1.1 设计 体外细胞实验,组间比较进行t检验或单因素方差分析。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2023年9月至2024年10月在齐鲁医药学院实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验细胞 MC3T3-E1细胞系购自大连美仑生物技术有限公司,培养于含1%青霉素-链霉素、体积分数10%胎牛血清的低糖α-MEM培养基(完全培养基)中,常规换液、传代。实验采用对数生长期的细胞。
1.3.2 实验试剂与仪器 绿原酸、牛血清白蛋白(美仑,中国);α-MEM 培养基、活性氧检测试剂盒(Servicebio,中国);CCK-8检测试剂盒(同仁,日本);壳聚糖(Sigma,美国);碱性磷酸酶活性检测试剂盒(碧云天,中国);聚己内酯(Macklin,中国);GAPDH(Diagbio,中国);碱性磷酸酶、RUNX2抗体(Abcam,美国);BCA蛋白质测定试剂盒(P0010,上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);2’,7’-二氯荧光素二乙酸酯探针(贝博生物);过氧化氢(华新制药);二氯甲烷、N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(国药集团);PVDF膜(Millipore,美国);扫描电镜(日立su8010,日本);透射电镜(Tecnai G2,美国);纳米粒度仪(马尔文帕纳科,英国);酶标仪(Multiskan SkyHigh,美国);荧光显微镜(MSHOT MF43-N,中国);直流高压电(泰思曼,大连);微量注射泵(好来宝,济南);紫外分光光度计(赛默飞,美国)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 绿原酸蛋白微球的合成 将100 mg牛血清白蛋白磁力搅拌溶于10 mL ddH2O中制备牛血清白蛋白溶液。将5 mg绿原酸溶于1 mL无水乙醇中制备绿原酸溶液。使用微量注射泵将绿原酸溶液泵入牛血清白蛋白溶液中,滴加速度为60 mL/h,然后再以30 mL/h的速度将40 mL无水乙醇滴加到牛血清白蛋白-绿原酸混合溶液中,此为A液。将3 mL乙酸加入到47 mL ddH2O中制备乙酸溶液,称取50 mg壳聚糖磁力搅拌溶于乙酸溶液中,此为B液。使用微量注射泵将40 mL B液加入A液中,滴加速度为30 mL/h,磁力搅拌8 h;将最终制备的溶液在12 000 r/min离心15 min,向沉淀物中加入15 mL去离子水/无水乙醇(体积比50/50)混合溶液超声振荡20 min,至沉淀完全溶解,此步骤重复3次,直至离心后的上清液清澈,向最终沉淀物中加入2 mL离子水/无水乙醇(体积比50/50)混合溶液溶解沉淀,得到绿原酸蛋白微球溶液,将溶液冷冻干燥为冻干粉后置于4 ℃保存。收集每次离心后的上清液并混匀,置于4 ℃保存。
1.4.2 绿原酸蛋白微球的微观形貌
扫描电镜观察微球表面形态:抽取绿原酸蛋白微球溶液20 μL,用无水乙醇稀释200倍,取一滴稀释后的液体滴在5 mm×5 mm大小的锡箔纸上,置于扫描电镜下观察微球的形貌特征。
透射电镜观察微球内部结构:抽取绿原酸蛋白微球溶液20 μL,用无水乙醇稀释200倍,取一滴稀释后的液体滴在铜网上,置于无菌通风口风干,置于透射电镜下观察。
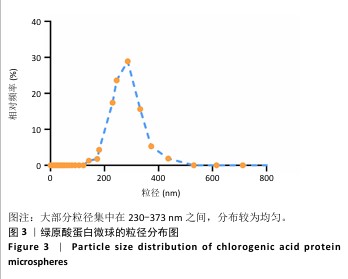
1.4.3 绿原酸蛋白微球的粒径、Zeta 电位分析 称取适量绿原酸蛋白微球冻干粉溶解于无水乙醇中,采用纳米粒度仪测量粒径分布与Zeta电位,调整各项参数:测试温度(25 ℃),测量模式选择(通用模式),测量次数(3次)。
