Satellite Cells in Exercise-Induced Hypertrophy. Function (Oxf). 2020;2(1):zqaa040.
[34] SUZUKI K. Cytokine response to exercise and its modulation. Antioxidants. 2018;7(1):17.
[35] DOCHERTY S, HARLEY R, MCAULEY JJ, et al. The effect of exercise on cytokines: implications for musculoskeletal health: a narrative review. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2022;14(1):5.
[36] VARLJEN T, SEKULOVIC G, RAKIC O, et al. Genetic variant rs16944 in IL1B gene is a risk factor for early-onset sepsis susceptibility and outcome in preterm infants. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(2):155-157.
[37] ROSA NETO JC, LIRA FS, ZANCHI NE, et al. Acute exhaustive exercise regulates IL-2, IL-4 and MyoD in skeletal muscle but not adipose tissue in rats. Lipids Health Dis. 2011;10:97.
[38] DE MIGUEL Z, KHOURY N, BETLEY MJ, et al. Exercise plasma boosts memory and dampens brain inflammation via clusterin. Nature. 2021;600(7889):494-499.
[39] 孙磊,李方晖.高强度间歇训练对老龄大鼠骨骼肌减少症及某些氧化应激、脂肪细胞因子和炎症因子的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(8):691-699.
[40] HADDAD F, ZALDIVAR F, COOPER DM, et al. IL-6-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005;98(3): 911-917.
[41] TIERNEY MT, AYDOGDU T, SALA D, et al. STAT3 signaling controls satellite cell expansion and skeletal muscle repair. Nat Med. 2014;20(10):1182-1186.
[42] DE SOUSA CAZ, SIERRA APR, MARTÍNEZ GALÁN BS, et al. Time Course and Role of Exercise-Induced Cytokines in Muscle Damage and Repair After a Marathon Race. Front Physiol. 2021;12:752144.
[43] LIN W, SONG H, SHEN J, et al. Functional role of skeletal muscle-derived interleukin-6 and its effects on lipid metabolism. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1110926.
[44] PIOTROWICZ Z, CZUBA M, CHALIMONIUK M, et al. The Impact of Acute Mild Normobaric Hypoxia and a Single Bout of Exercise to Volitional Exhaustion on Cognitive Performance in Endurance and Strength-Trained Athletes: The role of BDNF, EP-1, Catecholamines and Lactate. J Hum Kinet. 2023;87:77-93.
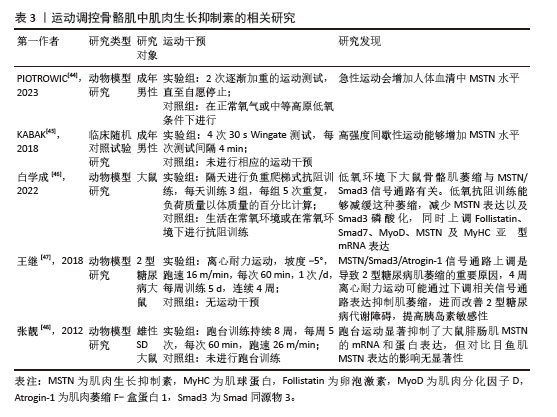
[45] KABAK B, BELVIRANLI M, OKUDAN N. Irisin and myostatin responses to acute high-intensity interval exercise in humans. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2018;35(3):20180008.
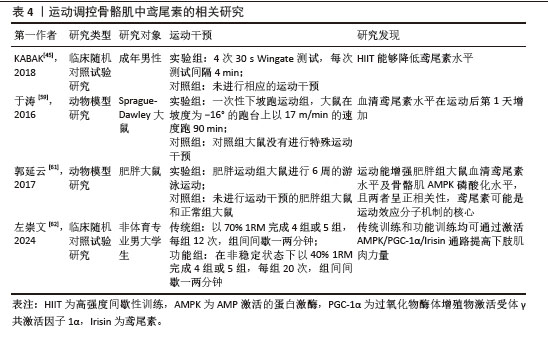
[46] 白学成.抗阻训练缓解低氧诱导的骨骼肌萎缩及对Myostatin/Smad3信号转导通路的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2022.
[47] 王继,周越,张荷,等.Myostatin信号通路在4周离心耐力运动改善2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌萎缩中的作用[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2018,34(3):223-228+282+292.
[48] 张靓,刘小园,杨洪涛.跑台运动对比目鱼肌和腓肠肌肌肉生长抑制素表达的影响[J].沈阳体育学院学报,2012,31(5): 73-75+88.
[49] WILLIAMS MS. Myostatin mutation associated with gross muscle hypertrophy in a child. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(10):1030-1031.
[50] LI W, ZHU Z, HE K, et al. Primary cilia in satellite cells are the mechanical sensors for muscle hypertrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(24):e2103615119.
