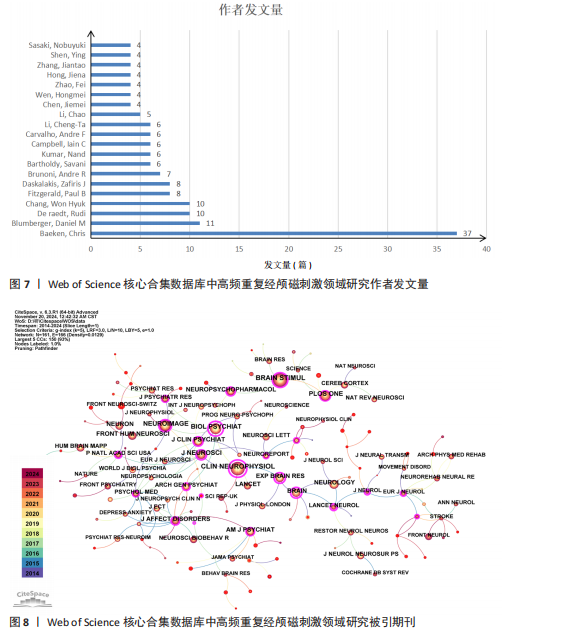
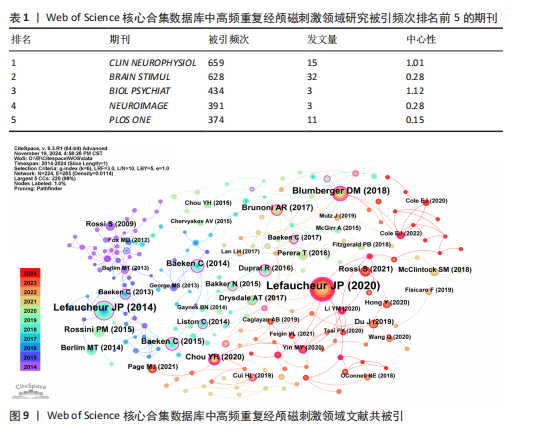
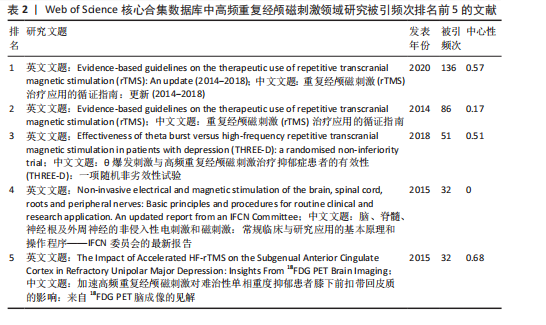
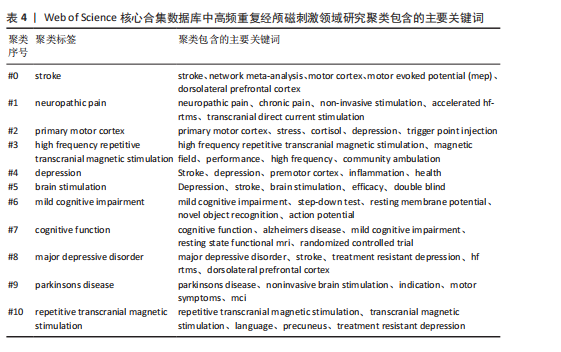
[1] BARKER AT, JALINOUS R, FREESTON IL. Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet. 1985;1(8437):1106-1107.
[2] HALLETT M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: a primer. Neuron. 2007;55(2): 187-199.
[3] CAPPON D, DEN BOER T, JORDAN C, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) for geriatric depression. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;74:101531.
[4] SHENG R, CHEN C, CHEN H, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for stroke rehabilitation: insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms of neuroinflammation. Front Immunol. 2023; 14:1197422.
[5] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ALEMAN A, BAEKEN C, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): An update (2014-2018). Clinical Neurophysiol. 2020; 131(2):474-528.
[6] 唐莺莹,吴毅,王继军.重复经颅磁刺激的临床应用与操作规范上海专家共识[J].上海医学,2022,45(2):65-70.
[7] 陈静,张长国,张红波,等.高频与低频重复经颅磁刺激治疗帕金森病的临床观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(5): 464-467.
[8] KIM SY, SHIN SB, LEE SJ, et al. Factors Associated With Upper Extremity Functional Recovery Following Low-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Stroke Patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(3):373-382.
