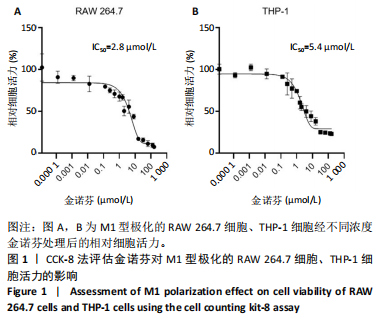
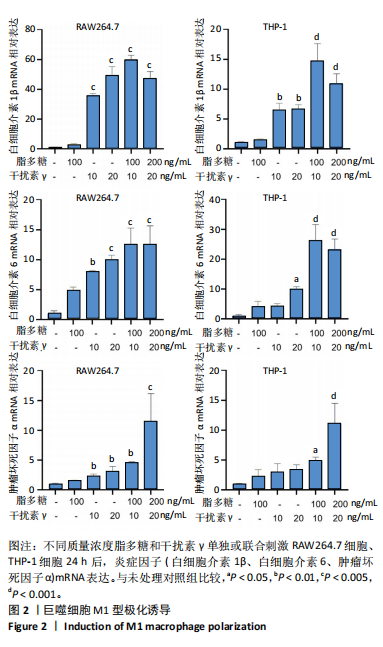
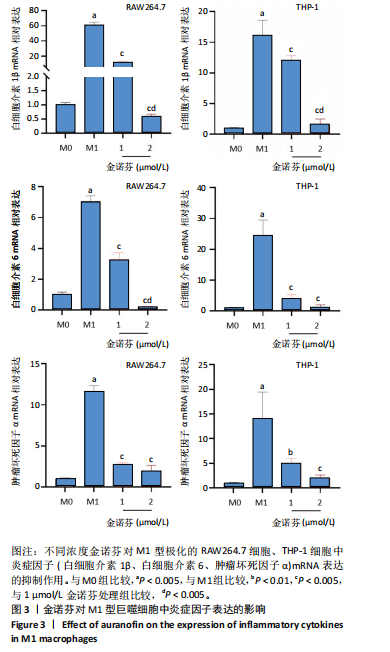
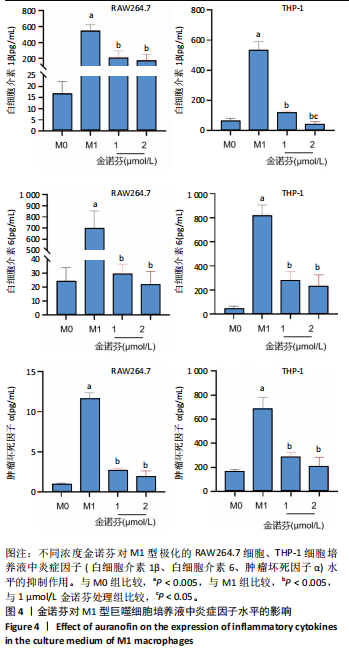
[1] MCDERMOTT K, FANG M, BOULTON AJM, et al. Etiology, Epidemiology, and Disparities in the Burden of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(1):209-221.
[2] LOUISELLE AE, NIEMIEC SM, ZGHEIB C, et al. Macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing. Transl Res. 2021;236:109-116.
[3] QI X, CAI E, XIANG Y, et al. An Immunomodulatory Hydrogel by Hyperthermia-Assisted Self-Cascade Glucose Depletion and ROS Scavenging for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Wound Therapeutics. Adv Mater. 2023;35(48):e2306632.
[4] LV D, CAO X, ZHONG L, et al. Targeting phenylpyruvate restrains excessive NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pathological inflammation in diabetic wound healing. Cell Rep Med. 2023;4(8): 101129.
[5] AITCHESON SM, FRENTIU FD, HURN SE, et al. Skin Wound Healing: Normal Macrophage Function and Macrophage Dysfunction in Diabetic Wounds. Molecules. 2021;26(16):4917.
[6] CELIK C, LEE STT, TANOTO FR, et al. Decoding the complexity of delayed wound healing following Enterococcus faecalis infection. Elife. 2024;13:RP95113.
[7] KANG Y, XU L, DONG J, et al. Programmed microalgae-gel promotes chronic wound healing in diabetes. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):1042.
[8] YI WJ, YUAN Y, BAO Q, et al. Analyzing Immune Cell Infiltration and Copper Metabolism in Diabetic Foot Ulcers. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17: 3143-3157.
[9] SAWAYA AP, STONE RC, BROOKS SR, et al. Deregulated immune cell recruitment orchestrated by FOXM1 impairs human diabetic wound healing. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4678.
[10] CLAYTON SM, SHAFIKHANI SH, SOULIKA AM. Macrophage and Neutrophil Dysfunction in Diabetic Wounds. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2024;13(9):463-484.
[11] LI HD, YOU YK, SHAO BY, et al. Roles and crosstalks of macrophages in diabetic nephropathy. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1015142.
[12] HASSANSHAHI A, MORADZAD M, GHALAMKARI S, et al. Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Skin Wound Healing. Cells. 2022;11(19):2953.
[13] LIU W, YU M, XIE D, et al. Melatonin-stimulated MSC-derived exosomes improve diabetic wound healing through regulating macrophage M1 and M2 polarization by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):259.
