中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1516-1526.doi: 10.12307/2026.584
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
巨噬细胞自噬与肺部疾病:作用的两面性
油惠娟1,吴姝臻1,2,荣 融1,陈立沅1,赵玉晴1,王清路1,欧小伟1,杨风英1
- 1山东体育学院,运动与健康学院,山东省济南市 250102;2临沂市中医医院康复医院,山东省临沂市 276000
-
收稿日期:2025-01-25接受日期:2025-03-14出版日期:2026-02-28发布日期:2025-07-17 -
通讯作者:杨风英,博士,山东体育学院,运动与健康学院,山东省济南市 250102 -
作者简介:油惠娟,女,2001年生,山东体育学院在读硕士,主要从事自噬与肺部炎症性疾病的研究。 -
基金资助:山东省自然科学基金资助项目(ZR2022MH163),项目负责人:杨风英;国家自然科学基金青年基金项目(81601962),项目负责人:杨风英
Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects
You Huijuan1, Wu Shuzhen1, 2, Rong Rong1, Chen Liyuan1, Zhao Yuqing1, Wang Qinglu1, Ou Xiaowei1, Yang Fengying1
- 1School of Sports and Health, Shandong Sport University, Jinan 250102, Shandong Province, China; 2Rehabilitation Hospital, Linyi Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Linyi 276000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2025-01-25Accepted:2025-03-14Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-17 -
Contact:Yang Fengying, MD, School of Sports and Health, Shandong Sport University, Jinan 250102, Shandong Province, China -
About author:You Huijuan, Master candidate, School of Sports and Health, Shandong Sport University, Jinan 250102, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, No. ZR2022MH163 (to YFY); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Foundation), No. 81601962 (to YFY)
摘要:
文题释义:
巨噬细胞自噬:自噬作为细胞内的重要降解途径,参与蛋白质质量平衡和内环境稳态调节,这对于具有吞噬功能的巨噬细胞尤为重要。自噬通过参与巨噬细胞胞葬作用及极化过程进而维持巨噬细胞功能稳定性,在维持机体系统和局部免疫平衡中发挥重要作用。
肺巨噬细胞:分为常驻巨噬细胞和外来浸润巨噬细胞,常驻巨噬细胞又分为肺泡巨噬细胞和肺间质巨噬细胞,其中以肺泡巨噬细胞为主,且目前对肺间质巨噬细胞研究甚少。当肺部出现炎症损伤时,骨髓源单核细胞浸润入肺增加并演变为肺泡巨噬细胞或肺间质巨噬细胞。
背景:巨噬细胞在肺部疾病的发生和进展过程中发挥关键作用,而自噬在维持巨噬细胞内环境稳态和功能稳定中扮演重要角色。已有研究认为巨噬细胞自噬活性在肺部疾病中具有两面性。
目的:通过总结巨噬细胞自噬及与肺部疾病的关系,为靶向巨噬细胞自噬探索肺部疾病的防治策略提供参考依据。
方法:检索中国知网、PubMed数据库建库至2024年9月发表的相关文献,中文检索词为“巨噬细胞自噬、胞葬作用、巨噬细胞极化、急性肺损伤、肺炎、慢性阻塞性肺疾病、肺纤维化、哮喘”;英文检索词为“macrophage autophagy,efferocytosis,macrophage polarization,acute lung injury,pneumonia,chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,pulmonary fibrosis,asthma”,依据选择标准对检索结果进行纳入或排除,最终纳入符合标准的100篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①自噬流受阻诱发巨噬细胞极化失衡并损害其胞葬作用,导致M1型巨噬细胞增多,加重炎症损害。②自噬活性的判断应该以自噬流是否通畅为依据,对自噬降解能力的评价必不可少。部分研究未能全面检测自噬溶酶体降解能力以评估自噬流是否通畅,导致此类研究中所谓肺巨噬细胞自噬在肺部疾病中存在两面性的观点实则与自噬活性的片面判断有关。③不同肺部疾病以及同一疾病的不同发展阶段的病理表现各有差异,激活巨噬细胞自噬对调控急性肺损伤、感染性肺炎、轻度慢性阻塞性肺病、肺纤维化前期以及继发性哮喘等疾病的肺部炎症稳态具有积极作用,但在重度慢性阻塞性肺疾病的纤维化阶段以及肺纤维化进展期,肺巨噬细胞自噬激活加重肺纤维化,体现出巨噬细胞自噬的两面性;过敏性哮喘存在肺常驻巨噬细胞自噬激活和循环血中单核细胞源性浸润巨噬细胞自噬抑制现象,前者与气道狭窄关系密切,后者加重肺炎症紊乱。④因此,明确肺部疾病类型和疾病的进展阶段以及合理评价自噬活性均是今后探讨巨噬细胞自噬活性与疾病关系进而探索疾病治疗策略的重要保障。
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-8924-944X(油惠娟);https://orcid.org/0009-0008-2522-9617(杨风英)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
油惠娟, 吴姝臻, 荣 融, 陈立沅, 赵玉晴, 王清路, 欧小伟, 杨风英. 巨噬细胞自噬与肺部疾病:作用的两面性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526.
You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526.