[51] SNIJDERS T, VERDIJK LB, VAN LOON LJ. The impact of sarcopenia and exercise training on skeletal muscle satellite cells. Ageing Res Rev. 2009;8(4):328-338.
[52] ORAL O. Nitric oxide and its role in exercise physiology. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2021;61(9):1208-1211.
[53] ABREU P, KOWALTOWSKI AJ. Satellite cell self-renewal in endurance exercise is mediated by inhibition of mitochondrial oxygen consumption. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(6):1661-1676.
[54] CARIATI I, SCIMECA M, BONANNI R, et al. Role of Myostatin in Muscle Degeneration by Random Positioning Machine Exposure: An in vitro Study for the Treatment of Sarcopenia. Front Physiol. 2022;13:782000.
[55] 张嫆嫆,司芹芹.鸢尾素在肌肉减少症中的作用[J].生命的化学,2024,44(5): 837-843.
[56] DEWI L, LIN YC, NICHOLLS A, et al. Pax7+ Satellite Cells in Human Skeletal Muscle After Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2023;53(2): 457-480.
[57] ALMADA AE, WAGERS AJ. Molecular circuitry of stem cell fate in skeletal muscle regeneration, ageing and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17(5):267-279.
[58] HUGHES DC, ELLEFSEN S, BAAR K. Adaptations to Endurance and Strength Training. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(6):a029769.
[59] 于涛,李鹏飞,房国梁,等.大鼠一次性下坡跑运动后FNDC5和Irisin水平变化特点[J].中国运动医学杂志,2016,35(10): 908-912.
[60] LIU C, CHU D, KALANTAR-ZADEH K, et al. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021; 8(15):e2004433.
[61] 郭延云,霍琴琴,寿盼盼,等.运动对肥胖大鼠肌因子Irisin及骨骼肌AMPK的影响[J].安徽医科大学学报,2017,52(12): 1778-1782.
[62] 左崇文.功能性和传统抗阻训练对男大学生肌肉适能和血清AMPK/PGC-1α/Irisin通路的影响[D].北京:首都体育学院,2024.
[63] WEI W, RILEY NM, LYU X, et al. Organism-wide, cell-type-specific secretome mapping of exercise training in mice. Cell Metab. 2023;35(7):1261-1279.e11.
[64] ROTTER R, MENSHYKOVA M, WINKLER T, et al. Erythropoietin improves functional and histological recovery of traumatized skeletal muscle tissue. J Orthop Res. 2008; 26(12):1618-1626.
[65] BECKER M, JOSEPH SS, GARCIA-CARRIZO F, et al. Regulatory T cells require IL6 receptor alpha signaling to control skeletal muscle function and regeneration. Cell Metab. 2023;35(10):1736-1751.e7.
[66] ZUO Q, WANG SC, YU XK, et al. Response of macrophages in rat skeletal muscle after eccentric exercise. Chin J Traumatol. 2018;21(2):88-95.
[67] WALTON RG, KOSMAC K, MULA J, et al. Human skeletal muscle macrophages increase following cycle training and are associated with adaptations that may facilitate growth. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):969.
[68] NARKAR VA, DOWNES M, YU RT, et al. AMPK and PPARdelta agonists are exercise mimetics. Cell. 2008;134(3):405-415.
[69] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969.
[70] SOKOL CL, LUSTER AD. The chemokine system in innate immunity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(5):a016303.
[71] ZHANG C, CHENG N, QIAO B, et al. Age-related decline of interferon-gamma responses in macrophage impairs satellite cell proliferation and regeneration. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(5): 1291-1305.
[72] RATNAYAKE D, NGUYEN PD, ROSSELLO FJ, et al. Macrophages provide a transient muscle stem cell niche via NAMPT secretion. Nature. 2021;591(7849):281-287.
[73] GRIFFIN CA, APPONI LH, LONG KK, et al. Chemokine expression and control of muscle cell migration during myogenesis. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 18):3052-3060.
[74] LUTHER SA, BIDGOL A, HARGREAVES DC, et al. Differing activities of homeostatic chemokines CCL19, CCL21, and CXCL12 in lymphocyte and dendritic cell recruitment and lymphoid neogenesis. J Immunol. 2002; 169(1):424-433.
[75] PUCHERT M, ADAMS V, LINKE A, et al. Evidence for the involvement of the CXCL12 system in the adaptation of skeletal muscles to physical exercise. Cell Signal. 2016;28(9):1205-1215.
[76] MACNEIL LG, TARNOPOLSKY MA, CRANE JD. Acute, Exercise-Induced Alterations in Cytokines and Chemokines in the Blood Distinguish Physically Active and Sedentary Aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2021; 76(5):811-818. |