中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1486-1498.doi: 10.12307/2026.585
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
运动影响铁代谢对免疫性炎症疾病调控的潜在机制
孙尧天1,徐 凯1,王沛云2
- 1长江大学教育与体育学院,湖北省荆州市 434023;2荆州市中心医院肛肠外科,湖北省荆州市 434000
-
收稿日期:2024-12-25接受日期:2025-03-07出版日期:2026-02-28发布日期:2025-07-17 -
通讯作者:王沛云,硕士,主治医师,荆州市中心医院肛肠外科,湖北省荆州市 434000 -
作者简介:孙尧天,男,1996年生,湖北省石首市人,汉族,2024年长江大学毕业,硕士,主要从事运动人体科学相关研究。 并列第一作者:徐凯,男,1999年生,山东省滨州市人,汉族,2024年长江大学毕业,硕士,主要从事运动人体科学相关研究。
Potential mechanisms by which exercise regulates iron metabolism in immune inflammatory diseases
Sun Yaotian1, Xu Kai1, Wang Peiyun2
- 1College of Education and Sports, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Anorectal Surgery, Jingzhou Central Hospital, Jingzhou 434000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-25Accepted:2025-03-07Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-17 -
Contact:Wang Peiyun, MS, Attending physician, Department of Anorectal Surgery, Jingzhou Central Hospital, Jingzhou 434000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Sun Yaotian, MS, College of Education and Sports, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China Xu Kai, MS, College of Education and Sports, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China Sun Yaotian and Xu Kai contributed equally to this work.
摘要:
文题释义:
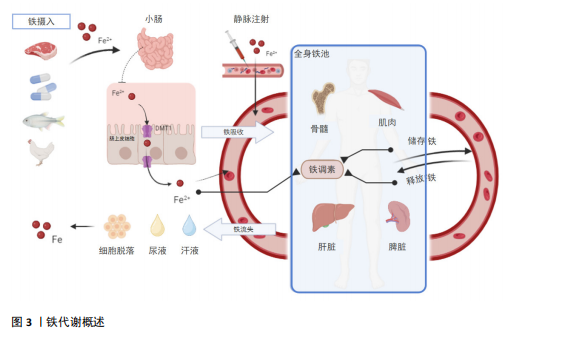
铁代谢:是人体维持铁平衡的复杂过程。铁在小肠吸收,巨噬细胞可回收利用,经肠道、汗液及尿液排出。正常人体总铁量维持在4.0-
5.0 g。免疫性炎症疾病中,铁代谢意义重大。像炎症性肠病患者铁调素、转铁蛋白等指标异常;类风湿性关节炎患者铁蛋白、血红蛋白含量水平变化明显。铁代谢异常与疾病发展紧密相关,是诊断、预防、治疗的关键方向。
免疫性炎症疾病:是免疫调节失衡引发的炎症性疾病,如类风湿性关节炎、系统性红斑狼疮等。这类疾病常累及多器官系统,药物治疗不良反应多。免疫性炎症疾病患者常伴有铁代谢紊乱,如炎症性肠病易出现缺铁性贫血,系统性红斑狼疮存在铁缺乏与铁调素异常。免疫性炎症疾病和铁代谢相互影响,铁代谢异常会加剧炎症,炎症也会破坏铁平衡。
背景:铁代谢的异常与免疫性炎症疾病密切相关。运动干预是一种有效的治疗方式,能够通过调节铁代谢和改善免疫反应减轻炎症反应,但运动如何通过铁代谢调节免疫系统功能仍需深入探讨。
目的:回顾并总结铁代谢在免疫性炎症疾病中的研究进展,分析运动干预对铁代谢的调节作用以及调控免疫性炎症疾病的潜在机制,为未来免疫性炎症疾病的治疗提供新思路。
方法:资料来源于中国知网和PubMed数据库,检索文献时限为2010年1月至2024年6月。中文关键词为“铁代谢,铁稳态,铁调素,免疫性炎症,类风湿性关节炎,炎症性肠病,多发性硬化症,系统性红斑狼疮,运动”;英文关键词为“iron metabolism,iron homeostasis,hepcidin,immune inflammation,rheumatoid arthritis (RA),inflammatory bowel disease (IBD),multiple sclerosis (MS),systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE),exercise”,最终纳入 101篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①铁代谢的异常与多种免疫性炎症疾病,如类风湿性关节炎、系统性红斑狼疮、炎症性肠病等的发生和发展密切相关。铁过载或铁缺乏会导致免疫系统功能的紊乱,进而引发或加重炎症反应。②运动干预是调节铁代谢的重要手段,短期有氧运动或剧烈运动可能会导致短期性铁代谢紊乱,长期有氧运动能够促进铁稳态的恢复。规律的有氧运动可降低血清铁浓度,减少肝脏和肌肉中的铁储存,并改善机体的铁分布。长期坚持运动可帮助恢复铁代谢平衡,从而减轻由于铁代谢紊乱引起的炎症反应。力量训练和柔韧性训练等运动类型也对铁代谢有显著影响。运动对免疫性疾病的影响具有个体差异,运动强度、持续时间、频率等因素可能会对铁代谢产生不同的影响。③总体而言,运动干预手段发挥着对免疫性炎症疾病的防治作用。然而,现有研究在机制阐明、长期效果及个体差异方面仍存在一定的局限,未来需进一步深入探讨运动对铁代谢的具体调节机制以及不同类型运动的个体化治疗效果。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-6937-9920(王沛云)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
孙尧天, 徐 凯, 王沛云. 运动影响铁代谢对免疫性炎症疾病调控的潜在机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1486-1498.
Sun Yaotian, Xu Kai, Wang Peiyun. Potential mechanisms by which exercise regulates iron metabolism in immune inflammatory diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1486-1498.
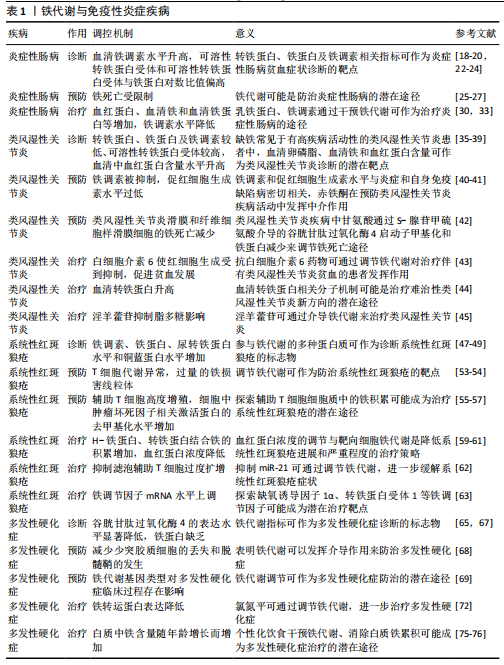
2.2 铁代谢在免疫性炎症疾病中的作用机制 免疫性炎症疾病与铁平衡有着密切的相关性,一方面,炎症可影响铁的吸收和转运,从而导致人体内铁平衡被扰乱;另一方面铁代谢的异常会加剧人体内炎症反应,使得免疫性炎症疾病恶化[9-10]。大量的研究已证明,在治疗免疫性炎症疾病时需要关注铁代谢的状态,且通过干预铁代谢在调节免疫细胞分化、增殖和功能中发挥的关键作用,改善免疫性炎症
疾病的症状[11]。因此基于铁代谢机制的治疗方法正被不断开发,为免疫性炎症疾病的治疗和预防提供了思路和手段[12-13]。
2.2.1 铁代谢与炎症性肠病 炎症性肠病是一种慢性、复发性的复杂疾病,主要包括溃疡性结肠炎和克罗恩病,目前主要认为是基因突变、免疫系统失调、微生物菌群失调以及肠道上皮屏障功能紊乱等多重因素引发了肠道黏膜的免疫反应并导致炎症[14-16]。研究发现,缺铁性贫血是一种在炎症性肠病患者中非常常见的肠外系统性并发症,这种缺铁性贫血通常与铁缺乏症有关,对炎症性肠病的恢复过程造成严重的负面影响[17]。炎症性肠病患者中如血清铁、转铁蛋白、血清铁饱和度、血清铁蛋白、铁调素等铁稳态的传统指标与健康人群或存在相似症状的非炎症性肠病人群具有显著差异。几项研究检测了炎症性肠病患者血清与尿液中的铁调素浓度,结果表明,与健康对照组相比,患者的铁调蛋白水平升高,并且与疾病活动和血清铁蛋白浓度相关[18-20]。故目前炎症性肠病缺铁的诊断基于铁蛋白和转铁蛋白饱和度2种标记物的组合,并以此评估患者的炎症状态[21]。另外,相关研究表明儿童与成人炎症性肠病患者中可溶性转铁蛋白受体(soluble transferrin receptor,sTfR)和sTfR与铁蛋白对数比值(sTfR/log ferritin)明显偏高于患有功能性便秘和功能性腹痛的对照组,sTfR、sTfR/log ferritin指标与铁稳态的传统指标也呈现出显著的相关性[22-24]。基于以上研究表明,铁代谢相关指标可以用来辅助炎症性肠病的诊断。
铁代谢紊乱目前被认为与炎症性肠病的发病机制有着密切的联系,且在炎症性肠病中的病理作用中表现出其潜在治疗靶点。相关研究在溃疡性结肠炎和克罗恩病患者炎症部位的肠上皮细胞中观察到了细胞铁死亡,克罗恩病患者肠上皮细胞中谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4活性降低,同时溃疡性结肠炎中活性氧和脂质过氧化产物水平升高,溃疡性结肠炎患者和小鼠分离的肠上皮细胞也表现出前列腺素内过氧化物合酶2增加和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4减少,这些铁死亡主要生物标志物的变化是铁代谢与炎症性肠病高关联度的表现[25-27]。一些研究进一步表明,包括铁沉积、脂质过氧化积累和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4失活铁死亡的一些核心事件与炎症性肠病发病机制相关,如铁超载导致肠道氧化损伤引发脂质过氧化积累,可能正是炎症性肠病的病理表现[28-29]。以上对炎症性肠病发病机制与铁代谢关联的研究可知,通过干预铁代谢调控铁死亡可能有助于炎症性肠病发展的防治与改善。
通过多种形式对铁代谢进行针对性调整可以减缓炎症性肠病症状,对缺铁性贫血等并发症也有着治疗作用。目前铁治疗主要包括口服和静脉注射铁剂,由于口服铁剂易于使用且廉价目前被广泛使用,相关研究比较了硫酸亚铁与乳铁蛋白治疗对炎症性肠病儿童缺铁性贫血的疗效与安全性,发现口服乳铁蛋白治疗效果更显著且胃肠道不良反应发生率更低,因此患者的依从性更好[30]。但总的来说,口服铁制剂吸收效果并不理想,并且可能会产生许多不良反应,如恶心、腹痛、便秘等[31]。而静脉注射铁制剂由于克服了肠道吸收中的不良反应,目前被认为是治疗慢性炎症性疾病患者更有价值的选择,欧洲克罗恩病和结肠炎组织指南中已建议将静脉注射铁剂作为炎症性肠病的主要治疗方法之一[32]。另外,通过分析接受英夫利西单抗或维多利珠单抗诱导治疗第6,14周的炎症性肠病患者的血清样本发现,对诱导治疗有反应的患者中诱导治疗降低了铁调素水平,这使得铁的生物利用度提高,而铁调素与全身铁指数有显著相关性,可以铁调素为重点研究铁代谢以进一步优化炎症性肠病与缺铁性贫血的诊断和治疗[33]。因此,通过口服或注射影响体内铁调素等铁代谢重要因素的药物是目前治疗缺铁性贫血改善炎症性肠病的有效途径,但静脉注射铁制剂相对表现出更好的治疗效果,大量实验为此提供了有力支撑。