2.2 巨噬细胞自噬 巨噬细胞是免疫系统的重要组成部分,可监测病毒、细菌等病原微生物以及烟尘等颗粒物,通过吞噬作用对其进行降解,以及可通过胞葬作用特异性识别并清除凋亡细胞以维持局部和系统免疫稳态[25]。自噬是维持细胞内微环境蛋白质质量平衡的高度保守的分解代谢过程,可识别并吞食细胞内变性的蛋白质、受损的细胞器和入侵的病原体,
并将它们降解为可以被细胞重新利用的小分子物质,对于维持细胞内环境稳态至关重要[26]。对于具有吞噬作用的巨噬细胞,其自噬活性尤为重要,不仅影响巨噬细胞极化状态而且直接参与巨噬细胞胞葬作用。然而,多个研究提出自噬存在两面性,即研究认为基础水平自噬可以促进巨噬细胞胞葬作用以及极化反应平衡,最终减轻炎症反应[27-28];而病理情况下出现自噬过度激活现象,导致巨噬细胞胞葬作用受损以及极化反应失衡[29-31]。近期研究指出,个别自噬相关基因的高表达不足以说明自噬活性升高,自噬活性的评价应综合考虑整个自噬流过程,尤其是自噬底物的降解能力[32]。因此,自噬活性与巨噬细胞功能状态的关系及其对机体炎症稳态的影响值得综合分析及深入探讨。
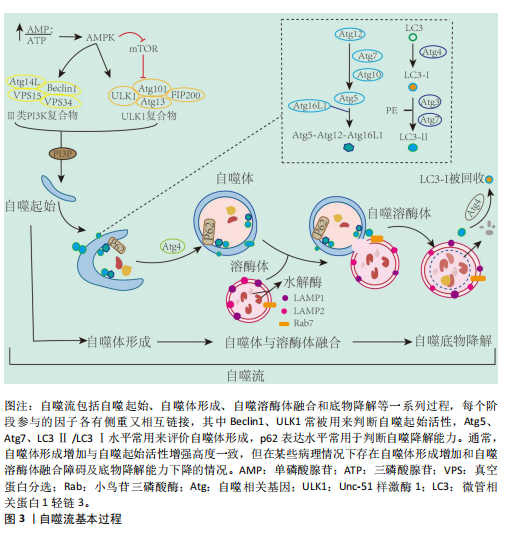
2.2.1 自噬过程 自噬是细胞在自噬相关基因(autophagy related genes,Atg)的调控下利用溶酶体降解自身受损细胞器和大分子物质的过程,按顺序主要分为自噬发生、自噬体形成、自噬溶酶体融合和底物降解等步骤[33]。从自噬发生到最终底物降解的一系列连续且动态的过程称为自噬流(autophagy flux),自噬流中的任一环节受损都会导致自噬无法完成。迄今为止,已经发现40多个自噬相关基因,他们互相协调又分工作用于自噬的各个环节[33]。Unc-51样激酶1(Unc-51-like kinase 1,ULK1)-Atg13-Atg101-FIP200复合物是自噬发生的关键,并受上游腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路的调控[34-35],该复合物在Ⅲ型磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(phosphatidylinostitol3-kinases,PI3K)介导下进一步扩增。Atg12-Atg5-Atg16复合物的形成和Atg8的激活在自噬体的形成中至关重要[36],Atg8是酵母中微管相关蛋白1轻链3(microtubul-associated protein 1 light chain 3,LC3)的同源物,存在LC3-Ⅰ和活化型LC3-Ⅱ两种形式[37],并通过整合体1(sequestosome 1,SQSTM1)又名p62,与泛素化底物链接,促进自噬体成熟[38]。成熟的自噬体与溶酶体融合形成自噬溶酶体,并借助溶酶体水解酶降解为可被细胞重新利用的小分子物质,同时伴有p62表达下降,至此整个自噬流完成(图3)。LC3是目前公认的自噬标记物,LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值增加曾被认为是判断自噬活性增强的金标准[39]。但近年来研究提出,LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值增加只代表自噬体合成增加,若p62表达未能协同下降将出现自噬空泡聚集现象,是自噬降解能力下降,自噬流受阻的表现[18]。
此前也有研究发现溶酶体膜蛋白2缺失小鼠由于溶酶体合成障碍,导致自噬溶酶体无法融合,细胞内出现自噬空泡聚集现象,此时虽然LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值增加,但自噬流停滞在自噬体形成阶段,自噬未完成[19]。因此,LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值增加的同时p62表达降低才是自噬流完成和自噬效率评价的标准[18,40]。
2.2.2 自噬调控巨噬细胞极化 巨噬细胞具有高度异质性和可塑性,其表型和功能取决于所处微环境[41]。其中主要包括经典活化(或促炎)巨噬细胞(M1)和替代活化(或抗炎)巨噬细胞(M2)。促炎M1与抗炎M2两种表型间的转化,或其表型丰度分布的变化称为巨噬细胞极化[42]。在经脂多糖处理的巨噬细胞中发现LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值和p62蛋白的表达水平协同增加现象,同时溶酶体相关标记蛋白LAMP1/2表达降低,说明巨噬细胞自噬流受阻,此时巨噬细胞表型以M1为主,诱导机体脓毒症反应[43]。富氢盐水溶液可增加LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ的比值同时降低p62蛋白的表达,促进自噬流通畅,使巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,从而缓解大鼠的肺部炎症反应[44]。而自噬基因Atg5敲除导致巨噬细胞M1表型增加,诱发炎症紊乱[45]。上述研究提示,自噬流受阻将促进巨噬细胞向促炎M1表型极化,增加促炎因子和趋化因子的释放,自噬流通畅可促进巨噬细胞极化为M2表型,抑制机体炎症反应。
2.2.3 自噬调控巨噬细胞胞葬作用 胞葬作用是指吞噬细胞清除凋亡细胞的过程。经典的胞葬作用包括“寻我”“食我”、细胞骨架重组和消化4个过程[46-49]。通过胞葬作用,一方面清除凋亡细胞,以免其继发性坏死引起机体炎症损害;另一方面实现巨噬细胞由促炎向抗炎表型的转化,共同维持机体炎症稳态。自噬与巨噬细胞胞葬作用关系密切,具有多种共同调节因子[50],尤其体现在细胞骨架重组和消化阶段。研究发现自噬相关蛋白Atg5、Atg7等参与了巨噬细胞骨架凹陷并形成“吞噬杯”(phagocytic cup)的过程。此外,LC3相关的吞噬,即通过自噬溶酶体形式降解内吞物,是胞葬作用重要的消化机制[51-52]。抑制巨噬细胞自噬活性将严重影响其吞噬以及消化降解能力。SANJURJO等[53]发现,Atg7基因敲除使巨噬细胞食我受体c-mer原癌基因酪氨酸激酶表达水平降低,并抑制胞葬作用,且减少M2型巨噬细胞标志物CD163的表达;Atg5缺陷或高脂孵育诱导自噬流受阻的巨噬细胞均存在吞噬后的降解能力显著下降现象[35,54]。
综上,自噬障碍将导致巨噬细胞极化反应失衡,并损害巨噬细胞胞葬作用,使得M1巨噬细胞数量激增,加剧机体炎症反应;自噬流通畅可调节巨噬细胞极化稳态并促进胞葬作用,减轻凋亡细胞堆积,缓解炎症损伤(图4)。
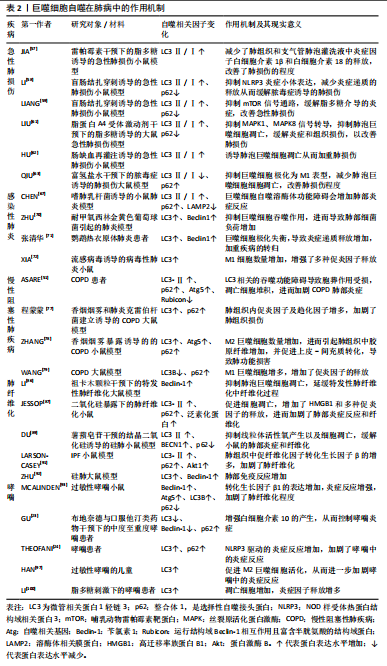
2.3 巨噬细胞自噬在肺部疾病中的作用机制 急性或持续的慢性炎症反应是肺部疾病的共同病理特征。巨噬细胞参与肺部免疫调节、病原体和凋亡细胞的清除以及损伤修复等多个环节。多数研究认为激活巨噬细胞自噬可抑制肺部炎症反应,但部分研究提出巨噬细胞自噬过度激活加剧肺部炎症反应。因此,深入剖析巨噬细胞自噬活性与肺部疾病的关系,对于理清疾病的发病机制和防治策略至关重要。
2.3.1 巨噬细胞自噬在急性肺损伤中的作用 急性肺损伤是由细菌感染、脂多糖、脓毒症、高氧和氯等多种致

病因素引起的临床综合征,其病理特征是肺泡和肺实质的急性炎症反应,伴有中性粒细胞、巨噬细胞等炎症细胞浸润和肺泡出血[55],随着病情加重可发展为急性呼吸窘迫综合征[56]。
大部分研究表明巨噬细胞自噬的激活可抑制炎症反应、减少细胞凋亡,从而在急性肺损伤中起到保护作用。如在脂多糖或脓毒症诱导的急性肺损伤模型中发现,通过增强肺泡巨噬细胞自噬活性,可抑制NOD样受体蛋白3(Nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat protein 3,NLRP3)炎症小体的合成,释放缓解炎症状态,从而改善了肺损伤[57-58]。多个研究发现靶向mTOR信号通路抑制巨噬细胞自噬参与了急性肺损伤的病理过程[59-60],新型 H2S 供体 GYY4137等抑制mTOR信号通路进而激活肺泡巨噬细胞自噬活性的策略均表现出良好的缓解急性肺损伤效果[60-61]。但是,有研究提出肺泡巨噬细胞自噬的激活可通过诱导自身凋亡进而加剧肺损伤。例如,在肠缺血再灌注诱导的急性肺损伤小鼠模型中发现,受损肺组织产生的补体C5a可促进LC3Ⅱ的表达,但诱导肺泡巨噬细胞凋亡,加重肺损伤;沉默小鼠Atg5基因后,缓解了巨噬细胞凋亡,并降低肺损伤程度[62]。据此指出,自噬过度激活将诱导巨噬细胞凋亡,导致病理蛋白的累积和炎症因子释放增多,进而加剧肺损伤。但上述研究仅仅用LC3Ⅱ蛋白表达水平或者电镜下自噬体数量来衡量自噬活性显然存在局限性,此类研究未进一步探索自噬降解能力,实际上很有可能是自噬体累积和自噬空泡现象导致自噬流受阻进而诱发巨噬细胞凋亡。如有研究证实,急性肺损伤动物模型中存在LC3Ⅱ表达增加和自噬体累积现象,通过抑制自噬体形成,降低LC3Ⅱ表达同时增加p62表达水平,缓解了肺泡巨噬细胞凋亡并促进巨噬细胞向M2表型的极化,从而减轻肺损伤[63]。
综上,巨噬细胞自噬对于维持自身内环境稳态和功能稳定进而缓解急性肺损伤的炎症损伤至关重要,个别所谓巨噬细胞自噬过度激活对急性肺损伤不利的观点,由于其未探索自噬降解能力,进而评价自噬流是否通畅,因而存在片面性。
2.3.2 巨噬细胞自噬在感染性肺炎中的作用 感染性肺炎是由细菌、病毒、衣原体、支原体等病原微生物引起的肺炎,其中最为常见的是由细菌引起的细菌性肺炎[64]。研究表明,冠状病毒、嗜肺军团菌等病原体可在宿主肺泡巨噬细胞的液泡内复制,通过干扰巨噬细胞自噬逃避免疫防御[65-66]。CHEN等[28]在军团菌肺炎小鼠模型肺组织中发现巨噬细胞溶酶体功能受损并阻断自噬降解,敲除组蛋白去乙酰化酶6可上调溶酶体膜蛋白2和Rab7的蛋白水平,促进自噬-溶酶体通路,进而增强巨噬细胞的杀菌能力,缓解炎症反应。Rab7表达上调除了促进溶酶体功能外,还可促进巨噬细胞骨架重组进而促进胞葬作用效率[67-68]。此外,研究发现肺泡巨噬细胞自噬活性与其感染的菌株类型有关。DISTEL等[69]在鲍曼不动杆菌诱导的小鼠肺炎模型发现,感染非复制菌株(如19606菌株)的吞噬体会与LC3阳性空泡共定位,形成自噬溶酶体,将病原体降解;而感染复制菌株(如398菌株)的吞噬体不与LC3阳性空泡共定位,逃逸了LC3相关吞噬途径的降解,从而在巨噬细胞内存活和复制。综上,病原体的复制能力和逃避宿主免疫防御的机制与巨噬细胞自噬活性紧密相关,因此,巨噬细胞自噬可作为探究病原体与宿主之间相互作用机制的研究新靶向。