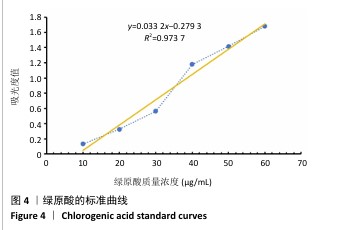
1.4.4 绿原酸蛋白微球的包封率检测 在290 nm 波长范围内测量绿原酸的吸光度值[11]。取10,20,30,40,50,60 μg/mL的绿原酸溶液(溶剂为无水乙醇),分别在最大吸收波长处测定各溶液的吸光度(A)值,通过线性回归建立绿原酸标准曲线及回归方程。取绿原酸蛋白微球制备时收集的上清液,利用紫外分光光度计测量吸光度值,代入绿原酸回归方程,确定游离绿原酸含量,进而确定纳米粒的包封率。包封率=(绿原酸总质量-绿原酸游离质量)/绿原酸总质量×100%。
1.4.5 绿原酸蛋白微球对MC3T3-E1细胞增殖的影响 将MC3T3-E1细胞以3×107 L-1的细胞浓度接种于96孔板内,每孔200 μL细胞悬液,分3组培养:对照组不进行任何处理,绿原酸组加入10 mg/L绿原酸[3],绿原酸微球组加入50 mg/L绿原酸蛋白微球,每组5复孔。培养1,4,7 d后,每孔加入100 μL CCK-8与培养基混合液(体积比1∶9),放入细胞培养箱中继续培养4 h,使用酶标仪在450 nm波长处测定A值。
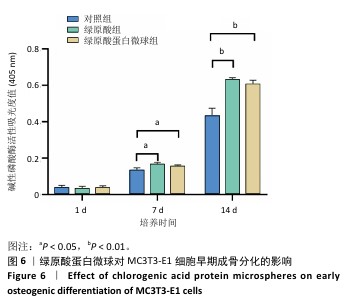
1.4.6 绿原酸蛋白微球对MC3T3-E1细胞碱性磷酸酶活性的影响 将MC3T3-E1细胞以3×107 L-1的细胞浓度接种在6孔板内,每孔1 mL细胞悬液,分3组培养:对照组不进行任何处理,绿原酸组加入10 mg/L绿原酸[3],绿原酸微球组加入50 mg/L绿原酸蛋白微球,每组3复孔。培养24 h后,更换为含成骨诱导液(10 mmol/L β-甘油磷酸钠、0.05 mmol/L维生素C、100 mmol/L地塞米松)的完全培养基。成骨诱导培养1,7,14 d后,每孔加入细胞裂解液覆盖住细胞并充分裂解,12 000 r/min离心15 min后取上清液,使用酶标仪检测波长为405 nm处的A值。
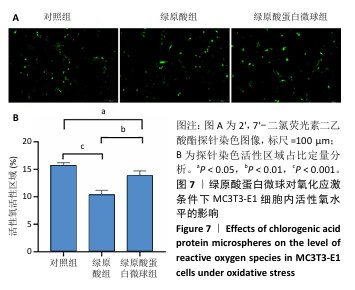
1.4.7 绿原酸蛋白微球对氧化应激条件下MC3T3-E1细胞活性氧水平的影响 将2’,7’-二氯荧光素二乙酸酯探针以1∶1 000的比例用无血清α-MEM低糖培养基稀释。将MC3T3-E1细胞以3×104/孔的密度接种于6孔板内,在37 ℃、体积分数5% CO2细胞培养箱中孵育24 h,直至细胞贴壁,加入0.5 mmol/L过氧化氢干预8 h以诱导氧化应激反应[12],8 h后去除过氧化氢,分组处理(分组处理同1.4.6)。培养24 h后除去细胞培养基,每孔加入2’,7’-二氯荧光素二乙酸酯探针工作液2 mL于37 ℃下孵育2 min,用无血清细胞培养基洗涤3次,置于荧光显微镜下观察,利用Image J软件对荧光染色面积进行定量分析。
1.4.8 绿原酸蛋白微球/聚己内酯静电纺丝膜的制备
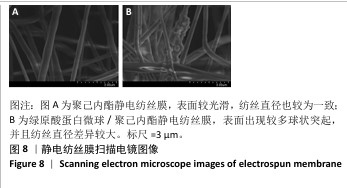
聚己内酯静电纺丝膜的制备:称取1.575 g聚己内酯溶于6 mL二氯甲烷和4.5 mL N,N-二甲基甲酰胺的混合溶液中,避光搅拌至少8 h,制备电纺丝溶液。用10 mL注射器吸取电纺丝溶液固定在微量注射泵中,通过聚氯乙烯管与9号针(内径0.6 mm)连接,直流高压电正极接针尖,负极接接收板并接地,进行静电纺丝:流量3 mL/h,电压(25±0.5) kV,针距接收板20 cm。真空干燥箱中干燥24 h。