综上所述,铁代谢与炎症性肠病的诊断、预防与治疗都表现出了高度的相关性。诊断方面,铁调素、转铁蛋白等铁代谢相关指标可作为炎症性肠病的缺铁性贫血等并发症的直接诊断靶点,用来辅助炎症性肠病的诊断;预防方面,通过调节铁代谢、调控细胞铁死亡可能有助于控制炎症性肠病的发展,甚至可以以此对炎症性肠病进行预防和早期干预;治疗方面,通过口服或注射影响体内铁调素等铁代谢重要因素的药物是目前治疗缺铁性贫血改善炎症性肠病的有效途径,但静脉注射铁制剂表现出相对更好的治疗效果。
2.2.2 铁代谢与类风湿性关节炎 类风湿性关节炎是一种比较系统的、常见的自身免疫性疾病,其表现包括周围关节不可逆的破坏和功能丧失[34]。其中贫血是类风湿性关节炎中最常发生的血液学问题,也是类风湿性关节炎的一种表现形式,主要包括缺铁性贫血和慢性疾病贫血两种贫血类型。在疾病活动度高的类风湿性关节炎患者中铁缺乏症状较为常见,且类风湿性关节炎疾病活动评分28(DAS-28)的降低和血红蛋白的减少是判断铁缺乏的最有力因素[35]。有相关研究对患者铁代谢相关指标进行评估,发现血红蛋白含量与类风湿性关节炎的慢性疾病贫血明显相关,与健康对照组相比,患者血清中的血红蛋白含量较高,且贫血患者的血清中血红蛋白含量高于无贫血患者,与铁蛋白呈强烈正相关[36-37]。同时,对血红蛋白含量与红细胞健康状况(由贫血、铁代谢和红细胞生成的标志物组成)因素、急性相反应物(由炎症和铁代谢的标志物组成)进行因素统计分析发现,血红蛋白含量在2个因子中负荷量均较大,表明它与炎症引起的贫血有明显相关性[38]。另外,还有研究发现血红蛋白含量和铁代谢参与了类风湿性关节炎的骨质疏松症,血清卵磷脂和血清铁与类风湿性关节炎患者的骨质疏松症有间接和直接关系[39]。以上表明,铁代谢相关指标可以用来对类风湿性关节炎进行辅助性诊断。
类风湿性关节炎的发病机制目前还未完全明确,但现有的研究表明铁代谢与它有着密切关系。有研究在对血红蛋白和促红细胞生成素的预后潜力评估中发现,临床疾病活动与血红蛋白水平的关系比与肿瘤坏死因子α或白细胞介素6受体效应的关系更为密切,促红细胞生成素水平与炎症和铁缺乏具有密切相关性[40]。在慢性病性贫血研究背景下,赤铁酮可以作为类风湿性关节炎一个新的标志物,它具有抑制血红蛋白含量的作用,对类风湿性关节炎疾病活动可能具有有益的红细胞生成作用[41]。不仅如此,铁死亡可能在维持类风湿性关节疾病滑膜增殖和死亡的平衡中发挥关键作用,相关研究证实了类风湿性关节炎滑膜和纤维细胞样滑膜细胞的铁死亡减少,甘氨酸通过S-腺苷甲硫氨酸介导的谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4启动子甲基化和减少铁蛋白来调节铁死亡途径[42]。基于以上研究认为,铁代谢在类风湿性关节炎的防治中具有潜在意义。
通过多种途径调节铁代谢,还可对治疗类风湿性关节炎的相关症状起到效果。白细胞介素6上调肝脏中铁调素的产生,铁调素通过下调巨噬细胞释放铁的速率来减少可用于红细胞生成的铁,活化的巨噬细胞也可能通过缩短红细胞寿命促进贫血的发展,而抗白细胞介素6药物可能对伴有类风湿性关节炎和特贫血患者有益[43]。有研究还通过同位素标记相对和绝对定量和平行反应监测蛋白质组学技术分析类风湿性关节炎患者对甲氨蝶呤+来氟米特+英夫利昔单抗治疗的分子机制,发现反应者和非反应者之间血清转铁蛋白的差异显著,表明了血清转铁蛋白参与了缺氧诱导因子1通路和铁死亡,这可能是治疗难治性类风湿性关节炎的新方向[44]。除此之外,最近一项研究表明,淫羊藿苷通过激活Xc-/谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4轴来抑制铁垂病,从而保护类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞免受脂多糖诱导的细胞死亡[45],表现出一种潜在的类风湿性关节炎治疗新策略。通过以上研究结果发现,调节铁代谢对类风湿性关节炎及其相关症状的治疗具有很重要的意义,并有着巨大的治疗潜力。
综上所述,铁代谢对于类风湿性关节炎的诊断、预防与治疗有着非常重要的意义。诊断方面,血红蛋白、血红蛋白含量等相关指标可作为类风湿性关节炎及并发症的诊断靶点;预防方面,通过干预铁代谢,减少铁死亡,对防治类风湿性关节炎有着重要作用;治疗方面,目前抗白细胞介素6药物、淫羊藿苷可能是治疗类风湿性关节炎的有效途径,血清转铁蛋白的分子机制研究也表现出它的巨大治疗潜力。
2.2.3 铁代谢与系统性红斑狼疮 系统性红斑狼疮是一种影响人体多器官系统的慢性自身免疫性疾病,致病性T细胞的异常分化和自身抗体的过度产生使得机体免疫系统攻击自身组织和器官,导致多种症状和体征[46]。其中狼疮性肾炎是系统性红斑狼疮中最常见的末端器官表现,影响着高达40%的成人和80%的儿童系统性红斑狼疮患者,也是发病和死亡的主要原因。大量研究已表明,参与铁代谢的多种蛋白质可作为狼疮性肾炎和发病的血浆或尿液生物标志物,其中包括了铁载体蛋白转铁蛋白、中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白、铁氧化酶铜蓝蛋白、调节蛋白铁调素和铁储存蛋白铁蛋白等[47-48]。相关研究用细胞渗透性亚铁离子荧光探针检测系统性红斑狼疮患者体内游离Fe2+水平,对比健康供者也发现患者辅助 T细胞中Fe2+水平显著升高,狼疮辅助 T细胞中分别编码人类铁蛋白重链和轻链的mRNA水平以及铁蛋白水平显著增加[49]。另外,通过对系统性红斑狼疮患者的尿液采集分析发现,狼疮性肾炎患者尿转铁蛋白和铜蓝蛋白两种生物标志物的水平显著高于非狼疮性肾炎患者,可成为系统性红斑狼疮患者中狼疮性肾炎的潜在诊断标志物,甚至还可区分活动期与非活动期狼疮性肾炎[50-51]。因此,铁代谢相关生物指标可以作为系统性红斑狼疮及狼疮性肾炎的潜在诊断靶点。
铁代谢在系统性红斑狼疮发病机制中的具体作用尚不明晰,但可以肯定的是二者之间存在着密切联系[52]。相关研究提出系统性红斑狼疮的T细胞表现出多种代谢异常,而过量的铁损害线粒体可能与此相关[53-54]。滤泡辅助T细胞在系统性红斑狼疮的发病机制中不可或缺,相关研究表明患者体内辅助 T细胞的细胞质中铁不断积累,辅助 T细胞向滤泡辅助T细胞细胞分化,使得系统性红斑狼疮中致病效应物发展[55]。另外研究发现,系统性红斑狼疮中miR-21的表达增加是由于TLR7/Ⅰ型干扰素通路的激活,是发病的主要驱动因素,而miR-21/BDH2通路在调控T细胞内铁离子蓄积方面起到重要作用[56-57]。此外,缺氧也被认为是miR-21的主要诱导因素,缺氧诱导因子1α是缺氧反应的主要调节因子,实验表明缺氧诱导因子1α通过抑制雷帕霉素靶蛋白活化,抑制淋巴细胞脉络膜脑膜炎病毒感染小鼠滤泡辅助T细胞细胞的分化[58]。因此探寻Toll样受体/Ⅰ型干扰素通路、miR-21/BDH2/Fe2+通路、缺氧诱导因子1α、雷帕霉素靶蛋白等活化关系可能对发现系统性红斑狼疮的病理机制有着关键作用。以上研究探寻了铁在系统性红斑狼疮发病机制中的作用,虽未完全明晰,但对铁离子的调控可能有助于系统性红斑狼疮的防治。
调控铁代谢的生物指标目前在系统性红斑狼疮人体与动物模型中表现出了显著的治疗作用。有学者通过回顾分析2012-2020年间诊断为青少年系统性红斑狼疮的患者,发现70%的患者有血液系统受累,其中贫血是最常见的血细胞减少症,红细胞沉降率、血清铁蛋白、系统性红斑狼疮疾病活动指数评分与贫血患者的血红蛋白水平呈负相关,缺铁是贫血的重要原因之一,在发病时血红蛋白浓度较低和肾脏受累的青少年系统性红斑狼疮患者中表现得更为显著[59]。最近研究中也报告了雌性MRL/lpr小鼠肾脏内铁沉积的组织学证据,并且用外源性铁调素治疗MRL/lpr小鼠减轻了系统性红斑狼疮中的肾损伤,降低了已建立的系统性自身免疫和蛋白尿老年小鼠肾炎的进展和严重程度,认为用铁调素靶向细胞铁代谢是狼疮性肾炎一种有前途的治疗策略[60-61]。用体内特异性抑制miR-21的Antagomir-21处理12周龄的MRL/lpr小鼠,经过12周治疗后,检测滤泡辅助T细胞和生发中心B细胞比例以及血清自身抗体水平,并通过组织学评分和蛋白尿评估疾病严重程度,发现体内抑制miR-21可改善细胞内铁稳态,抑制滤泡辅助T细胞过度扩增,有助于减轻狼疮鼠自身免疫反应,缓解疾病症状[62]。基于上述相关研究成果所展现,铁代谢的调节在针对系统性红斑狼疮及相关疾病的治疗中有着重要的意义,通过外源性铁调素、miR-21抑制剂等方式可缓解和治疗系统性红斑狼疮的相关症状。KUMARI等[63]发现了涉及铁稳态的失调蛋白与狼疮性肾炎的严重性有着密切联系,并在研究中探索缺氧诱导因子1α、转铁蛋白受体1等铁调节因子发现,细胞内铁水平可以通过影响细胞内病毒的表达来影响系统性红斑狼疮病毒的复制。
综上所述,铁代谢对于系统性红斑狼疮的诊断、预防与治疗都有着显著的价值。诊断方面,铁载体蛋白转铁蛋白铁氧化酶铜蓝蛋白、铁储存蛋白铁蛋白、中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂质运载蛋白、尿转铁蛋白和铁调素等铁代谢相关生物指标可以作为系统性红斑狼疮及狼疮性肾炎的潜在诊断靶点;预防方面,对铁离子的调控可能有助于系统性红斑狼疮的防治,未来在探寻miR-21/BDH2/Fe2+通路、缺氧诱导因子1α、雷帕霉素靶蛋白等活化关系可能对发现系统性红斑狼疮病理机制研究有着关键作用,从而实现干预铁代谢预防系统性红斑狼疮病发病;治疗方面,铁代谢的调节在针对系统性红斑狼疮及相关疾病的治疗中有着重要的意义,通过外源性铁调素、miR-21抑制剂等方式可缓解和治疗系统性红斑狼疮的相关症状。
2.2.4 铁代谢与多发性硬化症 多发性硬化症是一种慢性、自身免疫性、神经系统疾病,主要特点是神经炎症、脱髓鞘、少突胶质细胞丢失和神经变性导致神经信号传递受到干扰或中断,从而引起多种不同的神经症状,包括视力受损、肌无力、感觉异常、平衡困难等[64]。有研究通过观测多发性硬化症和实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠模型中铁死亡抑制剂谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4表达的变化,发现小鼠模型中谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4的表达水平显著降低,表明多发性硬化症小鼠模型神经元和胶质细胞中铁死亡的增加[65]。
MATROSOVA等[66]提出应用定量磁化率图测定大脑中的铁浓度,获得的磁化率值可能成为反映多发性硬化症潜在活动和进展的生物标志物,进而影响诊断和治疗;另外,采集了90例多发性硬化症患者的静脉血液样本用于血细胞计数测定,获得血清,分析铁、铁蛋白、转铁蛋白、转铁蛋白饱和度、不饱和铁结合能力和总铁结合能力的浓度,并根据疲劳严重程度量表、贝克抑郁量表和多发性硬化症功能评分进行评估,发现多发性硬化症患者的铁蛋白缺乏与抑郁障碍恶化和生活质量下降相关[67]。基于以上研究表明,可通过谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4、大脑中铁浓度、铁蛋白、转铁蛋白、转铁蛋白饱和度等铁代谢相关指标对多发性硬化症患者进行辅助诊断,判断其发展程度与状况。
多发性硬化症发病机制目前尚未完全阐明,但越来越多的研究已展现出了铁代谢变化与多发性硬化症发病机制之间的关系。多发性硬化症是中枢神经系统的一种慢性脱髓鞘疾病,铜螯合剂(Cuprizone)可诱导脱髓鞘,其机制尚未完全明晰。JHELUM等[68]通过在饮食中给予雄性小鼠Cuprizone,导致胼胝体中的少突胶质细胞在2 d内迅速丢失,同时伴随着一些铁死亡标志物的表达,而使用铁死亡的小分子抑制剂可以防止少突胶质细胞丢失和脱髓鞘发生,表明了铁死亡于多发性硬化症发病机制中的介导作用。另外,有关研究对含有3种铁代谢相关基因多态性的多发性硬化症患者进行了基因分型和基因频率分析,发现铁代谢在多发性硬化症的发病中发挥作用,而铁调素、转铁蛋白、转铁蛋白受体等铁代谢相关基因的多态性可能是多发性硬化症发病机制的一个重要因素[69]。还有相关研究表明,过量的铁增加了活性氧的生成,导致髓鞘和神经元丢失,继而发生脱髓鞘和神经变性[70]。另外,铁可能是少突胶质细胞前体细胞成熟为少突胶质细胞的重要元素,在髓鞘再生过程中,少突胶质细胞前体细胞被募集至多发性硬化症损伤处,进而分化为成熟少突胶质细胞,促进受损的轴突髓鞘再生,因此认为铁缺乏可能严重影响多发性硬化症的发病[71]。基于以上研究发现,铁代谢的相关机制与多发性硬化症病理紧密联系,无论是铁死亡、铁超载、铁缺乏都会导致病情的恶化,故而加强对铁代谢的调控将成为多发性硬化症改善与预防的有效机制。