然而,部分研究提出巨噬细胞自噬可能被某些病原体利用来促进自身的存活和繁殖进而加重肺部炎症损害。如:在金黄色葡萄球菌诱导的小鼠肺炎模型中发现,巨噬细胞LC3和Beclin1表达上调,进而抑制巨噬细胞对金黄色葡萄球菌的吞噬作用。3-甲基腺嘌呤抑制自噬体形成可增强巨噬细胞吞噬作用,进而减轻肺组织炎症损害[70];对鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎人群的研究发现,肺组织Beclin1、LC3蛋白表达增加,巨噬细胞吞噬作用存在缺陷[71]。但是,上述研究只用Beclin1、LC3等自噬发生和自噬体形成的相关因子表达来衡量自噬活性,没有对自噬降解效率进行监测,不能准确反映自噬活性,上述结论的依据并不充分。实际上XIA等[72]在型病毒性肺炎小鼠模型中发现,巨噬细胞LC3表达上调的同时存在p62表达升高现象,提示自噬流阻断和自噬体累积,与细胞因子风暴现象密切相关。
综上所述,病原体可通过干扰自噬途径来逃避免疫防御。虽然巨噬细胞自噬与感染性肺炎发生发展的关系存在一定的争议,但经深入分析不难发现,肺巨噬细胞自噬流通畅是巨噬细胞发挥其免疫防御功能,防止肺炎进一步恶化的关键。今后研究中,应全面评价自噬流是否通畅来反映自噬活性,并为巨噬细胞自噬在病原体与宿主相互作用中的机制研究提供可靠的理论依据。
2.3.3 巨噬细胞自噬在慢性阻塞性肺疾病中作用的两面性 COPD是以气流阻塞为典型症状的慢性支气管炎症和(或)肺气肿,可诱发肺心病和呼吸衰竭,严重影响患者生命质量。全球40岁以上人群COPD发病率高达9%-10%,是全球公共卫生安全的重大威胁[73]。长期直接或间接接触香烟烟雾是引起COPD的主要诱因,研究表明,香烟烟雾会阻碍COPD患者肺泡巨噬细胞自噬降解过程[74-75]。多个研究发现COPD患者肺泡巨噬细胞中存在LC3Ⅱ和p62协同升高现象同时伴有泛素化蛋白的积累,提示自噬降解障碍和自噬流受阻[51]。此外,研究发现,脂质激酶Rubicon在肺泡巨噬细胞中的表达降低,进而造成LC3相关吞噬的功能障碍,胞葬作用受损,增加了炎症递质的释放[51,76-78]。WANG等[79]在细颗粒物(particulate matter 2.5,PM 2.5)诱导的COPD大鼠模型中发现,肺泡巨噬细胞溶酶体功能受损使自噬体与溶酶体融合障碍,自噬体积累,导致M1巨噬细胞比例增多,增加了促炎因子的释放。通过补肺益肾方上调肺泡巨噬细胞的自噬通量可抑制COPD大鼠中PM 2.5诱导的肺部炎症。上述研究表明,巨噬细胞自噬流受损会造成胞葬作用受损或极化反应失调,进而导致坏死性细胞凋亡增多,以及M1巨噬细胞数量增加,加剧机体炎症反应。
但值得注意的是,不同于急性肺损伤和感染性肺炎,COPD是一种慢性渐进性疾病,疾病后期易引起肺组织胶原纤维增生,此时,M2巨噬细胞数量增多并参与肺组织损伤修复过程[80],激活自噬将促使巨噬细胞向M2型极化,但此时M2巨噬细胞对肺组织损伤修复的作用易导致肺纤维化,加剧COPD病情[81]。
综上所述,维持巨噬细胞自噬流通畅仍然是COPD患者肺部炎症稳态的关键,但是由于重度COPD常伴有肺组织胶原纤维增生,此时M2巨噬细胞的主要作用体现在促进组织损伤修复,自噬的持续激活增加了M2巨噬细胞表型极化,加剧胶原纤维增生,对疾病恢复产生不利影响,体现出肺巨噬细胞自噬的两面性。
2.3.4 巨噬细胞自噬在肺纤维化中的双重效应 肺纤维化是由遗传、感染和环境暴露等多种原因引起的间质性肺病,最为常见的是病因不明的特发性肺纤维化[82]。另外,长期接触某些有害物质如硅尘、煤尘、石棉等,也可能导致肺纤维化[83]。在肺纤维化早期阶段,以慢性肺部炎症及弥漫性肺泡损伤为主要病理表现,随着肺纤维化的进展,以成纤维细胞增殖和大量的细胞外基质沉积为特征[84-85]。
肺纤维化初期,M1巨噬细胞表型丰度增加,肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和趋化因子等大量促炎因子导致急性炎症和肺组织损伤[20]。巨噬细胞自噬流通畅可通过调控M1/M2表型平衡以及减少巨噬细胞凋亡等多种途径缓解肺纤维化初期的炎症紊乱[85-89]。二氧化硅暴露使肺组织LC3Ⅱ、p62以及泛素化蛋白表达增加,以及肺泡巨噬细胞中自噬体增加、溶酶体减少,导致自噬流受阻,从而诱导凋亡和高迁移率族蛋白B1释放增多,加剧肺部炎症反应和肺纤维化进程[87-89];祖卡姆颗粒和薯蓣皂甙等中药及天然提取物均可通过促进肺巨噬细胞自噬流通畅,控制炎症反应、延缓肺纤维化进展[86,89]。
随着肺纤维化进展,肺部病理表现以细胞外基质成分沉积和纤维增生为主,此时M2巨噬细胞可通过释放抗炎因子如转化生长因子β等促进成纤维细胞分裂增殖,加重肺组织纤维化[20]。二氧化硅粉尘暴露会抑制mTOR通路,进而增加巨噬细胞中LC3和Beclin1蛋白表达和炎症因子的释放,促进人胚肺成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞转化[90]。从特发性肺纤维化患者肺组织分离的巨噬细胞中发现LC3Ⅱ表达增加和线粒体自噬增强现象,激活自噬将使M2巨噬细胞标记物转化生长因子β1表达进一步增加,加重其纤维化程度,而抑制自噬会阻断转化生长因子β1的表达和成纤维细胞分化,缓解肺纤维化[91]。同样,ZHU等[92]在硅肺大鼠模型肺泡巨噬细胞中亦发现,LC3和Beclin1表达水平升高,抑制肺泡巨噬细胞自噬活性可减轻病理损伤。因此,肺纤维化晚期,巨噬细胞自噬的持续激活促进肺泡巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,激活成纤维细胞分裂增殖从而加剧肺纤维化,体现出巨噬细胞自噬活性的不利面。
2.3.5 巨噬细胞自噬在哮喘中的双重效应 哮喘是以咳嗽、喘息、鼻塞、呼气性气流受阻等为主要临床症状的肺部慢性疾病,与遗传、过敏反应和环境刺激等多种因素有关。虽然临床症状类似,但由于发病原因、病情严重程度不同其病理机制和治疗策略均有差异,体现出该疾病的复杂性,关于巨噬细胞自噬与哮喘发生发展的关系亦具有两面性。
通过检测Beclin1、Atg5、LC3Ⅱ、p62等自噬相关蛋白发现,在包括室内尘螨等致敏原诱导的过敏性哮喘,无论是气道平滑肌细胞、小气道上皮细胞和纤毛细胞,还是肺巨噬细胞均存在不同程度的自噬激活现象,并且用自噬抑制剂氯喹抑制自噬溶酶体融合以阻碍自噬流后,可以缓解转化生长因子β1高表达和与其相关的纤维化倾向[93]。体外和体内实验均显示布地奈德和辛伐他汀干预后,气道巨噬细胞Beclin1和LC3的表达降低,同时p62表达增加,并缓解气道炎症反应,说明布地奈德和辛伐他汀可通过阻碍自噬流抑制自噬活性进而发挥治疗哮喘的作用[93]。此外,在丙烯酰胺暴露诱发的过敏性哮喘中亦发现肺巨噬细胞线粒体自噬增强现象[94]。多个研究共同提示肺巨噬细胞自噬活性的应激性增强,导致黏液生成增多、平滑肌厚度增加和肺纤维增生等,影响肺功能[95-96]。
不同于肺常驻巨噬细胞,过敏性哮喘患者外周单核细胞来源的巨噬细胞存在自噬抑制现象。虽然HAN等[97]对儿童过敏性哮喘患者的研究发现单核细胞来源的巨噬细胞中自噬相关基因LC3蛋白表达增加,但THEOFANI等[24]的研究显示外周单核细胞来源的巨噬细胞中LC3蛋白表达增加同时存在p62蛋白累积现象,提示其自噬流受阻。因此,HAN等[97]的研究由于未检测代表自噬流状态的p62表达水平,对自噬活性的评价存在一定局限性。同时THEOFANI等[24]研究提示,不同于肺常驻巨噬细胞,过敏原刺激将阻碍外周单核细胞源性巨噬细胞自噬流并促使M1促炎表型丰度增加,哮喘发生时外周巨噬细胞的持续浸润将进一步加重肺部炎症反应[91]。
除了过敏反应引起的哮喘,病原体感染、颗粒物暴露或者脂多糖刺激亦可继发哮喘[98-100],此时其发病机制与过敏性哮喘存在诸多差异,而与前述的感染性肺炎和急性肺损伤等病理特点一致。现有文献分析显示,继发哮喘疾病初期病理特点与感染性肺炎或急性肺损伤类似,此时肺巨噬细胞自噬流受阻和促炎M1表型丰度增加。而关于过敏性哮喘,致敏原引起的应激性超敏反应可激活肺常驻巨噬细胞自噬,促进M2巨噬细胞的极化,与哮喘患者肺胶原蛋白合成增加和基质细胞过度激活进而加剧哮喘症状相关;同时致敏原可使外周单核细胞源巨噬细胞自噬流受阻,促使M1表型极化和肺组织浸润增加,进一步加重哮喘的炎症反应。因此,关于巨噬细胞自噬活性与哮喘关系的研究应在细化致病原因的基础上进行。
综上所述,巨噬细胞自噬在肺部疾病中存在两面性(图5,表2)。当肺组织病理表现以炎症紊乱为主要特征时,如急性肺损伤、感染性肺炎、轻度COPD和肺纤维化初期以及继发性哮喘,普遍存在巨噬细胞自噬流受阻和活性下降现象,激活自噬并保持自噬流通畅可以通过调控巨噬细胞极化和促进胞葬作用促使肺泡巨噬细胞向M2表型转化,进而维持炎症稳态;但在重度COPD的纤维化阶段和随着肺纤维化进展,巨噬细胞自噬的应激性激活将进一步促进肺泡巨噬细胞向M2表型转化,并参与激活成纤维细胞从而加重细胞外基质沉积和肺纤维化,表现出不利的一面。此外,在过敏性哮喘发病过程中,巨噬细胞自噬的两面性还体现在肺常驻巨噬细胞自噬的激活和外周浸润巨噬细胞自噬的抑制。
