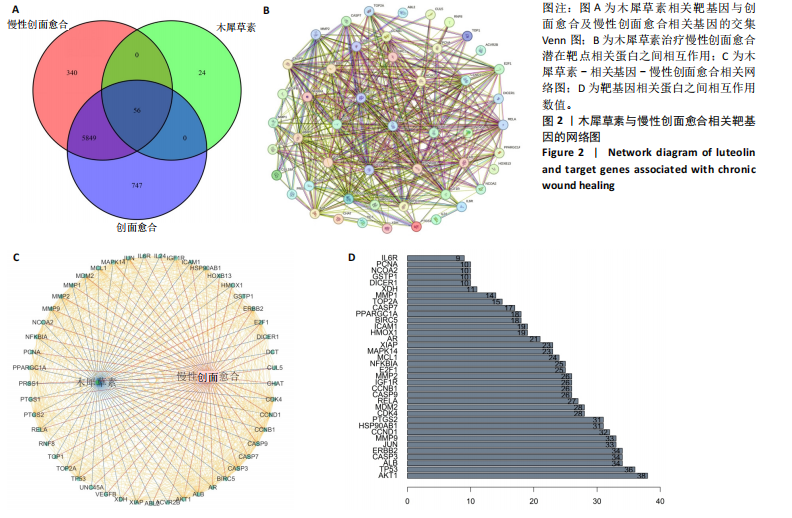
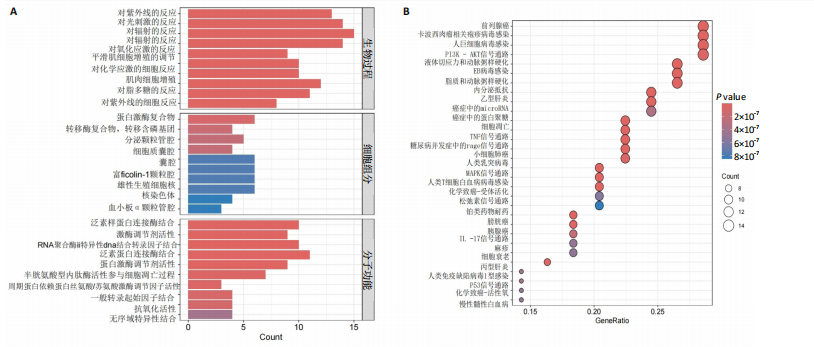
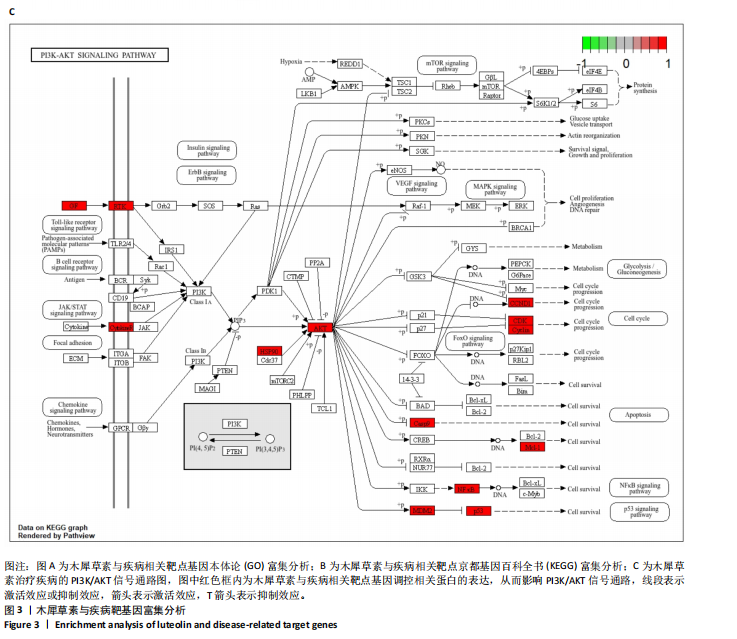
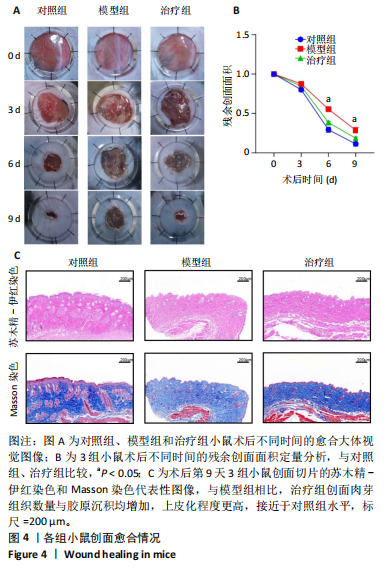
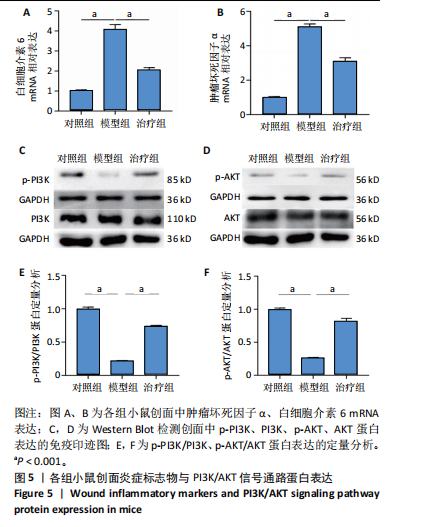
[1] HARTINGER R, SINGH K, LEVERETT J, et al. Enhancing Cellular Homeostasis: Targeted Botanical Compounds Boost Cellular Health Functions in Normal and Premature Aging Fibroblasts. Biomolecules. 2024;14(10):1310.