[9] MOHAMAD SAFIAI NI, MOHAMAD NA, BASRI H, et al. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation at dorsolateral prefrontal cortex for migraine prevention: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cephalalgia. 2022;42(10): 1071-1085.
[10] SHIM J, LEE S. Effects of High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Combined with Motor Learning on Motor Function and Grip Force of the Upper Limbs and Activities of Daily Living in Patients with a Subacute Stroke. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(12):6093.
[11] WEI L, ZHANG Y, WANG J, et al. Parietal-hippocampal rTMS improves cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease and increases dynamic functional connectivity of default mode network. Psychiatry Res. 2022;315:114721.
[12] CHEN CM. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol. 2006;57(3):359-377.
[13] ZHONG D, LI Y, HUANG Y, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Exercise on Cancer: A Bibliometrics Study and Visualization Analysis via CiteSpace. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:797902.
[14] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):5303-5310.
[15] LIU F, CHEN N, WANG R, et al. Visual analysis of allergic rhinitis in children based on web of science and CiteSpace software. Front Pediatr. 2022;10:911293.
[16] DING X, YANG Z. Knowledge mapping of platform research: a visual analysis using VOSviewer and CiteSpace. Electron. Commer. 2022;22(3):787-809.
[17] ZHOU Y, HU Z, YUAN H, et al. CiteSpace-based visual analysis of hypothermia studies in surgical patients. Nursing Open. 2023;10(9):6228-6236.
[18] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ANDRÉ-OBADIA N, ANTAL A, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;125(11):2150-2206.
[19] BAEKEN C, MARINAZZO D, EVERAERT H,
et al. The Impact of Accelerated HF-rTMS on the Subgenual Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Refractory Unipolar Major Depression: Insights From <SUP>18</SUP>FDG PET Brain Imaging. Brain Stimul. 2015;8(4):808-815.
[20] BLUMBERGER DM, VILA-RODRIGUEZ F, THORPE KE, et al. Effectiveness of theta burst versus high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with depression (THREE-D): a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2018;391(10131):1683-1692.
[21] 高明波,韩婷.基于Web of Science的生酮饮食与肠道菌群研究文献计量学分析[J].中国微生态学杂志,2023,35(11):1257-1264+1271.
[22] 闫伟娜.我国科普期刊研究的进展、热点与趋势:基于CiteSpace知识图谱的可视化分析[J].中国科技期刊研究,2024, 35(2):163-170.
[23] SCHRIJVERS DL, BAEKEN C, DE RAEDT R,et al. The Impact of High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Fine Motor Functions in Medication-Resistant Major Depression. Neuropsychobiology. 2012;66(4):252-258.
[24] WU GR, BAEKEN C. Exploring potential working mechanisms of accelerated HF-rTMS in refractory major depression with a focus on locus coeruleus connectivity. Eur Psychiatry. 2024;67(1):e70.
[25] CHEN JM, ZHAO F, HONG JN, et al. Effect of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on swallowing function and pneumonia in poststroke dysphagia in rats. Brain Res. 2024;1832:148846.
[26] ZHAO F, CHEN JM, SHAN YL, et al. Comprehensive assessment of HF-rTMS treatment mechanism for post-stroke dysphagia in rats by integration of fecal metabolomics and 16S rRNA sequencing. Front Cell Infect. 2024;14:8846.
[27] FITZGERALD PB, DASKALAKIS ZJ. A practical guide to the use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of depression. Brain Stimul. 2012;5(3):287-296.
[28] SCHUTTER DJ. Antidepressant efficacy of high-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in double-blind sham-controlled designs: a meta-analysis. Psychol Med, 2009;39(1):65-75.
[29] 姜霖霖,牛陵川,王愉乐,等.高频重复经颅磁刺激对脑梗死后抑郁患者的影响[J].康复学报,2021,31(6):455-460.
[30] 王铭琛,李作伟.高频重复经颅磁刺激治疗脑卒中后抑郁的Meta分析[J].中医临床研究,2024,16(9):22-27.
[31] CAULFIELD KA, FLEISCHMANN HH, GEORGE MS, et al. A transdiagnostic review of safety, efficacy, and parameter space in accelerated transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;152:384-396.