| [1] BHAT AA, AFZAL M, GOYAL A, et al. The impact of formaldehyde exposure on lung inflammatory disorders: Insights into asthma, bronchitis, and pulmonary fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 2024;394:111002. [2] SHAN Q, QIU J, DONG Z, et al. Lung Immune Cell Niches and the Discovery of New Cell Subtypes. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(45): e2405490. [3] WOO YD, JEONG D, CHUNG DH. Development and Functions of Alveolar Macrophages. Mol Cells. 2021;44(5):292-300. [4] NIU X, YOU Q, HOU K, et al. Autophagy in cancer development, immune evasion, and drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2025;78: 101170. [5] WANG EJ, WU MY, REN ZY, et al. Targeting macrophage autophagy for inflammation resolution and tissue repair in inflammatory bowel disease. Burns Trauma. 2023;11: tkad4. [6] HASPEL JA, CHOI AM. Autophagy: a core cellular process with emerging links to pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;184(11):1237-1246. [7] ZHAO H, WANG Y, QIU T, et al. Autophagy, an important therapeutic target for pulmonary fibrosis diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;502:139-147. [8] HARNETT MM, PINEDA MA, LATRÉ DE LATÉ P, et al. From Christiande Duve to Yoshinori Ohsumi: More to autophagy than just dining athome. Biomed J. 2017;40(1):9-22. [9] DUNN WA Jr. Studies on the mechanisms of autophagy: formation of the autophagic vacuole. J Cell Biol. 1990;110(6):1923-1933. [10] MIZUSHIMA N, NODA T, YOSHIMORI T, et al. A protein conjugation system essential for autophagy. Nature. 1998;395(6700):395-398. [11] JAMES DE, NIJKAMP FP. Neuroendocrine and immune interactions with airway macrophages.Inflamm Res. 2000;49(6): 254-265. [12] OHTANI S, IWAMARU A, DENG W, et al. Tumor suppressor 101F6 and ascorbate synergistically and selectively inhibit non-small cell lung cancer growth by caspase-independent apoptosis and autophagy. Cancer Res. 2007;67(13):6293-6303. [13] KIM HP, CHEN ZH, CHOI AM, et al. Analyzing autophagy in clinical tissues of lung and vascular diseases. Methods Enzymol. 2009; 453:197-216. [14] RYTER SW, CHEN ZH, KIM HP, et al. Autophagy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: homeostatic or pathogenic mechanism? Autophagy. 2009;5(2):235-237. [15] RYTER SW, CHOI AM. Autophagy in the lung. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010;7(1):13-21. [16] CHEN ZH, KIM HP, Sciurba FC, et al. Egr-1 regulates autophagy in cigarette smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3316. [17] BONILLA DL, BHATTACHARYA A, SHA Y, et al. Autophagy regulates phagocytosis by modulating the expression of scavenger receptors. Immunity. 2013;39(3):537-547. [18] SOS L, GARABUCZI É, SAGHY T, et al. Palmitate Inhibits Mouse Macrophage Efferocytosis by Activating an mTORC1-Regulated Rho Kinase 1 Pathway: Therapeutic Implications for the Treatment of Obesity. Cells. 2022;11(21):3502. [19] CHI C, LEONARD A, KNIGHT WE, et al. LAMP-2B regulates human cardiomyocyte function by mediating autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(2):556-565. [20] LIU C, XIAO K, XIE L. Progress in preclinical studies of macrophage autophagy in the regulation of ALI/ARDS. Front Immunol. 2022;13:922702. [21] 欧阳倪冰, 张冉阳, 王鹏, 等. 肺泡巨噬细胞在急性肺损伤中的作用[J].免疫学杂志,2024,40(6):551-554. [22] HU Y, HUANG Y, ZONG L, et al. Emerging roles of ferroptosis in pulmonary fibrosis: current perspectives, opportunities and challenges. Cell Death Discov. 2024;10(1): 301. [23] GU W, CUI R, DING T, et al. Simvastatin alleviates airway inflammation and remodelling through up-regulation of autophagy in mouse models of asthma. Respirology. 2017;22(3):533-541. [24] THEOFANI E, SEMITEKOLOU M, SAMITAS K, et al. TFEB signaling attenuates NLRP3-driven inflammatory responses in severe asthma. Allergy. 2022;77(7):2131-2146. [25] YANG S, ZHAO M, JIA S. Macrophage: Key player in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1080310. [26] RAO L, EISSA NT. Autophagy in Pulmonary Innate Immunity. J Innate Immun. 2020; 12(1):21-30. [27] YANG Y, WEI S, CHU K, et al. Upregulation of autophagy in M2 macrophage by vitamin D alleviates crystalline silica-induced pulmonary inflammatory damage. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2021;225:112730. [28] CHEN M, CAO X, ZHENG R, et al. The role of HDAC6 in enhancing macrophage autophagy via the autophagolysosomal pathway to alleviate legionella pneumophila-induced pneumonia. Virulence. 