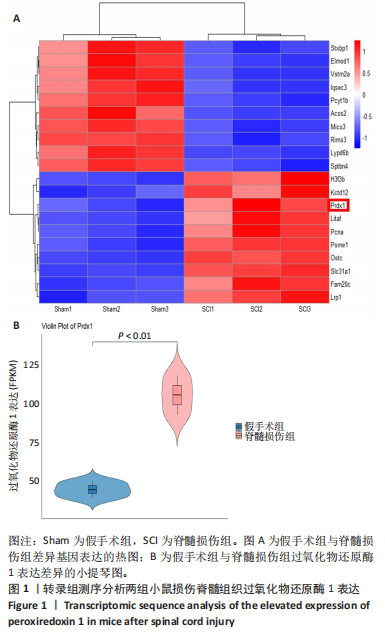
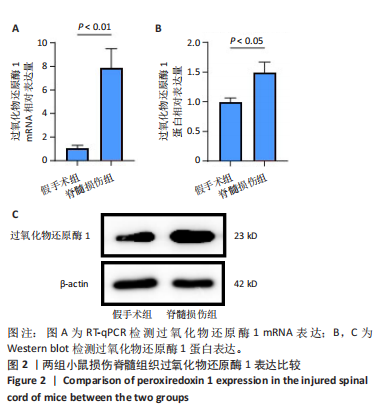
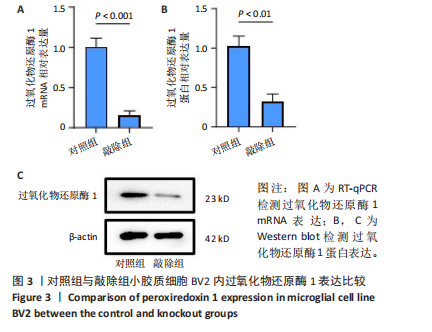
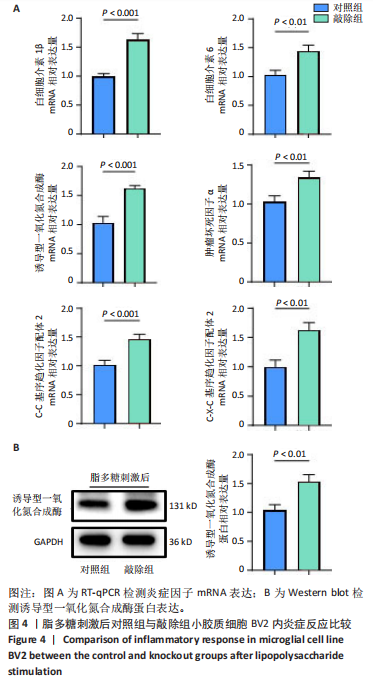
[1] WARNER FM, CRAGG JJ, JUTZELER CR, et al. Progression of Neuropathic Pain after Acute Spinal Cord Injury: A Meta-Analysis and Framework for Clinical Trials. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(9):1461-1468.
[2] KATHE C, SKINNIDER MA, HUTSON TH, et al. The neurons that restore walking after paralysis. Nature. 2022;611(7936):540-547.
[3] RIVERS CS, FALLAH N, NOONAN VK, et al. Health Conditions: Effect on Function, Health-Related Quality of Life, and Life Satisfaction After Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. A Prospective Observational Registry Cohort Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018;99(3):443-451.
[4] BADHIWALA JH, WILSON JR, FEHLINGS MG. Global burden of traumatic brain and spinal cord injury. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1):24-25.
[5] DIOP M, EPSTEIN D. A Systematic Review of the Impact of Spinal Cord Injury on Costs and Health-Related Quality of Life. Pharmacoecon Open. 2024;8(6):793-808.
[6] FREYERMUTH-TRUJILLO X, SEGURA-URIBE JJ, SALGADO-CEBALLOS H, et al. Inflammation: A Target for Treatment in Spinal Cord Injury. Cells. 2022;11(17):2692.