基于铁对小胶质细胞的影响,以及铁的累积对多发性硬化症发病的影响,研究者们以调控铁代谢、铁死亡等方式对治疗多发性硬化症进行了研究。有研究使用铁和氯氮平干预小胶质细胞,然后对脊髓炎症、脱髓鞘、小胶质细胞活化和铁积累以及铁代谢和炎症调节因子的转录变化进行组织学分析,发现在体外铁损害了小胶质细胞的吞噬功能和炎症标志物,但受氯氮平调节减轻了脱髓鞘,且对炎症的作用与铁沉积的减少相关,同时伴随铁转运蛋白的表达降低[72]。还有研究表明,通过补充充足的维生素D可降低铁调素,对多发性硬化症具有保护作用,并改善临床症状[73-74]。但一些改善多发性硬化症治疗的相关临床研究中出现了似乎矛盾的结果,部分研究发现铁含量高对多发性硬化症的结果不利[75],还有部分研究认为多发性硬化症患者在补充铁后表现出临床改善[76]。因此,可以发现氯氮平、维生素D等对铁代谢有影响的药物均对多发性硬化症具有一定的治疗效果,而铁含量的高低为多发性硬化症病情带来的影响可能因人而异,无论铁超载与铁缺乏都会带来负面影响。
综上所述,多发性硬化症虽病因尚不清晰,但铁代谢在其诊断、预防与治疗中均有着重要作用。诊断方面,可通过谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4、大脑中铁浓度、铁蛋白、转铁蛋白、转铁蛋白饱和度等铁代谢相关指标对多发性硬化症患者进行辅助诊断,判断其发展程度与状况;预防方面,铁代谢的相关机制与多发性硬化症病理紧密联系,无论是铁死亡、铁超载、铁缺乏都会导致病情的恶化,加强对铁代谢的调控将成为多发性硬化症改善与预防的有效机制。治疗方面,氯氮平、维生素D等对铁代谢有影响的药物均对多发性硬化症具有一定的治疗效果,而铁含量的高低为多发性硬化症病情带来的影响可能因人而异,因此需基于患者不同的实际情况做出抑制或增加的铁代谢调控方案。
铁代谢与免疫性炎症疾病的关系见表1。
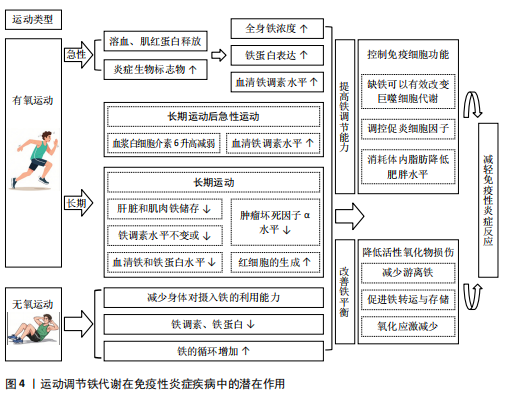
2.3 运动调节铁代谢在免疫性炎症疾病中的潜在作用 目前研究显示,在免疫性炎症疾病中铁的平衡被破坏导致铁代谢异常,从而加剧炎症过程。而运动对免疫性炎症疾病中的铁代谢有着潜在多种机制的调节作用(图4),主要表现为调节免疫细胞活性恢复铁平衡、改善铁代谢降低活性氧化物损伤2个方面。
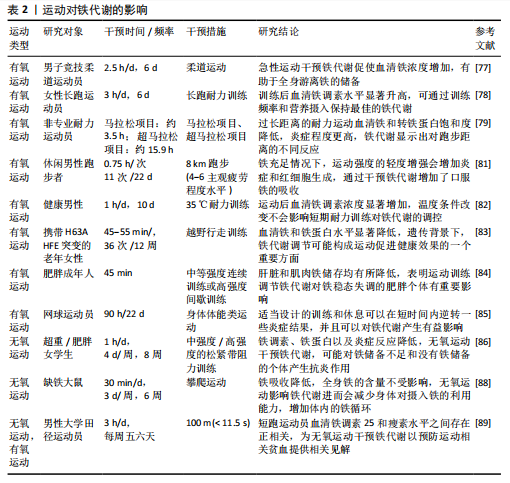
2.3.1 运动与铁代谢 从发文量上可发现,近年关于运动与铁代谢的相关研究不断增加,显然运动调控铁代谢的影响与作用都受到广大学者的关注[77]。大量研究也表明不同运动形式对铁代谢产生了不同的影响[77-89],有
氧运动与无氧运动对铁代谢作用的最新研究分析总结见表2。
(1)铁代谢与有氧运动:有氧运动是一种身体需要不断地利用氧气来参与代谢供能以维持运动的持续性和强度的运动形式,特征主要表现为需要依靠有氧气,有全身主要肌群的参与,且运动时间较长有节奏。常见的有氧运动包括步行、跑步、骑自行车、游泳、跳绳等,这些运动可以有助于提高心肺功能、增强肌肉耐力、改善心血管健康、减轻体质量和增强免疫系统功能等。在有氧运动干预铁代谢的相关研究中,主要针对急性与长期有氧运动的影响进行了探究。
急性有氧运动是一种身体在运动过程中需不断利用氧气参与代谢供能,以维持运动持续性和强度的运动形式,具有需依靠氧气、全身主要肌群参与、运动时间较长且有节奏的特征[78]。急性有氧运动的相关研究中,急性运动引起的负荷和循环应力导致的溶血可能会导致急性有氧运动后全身铁浓度的升高,同时运动过程中骨骼肌微观结构损伤可能将含铁血红蛋白和肌红蛋白释放到循环中,从而有助于全身游离铁的储备[79-80]。还有研究对女性运动员同一天内反复进行耐力锻炼对铁代谢的影响进行了探究,认为每天2次耐力运动导致女性长跑运动员完成运动后24 h血清铁调素水平显著升高[81]。而通过对马拉松和超马拉松等高强度耐力运动中的炎症和铁稳态变化观测,赛后立即检测发现炎症生物标志物与铁蛋白的表达显著增加,马拉松后观察到血清铁和转铁蛋白饱和度增加,而超马拉松后血清铁和转铁蛋白的饱和度降低[82]。在超马拉松赛后连续补充维生素D可影响血清铁的代谢,使铁浓度下降幅度变小[83]。可见急性有氧运动对铁代谢影响显著,运动后短时间内炎症与铁蛋白显著增加,而后铁调素增加对体内铁代谢进行调控。
在长期有氧运动的相关研究中,通过对男性跑步者进行3周的训练试验,发现在铁充足的男性中,运动强度的轻度加强会增加炎症和红细胞的
生成,且认为其净效应是降低铁调素浓度并增加口服铁的吸收[84]。还有研究针对有氧运动环境影响进行了探究,对两组健康男性分别在35 ℃与18 ℃环境下进行为期10 d的有氧耐力训练,发现在训练期结束后再进行运动时两组血浆白细胞介素6水平升高均减弱,结果显示在运动后血清铁调素浓度显著增加,而且温度条件的改变并不会影响短期耐力训练对铁代谢的调控[85]。此外,相关研究通过对老年女性进行12周的北欧式健走训练试验,发现训练导致血清铁和铁蛋白水平显著降低,铁调素水平保持不变,可认为定期有氧运动训练可降低健康成人的血清铁浓度[86]。还有研究通过有氧与无氧运动对肥胖成年人进行12周的干预,发现肝脏和肌肉铁储存均有所降低,结果表明运动对铁稳态失调的肥胖个体有重要影响[87]。而一项关于探究不同训练营的训练负荷对网球运动员免疫反应与铁代谢影响的试验中发现,所有运动员的肿瘤坏死因子α水平在训练营结束时和技术训练营结束后都有所下降,2个训练营结束后,铁调素水平也可能下降,同时还发现适当设计的训练和休息可以在短时间内逆转一些炎症结果,并且可以对铁代谢产生有益影响[88]。因此可知,长期进行有氧运动使得血清铁浓度降低,使得人体肝脏和肌肉铁储存均有所降低,辅以休息恢复将对铁代谢的稳态产生有益影响。
综上所述,单次的有氧运动短时间会使得炎症生物标志物与全身铁浓度提高,长时间的高强度耐力运动也会对铁代谢造成不利影响,一段时间后血清铁调素的提高也使得人体铁代谢的调控作用增强。通过定期坚持进行规律性有氧运动益于机体铁稳态的维持,并使得血清铁浓度降低,使肥胖人群肝脏和肌肉的高铁储存降低,显著改善机体内的铁分布与状况,同时结合合理的饮食与休息将更利于机体铁代谢的稳定性与短时间内的炎症情况。对于定期有氧运动通过铁代谢介导抗炎症反应的路径机制还不够明细,仍需进一步研究分析。
(2)铁代谢与无氧运动:无氧运动是指人体肌肉在无氧供能代谢状态下活动的运动形式,其特征为运动时以无氧代谢供能系统为主,依赖糖酵解来提供能量,氧气的摄取量非常低。常见的无氧运动包括举重、短跑、俯卧撑、引体向上、仰卧起坐等负荷强度高、瞬间性强的运动。无氧运动可以有效地增加肌肉质量、改善身体姿势、增加骨密度和改善身体代谢等。
无氧运动干预铁代谢的研究较少,其中主要针对长期进行无氧运动训练所带来的影响进行了探究。相关人体研究结果表明,中等和高强度的抗阻运动训练干预均对铁调素、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平产生影响,可以降低铁调素、铁蛋白以及炎症反应[89]。有实验提出激活转录因子4(activating transcription factor 4,ATF4)作为一种重要的糖酵解激活剂,通过ATF4-HIF-1α-HK2-糖酵解轴调控糖酵解等代谢途径,间接地影响了炎症反应的强度和持续时间,有助于巨噬细胞的免疫耐受性,而血清铁蛋白参与并影响缺氧诱导因子1α通路[90]。而通过对大鼠为期6周的抗阻运动干预,发现进行抗阻力运动的大鼠显示出明显的铁吸收降低,但体内整体铁含量未受影响;同时血液中的铁状况和组织中的铁含量在运动的大鼠和静止的大鼠之间没有差别,认为是因为阻力运动使得体内铁的循环增加;另外运动组和静息组的铁调素、铁转运蛋白1等的基因表达水平没有差异,这表明了抗阻力运动不会直接影响身体内的整体铁储备,但会减少身体对摄入铁的利用能力,导致较少的铁进入到血液中[91]。另外通过研究短跑运动员与长跑运动员血液中铁调素、瘦素水平、铁状态以及体脂肪之间的关系,发现长跑运动员的铁调素水平相较短跑运动员更低,瘦素和脂联素水平较高[92]。以上研究表明,长期进行无氧运动可以降低铁调素等水平并降低铁的吸收,同时还能降低炎症反应。
综上,对无氧运动的探究试验虽较少,但现有的研究成果表明,与长期进行有氧运动相似,长期的无氧运动也可使得铁调素、铁蛋白等指标降低,且均可以有效减弱炎症反应,但使铁调素水平的降低程度不如长期的有氧运动。同时,由于相关试验较少,暂时无法得知急性无氧运动对铁代谢所带来的影响。因此,要进一步揭示运动与铁代谢之间的关系与影响机制,仍需更深入的对无氧运动进行研究。
2.3.2 运动调节铁代谢在免疫性炎症疾病中的潜在作用机制(1)运动恢复铁平衡降低活性氧化物损伤:活性氧如果不受抗氧化防御系统的适当调节,会破坏蛋白质、脂质和DNA等细胞成分,游离铁离子具有催化活性氧产生的潜力,过量的游离铁离子会因此促进体内的氧化应激和炎症。目前研究发现,体内出现铁超载与铁缺乏会对免疫性炎症疾病带来不良影响,并与其发病机制息息相关[17,53,75];通过药物注射等多种手段调节体内铁离子代谢的平衡,在免疫性炎症疾病的治疗中发挥了积极作用[30,57,73]。这些研究显示,通过促进铁转运与存储、减少游离铁可以达到治疗免疫性炎症疾病的效果。
类风湿性关节炎、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症、系统性红斑狼疮等免疫性炎症疾病都有机体无法正常吸收和利用所需足够量的铁,而出现贫血、储存铁被大量释放以及细胞内外铁分布失调等相关特征。MACKAY等[93]通过对实验小鼠进行5 d运动与药物辅助治疗干预,发现可以降低转运蛋白受体水平,有效改善了铁代谢的失调并预防氧化应激,从而减轻炎症反应。KORTAS等[86]试图探究人体组织中铁沉积与运动、遗传基因间的关系,对76名老年女性进行为期12周的越野行走训练,发现血清铁和铁蛋白水平降低,铁调素水平保持不变,认为无论遗传背景如何,体内铁储备的减少可能构成运动促进健康的一个重要方面。人体铁的吸收部位主要在十二指肠和空肠上段,已有大量研究证明运动可以有效改善肠道益生菌群,对炎症产生抑制,MOKHTARZADE等[94]对42例多发性硬化症患者(实际完成35例)进行了每周5次、为期6个月的家庭运动干预,不仅发现定期的体育活动与肠道菌群改变相关联,同时白细胞介素10与肿瘤坏死因子α水平等也显著下降,氧化应激减少,机体炎症得到了缓解,有效抑制了患者多发性硬化症。
由此可见,可通过运动干预改善机体的铁平衡,有效降低机体铁储备,预防氧化应激,来达到防治免疫性炎症疾病的目的。从免疫性炎症疾病角度看,短时间运动可能针对疾病中铁代谢异常导致的氧化应激问题,快速调整铁平衡,缓解因铁超载或缺乏引发的活性氧化物损伤,对疾病起到一定的改善作用,但这种影响可能较为有限且短期。长期运动还可抑制炎症,减少氧化应激。这是因为长期运动持续促进铁转运与存储,稳定降低游离铁离子水平,持续减轻活性氧化物对蛋白质、脂质和DNA等细胞成分的破坏,对免疫性炎症疾病的防治效果更持久、更深入,有助于长期维持机体健康,降低疾病发生风险或缓解疾病症状。虽然研究表明运动、铁平衡、氧化应激和炎症之间存在关联,但对其确切的内在机制仍不完全了解,而要揭示运动恢复铁平衡、降低活性氧化物损伤防治免疫性炎症疾病的机制,需要进一步研究确定运动影响铁代谢和氧化应激的具体分子和细胞途径。同时,虽然运动在调节铁平衡和氧化应激方面显示出良好的前景,但迄今为止进行的研究主要是探讨一般性的关联,需要更多的研究来调查运动、铁代谢和免疫性炎症疾病之间的具体联系,了解运动对疾病的特定影响,有助于调整干预措施,使其效益最大化。