2024;15(1):2327096. [29] LIU X, GAO C, WANG Y, et al. BMSC-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury by miR-384-5p-Controlled Alveolar Macrophage Autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:9973457. [30] SHEN J, FU Y, LIU F, et al. Ursolic Acid Promotes Autophagy by Inhibiting Akt/mTOR and TNF-α/TNFR1 Signaling Pathways to Alleviate Pyroptosis and Necroptosis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Infected Macrophages.Inflammation. 2023;46(5): 1749-1763. [31] FU J, LU L, WANG H, et al .Hirsutella sinensis mycelium regulates autophagy of alveolar macrophages via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway . Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(8):1810-1823. [32] THEOFANI E, XANTHOU G. Autophagy: A Friend or Foe in Allergic Asthma? Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6314. [33] DEBNATH J, GAMMOH N, RYAN KM. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24(8):560-575. [34] PAREEK G, KUNDU M. Physiological functions of ULK1/2. J Mol Biol. 2024; 436(15):168472 [35] CAI YY, LI L, ZHU XM, et al. The crucial role of the regulatory mechanism of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in fungi. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:1019543. [36] WANG S, LI H, YUAN M, et al. Role of AMPK in autophagy. Front Physiol. 2022;13: 1015500. [37] ZOU L, LIAO M, ZHEN Y, et al. Autophagy and beyond: Unraveling the complexity of UNC-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) from biological functions to therapeutic implications. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022;12(10):3743-3782. [38] VARGAS JNS, HAMASAKI M, KAWABATA T, et al. The mechanisms and roles of selective autophagy in mammals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24(3):167-185. [39] KE PY. Molecular Mechanism of Autophagosome-Lysosome Fusion in Mammalian Cells. Cells. 2024;13(6):500. [40] ESCOBAR KA, COLE NH, MERMIER CM, et al. Autophagy and aging: Maintaining the proteome through exercise and caloric restriction. Aging Cell. 2019;18(1):e12876. [41] DENG L, JIAN Z, XU T, et al. Macrophage Polarization: An Important Candidate Regulator for Lung Diseases. Molecules. 2023;28(5):2379. [42] PENG Y, ZHOU M, YANG H, et al. Regulatory Mechanism of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in the Development of Autoimmune Diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2023;2023:8821610. [43] ZHOU J, LI C, LU M, et al. Pharmacological induction of autophagy reduces inflammation in macrophages by degrading immunoproteasome subunits. PLoS Biol. 2024;22(3):e3002537. [44] YIN Z, XU W, LING J, et al. Hydrogen-rich solution alleviates acute radiation pneumonitis by regulating oxidative stress and macrophages polarization. J Radiat Res. 2024;65(3):291-302. [45] LIU K, ZHAO E, ILYAS G, et al. Impaired macrophage autophagy increases the immune response in obese mice by promoting proinflammatory macrophage polarization. Autophagy. 2015;11(2):271-284. [46] 杨风英, 赵玉晴, 油惠娟, 等. 巨噬细胞的胞葬作用:肥胖相关代谢性疾病治疗的新靶向[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(2):430-440. [47] ZHANG Y, WANG Y, DING J, et al. Efferocytosis in multisystem diseases (Review) . Mol Med Rep. 2022;25(1):13. [48] DORAN AC, YURDAGUL A JR, TABAS I. Efferocytosis in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20(4):254-267. [49] LI Q, LIU H, YIN G, et al. Efferocytosis: Current status and future prospects in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Heliyon. 2024;10(7):e28399. [50] FAZELI G, WEHMAN AM. Safely removing cell debris with LC3-associated phagocytosis. Biol Cell. 2017;109(10):355-363. [51] ASARE PF, ROSCIOLI E, HURTADO PR, et al. LC3-Associated Phagocytosis (LAP): A Potentially Influential Mediator of Efferocytosis-Related Tumor Progression and Aggressiveness. Front Oncol. 2020;10:1298. [52] TANZER MC. You are what you eat and how you digest it! A discussion on inflammatory efferocytosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11: 1132696. [53] SANJURJO L, ARAN G, TELLEZ É, et al. CD5L Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization through Autophagy-Mediated Upregulation of ID3. Front Immunol. 2018;9:480. [54] OUIMET M, EDIRIWEERA H, AFONSO MS, et al. microRNA-33 Regulates Macrophage Autophagy in Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37(6):1058-1067. [55] REN Z, ZHENG Z, FENG X. Role of gut microbes in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Gut Microbes. 