[14] CHEN J, MA H, MENG Y, et al. Analysis of the mechanism underlying diabetic wound healing acceleration by Calycosin-7-glycoside using network pharmacology and molecular docking. Phytomedicine. 2023; 114:154773.
[15] GENG K, MA X, JIANG Z, et al. High glucose-induced STING activation inhibits diabetic wound healing through promoting M1 polarization of macrophages. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):136.
[16] KANG ML, KIM HS, YOU J, et al. Hydrogel cross-linking-programmed release of nitric oxide regulates source-dependent angiogenic behaviors of human mesenchymal stem cell. Sci Adv. 2020;6(9):eaay5413.
[17] LIU Y, ZHANG X, YANG L, et al. Proteomics and transcriptomics explore the effect of mixture of herbal extract on diabetic wound healing process. Phytomedicine. 2023;116:154892.
[18] MUKHERJEE S, IM SS. Impact of tibial transverse transport in tissue regeneration and wound healing with perspective on diabetic foot ulcers. World J Diabetes. 2024;15(5):810-813.
[19] YANG J, XIONG G, HE H, et al. SFRP2 modulates functional phenotype transition and energy metabolism of macrophages during diabetic wound healing. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1432402.
[20] ZENG R, LV B, LIN Z, et al. Neddylation suppression by a macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticle promotes dual immunomodulatory repair of diabetic wounds. Bioact Mater. 2024;34:366-380.
[21] SHEN S, SHEN J, LUO Z, et al. Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications of the gold drug auranofin. Coord Chem Rev. 2023;493: 215323.
[22] LIU H, SHUKLA S, VERA-GONZÁLEZ N, et al. Auranofin Releasing Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Polyurethane Intravascular Catheter Coatings. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019;9:37.
[23] LUO J, SHANG Y, ZHAO N, et al. Hypoxia-responsive micelles deprive cofactor of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 and sensitize ferroptotic ovarian cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2025;314:122820.
[24] JOO MK, SHIN S, YE DJ, et al. Combined treatment with auranofin and trametinib induces synergistic apoptosis in breast cancer cells. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2021;84(2):84-94.
[25] KINOSHITA H, SHIMOZATO O, ISHII T, et al. The Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibitor Auranofin Suppresses Pulmonary Metastasis of Osteosarcoma, But Not Local Progression. Anticancer Res. 2021;41(10):4947-4955.
[26] LEE SM, KOH DH, JUN DW, et al. Auranofin attenuates hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via NRF2 and NF- κB signaling pathways. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2022;28(4):827-840.
[27] STEERS GJ, CHEN GY, O’LEARY BR, et al. Auranofin and Pharmacologic Ascorbate as Radiomodulators in the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(5):971.
[28] YANG L, WANG H, YANG X, et al. Auranofin mitigates systemic iron overload and induces ferroptosis via distinct mechanisms. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):138.
[29] HWANGBO H, JI SY, KIM MY, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Auranofin on Palmitic Acid and LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response by Modulating TLR4 and NOX4-Mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathway in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5920.
[30] NDUGIRE W, RAVIRANGA NGH, LAO J, et al. Gold Nanoclusters as Nanoantibiotic Auranofin Analogues. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(9): e2101032.
[31] HU H, JIANG H, ZHANG K, et al. Memantine nitrate MN-08 suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation to protect against sepsis-induced acute lung injury in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156:113804.
[32] SUBIN P, SABUHOM P, NALADTA A, et al. An Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Thai Traditional Polyherbal Recipe TPDM6315 in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages and TNF-α-Induced 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023;45(6):4891-4907.
[33] DUNKHUNTHOD B, TALABNIN C, MURPHY M, et al. Gymnema inodorum (Lour.) Decne. Extract Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Mediators Produced by RAW264.7 Macrophages. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8658314.
[34] CUI XY, PARK SH, PARK WH. Auranofin inhibits the proliferation of lung cancer cells via necrosis and caspase‑dependent apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 2020;44(6):2715-2724.
[35] HOU GX, LIU PP, ZHANG S, et al. Elimination of stem-like cancer cell side-population by auranofin through modulation of ROS and glycolysis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):89.
[36] HESKETH M, SAHIN KB, WEST ZE, et al. Macrophage Phenotypes Regulate Scar Formation and Chronic Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(7):1545.
[37] SHARIFIAGHDAM M, SHAABANI E, FARIDI-MAJIDI R, et al. Macrophages as a therapeutic target to promote diabetic wound healing. Mol Ther. 2022;30(9):2891-2908.
[38] HAN S, KIM K, KIM H, et al. Auranofin inhibits overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, cyclooxygenase expression and PGE2 production in macrophages. Arch Pharm Res. 2008;31(1):67-74.
[39] WANG S, LIU G, LI Y, et al. Metabolic Reprogramming Induces Macrophage Polarization in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2022;13:840029.
[40] RODRÍGUEZ-ENRÍQUEZ S, ROBLEDO-CADENA DX, PACHECO-VELÁZQUEZ SC, et al. Repurposing auranofin and meclofenamic acid as energy-metabolism inhibitors and anti-cancer drugs. PLoS One. 2024;19(9):e0309331.
|