(2)运动调节铁代谢控制免疫细胞功能:免疫细胞在免疫性炎症中起着至关重要的作用,这些细胞是免疫系统的关键组成部分,有助于炎症的启动、调节和解决[95]。而铁是人体内DNA合成、能量产生和氧气运输等过程的必要因素,在免疫细胞发育、增殖过程中更是发挥着不可或缺的作用,巨噬细胞、中性粒细胞和淋巴细胞等免疫细胞依靠铁来维持其正常功能,包括病原体识别、吞噬作用和细胞因子的产生等[96]。目前研究已表明可以通过调控机体内铁的变化影响免疫细胞群的活动,PEREIRA等[97]发现在小鼠体内一定程度的缺铁可以有效改变巨噬细胞代谢,从而减少体内炎症;ODEH等[98]通过对大鼠注射右旋糖酐铁溶液使其发生铁摄入过量,发现过量铁摄入会导致氧化应激增加、炎症和白细胞介素12/白细胞介素10细胞因子与M1巨噬细胞表型的比例增加。
运动对铁代谢有着明显的影响,而二者与免疫细胞的活动也有着密不可分的联系。有研究分别对93名受试者进行为期12周、每周3次的高强度间歇训练以及中等强度持续训练干预,发现进行这两种运动后IgA、淋巴细胞和淋巴细胞百分比等炎症因子较对照组显著降低,并且中等强度持续训练干预方式比高强度间歇训练更有助于增强积极影响,表明这两种运动均对免疫细胞具有调节作用,可以减轻免疫性炎症,对免疫系统有益[99]。另外,肥胖会导致循环中促炎细胞因子增加和抗炎细胞因子减少,低水平的慢性炎症也成为其关键特征,对此ASGHAR等[100]通过对大鼠16周的饮食干预后解剖发现,脾切片淋巴细胞募集增加,淋巴细胞坏死,红髓中的含铁血黄素和铁沉积表明免疫系统激活;骨骼肌切片显示肌纤维退化,脂肪堆积增加,以及巨噬细胞的募集等现象。也表明了脂肪和肥胖对免疫系统的不利影响,而通过锻炼可以消耗体内脂肪并降低肥胖水平,结合饮食控制对免疫细胞产生积极作用,达到减轻体内炎症水平的目的。HALADE等[101]以雄性 C57BL/6J 小鼠为研究对象,探究志愿运动和肥胖饮食的作用,发现运动可改变脾脏结构和免疫细胞状态,调节炎症反应和脂质代谢。这提示运动可通过影响铁代谢关联的免疫细胞、炎症及脂质代谢途径,在免疫性炎症疾病中发挥潜在调节作用。
此外,白细胞介素6可以诱导活化的B细胞生产抗体,持续产生会导致各种自身免疫性炎症疾病。BEHZADNEZHAD等[89]通过对40名大学生进行为期8周的抗阻运动干预试验,血样采集发现不同强度的抗阻运动均可降低铁调素、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α水平,而且铁储存不同的受试者通过抗阻运动都有效减少了人体炎症。
因此,通过运动调节铁代谢,对免疫细胞的分化与活动产生影响,减轻免疫性炎症反应,抑制免疫性炎症疾病的发展可以实现,其中短时间运动可快速调节免疫细胞对铁的利用,影响其病原体识别、吞噬作用和细胞因子产生等功能,从而减轻免疫性炎症反应,不过这种调节仅能在短期起到一定作用,可能不够全面和稳定。长期运动则能够调节免疫细胞的分化与活动,全面改善免疫细胞功能。这是因为长期运动能降低肥胖导致的促炎细胞因子增加和抗炎细胞因子减少的失衡状态,结合饮食控制对免疫细胞产生积极影响,进一步调节铁代谢,形成良性循环。虽然当前研究表明运动可以调节免疫细胞的活性减少免疫炎症反应,但还需要进一步的研究来阐明铁代谢在这个过程中的确切作用。调查运动强度、持续时间、铁的补充、分子机制和个体差异性的影响,将增强对如何利用运动促进免疫健康和预防免疫炎症疾病的理解。

| [1] GOLDBLATT F, O’NEILL SG. Clinical aspects of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Lancet. 2013;382(9894):797-808. [2] 冯乃波.双响应性靶向性纳米材料负载siERN1在自身免疫性炎症疾病中的治疗作用及机制研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学, 2022. [3] ZHANG DL, GHOSH MC, ROUAULT TA. The physiological functions of iron regulatory proteins in iron homeostasis - an update. Front Pharmacol. 2014,5:124. [4] HENTZE MW, MUCKENTHALER MU, ANDREWS NC. Balancing acts: molecular control of mammalian iron metabolism. Cell. 2004;117:285-297. [5] BURTSCHER J, PASHA Q, CHANANA N, et al. Immune consequences of exercise in hypoxia: A narrative review. J Sport Health Sci. 2024;13(3):297-310. [6] KARDASIS W, NAQUIN ER, GARG R, et al. The IRONy in Athletic Performance. Nutrients. 2023;15(23):4945. [7] LUO B, XIANG D, JI X, et al. The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise on autoimmune diseases: A 20-year systematic review. J Sport Health Sci. 2024;13(3):353-367. [8] GANZ T, NEMETH E. Iron balance and the role of hepcidin in chronic kidney disease. Semin Nephrol. 2015;35(4):337-348. [9] MU Q, CHEN L, GAO X, et al. The role of iron homeostasis in remodeling immune function and regulating inflammatory disease. Sci Bull. 2021;66(17):1806-1816. [10] NI S, YUAN Y, KUANG Y, et al. Iron metabolism and immune regulation. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 816282. [11] CHERAYIL BJ. Iron and immunity: immunological consequences of iron deficiency and overload. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2010;58(6):407-415. [12] ROSENBLUM MD, REMEDIOS KA, ABBAS AK. Mechanisms of human autoimmunity. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(6):2228-2233. [13] WAWER AA, JENNINGS A, FAIRWEATHER-TAIT SJ. Iron status in the elderly: A review of recent evidence. Mech Ageing Dev. 2018;175:55-73. [14] NEURATH MF. Current and emerging therapeutic targets for IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14(11):688. [15] LI Y, DEURING JJ, PEPPELENBOSCH MP, et al. Gut microbiota in IBD: role in pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36(2): 277-286. [16] SOKOL H, LEDUCQ V, ASCHARD H, et al. Fungal microbiota dysbiosis in IBD. Gut. 2017;66(6):1039-1048. [17] CAPPELLINI MD, SCARAMELLINI N, MOTTA I. Iron status in chronic inflammatory disease: therapeutic implications. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2023;133(2):16430. [18] BASSERI RJ, NEMETH E, VASSILAKI ME, et al. Hepcidin is a key mediator of anemia of inflammation in Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7(8):e286-e291. [19] MARTINELLI M, STRISCIUGLIO C, ALESSANDRELLA A, et al. Serum Hepcidin and Iron Absorption in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2016;10(5):566-574. [20] MECKLENBURG I, REZNIK D, FASLER-KAN E, et al. Serum hepcidin concentrations correlate with ferritin in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2014;8(11):1392-1397. [21] PEYRIN-BIROULET L, LOPEZ A, CUMMINGS JRF, et al. Review article: treating-to-target for inflammatory bowel disease-associated anaemia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 48(6):610-617. [22] OUSTAMANOLAKIS P, KOUTROUBAKIS IE, MESSARITAKIS I, et al. Soluble transferrin receptor-ferritin index in the evaluation of anemia in inflammatory bowel disease: a case-control study. Ann Gastroenterol. 