[2] LIAO Y, ZHANG Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Glucose oxidase: An emerging multidimensional treatment option for diabetic wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2025;44:131-151.
[3] SUN R, LIU C, LIU J, et al. Integrated network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the mechanisms underlying naringenin treatment of chronic wounds. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):132.
[4] O’REILLY S, MARKIEWICZ E, IDOWU OC. Aging, senescence, and cutaneous wound healing-a complex relationship. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1429716.
[5] KOMI D, KHOMTCHOUK K, SANTA MP. A Review of the Contribution of Mast Cells in Wound Healing: Involved Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2020;58(3):298-312.
[6] HOSEMANN W, WIGAND ME, GÖDE U, et al. Normal wound healing of the paranasal sinuses: clinical and experimental investigations. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1991;248(7):390-394.
[7] GONG C, XIA C, LIU L. Exosomes derived from epidermal growth factor-like domain protein 6-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells for diabetic wound healing. Regen Ther. 2024;26:932-940.
[8] BLAIR M. Diabetes Mellitus Review. Urol Nurs. 2016;36(1):27-36.
[9] YAZDANPANAH L, SHAHBAZIAN H, NAZARI I, et al. Risk factors associated with diabetic foot ulcer-free survival in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018;12(6):1039-1043.
[10] DEN DEKKER A, DAVIS FM, KUNKEL SL, et al. Targeting epigenetic mechanisms in diabetic wound healing. Transl Res. 2019;204:39-50.
[11] SCHAPER NC, Van NETTEN JJ, APELQVIST J, et al. Prevention and management of foot problems in diabetes: a Summary Guidance for Daily Practice 2015, based on the IWGDF Guidance Documents. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32 Suppl 1:7-15.
[12] EZHILARASU H, VISHALLI D, DHEEN ST, et al. Nanoparticle-Based Therapeutic Approach for Diabetic Wound Healing. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(6):1234.
[13] SUN S, DING C, LIU X, et al. Silk protein/polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofiber membranes loaded with puerarin accelerate wound healing in mice by reducing the inflammatory response. Biomater Adv. 2022;135:212734.
[14] 谭海燕,吴仁擎.益气活血通阳法治疗糖尿病足临床研究[J].实用中医药杂志,2023,39(5):859-861.
[15] 刘振华,张云霞.中药毛稔对伤口愈合的治疗效果与机制预测[J].中国药物应用与监测,2024,21(3):310-314.
[16] 宁永玲,沃达,袁志莹,等.绿茶多酚表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯对高脂高糖饮食诱导肥胖小鼠伤口愈合的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2023,43(3):337-344.
[17] HOPKINS AL. Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4(11):682-690.
[18] DENG Y, YE X, CHEN Y, et al. Chemical Characteristics of Platycodon grandiflorum and its Mechanism in Lung Cancer Treatment. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:609825.
[19] LUO TT, LU Y, YAN SK, et al. Network Pharmacology in Research of Chinese Medicine Formula: Methodology, Application and Prospective. Chin J Integr Med. 2020;26(1):72-80.
[20] SU M, GUO C, LIU M, et al. Therapeutic targets of vitamin C on liver injury and associated biological mechanisms: A study of network pharmacology. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;66:383-387.
[21] EMIG D, IVLIEV A, PUSTOVALOVA O, et al. Drug target prediction and repositioning using an integrated network-based approach. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60618.
[22] LOTFI SM, GHADIRI N, MOUSAVI SR, et al. A review of network-based approaches to drug repositioning. Brief Bioinform. 2018;19(5):878-892.
[23] KOTLYAR M, FORTNEY K, JURISICA I. Network-based characterization of drug-regulated genes, drug targets, and toxicity. Methods. 2012; 57(4):499-507.
