[1] CARRIÓN M, FROMMER KW, PÉREZ-GARCÍA S, et al. The Adipokine Network in Rheumatic Joint Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(17):4091.
[2] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, MCINNES IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016; 388(10055):2023-2038.
[3] ISHIGAKI K, SAKAUE S, TERAO C, et al. Multi-ancestry genome-wide association analyses identify novel genetic mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet. 2022; 54(11):1640-1651.
[4] SHAMS S, MARTINEZ JM, DAWSON JRD, et al. The Therapeutic Landscape of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current State and Future Directions. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:680043.
[5] HUANG J, FU X, CHEN X, et al. Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:686155.
[6] 赵泽良.类风湿性关节炎的治疗研究进展[J].临床医学进展,2023,13(4):6993-6998.
[7] SUN BB, MARANVILLE JC, PETERS JE, et al. Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome. Nature. 2018;558(7708):73.
[8] EMILSSON V, GUDMUNDSDOTTIR V, GUDJONSSON A, et al. Coding and regulatory variants are associated with serum protein levels and disease. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):481.
[9] NYS G, COBRAIVILLE G, SERVAIS AC, et al. Targeted proteomics reveals serum amyloid A variants and alarmins S100A8-S100A9 as key plasma biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis. Talanta. 2019;204:507-517.
[10] POPE JE, CHOY EH. C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;51(1):219-229.
[11] ZHOU J, DAI Y, LIN Y, et al. Association between serum amyloid A and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;52: 151943.
[12] SCHERER HU, HÄUPL T, BURMESTER GR. The etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102400.
[13] IRURE-VENTURA J, DÍAZ-TOLEDO M, PALAZUELOS-CAYÓN N, et al. Impact of Likelihood Ratios of Rheumatoid Factor and Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody in Clinical Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Two Available Platforms. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025;15(2):135.
[14] DÍAZ-GONZÁLEZ F, HERNÁNDEZ-HERNÁNDEZ MV. Rheumatoid arthritis. Med Clin (Barc). 2023;161:533-542.
[15] SANTOS SAVIO A, MACHADO DIAZ AC, CHICO CAPOTE A, et al. Differential expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-15Ralpha, IL-15, IL-6 and TNFalpha in synovial fluid from Rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:51.
[16] ANDERSON NL. The clinical plasma proteome: a survey of clinical assays for proteins in plasma and serum. Clin Chem. 2010;56(2):177-185.
[17] GU Y, JIN Q, HU J, et al. Causality of genetically determined metabolites and metabolic pathways on osteoarthritis: a two-sample mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):357.
[18] PIERCE BL, BURGESS S. Efficient design for Mendelian randomization studies: subsample and 2-sample instrumental variable estimators. Am J Epidemiol. 2013; 178(7):1177-1184.
[19] HARTWIG FP, DAVIES NM, HEMANI G, et al. Two-sample Mendelian randomization: avoiding the downsides of a powerful, widely applicable but potentially fallible technique. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45:1717-1726.
[20] TERCIC D, BOZIC B. The basis of the synovial fluid analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2001;39:1221-1226.
[21] REAY WR, CAIRNS MJ. Advancing the use of genome-wide association studies for drug repurposing. Nat Rev Genet. 2021; 22(10):658-671.
[22] EMDIN CA, KHERA AV, KATHIRESAN S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA. 2017;318: 1925-1926.
[23] Skrivankova VW, Richmond RC, Woolf BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621.
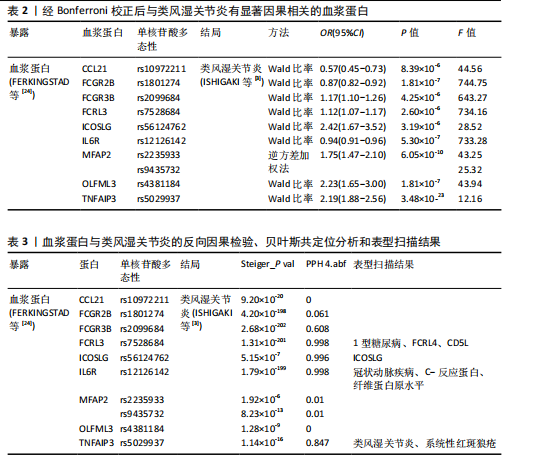
[24] FERKINGSTAD E, SULEM P, ATLASON BA, SVEINBJORNSSON G, et al. Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease. Nat Genet. 2021;53:1712-1721.
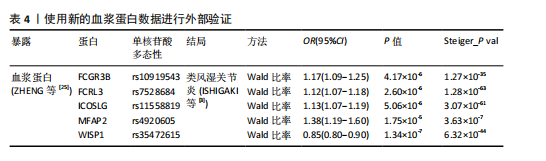
[25] ZHENG J, HABERLAND V, BAIRD D, et al. Phenome-wide Mendelian randomization mapping the influence of the plasma proteome on complex diseases. Nature genetics. 2020;52(10):1122-1131.
[26] ZHANG J, DUTTA D, KÖTTGEN A, et al. Plasma proteome analyses in individuals of European and African ancestry identify cis-pQTLs and models for proteome-wide association studies. Nat Genet. 2022;54(5): 593-602.
[27] WANG Q, DAI H, HOU T, et al. Dissecting Causal Relationships Between Gut Microbiota, Blood Metabolites, and Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J Stroke. 2023;25(3):350-360.
[28] YAN W, JIANG M, HU W, et al. Causality Investigation between Gut Microbiota, Derived Metabolites, and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(21):4544.
[29] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: the role of the I2 statistic. Int J Epidemiol. 2016; 145(6):1961-1974.
