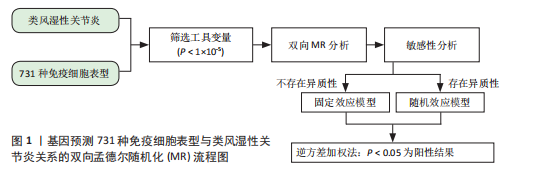
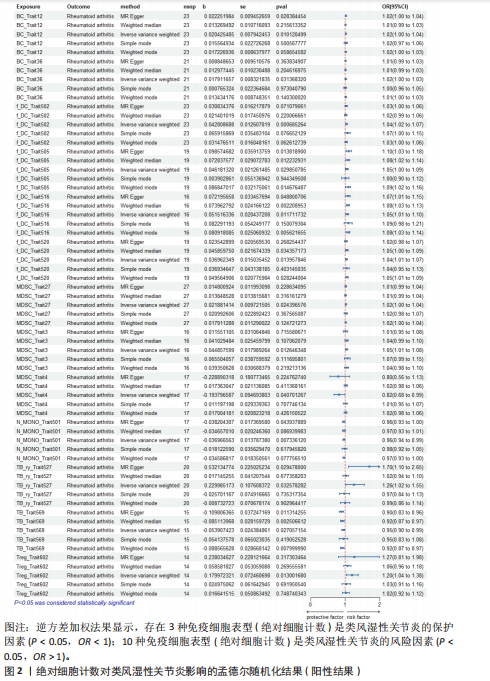
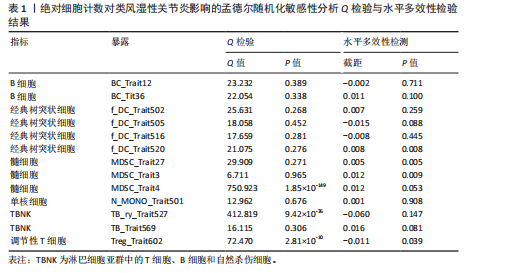
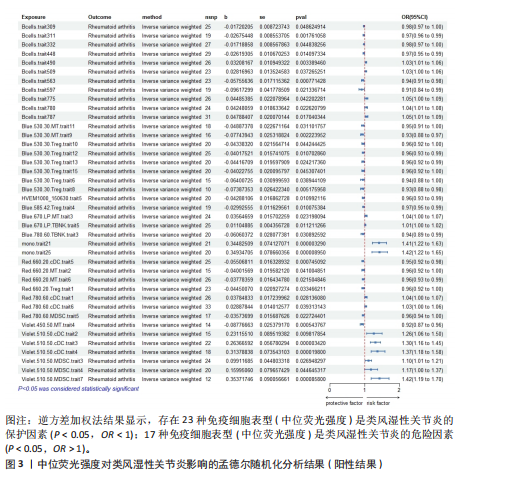
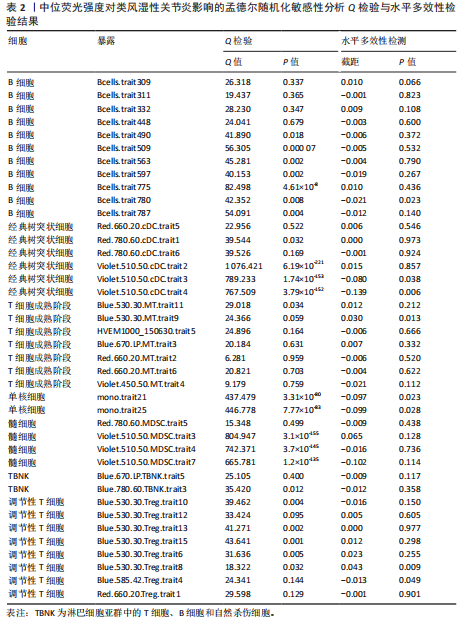
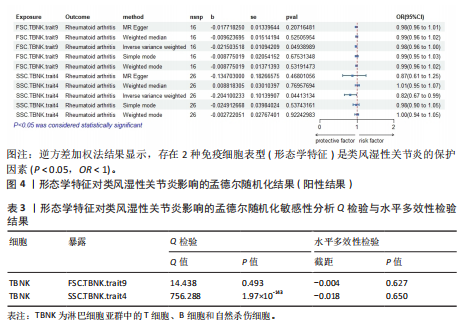
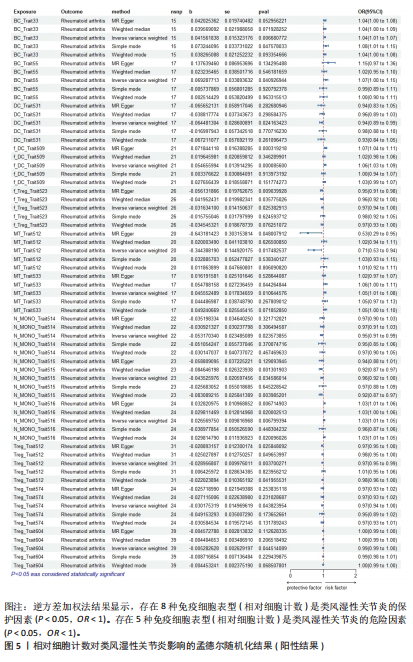
[1] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, MCINNES IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet(London, England). 2016;388(10055):2023-2038.