[32] BAEKEN C, LEFAUCHEUR JP, VAN SCHUERBEEK P. The impact of accelerated high frequency rTMS on brain neurochemicals in treatment-resistant depression: Insights from (1)H MR spectroscopy. J Clin Neurosci. 2017; 128(9):1664-1672.
[33] MURASE N, DUQUE J, MAZZOCCHIO R, et al. Influence of interhemispheric interactions on motor function in chronic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2004;55(3):400-409.
[34] WANG Q, ZHANG D, ZHAO YY, et al. Effects of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the contralesional motor cortex on motor recovery in severe hemiplegic stroke: A randomized clinical trial. Brain Stimul. 2020;13(4):979-986.
[35] DI PINO G, PELLEGRINO G, ASSENZA G, et al. Modulation of brain plasticity in stroke: a novel model for neurorehabilitation. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10(10):597-608.
[36] BUETEFISCH CM. Role of the Contralesional Hemisphere in Post-Stroke Recovery of Upper Extremity Motor Function. Front Neurol. 2015;6:214.
[37] HARRINGTON RM, CHAN E, ROUNDS AK, et al. Roles of Lesioned and Nonlesioned Hemispheres in Reaching Performance Poststroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2020;34(1):61-71.
[38] 高飞,张玉阁,马琳,等.健侧半球高频重复经颅磁刺激对左侧大面积脑梗死后完全性失语的效果观察[J].华西医学, 2024,39(10):1625-1630.
[39] KOMATSU T, HADA T, SASAKI N, et al. Effects and safety of high-frequency rTMS in subacute ischemic stroke patients. J Neurol Sci. 2024;462:123069.
[40] LIU L, DING M, WU J F, et al. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation promotes ipsilesional functional hyperemia and motor recovery in mice with ischemic stroke. Cerebral Cortex. 2024; 34(3):bhae074.
[41] LUO J, FENG Y, HONG Z, et al. High-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation promotes neural stem cell proliferation after ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1772-1780.
[42] DU J, YANG F, HU J, et al. Effects of high- and low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on motor recovery in early stroke patients: Evidence from a randomized controlled trial with clinical, neurophysiological and functional imaging assessments. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;21: 101620.
[43] GUO Z, JIN Y, BAI X, et al. Distinction of High- and Low-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on the Functional Reorganization of the Motor Network in Stroke Patients. Neural Plast. 2021;2021:8873221.
[44] ANDRÉ-OBADIA N, MAGNIN M, GARCIA-LARREA L. Theta-burst versus 20 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in neuropathic pain: A head-to-head comparison. J Clin Neurosci. 2021;132(10): 2702-2710.
[45] DIAO Y, XIE Y, PAN J, et al. The Effectiveness of High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Patients with Neuropathic Orofacial Pain: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Neural Plast. 2022;2022:6131696.
[46] JIN Y, XING G, LI G, et al. High Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Therapy For Chronic Neuropathic Pain: A Meta-analysis. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6): E1029-1046.
[47] MYLIUS V, AYACHE SS, TEEPKER M, et al. [Transcranial magnetic stimulation and motor cortex stimulation in neuropathic pain]. Schmerz (Berlin, Germany). 2012; 26(6):655-660.
[48] QUESADA C, POMMIER B, FAUCHON C, et al. New procedure of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for central neuropathic pain: a placebo-controlled randomized crossover study. Pain. 2020;161(4):718-728.
[49] TSAI YY, WU WT, HAN DS, et al. Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review. Life (Basel, Switzerland). 2023;13(2):0258.
[50] YOKOE M, MANO T, MARUO T, et al. The optimal stimulation site for high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: A double-blind crossover pilot study. J Clin Neurosci. 2018; 47:72-78.
[51] KANG X, ZHANG B, DU W, et al. High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Regulates Astrocyte Activation by Modulating the Endocannabinoid System in Parkinson’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(8):5121-5134.
[52] PAPALLO S, DI NARDO F, SICILIANO M, et al. Functional Connectome Controllability in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment after Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. J Clin Med. 2024;13(18):5763.
[53] YUAN L Q, ZENG Q, WANG D, et al. Neuroimaging mechanisms of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for treatment of amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a double-blind randomized sham-controlled trial. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(4):707-713.
[54] WANG T, GUO Z, WU H, et al. High-Frequency rTMS Could Improve Impaired Memory in Mild Cognitive Impairment Patients in China: A Randomized Controlled Study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2023; 37(4):296-302.
|