[30] CHENG J, YANG L, YE Y, et al. Mendelian Randomisation Analysis of Causal Association between Lifestyle, Health Factors, and Keratoconus. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024;11:221.
[31] ZHANG Y, XIE J, WEN S, et al. Evaluating the causal effect of circulating proteome on the risk of osteoarthritis-related traits. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(12):1606-1617.
[32] BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON SG. Mendelian Randomization Analysis With Multiple Genetic Variants Using Summarized Data. Genet Epidemiol. 2013;37(7):658-665.
[33] HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SMITH G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(11):e1007081.
[34] WALLACE C. A more accurate method for colocalisation analysis allowing for multiple causal variants. PLoS Genet. 2021; 17(9):e1009440.
[35] GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, VUKCEVIC D, SCHADT EE, et al. Bayesian Test for Colocalisation between Pairs of Genetic Association Studies Using Summary Statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(5):e1004383.
[36] KAMAT MA, BLACKSHAW JA, YOUNG R, et al. PhenoScanner V2: an expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics. 2019;35(22):4851-4853.
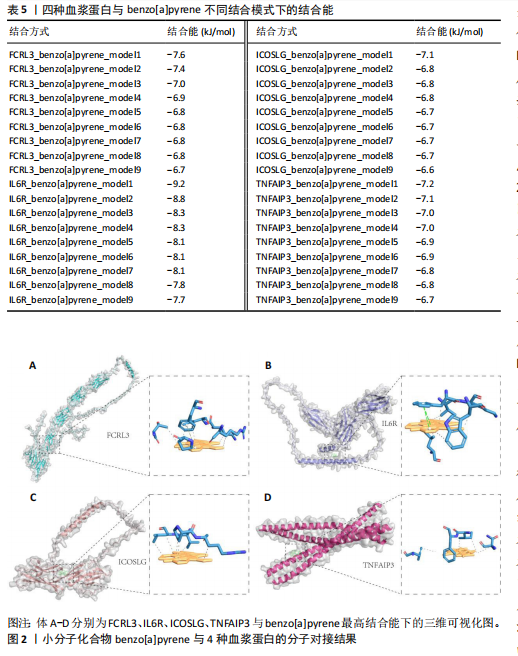
[37] BURLEY SK, BHIKADIYA C, BI C, et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D437-451.
[38] MCGOWAN LM, DAVEY SMITH G, GAUNT TR, et al. Integrating Mendelian randomization and multiple-trait colocalization to uncover cell-specific inflammatory drivers of autoimmune and atopic disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2019;28(19):3293-2300.
[39] MONTGOMERY SB, DERMITZAKIS ET. From expression QTLs to personalized transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(4): 277-282.
[40] LI FJ, SCHREEDER DM, LI R, et al. FCRL3 promotes TLR9-induced B-cell activation and suppresses plasma cell differentiation. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43(11):2980-2992.
[41] AGARWAL S, KRAUS Z, DEMENT-BROWN J, et al. Human Fc Receptor-like 3 Inhibits Regulatory T Cell Function and Binds Secretory IgA. Cell Rep. 2020;30(5):1292-1299.e3.
[42] BAJPAI UD, SWAINSON LA, MOLD JE, et al. A functional variant in FCRL3 is associated with higher Fc receptor-like 3 expression on T cell subsets and rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(8):2451-2459.
[43] CHALAYER E, GRAMONT B, ZEKRE F, et al. Fc receptors gone wrong: A comprehensive review of their roles in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2022;21(3):103016.
[44] LIN X, ZHANG Y, CHEN Q. FCRL3 gene polymorphisms as risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol. 2016; 77(2):223-229.
[45] TANAKA T, NARAZAKI M, MASUDA K, et al. Regulation of IL-6 in Immunity and Diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;941:79-88.
[46] EDWARDS CJ, WILLIAMS E. The role of interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis-associated osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(8):1287-1293.
[47] KHAN AW, FAROOQ M, HWANG MJ, et al. Autoimmune Neuroinflammatory Diseases: Role of Interleukins. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):7960.
[48] MARINOU I, WALTERS K, WINFIELD J, et al. A gain of function polymorphism in the interleukin 6 receptor influences RA susceptibility. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69(6):1191-1194.
[49] HER M, KIM D, OH M, et al. Increased expression of soluble inducible costimulator ligand (ICOSL) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2009;18(6):501-507.
[50] HUO FF, ZOU XY, ZHANG Y, et al. Aire attenuate collagen-induced arthritis by suppressing T follicular helper cells through ICOSL. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025;144: 113732.
[51] MOONEY EC, SAHINGUR SE. The Ubiquitin System and A20: Implications in Health and Disease. J Dent Res. 2021;100(1):10-20.
[52] RAMOS PS, CRISWELL LA, MOSER KL, et al. A Comprehensive Analysis of Shared Loci between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and Sixteen Autoimmune Diseases Reveals Limited Genetic Overlap. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(12):e1002406.
[53] GRAHAM RR, COTSAPAS C, DAVIES L, et al. Genetic Variants Near TNFAIP3 on 6q23 are Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Nat Genet. 2008; 40(9):1059-1061.
[54] CICCACCI C, LATINI A, PERRICONE C, CONIGLIARO P, et al. TNFAIP3 Gene Polymorphisms in Three Common Autoimmune Diseases: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Primary Sjogren Syndrome—Association with Disease Susceptibility and Clinical Phenotypes in Italian Patients. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:6728694.
[55] LEE YH, SONG GG. Associations between TNFAIP3 Polymorphisms and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Update with Trial Sequential Analysis. Public Health Genomics. 2022: 1-11. doi: 10.1159/000526212.
|