2011;24(2):108-114. [23] KRAWIEC P, PAC-KOŻUCHOWSKA E. Soluble transferrin receptor and soluble transferrin receptor/log ferritin index in diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Liver Dis. 2019;51(3):352-357. [24] KRAWIEC P, PAC-KOŻUCHOWSKA E. Biomarkers and Hematological Indices in the Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutrients. 2020;12(5):1358. [25] XU C, LIU Z, XIAO J. Ferroptosis: A Double-Edged Sword in Gastrointestinal Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12403. [26] XU M, TAO J, YANG Y, et al. Ferroptosis involves in intestinal epithelial cell death in ulcerative colitis. Cell Death Dis. 2020; 11(2):86. [27] WANG S, LIU W, WANG J, et al. Curculigoside inhibits ferroptosis in ulcerative colitis through the induction of GPX4. Life Sci. 2020;259:118356. [28] CHIEPPA M, GALLEGGIANTE V, SERINO G, et al. Iron Chelators Dictate Immune Cells Inflammatory Ability: Potential Adjuvant Therapy for IBD. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(16):2289-2298. [29] ZHANG X, MA Y, LV G, et al. Ferroptosis as a therapeutic target for inflammation-related intestinal diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1095366. [30] EL AMROUSY D, EL-AFIFY D, ELSAWY A, et al. Lactoferrin for iron-deficiency anemia in children with inflammatory bowel disease: a clinical trial. Pediatr Res. 2022;92(3):762-766. [31] RESÁL T, FARKAS K, MOLNÁR T. Iron Deficiency Anemia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: What Do We Know?. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:686778. [32] TORRES J, BONOVAS S, DOHERTY G, et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Medical Treatment. J Crohns Colitis. 2020;14(1):4-22. [33] LOVEIKYTE R, BOURGONJE AR, VAN DER REIJDEN JJ, et al. Hepcidin and Iron Status in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease Undergoing Induction Therapy With Vedolizumab or Infliximab. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2023;29(8):1272-1284. [34] SCOTT DL, WOLFE F, HUIZINGA TW. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010; 376(9746):1094-1108. [35] TAŃSKI W, CHABOWSKI M, JANKOWSKA-POLAŃSKA B, et al. Iron metabolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(12): 4325-4335. [36] KHALAF W, AL-RUBAIE HA, SHIHAB S. Studying anemia of chronic disease and iron deficiency in patients with rheumatoid arthritis by iron status and circulating hepcidin. Hematol Rep. 2019;11(1):7708. [37] CHEN Y, XU W, YANG H, et al. Serum Levels of Hepcidin in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Correlation with Disease Activity and Anemia: A Meta-analysis. Immunol Invest. 2021;50(2-3):243-258. [38] NITA E, BAIRAKTARI E, KOLIOS G, et al. Role of Hepcidin in Anemia of Chronic Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Lab Physicians. 2021;13(4):317-322. [39] SATO H, TAKAI C, KAZAMA JJ, et al. Serum hepcidin level, iron metabolism and osteoporosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):9882. [40] SCHOLZ GA, LEICHTLE AB, SCHERER A, et al. The links of hepcidin and erythropoietin in the interplay of inflammation and iron deficiency in a large observational study of rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Haematol. 2019;186(1):101-112. [41] YOUSSEF SR, HASSAN EH, MORAD CS, et al. Erythroferrone Expression in Anemic Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Is It Disordered Iron Trafficking or Disease Activity? J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:4445-4455. [42] LING H, LI M, YANG C, et al. Glycine increased ferroptosis via SAM-mediated GPX4 promoter methylation in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022; 61(11):4521-4534. [43] KAWABATA H. [The pathogenesis of anemia in inflammation]. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2020;61(9):1105-1111. [44] CHEN J, LI S, GE Y, et al. iTRAQ and PRM-Based Proteomic Analysis Provides New Insights into Mechanisms of Response to Triple Therapy in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:6993-7006. [45] LUO H, ZHANG R. Icariin enhances cell survival in lipopolysaccharide-induced synoviocytes by suppressing ferroptosis via the Xc-/GPX4 axis. Exp Ther Med. 2021; 21(1):72. [46] CHEN PM, TSOKOS GC. T Cell Abnormalities in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: an Update. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(2):12. [47] LOZOVOY MA, SIMÃO AN, OLIVEIRA SR, et al. Relationship between iron metabolism, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol. 2013;42(4):303-310. [48] MOHAMMED MF, BELAL D, BAKRY S, et al. A study of hepcidin and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in Egyptian females with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Lab Anal. 2014;28(4):306-309. [49] GAO X, SONG Y, WU J, et al. Iron-dependent epigenetic modulation promotes pathogenic T cell differentiation in lupus. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(9):e152345. [50] URREGO T, ORTIZ-REYES B, VANEGAS-GARCÍA AL, et al. Utility of urinary transferrin and ceruloplasmin in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus for differentiating patients with lupus nephritis. Transferrina y ceruloplasmina en orina de pacientes con lupus eritematoso sistémico. ¿Son útiles para diferenciar pacientes con nefritis lúpica?. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 2020;16(1):17-23. [51] SHANG Y, LUO M, YAO F, et al. Ceruloplasmin suppresses ferroptosis by regulating iron homeostasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Signal. 2020;72:109633. [52] WLAZLO E, MEHRAD B, MOREL L, et al. Iron Metabolism: An Under Investigated Driver of Renal Pathology in Lupus Nephritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:643686. [53] VOSS K, SEWELL AE, KRYSTOFIAK ES, et al. Elevated transferrin receptor impairs T cell metabolism and function in systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci Immunol. 2023; 8(79):eabq0178. [54] WINCUP C, SAWFORD N, RAHMAN A. Pathological mechanisms of abnormal iron metabolism and mitochondrial dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021;17(9):957-967. [55] SCINDIA Y, MEHRAD B, MOREL L. Labile iron accumulation augments T follicular helper cell differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(9):e159472. [56] SCHELL SL, BRICKER KN, FIKE AJ, et al. Context-Dependent miR-21 Regulation of TLR7-Mediated Autoimmune and Foreign Antigen-Driven Antibody-Forming Cell and Germinal Center Responses. J Immunol. 2021;206(12):2803-2818. [57] YANG B, HOU S, ZHAO J, et al. 3-hydroxy butyrate dehydrogenase 2 deficiency aggravates systemic lupus erythematosus progression in a mouse model by promoting CD40 ligand demethylation. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):2685-2695. [58] HUANG B, PHELAN JD, PREITE S, et al. In vivo CRISPR screens reveal a HIF-1α-mTOR-network regulates T follicular helper versus Th1 cells. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):805. [59] KISAOGLU H, BABA O, KALYONCU M. Hematologic manifestations of juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus: An emphasis on anemia. Lupus. 2022;31(6):730-736. [60] SCINDIA Y, WLAZLO E, GHIAS E, et al. Modulation of iron homeostasis with hepcidin ameliorates spontaneous murine lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2020;98(1):100-115. [61] GAO X, SONG Y, DU P, et al. Administration of a microRNA-21 inhibitor improves the lupus-like phenotype in MRL/lpr mice by repressing Tfh cell-mediated autoimmune responses. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022; 106:108578. [62] MARKS ES, BONNEMAISON ML, BRUSNAHAN SK, et al. Renal iron accumulation occurs in lupus nephritis and iron chelation delays the onset of albuminuria. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):12821. [63] KUMARI N, AHMAD A, WANG S, et al. HIV-1 Restriction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Involves Iron Homeostasis. Blood. 2023;142 (Supplement 1):5237-5237. [64] 王佳颖,阮邹荣,江波.治疗多发性硬化症药物临床试验现状及展望[J].中国现代应用药学,2022,39(18):2405-2411. [65] HU CL, NYDES M, SHANLEY KL, et al. Reduced expression of the ferroptosis inhibitor glutathione peroxidase-4 in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neurochem. 2019;148(3):426-439. [66] MATROSOVA MS, BRYUKHOV VV, BELSKAYA GN, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping in assessment of inflammation and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2022; 122(12):16-22. [67] KNYSZYŃSKA A, RADECKA A, ZABIELSKA P, et al. The Role of Iron Metabolism in Fatigue, Depression, and Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(18):6818. [68] JHELUM P, SANTOS-NOGUEIRA E, TEO W, et al. Ferroptosis Mediates Cuprizone-Induced Loss of Oligodendrocytes and Demyelination. J Neurosci. 2020;40(48): 9327-9341. [69] STACHOWSKA L, KOZIARSKA D, KARAKIEWICZ B, et al. Hepcidin (rs10421768), Transferrin (rs3811647, rs1049296) and Transferrin Receptor 2 (rs7385804) Gene Polymorphism Might Be Associated with the Origin of Multiple Sclerosis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(11):6875. [70] KUHN S, GRITTI L, CROOKS D, et al. Oligodendrocytes in Development, Myelin Generation and Beyond. Cells. 2019;8(11):1424. [71] ROSKO L, SMITH VN, YAMAZAKI R, et al. Oligodendrocyte Bioenergetics in Health and Disease. Neuroscientist. 2019;25(4):334-343. [72] CEYLAN U, HAUPELTSHOFER S, KÄMPER L, et al. Clozapine Regulates Microglia and Is Effective in Chronic Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:656941. [73] SINTZEL MB, RAMETTA M, REDER AT. Vitamin D and Multiple Sclerosis: A Comprehensive Review. Neurol Ther. 2018; 7(1):59-85. [74] ABBATEMARCO JR, FOX RJ, LI H, et al. Vitamin D and MRI measures in progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019;35:276-282. [75] HAMETNER S, WIMMER I, HAIDER L, et al. Iron and neurodegeneration in the multiple sclerosis brain. Ann Neurol. 2013;74(6): 848-861. [76] ARMON-OMER A, WALDMAN C, SIMAAN N, et al. New Insights on the Nutrition Status and Antioxidant Capacity in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Nutrients. 2019;11(2): 427. [77] 钱海,肖德生.