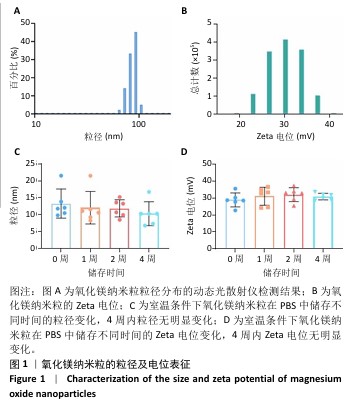
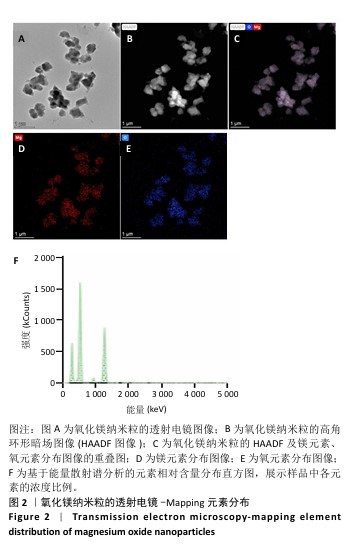
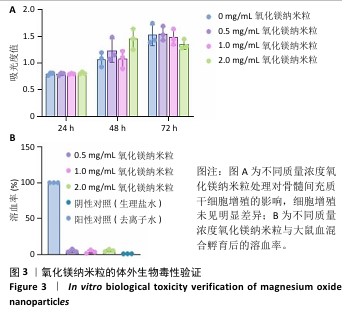
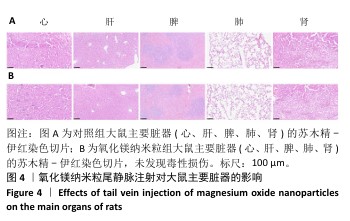
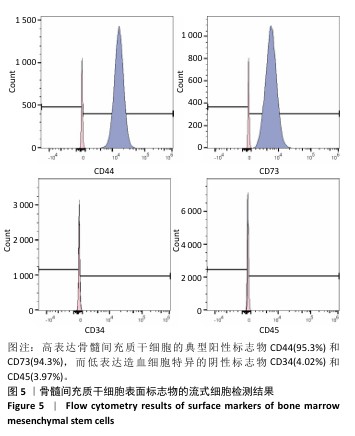
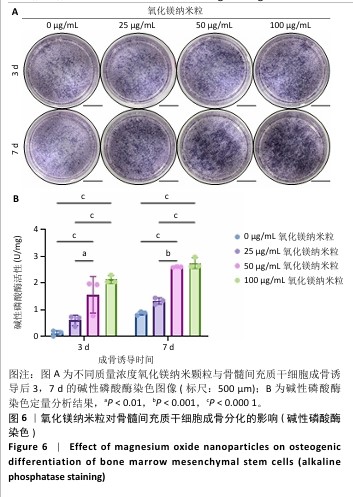
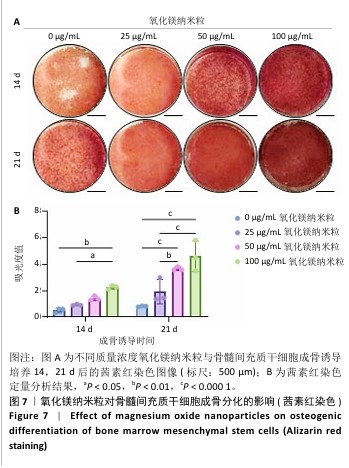
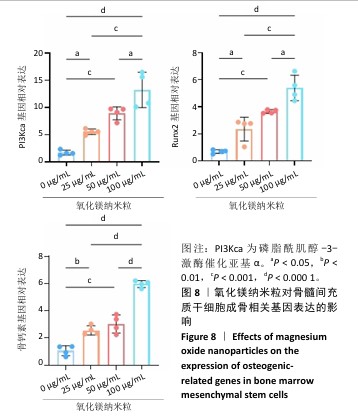
[1] WU Y, ZHANG X, ZHAO Q, et al. Role of Hydrogels in Bone Tissue Engineering: How Properties Shape Regeneration. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2020;16(12):1667-1686.
[2] YANG Y, CHU L, YANG S, et al. Dual-functional 3D-printed composite scaffold for inhibiting bacterial infection and promoting bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2018;79:265-275.
[3] PENG Z, WANG C, LIU C, et al. 3D printed polycaprolactone/beta-tricalcium phosphate/magnesium peroxide oxygen releasing scaffold enhances osteogenesis and implanted BMSCs survival in repairing the large bone defect. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(28):5698-5710.
[4] FAN J, PARK H, LEE MK, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and BMP-2 Delivery in Chitosan-Based 3D Constructs to Enhance Bone Regeneration in a Rat Mandibular Defect Model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(15-16):2169-2179.
