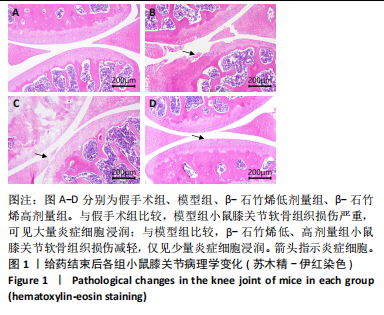
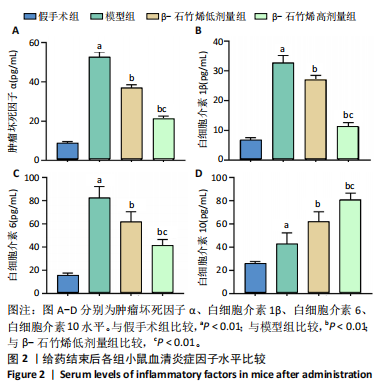
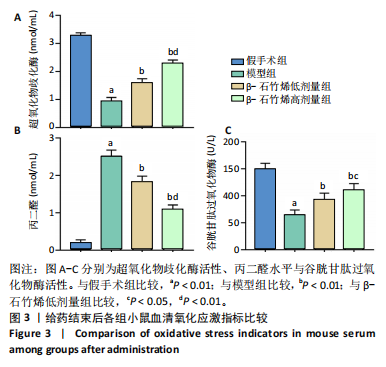
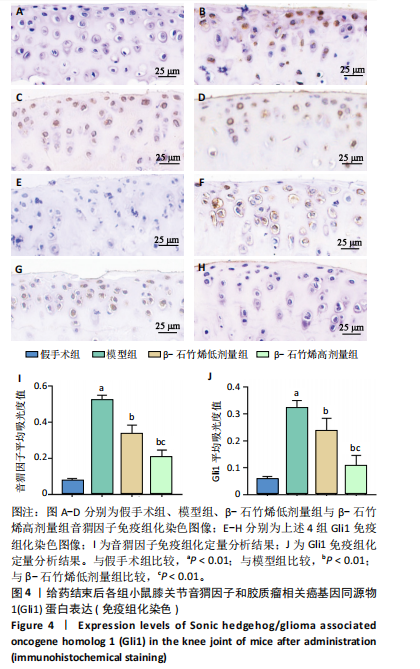
[1] ZENG C, DOHERTY M, PERSSON MSM, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of acetaminophen, topical and oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for knee osteoarthritis: evidence from a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and real-world data. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(9):1242-1251.
[2] BUCHANAN WW, KEAN CA, KEAN WF, et al. Osteoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology. 2024;32(1):13-22.
[3] BRAATEN JA, BANOVETZ MT, DEPHILLIPO NN, et al. Biomarkers for osteoarthritis diseases. Life (Basel). 2022;12(11):1799.
[4] GRÄSSEL S, ZAUCKE F, MADRY H. Osteoarthritis: novel molecular mechanisms increase our understanding of the disease pathology. J Clin Med. 2021;10(9):1938.
[5] LI H, KONG W, LIANG Y, et al. Burden of osteoarthritis in china, 1990-2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(3):1189-1197.
[6] HU S, LI Y, ZHANG X, et al. Increasing burden of osteoarthritis in china: trends and projections from the global burden of disease study 2019. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30:e942626.
[7] KULKARNI P, MARTSON A, VIDYA R, et al. Pathophysiological landscape of osteoarthritis. Adv Clin Chem. 2021;100:37-90.
[8] JADIDI S. A review of non-surgical pain management in osteoarthritis. Cureus. 2020;12(10):e10829.
[9] RICHARD MJ, DRIBAN JB, MCALINDON TE. Pharmaceutical treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023;31(4):458-466.
[10] BRUMAT P, KUNŠIČ O, NOVAK S, et al. The surgical treatment of osteoarthritis. life (Basel). 2022;12(7):982.
[11] GRESS K, CHARIPOVA K, AN D, et al. Treatment recommendations for chronic knee osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2020; 34(3):369-382.
[12] EMAMI A, NAMDARI H, PARVIZPOUR F, et al. Challenges in osteoarthritis treatment. Tissue Cell. 2023;80:101992.
[13] LIAO B, GUAN M, TAN Q, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound inhibits fibroblast-like synoviocyte proliferation and reduces synovial fibrosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Orthop Translat. 2021;30:41-50.
[14] ZHU R, FANG H, WANG J, et al. Inflammation as a therapeutic target for osteoarthritis: A literature review of clinical trials. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(8):2417-2433.
[15] ATIK I, GUL E, ATIK S. Evaluation of the relationship between Knee Osteoarthritis and Meniscus Pathologies. Malawi Med J. 2024;36(1):48-52.