运动对铁吸收的影响及其作用途径[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,286(30):6069-6072. [78] EKKEKAKIS P, PETRUZZELLO SJ. Acute aerobic exercise and affect: current status, problems and prospects regarding dose-response. Sports Med. 1999;28(5):337-374. [79] LIPPI G, SANCHIS-GOMAR F. Epidemiological, biological and clinical update on exercise-induced hemolysis. Ann Transl Med. 2019; 7(12):270. [80] NISHIIE-YANO R, HIRAYAMA S, TAMURA M, et al. Hemolysis Is Responsible for Elevation of Serum Iron Concentration After Regular Exercises in Judo Athletes. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020;197(1):63-69. [81] ISHIBASHI A, MAEDA N, KOJIMA C, et al. Iron Metabolism following Twice a Day Endurance Exercise in Female Long-Distance Runners. Nutrients. 2022;14(9):1907. [82] KAUFMANN CC, WEGBERGER C, TSCHARRE M, et al. Effect of marathon and ultra-marathon on inflammation and iron homeostasis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31(3):542-552. [83] KASPROWICZ K, RATKOWSKI W, WOŁYNIEC W, et al. The Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Hepcidin, Iron, and IL-6 Responses after a 100 km Ultra-Marathon. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(8):2962. [84] MORETTI D, METTLER S, ZEDER C, et al. An intensified training schedule in recreational male runners is associated with increases in erythropoiesis and inflammation and a net reduction in plasma hepcidin. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018;108(6):1324-1333. [85] SUMI D, NAGATSUKA H, MATSUO K, et al. Heat acclimation does not attenuate hepcidin elevation after a single session of endurance exercise under hot condition. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022;122(8):1965-1974. [86] KORTAS J, ZIEMANN E, ANTOSIEWICZ J. Effect of HFE Gene Mutation on Changes in Iron Metabolism Induced by Nordic Walking in Elderly Women. Clin Interv Aging. 2020; 15:663-671. [87] RYAN BJ, FOUG KL, GIOSCIA-RYAN RA, et al. Exercise training decreases whole-body and tissue iron storage in adults with obesity. Exp Physiol. 2021;106(4):820-827. [88] ŻUREK P, LIPIŃSKA P, ANTOSIEWICZ J, et al. Planned Physical Workload in Young Tennis Players Induces Changes in Iron Indicator Levels but Does Not Cause Overreaching. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(6): 3486. [89] BEHZADNEZHAD N, ESFARJANI F, MARANDI SM. Impact of resistance training and basic ferritin on hepcidin, iron status and some inflammatory markers in overweight/obese girls. J Res Med Sci. 2021;26:95. [90] LIU T, WEN Z, SHAO L, et al. ATF4 knockdown in macrophage impairs glycolysis and mediates immune tolerance by targeting HK2 and HIF-1α ubiquitination in sepsis. Clin Immunol. 2023;254:109698. [91] FUJII T, MATSUO T, OKAMURA K. Effects of resistance exercise on iron absorption and balance in iron-deficient rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014;161(1):101-106. [92] NIRENGI S, TANIGUCHI H, ISHIBASHI A, et al. Comparisons Between Serum Levels of Hepcidin and Leptin in Male College-Level Endurance Runners and Sprinters. Front Nutr. 2021;8:657789. [93] MACKAY AD, MARCHANT ED, MUNK DJ, et al. Multitissue analysis of exercise and metformin on doxorubicin-induced iron dysregulation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019;316(5):E922-E930. [94] MOKHTARZADE M, MOLANOURI SHAMSI M, ABOLHASANI M, et al. Home-based exercise training influences gut bacterial levels in multiple sclerosis. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2021;45:101463. [95] YASMEEN F, PIRZADA RH, AHMAD B, et al. Understanding Autoimmunity: Mechanisms, Predisposing Factors, and Cytokine Therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(14):7666. [96] MUSALLAM KM, TAHER AT. Iron deficiency beyond erythropoiesis: should we be concerned? Curr Med Res Opin. 2018;34(1): 81-93. [97] PEREIRA M, CHEN TD, BUANG N, et al. Acute Iron Deprivation Reprograms Human Macrophage Metabolism and Reduces Inflammation In Vivo. Cell Rep. 2019;28(2): 498-511.e5. [98] ODEH D, ORŠOLIĆ N, ADROVIĆ E, et al. Effects of Volatile Anaesthetics and Iron Dextran on Chronic Inflammation and Antioxidant Defense System in Rats. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(4):708. [99] LIU J, ZHANG Y, LI X, et al. Exercise improves mental health status of young adults via attenuating inflammation factors but modalities matter. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:1067890. [100] ASGHAR A, AKHTAR T, BATOOL T, et al. High-fat diet-induced splenic, hepatic, and skeletal muscle architecture damage: cellular and molecular players. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(10):3671-3679. [101] HALADE GV, UPADHYAY G, MARIMUTHU M, et al. Exercise reduces pro-inflammatory lipids and preserves resolution mediators that calibrate macrophage-centric immune metabolism in spleen and heart following obesogenic diet in aging mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024;188:79-89. |
| [1] | 温小龙, 翁锡全, 冯 瑶, 曹文燕, 刘玉倩, 王海涛, . 炎症对2型糖尿病患者血清抗菌多肽及铁代谢相关参数影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [2] | 兰双笠, 向飞帆, 邓光慧, 肖喻琨, 阳运康, 梁 杰. 柚皮苷抑制骨质疏松大鼠骨组织的铁沉积及细胞凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [3] | 刘 璇, 丁雨晴, 夏若寒, 汪献旺, 胡淑娟. 运动防治胰岛素抵抗:Keap1/核因子E2相关因子2信号通路的作用与分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [4] | 樊佳欣, 贾 祥, 徐田杰, 刘凯楠, 郭小玲, 张 辉, 王 茜. 二甲双胍抑制铁死亡改善骨关节炎模型大鼠的软骨损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(30): 6398-6408. |