[5] YAO H, ZOU Y, YANG K, et al. TGFβ1 induces bone formation from BMP9-activated Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells, with possible involvement of non-canonical pathways. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17(12):1692-1703.
[6] XIAO X, XU M, YU H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles mitigate oxidative stress-induced senescence in endothelial cells via regulation of miR-146a/Src. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):354.
[7] FENG Y, HAN Z, JIANG W, et al. Promotion of osteogenesis in BMSC under hypoxia by ATF4 via the PERK–eIF2α signaling pathway. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022;58(10):886-897.
[8] ZHAO Y, MENG L, ZHANG K, et al. Ultra-small nanodots coated with oligopeptides providing highly negative charges to enhance osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs better than osteogenic induction medium. Chin Chem Lett. 2021;32(1):266-270.
[9] DIAS AM, DO NASCIMENTO CANHAS I, BRUZIQUESI CGO, et al. Magnesium (Mg2 +), Strontium (Sr2 +), and Zinc (Zn2 +) Co-substituted Bone Cements Based on Nano-hydroxyapatite/Monetite for Bone Regeneration. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023;201(6):2963-2981.
[10] FU M, YANG C, SUN G. Recent advances in immunomodulatory hydrogels biomaterials for bone tissue regeneration. Mol Immunol. 2023;163:48-62.
[11] LV Z, HU T, BIAN Y, et al. A MgFe-LDH Nanosheet-Incorporated Smart Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel with Controllable Growth Factor Releasing Capability for Bone Regeneration. Adv Mater. 2023;35(5):e2206545.
[12] LU X, SHI S, LI H, et al. Magnesium oxide-crosslinked low-swelling citrate-based mussel-inspired tissue adhesives. Biomaterials. 2020;232:119719.
[13] KANG Y, XU C, MENG L, et al. Exosome-functionalized magnesium-organic framework-based scaffolds with osteogenic, angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties for accelerated bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:26-41.
[14] TARAFDER S, DERNELL WS, BANDYOPADHYAY A, et al. SrO- and MgO-doped microwave sintered 3D printed tricalcium phosphate scaffolds: mechanical properties and in vivo osteogenesis in a rabbit model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(3):679-690.
[15] XIONG Y, LIN Z, BU P, et al. A Whole-Course-Repair System Based on Neurogenesis-Angiogenesis Crosstalk and Macrophage Reprogramming Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Mater. 2023;35(19):e2212300.
[16] DAI Y, WU J, WANG J, et al. Magnesium Ions Promote the Induction of Immunosuppressive Bone Microenvironment and Bone Repair through HIF-1α-TGF-β Axis in Dendritic Cells. Small. 2024;20(33):e2311344.
[17] HU X, CHEN J, YANG S, et al. 3D Printed Multifunctional Biomimetic Bone Scaffold Combined with TP-Mg Nanoparticles for the Infectious Bone Defects Repair. Small. 2024;20(40):e2403681.
[18] MAO J, SUN Z, WANG S, et al. Multifunctional Bionic Periosteum with Ion Sustained-Release for Bone Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(39): e2403976.
[19] LI J, WU J, LIU F, et al. Magnesium-Organic Framework-Loaded Bisphosphonate-Functionalized Gel Scaffolds for Enhanced Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(12):6849-6859.
[20] LIU L, WANG F, SONG W, et al. Magnesium promotes vascularization and osseointegration in diabetic states. Int J Oral Sci. 2024;16(1):10.
[21] SHU M, WANG J, XU Z, et al. Targeting nanoplatform synergistic glutathione depletion-enhanced chemodynamic, microwave dynamic, and selective-microwave thermal to treat lung cancer bone metastasis. Bioact Mater. 2024;39:544-561.
[22] GAO G, JIANG YW, JIA HR, et al. Near-infrared light-controllable on-demand antibiotics release using thermo-sensitive hydrogel-based drug reservoir for combating bacterial infection. Biomaterials. 2019;188:83-95.
[23] FENTON OS, OLAFSON KN, PILLAI PS, et al. Advances in Biomaterials for Drug Delivery. Adv Mater. 2018;30(29):1705328.
[24] LI J, WEI G, LIU G, et al. Regulating Type H Vessel Formation and Bone Metabolism via Bone-Targeting Oral Micro/Nano-Hydrogel Microspheres to Prevent Bone Loss. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(15):e2207381.
[25] ZOU D, ZHANG Z, HE J, et al. Blood vessel formation in the tissue-engineered bone with the constitutively active form of HIF-1α mediated BMSCs. Biomaterials. 2012;33(7):2097-2108.
[26] MEURY T, VERRIER S, ALINI M. Human endothelial cells inhibit BMSC differentiation into mature osteoblasts in vitro by interfering with osterix expression. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98(4):992-1006.