2024;16(1):2440125. [56] DONG JY, YIN HL, HAO H, et al. Research Progress on Autophagy Regulation by Active Ingredients of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Treatment of Acute Lung Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:1671-1691. [57] JIA X, CAO B, AN Y, et al. Rapamycin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting IL-1β and IL-18 production. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;67:211-219. [58] LI D, LI C, WANG T, et al. Geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase 1 knockdown suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activity via promoting autophagy in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108106. [59] LIANG J, LIU J, TANG Y, et al. Sophoridine inhibits endotoxin-induced acute lung injury by enhancing autophagy of macrophage and reducing inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;112(1):115-125. [60] ZHU P, BU H, TAN S, et al. A Novel Cochlioquinone Derivative, CoB1, Regulates Autophagy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection through the PAK1/Akt1/mTOR Signaling Pathway. J Immunol. 2020;205(5):1293-1305. [61] LIU H, ZHOU K, LIAO L, et al. Lipoxin A4 receptor agonist BML-111 induces autophagy in alveolar macrophages and protects from acute lung injury by activating MAPK signaling. Respir Res. 2018;19(1):243. [62] HU R, CHEN ZF, YAN J, et al. Complement C5a exacerbates acute lung injury induced through autophagy-mediated alveolar macrophage apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(7):e1330. [63] QIU P, LIU Y, CHEN K, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline regulates the polarization and apoptosis of alveolar macrophages and attenuates lung injury via suppression of autophagy in septic rats. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(12):974. [64] LONG ME, MALLAMPALLI RK, HOROWITZ JC. Pathogenesis of pneumonia and acute lung injury. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022;136(10):747-769. [65] LIANG H, LUO D, LIAO H, et al. Coronavirus Usurps the Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway and Induces Membranes Rearrangement for Infection and Pathogenesis. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:846543. [66] SHERWOOD RK, ROY CR. Autophagy Evasion and Endoplasmic Reticulum Subversion: The Yin and Yang of Legionella Intracellular Infection. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016;70: 413-433. [67] CHEN M, CAO X, ZHENG R, et al. The role of HDAC6 in enhancing macrophage autophagy via the autophagolysosomal pathway to alleviate legionella pneumophila-induced pneumonia. Virulence. 2024;15(1):2327096. [68] SUBRAMANIAM R, MUKHERJEE S, CHEN H, et al. Restoring cigarette smoke-induced impairment of efferocytosis in alveolar macrophages. Mucosal Immunol. 2016;9(4):873-883. [69] DISTEL JS, VENANZIO GD, MACKEL JJ, et al. Replicative Acinetobacter baumannii strains interfere with phagosomal maturation by modulating the vacuolar pH. PLoS Pathog. 2023;19(6):e1011173. [70] ZHU Y, TANG Z, HUO S, et al. Regulatory relationship between macrophage autophagy and PVL-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Immunobiology. 2022;227(3):152223. [71] 张清华, 郭国华, 肖建宏, 等. 鹦鹉热衣原体肺炎患者巨噬细胞功能变化及极化水平[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志,2024, 34(17):2599-2603. [72] XIA C, XU W, AI X, et al. Autophagy and Exosome Coordinately Enhance Macrophage M1 Polarization and Recruitment in Influenza A Virus Infection. Front Immunol. 2022;13:722053. [73] 戴振威, 杨悦, 付佳琪, 等.群医学及全球健康研究进展及启示[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2023,27(11):1336-1341. [74] LEVRA S, ROSANI U, GNEMMI I, et al. Impaired autophagy in the lower airways and lung parenchyma in stable COPD. ERJ Open Res. 2023;9(6):00423-2023. [75] LIU Y, XU J, LIU T, et al. FSTL1 aggravates cigarette smoke-induced airway inflammation and airway remodeling by regulating autophagy. BMC Pulm Med. 2021;21(1):45. [76] BARNES PJ, BAKER J, DONNELLY LE. Autophagy in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022;136(10):733-746. [77] 程蒙蒙, 刘新光, 魏焱鑫, 等.