[24] HOU X, WU W, ZHAO F, et al. Construction of an electrochemical sensor with graphene aerogel doped with ZrO2 nanoparticles and chitosan for the selective detection of luteolin. Mikrochim Acta. 2021;188(3):86.
[25] ZHANG X, XU W, LI H, et al. Luteolin prevents cadmium-induced PC12 cell death by suppressing the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(44):e40372.
[26] GENG YF, YANG C, ZHANG Y, et al. An innovative role for luteolin as a natural quorum sensing inhibitor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Life Sci. 2021;274:119325.
[27] ATTIQ A, JALIL J, HUSAIN K, et al. Luteolin and apigenin derived glycosides from Alphonsea elliptica abrogate LPS-induced inflammatory responses in human plasma. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;275:114120.
[28] WU HT, LIN J, LIU YE, et al. Luteolin suppresses androgen receptor-positive triple-negative breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by epigenetic regulation of MMP9 expression via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2021;81:153437.
[29] YU R, CHEN L, LAN R, et al. Computational screening of antagonists against the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) coronavirus by molecular docking. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;56(2):106012.
[30] XIE Y, ZHANG T, CHEN Y, et al. Fabrication of core-shell magnetic covalent organic frameworks composites and their application for highly sensitive detection of luteolin. Talanta. 2020;213:120843.
[31] KIM S. Exploring Chemical Information in PubChem. Curr Protoc. 2021; 1(8):e217.
[32] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13.
[33] CONSORTIUM TU. UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D480-D489.
[34] 鲍丹,郭蕊,侯道荣.角蛋白17基因敲除加剧糖尿病小鼠的创面愈合障碍[J].中国比较医学杂志,2023,33(10):54-60.
[35] MA Q, CHEN G, LI Y, et al. The molecular genetics of PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in the malformations of cortical development. Genes Dis. 2024;11(5):101021.
[36] JIN Y, HUANG Y, ZENG G, et al. Advanced glycation end products regulate macrophage apoptosis and influence the healing of diabetic foot wound through miR-361-3p/CSF1R and PI3K/AKT pathway. Heliyon. 2024;10(2):e24598.
[37] QIU F, FAN S, DIAO Y, et al. The mechanism of Chebulae Fructus Immaturus promote diabetic wound healing based on network pharmacology and experimental verification. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;322:117579.
[38] MING G, LIU J, WU Y, et al. Strictosamide promotes wound healing through activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Heliyon. 2024;10(9):e30169.
[39] WANG N, HONG B, ZHAO Y, et al. Dopamine-grafted oxidized hyaluronic acid/gelatin/cordycepin nanofiber membranes modulate the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway to promote diabetic wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;262:130079.
[40] WU S, ZHU L, NI S, et al. Hyaluronic acid-decorated curcumin-based coordination nanomedicine for enhancing the infected diabetic wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;263:130249.
[41] XIAO J, LIANG Y, SUN T, et al. A functional dual responsive CMC/OHA/SA/TOB hydrogel as wound dressing to enhance wound healing. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):26854.
[42] HUANG C, NG MY, LIN T, et al. Quercetin ameliorates advanced glycation end product-induced wound healing impairment and inflammaging in human gingival fibroblasts. J Dent Sci. 2024;19(1):268-275.
[43] GENG X, WANG Y, LI H, et al. Total iridoid glycoside extract of Lamiophlomis rotata (Benth) Kudo accelerates diabetic wound healing by the NRF2/COX2 axis. Chin Med. 2024;19(1):53.
[44] SHAH A, AMINI-NIK S. The Role of Phytochemicals in the Inflammatory Phase of Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(5):1068.
[45] YOUJUN D, HUANG Y, LAI Y, et al. Mechanisms of resveratrol against diabetic wound by network pharmacology and experimental validation. Annals of medicine (Helsinki). 2023;55(2):2280811.
[46] FANG C, RONG X, JIANG W, et al. Geniposide promotes wound healing of skin ulcers in diabetic rats through PI3K/Akt pathway. Heliyon. 2023; 9(11):e21331.
[47] ZHANG H, CHEN S, YAN X, et al. Egg white-derived peptide KPHAEVVLR promotes wound healing in rat palatal mucosa via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Peptides. 2023;168:171074.
[48] ZHU X, HU D, ZENG Z, et al. XB130 inhibits healing of diabetic skin ulcers through the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. World J Diabetes. 2023; 14(9):1369-1384.
[49] JERE SW, ABRAHAMSE H, HOURELD NN. Interaction of the AKT and β-catenin signalling pathways and the influence of photobiomodulation on cellular signalling proteins in diabetic wound healing. J Biomed Sci. 2023;30(1):81.
[50] LI Y, LU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Deciphering the Wound-Healing Potential of Collagen Peptides and the Molecular Mechanisms: A Review. J Agric Food Chem. 2024;72(47):26007-26026.
|