绿原酸蛋白微球/聚己内酯静电纺丝膜的制备:称取1.575 g 聚己内酯溶于6 mL二氯甲烷;称取100 mg绿原酸蛋白微球冻干粉溶于4.5 mL N,N-二甲基甲酰胺中;用微量注射泵将绿原酸蛋白微球-N,N-二甲基甲酰胺溶液滴加到含有聚己内酯的二氯甲烷混合溶液中,磁力搅拌至少8 h,制备电纺丝溶液。用10 mL注射器吸取电纺丝溶液固定在微量注射泵中,通过聚氯乙烯管与9号针(内径0.6 mm)连接,直流高压电正极接针尖,负极接接收板并接地,进行静电纺丝:流量3 mL/h,电压(25±0.5) kV,针距接收板20 cm。真空干燥箱中干燥24 h。
1.4.9 静电纺丝膜的扫描电镜观察 将聚己内酯静电纺丝膜、绿原酸蛋白微球/聚己内酯静电纺丝膜切成 5 mm×5 mm 大小,粘接到金属装载平台上,喷金 20 s,在 20 kV 扫描电镜下收集图像。
1.4.10 静电纺丝膜对MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化的影响
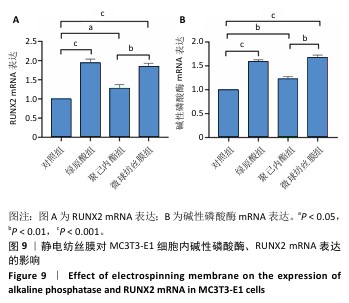
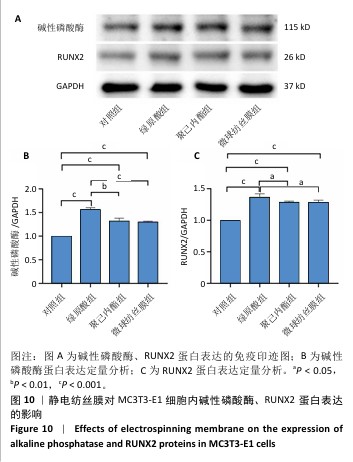
实验分组:将MC3T3-E1细胞以3×107 L-1的细胞浓度接种在6孔板内,每孔1 mL细胞悬液,分4组培养:对照组不进行任何处理,绿原酸组加入10 mg/L绿原酸,聚己内酯组加入聚己内酯静电纺丝膜,微球纺丝膜组加入绿原酸蛋白微球/聚己内酯静电纺丝膜,每组3复孔。培养24 h后,更换为含成骨诱导液(10 mmol/L β-甘油磷酸钠、0.05 mmol/L维生素C、100 mmol/L地塞米松)的完全培养基。
RT-qPCR检测碱性磷酸酶、RUNX2 mRNA表达:成骨诱导培养7 d后,提取各组细胞总RNA,通过紫外-可见光分光光度计检测各组A260/A280值均在1.8-2.1之间,参照反转录试剂盒说明书合成 cDNA。目的基因碱性磷酸酶、RUNX2及内参GAPDH的引物序列详见表1,RT-qPCR反应采用荧光染料法参照 SYBR Premix Ex Taq说明选择20 μL 体系:SYBRⅡ10 μL,上游引物 0.8 μL,下游引物0.8 μL,RT反应液1.6 μL,DEPC水6.8 μL。反应条件为:95 ℃预变性30 s,1个循环;95 ℃变性5 s,60 ℃退火30 s,45个循环。收集荧光信号熔融曲线分析,采用荧光阈值代表RT-qPCR 结果,根据 2-ΔΔCt计算目的基因表达量,定义对照组基因表达量为 1,计算各基因的相对表达。
Western blot 检测碱性磷酸酶、RUNX2蛋白表达:成骨诱导培养7 d后,使用含苯甲基磺酰氟的RIPA缓冲液裂解各组细胞,将裂解物置于冰上 30 min,反复吹打以确保细胞完全裂解;在 4 ℃下12 000 r/min离心10 min,从上清液中提取总蛋白,使用BCA蛋白质测定试剂盒检测蛋白浓度。将蛋白质在100 ℃下变性10 min,使用SDS-PAGE分离蛋白质,使用 PVDF 膜进行转移;使用5%脱脂奶粉封闭PVDF膜2 h,然后将膜与碱性磷酸酶(1∶2 000)、RUNX2(1∶2 000)、GAPDH(1∶20 000)抗体分别在4 ℃孵育过夜,16 h后洗膜,再与相应的二抗(1∶3 000)孵育1 h,检测蛋白信号强度,使用Image J软件分析蛋白相对表达量。
1.5 主要观察指标 绿原酸蛋白微球对MC3T3-E1细胞增殖、早期成骨分化及氧化应激条件下MC3T3-E1细胞内活性氧水平的影响,绿原酸蛋白微球/聚己内酯静电纺丝膜对MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化的影响。
1.6 统计学分析 应用 Prism 9软件进行统计处理。实验数据以 x±s表示,组间比较进行t检验或单因素方差分析。P < 0.05表示差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经由齐鲁医药学院生物统计学专家审核。