| [5] | 杨 城, 李玮民, 冉栋成, 许嘉木, 吴王祥, 胥家福, 陈晶晶, 蒋光福, 王春庆. 铁死亡与骨质疏松症[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(3): 554-562. |
| [6] | 张绵钰, 韩 杰, 曾 浩, 陈相汕, 高振罡. 中药调控成骨细胞铁死亡治疗激素性股骨头坏死[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(1): 185-192. |
| [7] | 姚 婷, 官蓉威, 高 原. SMAD4过表达干预骨质疏松大鼠铁代谢相关蛋白的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(23): 3648-3653. |
| [8] | 曾嘉旭, 何 琪, 陈柏豪, 黎 淼, 黎少聪, 杨均政, 潘兆丰, 王海彬. 以“血瘀”理论指导治疗:解读膝骨关节炎“铁超载”的相关机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(11): 1743-1748. |
| [9] | 农复香, 蒋志雄, 李英豪, 许文聪, 施智兰, 罗 慧, 张晴朗, 钟 爽, 唐梅文. 外泌体调控铁死亡在疾病诊断治疗中的应用与作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [10] | 范 筱, 陶经纬, 蒋昇源, 邓博文, 穆晓红. 川芎嗪对大鼠脊髓损伤后铁代谢的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(22): 3561-3566. |
| [11] | 农复香, 蒋志雄, 李英豪, 许文聪, 施智兰, 罗 慧, 张晴朗, 钟 爽, 唐梅文. 外泌体调控铁死亡在疾病诊断治疗中的应用与作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(15): 2443-2452. |
| [12] | 凡勇福, 苏凯奇, 袁 洁, 聂晨晨, 阮晓迪, 段昭远, 冯晓东. 铁代谢与缺血性脑卒中[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(32): 5223-5228. |
| [13] | 段昭远, 吴明莉, 罗 萌, 高 静, 李瑞青, 冯晓东. 脊髓损伤后神经元铁死亡:谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4的调控[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(12): 1956-1962. |
| [14] | 朱 蕊, 曾 庆, 黄国志. 铁死亡与脑卒中[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(23): 3734-3739. |
铁是细胞免疫功能的关键,可以促进细胞因子的合成与细胞毒性的识别和清除,而由于铁缺乏与过量均对健康有着不利影响,正常人体内总铁量被严格维持在4.0-5.0 g的范围内,维持正常的铁代谢[3-4]。当铁代谢紊乱时,体内过量的铁会引发促炎症细胞因子释放,使得免疫调节机制被破坏,已有大量研究表明铁代谢在免疫性炎症疾病中有着重要作用。
近年来,运动干预作为一种有效的非药物治疗手段,逐渐引起了学术界的广泛关注。研究表明,运动通过调节体内铁代谢,对免疫系统产生重要影响[5]。运动会影响铁的吸收、分配和储存,这不仅支持免疫细胞的正常功能,还能通过优化铁的利用产生抗炎作用,改善免疫反应[6-7]。然而,运动如何通过影响铁代谢发挥抗炎作用的机制仍不完全明了。
因而,此次综述旨在回顾和总结铁代谢在免疫性炎症疾病中的作用及运动干预对铁代谢的影响,探索运动在治疗免疫性炎症疾病中的潜力,并为未来的研究提供新思路;分析铁代谢与免疫性炎症之间的关系,同时梳理总结不同运动类型对铁代谢的影响,探寻运动干预铁代谢对免疫性炎症产生影响的可能通路,以期为未来免疫性炎症疾病的治疗提供新的思路与方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024-04-01/06-30进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 2010年1月至2024年6月发表的相关文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索途径 中文检索词为“铁代谢,铁稳态,铁调素,免疫性炎症,类风湿性关节炎,炎症性肠病,多发性硬化症,系统性红斑狼疮,运动”;英文检索词为“iron metabolism, iron homeostasis,hepcidin,immune inflammation,rheumatoid arthritis(RA),inflammatory bowel disease(IBD),multiple Sclerosis(MS),systemic lupus erythematosus(SLE),exercise”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、述评、博士学位论文。
1.1.6 检索策略 PubMed数据库检索策略见图1。
1.2 入选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①论点、论据可靠,论证过程清晰,文章结构完整的文献;②铁代谢与免疫性炎症疾病的相关研究;③运动与铁代谢的相关研究;④运动干预铁代谢对免疫性炎症疾病的相关研究。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①排除与研究主题无关或重复的文献;②排除文章结构残缺、缺乏可信性的文献。
1.3 质量评估与数据提取流程 通过对初步检索的文献进行标题、摘要及关键词阅读分析,根据入选标准进行提取与排除,查阅全文共保留101篇文献进行综述。文献检索筛选流程见图2。
然而,尽管铁代谢与免疫性炎症疾病的关系已得到一定程度的确认,现有研究仍面临一些关键问题:首先,铁在免疫细胞中的作用机制尚不明确,尤其是铁在不同免疫细胞类型中的功能差异以及如何在不同免疫微环境下调节免疫反应,仍然是亟待解决的问题;其次,尽管有一些研究提出通过运动干预调节铁代谢的潜力,但如何系统性地理解运动对铁代谢的具体影响,以及运动干预在不同免疫性炎症疾病中的作用机制,仍然缺乏足够的证据;最后,现有的研究大多集中于短期效果,缺乏关于长期运动干预对免疫性炎症疾病患者铁代谢调控的深入研究。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人之篇的特点 此次综述的独特性在于对铁代谢在免疫性炎症疾病中作用的全面整合与分析,同时强调了运动干预对铁代谢的潜在影响,并结合铁代谢对免疫细胞功能的调节,探讨了运动与铁代谢之间的相互关系。相较于以往研究,此次综述不仅仅集中于单一的铁代谢调控机制,而是多角度、系统性地分析了运动如何通过恢复铁稳态,减轻免疫性炎症反应。此外,此次综述在整合现有研究的基础上,提出了运动干预对免疫性炎症疾病的双重作用机制:短期运动虽可能导致铁代谢暂时紊乱,但长期规律的运动可显著改善铁稳态并减轻炎症反应,这一观点为运动干预策略的制定提供了新的思路。同时,此次综述结合了多种免疫性疾病的研究进展,避免了局限于某一特定疾病领域的狭隘视角,进一步提升了研究的广度和深度。
3.3 综述的局限性 此次综述在现有文献的基础上提供了铁代谢与免疫性炎症疾病关系的较为全面的分析,并探讨了运动干预对铁代谢的调节作用,但仍存在一些局限性:首先,现有的研究大多为小样本量或动物实验,缺乏大规模、长期临床研究数据来进一步验证运动干预在免疫性炎症疾病患者中的实际效果;关于运动干预如何具体影响铁代谢的分子机制尚不明确,现有的研究大多局限于描述铁代谢的变化,缺乏对细胞信号通路及基因表达的深入分析;此外,尽管此次综述强调了不同类型运动对铁代谢的不同影响,但对于不同个体的运动反应差异、运动方案的个性化调整等问题,现有文献仍缺乏深入的讨论。
3.4 综述的重要意义 此次综述的重要意义在于为免疫性炎症疾病的治疗提供了新的研究方向。铁代谢的紊乱在免疫性疾病的发生和发展中发挥着关键作用,而运动干预作为一种非药物治疗手段,通过调节铁代谢来改善免疫反应,已显示出显著的潜力。通过此次综述,研究人员和临床医生可以更全面地了解运动如何通过铁代谢发挥抗炎作用,从而为免疫性炎症疾病的治疗提供更加个性化的治疗方案。此外,此次综述还突出了铁代谢与免疫系统相互作用的复杂性,为未来进一步探索铁代谢在免疫性疾病中的分子机制提供了基础。此外,随着全球免疫性炎症疾病患者数量的增加,传统药物治疗可能面临不良反应及药物耐药性等问题,运动干预作为一种低成本、低不良反应的治疗手段,为临床提供了新的希望。因而,此次综述不仅具有学术价值,也为公共卫生领域提供了具有实际应用潜力的研究思路。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 针对目前的研究进展和存在的问题,课题专家组提出以下几点建议:①关于运动干预对铁代谢的作用主要集中于动物实验和短期临床观察,未来需要通过多中心、大样本的临床研究,验证不同运动类型、强度和周期对免疫性炎症疾病患者铁代谢的具体影响。②对于运动如何在分子层面上调节免疫细胞功能,尤其是免疫细胞内铁的代谢通路及其与炎症反应的关系,仍然缺乏深入研究。未来可以通过高通量基因组学、蛋白质组学等技术,进一步揭示运动对免疫细胞铁代谢的具体调控机制。③未来的研究需要探索如何根据个体的免疫状态、铁代谢特征等因素,制定个性化的运动干预方案,以达到最佳的治疗效果。④除了运动干预外,合理的饮食、药物治疗等手段的结合使用可能对铁代谢的调节及免疫性炎症疾病的治疗产生协同效应。未来的研究应关注多种干预手段联合使用的潜力,探索更为综合的治疗策略。⑤运动的长期效应和对免疫性疾病的持续影响仍需进一步探索。同时,运动对患者的安全性、耐受性等方面的影响也应纳入未来研究的重点。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
特点:文章详细阐述了铁代谢在免疫性炎症疾病中的复杂作用,涵盖多种疾病类型,深入分析了不同运动形式对铁代谢的影响,从急性运动到长期运动,从有氧运动到无氧运动,全面细致。同时,将运动与铁代谢、免疫性炎症疾病紧密联系,多角度论证三者之间的相互关系,逻辑严谨,层次分明。
意义:为免疫性炎症疾病的研究与治疗开辟了新路径。在理论层面,文章整合了大量前沿研究成果,丰富了运动、铁代谢与免疫性炎症疾病关系的理论体系,加深了人们对免疫性炎症疾病发病机制的理解。在实践方面,为临床治疗提供了非药物干预的新思路,运动作为一种低成本、低副作用的干预方式,能够改善患者的病情,提高生活质量,并为相关领域研究提供借鉴。
创新点:创新性地提出运动干预对免疫性炎症疾病的双重作用机制,为运动干预策略的制定提供了新的理论依据。此外,突破了以往单一研究铁代谢或运动对疾病影响的局限,将运动、铁代谢和免疫性炎症疾病三者有机结合,进行系统性研究,拓展了研究视野,提升了研究的深度与广度,为后续相关研究提供了全新的视角和思路。#br# 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||