通塞颗粒阻抑巨噬细胞炎症反应改善大鼠慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2024,44(10):1995-2003. [78] ZHANG L, CHENG T, LIU C, et al. The role and mechanism of macrophage autophagy in the experimental model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Tob Induc Dis. 2024;22:10.18332/tid/186403. [79] WANG J, HE W, YUE H, et al. Effective-components combination alleviates PM2.5-induced inflammation by evoking macrophage autophagy in COPD. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;321:117537. [80] HAN H, PENG G, MEISTER M, et al. Electronic Cigarette Exposure Enhances Lung Inflammatory and Fibrotic Responses in COPD Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 726586. [81] BALTAZAR-GARCIA EA, VARGAS-GUERRERO B, GASCA-LOZANO LE, et al. Molecular changes underlying pulmonary emphysema and chronic bronchitis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: An updated review. Histol Histopathol. 2024;39(7): 805-816. [82] GE Z, CHEN Y, MA L, et al. Macrophage polarization and its impact on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2024; 15:1444964. [83] KOUDSTAAL T, FUNKE-CHAMBOUR M, KREUTER M, et al. Pulmonary fibrosis: from pathogenesis to clinical decision-making. Trends Mol Med. 2023;29(12):1076-1087. [84] LI J, ZHAI X, SUN X, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of pulmonary fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1031890. [85] WEN JH, LI DY, LIANG S, et al. Macrophage autophagy in macrophage polarization, chronic inflammation and organ fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:946832. [86] LI S, LIU G, GU M, et al. A novel therapeutic approach for IPF: Based on the “Autophagy - Apoptosis” balance regulation of Zukamu Granules in alveolar macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;297:115568. [87] JESSOP F, HAMILTON RF, RHODERICK JF, et al. Autophagy deficiency in macrophages enhances NLRP3 inflammasome activity and chronic lung disease following silica exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016; 309:101-110. [88] TAN S, CHEN S. Macrophage Autophagy and Silicosis: Current Perspective and Latest Insights. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(1):453. [89] DU S, LI C, LU Y, et al. Dioscin Alleviates Crystalline Silica-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis through Promoting Alveolar Macrophage Autophagy. Theranostics. 2019;9(7):1878-1892. [90] 杜悦,黄芳财,关岚,等. PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路介导巨噬细胞自噬影响矽尘致肺成纤维细胞表型转化[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版),2023,48(8):1152-1162. [91] LARSON-CASEY JL, DESHANE JS, RYAN AJ, et al. Macrophage Akt1 Kinase-Mediated Mitophagy Modulates Apoptosis Resistance and Pulmonary Fibrosis. Immunity. 2016; 44(3):582-596. [92] ZHU HX, GAO JL, ZHAO MM, et al. Effects of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the autophagic activity of alveolar macrophages in a rat model of silicosis. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(6):2577-2582. [93] MCALINDEN KD, DESHPANDE DA, GHAVAMI S, et al. Autophagy Activation in Asthma Airways Remodeling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019;60(5):541-553. [94] ABDELAZIZ MH, ABDELWAHAB SF, WAN J, et al. Alternatively activated macrophages; a double-edged sword in allergic asthma. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):58. [95] SARADNA A, DO DC, KUMAR S, et al. Macrophage polarization and allergic asthma. Transl Res. 2018;191:1-14. [96] KI EY, JI KE, PARK H, et al. A study on specific factors related to inflammation and autophagy in BEAS-2B cells induced by urban particulate matter (PM, 1648a) and histological evaluation of PM-induced bronchial asthma model in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;123:110730. [97] HAN X, LIU L, HUANG S, et al. RNA m6A methylation modulates airway inflammation in allergic asthma via PTX3-dependent macrophage homeostasis. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):7328. [98] LIU X, WANG Y, CHEN C, et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and risk of childhood asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb Pathog. 2021;155:104893. [99] CHAN YL, WANG B, CHEN H, et al. Pulmonary inflammation induced by low-dose particulate matter exposure in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2019;317(3):L424-L430. [100] LI X, WANG W, SHAO Y, et al. LncTRPM2-AS inhibits TRIM21-mediated TRPM2 ubiquitination and prevents autophagy-induced apoptosis of macrophages in asthma. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(12):1153. |