[16] COLLINS JA, KAPUSTINA M, BOLDUC JA, et al. Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) regulates redox homeostasis and signaling events in human articular chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;166:90-103.
[17] CHOI M, MIN JS, MOON SW, et al. Mitoregulin modulates inflammation in osteoarthritis: Insights from synovial transcriptomics and cellular studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024;734:150652.
[18] FANG Z, HU Q, LIU W. Vitamin B6 alleviates osteoarthritis by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):447.
[19] HU Q, ZUO T, DENG L, et al. β-Caryophyllene suppresses ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia reperfusion via activation of the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway in MCAO/R rats. Phytomedicine. 2022;102: 154112.
[20] SANTOS NA, MARTINS NM, SISTI FM, et al. The cannabinoid beta-caryophyllene (BCP) induces neuritogenesis in PC12 cells by a cannabinoid-receptor-independent mechanism. Chem Biol Interact. 2017;261:86-95.
[21] FIDYT K, FIEDOROWICZ A, STRZĄDAŁA L, et al. β-caryophyllene and β-caryophyllene oxide-natural compounds of anticancer and analgesic properties. Cancer Med. 2016;5(10):3007-3017.
[22] ESPINOZA-GUTIÉRREZ HA, LÓPEZ-SALIDO SC, FLORES-SOTO ME, et al. Angiotensinergic effect of β-Caryophyllene on Lipopolysaccharide- induced systemic inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024; 719:150081.
[23] 周智华,杜琼颖,郅青.β-石竹烯激活自噬减轻小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的作用及机制[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2021,13(11): 1379-1382,1389.
[24] FU C, QIU Z, HUANG Y, et al. Protective role of Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides against chondrocyte extracellular matrix degeneration through lncRNA GAS5 in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2022;24(2):532.
[25] SU H, YAN Q, DU W, et al. Calycosin ameliorates osteoarthritis by regulating the imbalance between chondrocyte synthesis and catabolism. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024;24(1):48.
[26] LEFEBVRE V, SMITS P. Transcriptional control of chondrocyte fate and differentiation. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2005;75(3):200-12.
[27] GENG Y, BLANCO FJ, CORNELISSON M, et al. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in normal human articular chondrocytes. J Immunol. 1995;155(2):796-801.
[28] PELLETIER JP, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, ABRAMSON SB. Osteoarthritis, an inflammatory disease: potential implication for the selection of new therapeutic targets. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(6):1237-1247.
[29] ZHEN G, GUO Q, LI Y, et al. Mechanical stress determines the configuration of TGFβ activation in articular cartilage. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1706.
[30] 杨博,刘峻承,郑德勇,等.骨关节炎模型构建的研究进展[J].河北医药,2023,45(16):2515-2519.
[31] CHEN X, LI Z, HONG H, et al. Xanthohumol suppresses inflammation in chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritis in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137:111238.
[32] QIN R, SUN J, WU J, et al. Pyrroloquinoline quinone prevents knee osteoarthritis by inhibiting oxidative stress and chondrocyte senescence. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1460-1472.
[33] YEATER TD, CRUZ CJ, CRUZ-ALMEIDA Y, et al. Autonomic nervous system dysregulation and osteoarthritis pain: mechanisms, measurement, and future outlook. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2022;24(6):175-183.
[34] WANG Y. Novel drug discovery approaches for MMP-13 inhibitors in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2024;114:130009.
[35] KHAN NM, HASEEB A, ANSARI MY, et al. Dataset of effect of Wogonin, a natural flavonoid, on the viability and activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in IL-1β-stimulated human OA chondrocytes. Data Brief. 2017;12:150-155.
[36] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42.
[37] MORRIS G, GEVEZOVA M, SARAFIAN V, et al. Redox regulation of the immune response. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19(10):1079-1101.
[38] AHMAD N, ANSARI MY, HAQQI TM. Role of iNOS in osteoarthritis: Pathological and therapeutic aspects. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(10):6366-6376.
[39] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452.
[40] BALDISSERA MD, SOUZA CF, GRANDO TH, et al. Hypolipidemic effect of β-caryophyllene to treat hyperlipidemic rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017;390(2):215-223.
[41] LIU M, NIU W, OU L. β-Caryophyllene ameliorates the Mycoplasmal pneumonia through the inhibition of NF-κB signal transduction in mice. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(8):4240-4246.
[42] 涂仕娟,杨红亚,李桃,等.吴茱萸碱调节Shh/Gli1信号通路对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨损伤的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2024,53(9): 827-833.
[43] FENG M, LIU W, DING J, et al. Sonic hedgehog induces mesenchymal stromal cell senescence-associated secretory phenotype and chondrocyte apoptosis in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:716610.
[44] HU Z, CHEN Y, ZHU S, et al. Sonic hedgehog promotes proliferation and migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via rho/rock signaling. J Immunol Res. 2022;2022:3423692.
|