[7] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3(1):17018.
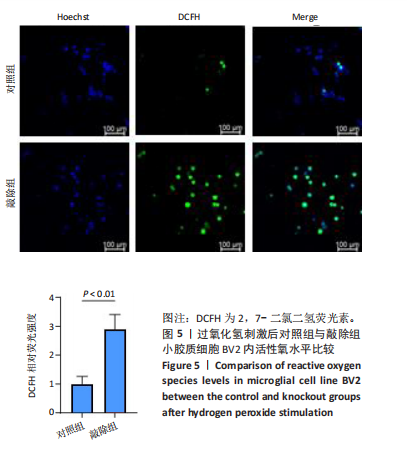
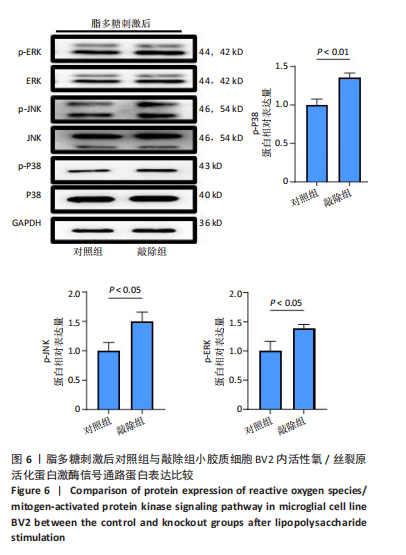
[8] 史旭,李瑞语,张兵,等.小胶质细胞极化介导炎症反应在脊髓损伤中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(1):121-129.
[9] JEONG SJ, CHO MJ, KO NY, et al. Deficiency of peroxiredoxin 2 exacerbates angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic aneurysm. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52(9):1587-1601.
[10] RHEE SG, KANG SW, JEONG W, et al. Intracellular messenger function of hydrogen peroxide and its regulation by peroxiredoxins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17(2):183-189.
[11] PARK JG, YOO JY, JEONG SJ, et al. Peroxiredoxin 2 deficiency exacerbates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circ Res. 2011; 109(7):739-749.
[12] MORIWAKI T, YOSHIMURA A, TAMARI Y, et al. PRDX1 is essential for the viability and maintenance of reactive oxygen species in chicken DT40. Genes Environ. 2021;43(1):35.
[13] GUAN X, RUAN Y, CHE X, et al. Dual role of PRDX1 in redox-regulation and tumorigenesis: Past and future. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024;210: 120-129.
[14] HAN YH, LIAN XD, LEE SJ, et al. Regulatory effect of peroxiredoxin 1 (PRDX1) on doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in triple negative breast cancer cells. Appl Biol Chem. 2022;65(1):63.
[15] LIU CH, KUO SW, HSU LM, et al. Peroxiredoxin 1 induces inflammatory cytokine response and predicts outcome of cardiogenic shock patients necessitating extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: an observational cohort study and translational approach. J Transl Med. 2016;14(1):114.
[16] SZELIGA M. Peroxiredoxins in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(12):1203.
[17] KIM S, LEE W, JO H, et al. The antioxidant enzyme Peroxiredoxin-1 controls stroke-associated microglia against acute ischemic stroke. Redox Biol. 2022;54:102347.
[18] ZHANG C, SHAO Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Therapeutic application of nicotinamide: As a potential target for inhibiting fibrotic scar formation following spinal cord injury. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024;30(7):e14826.
[19] XUE MT, SHENG WJ, SONG X, et al. Atractylenolide III ameliorates spinal cord injury in rats by modulating microglial/macrophage polarization. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28(7):1059-1071.
[20] LI C, ZHAO Z, LUO Y, et al. Macrophage-Disguised Manganese Dioxide Nanoparticles for Neuroprotection by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Modulating Inflammatory Microenvironment in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(20):e2101526.