| [1] | 孙 蕾, 张 琦, 张 宇. 绿原酸蛋白微球/聚己内酯静电纺丝膜的促成骨效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1877-1884. |
| [2] | 吴妍廷, 李 宇, 廖金凤. 氧化镁纳米粒调控成骨与血管生成相关基因表达促进骨缺损愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [3] | 黎清斌, 林建辉, 黄文杰, 王明爽, 杜间开, 劳永锵. 膝关节周围骨巨细胞瘤病灶扩大刮除后填充骨水泥:软骨下植骨与不植骨的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [4] | 蒋星海, 宋玉林, 李德津, 邵建敏, 徐军志, 刘华凯, 吴应国, 沈岳辉, 冯思诚. 血管内皮生长因子165基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞构建血管化两亲性肽凝胶模块[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [5] | 王奇飒, 卢雨征, 韩秀峰, 赵文玲, 石海涛, 徐 哲. 3D打印甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸/脱细胞皮肤水凝胶支架的细胞相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [6] | 高艳果, 郭 旭, 李晓晗, 陈仕琦, 朱海涛, 黄良永, 叶 方, 卢 伟, 王启斌, 郑 涛, 陈 黎. 糖尿病皮肤创面模型小鼠正交实验优选“红黄白”凝胶的处方配比[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1921-1928. |
| [7] | 刘宏杰, 牟秋菊, 申玉雪, 梁 飞, 祝丽丽. 金属有机框架/羧甲基壳聚糖-氧化海藻酸钠/富血小板血浆水凝胶促糖尿病感染创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [8] | 闵昌琴, 黄 英. pH值/近红外激光刺激响应型载药系统的构建及在抗口腔鳞癌中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1940-1951. |
| [9] | 邵子瑜, 李 倩, 曲曼姑丽·阿布都克力木, 韩友军, 胡 杨. 三种比例双相磷酸钙的制备及性能表征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1952-1961. |
| [10] | 郑旭颖, 胡洪成, 许礼兵, 韩建民, 邸 萍. 不同载荷形式和内连接形状下两段式粘接固位氧化锆种植体的应力大小和分布[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [11] | 周红丽, 王晓龙, 郭 蕊, 姚轩轩, 郭 茹, 周熊涛, 何祥一. 纳米羟基磷灰石/海藻酸钠/聚己内酯/阿仑膦酸钠支架的制备及表征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [12] | 杨利霞, 刁立琴, 李 华, 冯亚婵, 刘 鑫, 于月欣, 窦茜茜, 谷辉峰, 徐兰举. 重组Ⅲ型人源化胶原蛋白改善大鼠光老化皮肤的调控机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1988-2000. |
| [13] | 董春阳, 周天恩, 莫孟学, 吕文权, 高 明, 朱瑞凯, 高志伟. 二甲双胍联合血水草敷料治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013. |
| [14] | 潘之怡, 黄嘉雯, 薛文君, 徐建达. MXene柔性电子传感器的优势及在糖尿病足创面监测中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2023-2032. |
| [15] | 杨学涛, 朱梦菡, 张宸熙, 孙一民, 叶 玲. 抗氧化纳米材料在口腔中的应用和不足[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024年9月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据库建库至2024年9月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库和中国知网。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“macrophage autophagy,efferocytosis,macrophage polarization,acute lung injury,pneumonia,chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,pulmonary fibrosis,asthma”;中文检索词为“巨噬细胞自噬、胞葬作用、巨噬细胞极化、急性肺损伤、肺炎、慢性阻塞性肺疾病、肺纤维化、哮喘”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、文献综述和基础实验等。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 中英文数据库检索策略见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 共检索得到文献1 177篇,中文文献162篇来源于中国知网数据库,英文文献1 015篇来源于PubMed数据库,最终纳入引用100篇文献,其中英文文献94篇、中文文献6篇。
1.2 入选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①文献类型为中英文正式发表的、年份较新且高质量的研究原著或综述;②与巨噬细胞和各种肺病相关的文献;③与自噬和各种肺病相关的文献;④论文中论据、论点充分且可靠的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复或与研究主题无关的文献;②文献发表年份过于久远且对此文论点支撑作用不明显的文献;③Meta分析类文献;④无法获得全文的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据的提取 文献筛选与质量评估由所有作者共同讨论确认。英文文献借助EndNote检索软件进行质量评估,中文文献手动逐一排查评估。通过查阅相关数据库最初检索到1 177篇文献,其中PubMed 数据库1 015篇、中国知网数据库162篇;根据EndNote检索软件的排序优先选择排名靠前、质量较高及其重要析出文献;阅读题目及摘要后保留196篇,通过阅读全文并根据纳排标准,最终共纳入100篇文献,包括中文文献4篇及英文文献96篇。具体文献筛选流程见图2。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 此次研究在概括介绍自噬流通畅对巨噬细胞内环境稳定和其极化表型及胞葬作用活性的重要意义基础上,通过对比不同肺病以及同一疾病不同病理阶段肺巨噬细胞自噬活性特点及其与疾病的关系,解析肺部疾病中巨噬细胞自噬两面性的内在联系,提出肺巨噬细胞自噬活性应该以自噬流的最终完成作为判断标准,仅用LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值增加得出巨噬细胞自噬活性增强对肺部疾病不利的结论存在片面性;此外,巨噬细胞自噬在不同肺病以及同一疾病不同阶段表现出不同特点。目前未发现相关研究综述,此次综述研究结果提示,合理评价自噬活性以及明确肺部疾病类型和疾病的进展阶段至关重要,且对于以巨噬细胞自噬为靶向的治疗策略的研发和临床转化亦是关键问题,并具有重要学术和实践意义。
3.3 综述的局限性 肺部疾病种类繁多,且同一种疾病的致病因子不同引起的病理反应亦有差异,此次研究主要总结了近年来研究质量较高文献的观点,未能囊括所有相关文献;此外,虽然借助 EndNote检索软件充分考虑了析出文献,但难免存在以现用关键词和检索策略检索不到的文献信息。因此后续仍需要结合具体研究和新的技术辨证分析。
3.4 综述的重要意义 此次研究提出自噬流通畅是判断自噬活性的重要依据,亦是探讨巨噬细胞自噬活性与肺部疾病关系的基础;巨噬细胞自噬活性在肺部疾病中存在两面性,与疾病类型以及同一疾病的不同发展阶段密切相关,在靶向巨噬细胞自噬治疗肺部疾病时,需充分评估疾病类型和发展阶段。因而此次研究无论在学术方面还是在指导转化临床应用中均具有重要意义。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 此次研究提出,LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值和p62的表达水平是判断自噬流是否通畅和评价自噬活性的必需证据,仅用LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ比值增加判断自噬活性是片面的,未来可以结合蛋白组学、代谢组学或人工智能等高科技,深度探索自噬体-溶酶体动态作用模型;此外,疾病类型和发展阶段以及致病因素均是影响巨噬细胞自噬活性的重要依据,此外肺常驻巨噬细胞与外来浸润巨噬细胞在疾病发展过程中亦可能发挥不同作用,上述方面均是今后研究中必须慎重考虑的重要课题。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||