[27] QIN Q, LEE S, PATEL N, et al. Neurovascular coupling in bone regeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(11):1844-1849.
[28] ALAIZERI ZM, ALHADLAQ HA, ALDAWOOD S, et al. Facile Synthesis, Characterization, Photocatalytic Activity, and Cytotoxicity of Ag-Doped MgO Nanoparticles. Nanomater Basel Switz. 2021;11(11):2915.
[29] HE L, HE T, XING J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):276.
[30] DZAMUKOVA M, BRUNNER TM, MIOTLA-ZAREBSKA J, et al. Mechanical forces couple bone matrix mineralization with inhibition of angiogenesis to limit adolescent bone growth. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3059.
[31] RIBATTI D, D’AMATI A. Bone angiocrine factors. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023; 11:1244372.
[32] DARVISHI B, DINARVAND R, MOHAMMADPOUR H, et al. Dual l-Carnosine/Aloe vera Nanophytosomes with Synergistically Enhanced Protective Effects against Methylglyoxal-Induced Angiogenesis Impairment. Mol Pharm. 2021;8(9):3302-3325.
[33] VEIS A. Mineral-matrix interactions in bone and dentin. J Bone Miner Res. 1993;8 Suppl 2:S493-497.
[34] ZHENG L, ZHAO S, LI Y, et al. Engineered MgO nanoparticles for cartilage-bone synergistic therapy. Sci Adv. 2024;10(10):eadk6084.
[35] ZHENG G, XIE J, YAO Y, et al. MgO@polydopamine Nanoparticle-Loaded Photothermal Microneedle Patches Combined with Chitosan Gel Dressings for the Treatment of Infectious Wounds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024; 16(10):12202-12216.
[36] GAO Y, WANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Advancing neural regeneration via adaptable hydrogels: Enriched with Mg2+ and silk fibroin to facilitate endogenous cell infiltration and macrophage polarization. Bioact Mater. 2024;33:100-113.
[37] ZHANG B, LI KY, JIANG LC, et al. Rib Composite Flap With Intercostal Nerve and Internal Thoracic Vessels for Mandibular Reconstruction. J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(7):1815-1818.
[38] XU J, HE SJ, XIA TT, et al. Targeting type H vessels in bone-related diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(4):e18123.
[39] LIU Z, HUANG L, QI L, et al. Activating Angiogenesis and Immunoregulation to Propel Bone Regeneration via Deferoxamine-Laden Mg-Mediated Tantalum Oxide Nanoplatform. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(19): 24384-24397.
[40] LI Q, LIU W, HOU W, et al. Micropatterned photothermal double-layer periosteum with angiogenesis-neurogenesis coupling effect for bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2022;18:100536.
[41] SARKER M, IZADIFAR M, SCHREYER D, et al. Influence of ionic crosslinkers (Ca2+/Ba2+/Zn2+) on the mechanical and biological properties of 3D Bioplotted Hydrogel Scaffolds. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(10): 1126-1154.
[42] YAN C, ZHANG P, QIN Q, et al. 3D-printed bone regeneration scaffolds modulate bone metabolic homeostasis through vascularization for osteoporotic bone defects. Biomaterials. 2024;311:122699.
[43] LIAO P, CHEN L, ZHOU H, et al. Osteocyte mitochondria regulate angiogenesis of transcortical vessels. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2529.
[44] LIU M, WANG R, LIU J, et al. Incorporation of magnesium oxide nanoparticles into electrospun membranes improves pro-angiogenic activity and promotes diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112609.
[45] ASKAR MA, THABET NM, EL-SAYYAD GS, et al. Dual Hyaluronic Acid and Folic Acid Targeting pH-Sensitive Multifunctional 2DG@DCA@MgO-Nano-Core-Shell-Radiosensitizer for Breast Cancer Therapy. Cancers. 2021;13(21):5571.
[46] LI X, COATES DE. Hollow channels scaffold in bone regenerative: a review. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2023;34(12):1702-1715.
[47] LIU M, WANG R, LIU J, et al. Incorporation of magnesium oxide nanoparticles into electrospun membranes improves pro-angiogenic activity and promotes diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112609.
[48] SUN TW, YU WL, ZHU YJ, et al. Hydroxyapatite Nanowire@Magnesium Silicate Core-Shell Hierarchical Nanocomposite: Synthesis and Application in Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(19):16435-16447.
[49] YOSHIZAWA S, BROWN A, BARCHOWSKY A, et al. Magnesium ion stimulation of bone marrow stromal cells enhances osteogenic activity, simulating the effect of magnesium alloy degradation. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(6): 2834-2842.
[50] HONG X, YANG Y, LI X, et al. Enhanced anti-Escherichia coli properties of Fe-doping in MgO nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2021;11(5):2892-2897. |