[21] LIU J, WEI Y, JIA W, et al. Chenodeoxycholic acid suppresses AML progression through promoting lipid peroxidation via ROS/p38 MAPK/DGAT1 pathway and inhibiting M2 macrophage polarization. Redox Biol. 2022;56:102452.
[22] CHEN HR, SUN Y, MITTLER G, et al. MOF-mediated PRDX1 acetylation regulates inflammatory macrophage activation. Cell Rep. 2024;43(9): 114682.
[23] FAKHRI S, ABBASZADEH F, MORADI SZ, et al. Effects of Polyphenols on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Interconnected Pathways during Spinal Cord Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:8100195.
[24] MAO XY, ZHOU HH, JIN WL. Redox-Related Neuronal Death and Crosstalk as Drug Targets: Focus on Epilepsy. Front Neurosci. 2019;13: 512.
[25] HASSANZADEH K, RAHIMMI A. Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in the story of Parkinson’s disease: Could targeting these pathways write a good ending? J Cell Physiol. 2018;234(1):23-32.
[26] SOLLEIRO-VILLAVICENCIO H, RIVAS-ARANCIBIA S. Effect of Chronic Oxidative Stress on Neuroinflammatory Response Mediated by CD4(+)T Cells in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:114.
[27] LIU Z, REN Z, ZHANG J, et al. Role of ROS and Nutritional Antioxidants in Human Diseases. Front Physiol. 2018;9:477.
[28] SKINNIDER MA, GAUTIER M, TEO AYY, et al. Single-cell and spatial atlases of spinal cord injury in the Tabulae Paralytica. Nature. 2024; 631(8019):150-163.
[29] LI C, WU Z, ZHOU L, et al. Temporal and spatial cellular and molecular pathological alterations with single-cell resolution in the adult spinal cord after injury. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):65.
[30] ROJO AI, MCBEAN G, CINDRIC M, et al. Redox control of microglial function: molecular mechanisms and functional significance. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;21(12):1766-1801.
[31] JORDÃO MJC, SANKOWSKI R, BRENDECKE SM, et al. Single-cell profiling identifies myeloid cell subsets with distinct fates during neuroinflammation. Science. 2019;363(6425):eaat7554.
[32] MENDIOLA AS, RYU JK, BARDEHLE S, et al. Transcriptional profiling and therapeutic targeting of oxidative stress in neuroinflammation. Nat Immunol. 2020;21(5):513-524.
[33] YANG GQ, HUANG JC, YUAN JJ, et al. Prdx1 Reduces Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Induced Brain Injury via Targeting Inflammation- and Apoptosis-Related mRNA Stability. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:181.
[34] ATTARAN S, SKOKO JJ, HOPKINS BL, et al. Peroxiredoxin-1 Tyr194 phosphorylation regulates LOX-dependent extracellular matrix remodelling in breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 2021;125(8):1146-1157.
[35] LU Y, ZHANG XS, ZHOU XM, et al. Peroxiredoxin 1/2 protects brain against H2O2-induced apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage. FASEB J. 2019;33(2):3051-3062.
[36] SHICHITA T, HASEGAWA E, KIMURA A, et al. Peroxiredoxin family proteins are key initiators of post-ischemic inflammation in the brain. Nat Med. 2012;18(6):911-917.
[37] LIU CH, KUO SW, HSU LM, et al. Peroxiredoxin 1 induces inflammatory cytokine response and predicts outcome of cardiogenic shock patients necessitating extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: an observational cohort study and translational approach. J Transl Med. 2016;14(1):114.
[38] KANG JH, LEE HY, KIM NY, et al. Extracellular Prdx1 mediates bacterial infection and inflammatory bone diseases. Life Sci. 2023;333:122140.
[39] MORETTON A, KOURTIS S, GAÑEZ ZAPATER A, et al. A metabolic map of the DNA damage response identifies PRDX1 in the control of nuclear ROS scavenging and aspartate availability. Mol Syst Biol. 2023;19(7):e11267.
|