[2] HUANG J, FU X, CHEN X, et al. Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:686155.
[3] SMITH MH, BERMAN JR. What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? JAMA. 2022; 327(12):1194.
[4] DERKSEN VFAM, HUIZINGA TWJ, VAN DER WOUDE D. The role of autoantibodies in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 2017;39(4): 437-446.
[5] VAN DELFT MAM, HUIZINGA TWJ. An overview of autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102392.
[6] HU H, LUAN L, YANG K, et al. Burden of rheumatoid arthritis from a societal perspective: A prevalence-based study on cost of this illness for patients in China. Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(2):e13028.
[7] VENETSANOPOULOU AI, ALAMANOS Y, VOULGARI PV, et al. Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis: genetic and environmental influences. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2022;18(9):923-931.
[8] EDILOVA MI, AKRAM A, ABDUL-SATER AA. Innate immunity drives pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed J. 2021;44(2): 172-182.
[9] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2): 905.
[10] BROCK J, BASU N, SCHLACHETZKI JCM, et al. Immune mechanisms of depression in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19(12):790-804.
[11] KAUR J, CAIRNS E, BARRA L. Restoring Balance: Immune Tolerance in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2023;50(8): 991-1001.
[12] SHUAI Z, ZHENG S, WANG K, et al. Reestablish immune tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022; 13:1012868.
[13] O’NEIL LJ, KAPLAN MJ. Neutrophils in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Breaking Immune Tolerance and Fue ling Disease. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25(3):215-227.
[14] GORONZY JJ, SHAO L, WEYAND CM. Immune aging and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2010;36(2):297-310.
[15] TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology in 2014: Two-faced immunology-from osteogenesis to bon e resorption. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(2):74-76.
[16] DENG Z, ZHANG Q, ZHAO Z, et al. Crosstalk between immune cells and bone cells or chondrocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021; 101(Pt A):108179.
[17] SEIFRITZ T, BRUNNER M, CAMARILLO RETAMOSA E, et al. BRD3 Regulates the Inflammatory and Stress Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. Biomedicines. 2023;11(12):3188.
[18] FILIPPIN LI, VERCELINO R, MARRONI NP, et al. Redox signalling and the inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;152(3):415-422.
[19] CUPPEN BVJ, FU J, VAN WIETMARSCHEN HA, et al. Exploring the Inflammatory Metabolomic Profile to Predict Response to TNF-α Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PloS one. 2016;11(9):e0163087.
[20] ATZENI F, ANTIVALLE M, PALLAVICINI FB, et al. Predicting response to anti-TNF treatment in rheumatoid arthritis pati ents. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8(5):431-437.
[21] SANDERSON E, GLYMOUR MM, HOLMES MV, et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2022;2:6.
[22] LI W, XU JW, CHAI JL, et al. Complex causal association between genetically predicted 731 immunocyte phenotype and osteonecrosis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Int J Surg. 2024;110(6):3285-3293.
[23] ORRÙ V, STERI M, SIDORE C, et al. Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and i nform therapy. Nat Genet. 2020;52(10):1036-1045.
[24] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023;613(7944):508-518.
[25] LI W, CHAI JL, LI Z, et al. No evidence of genetic causality between diabetes and osteonecrosis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):970.
[26] MACHIELA MJ, CHANOCK SJ. LDlink: a web-based application for exploring population-specific haplotype structure and linking correlated alleles of possible functional variants. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(21):3555-3557.
[27] MORGAN SL. Counterfactuals, Causal Effect Heterogeneity, and the Catholic School Effect on Learning. Sociol Educ. 2001;74(4):341-374.
[28] 许崇彦, 叶晨, 陈洋丽, 等. 基于孟德尔随机化探讨免疫细胞与散发型克雅氏病的因果关系[J]. 生物医学,2024,14(4): 624-636.
[29] MEYER A, PARMAR PJ, SHAHRARA S. Significance of IL-7 and IL-7R in RA and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2022; 21(7):103120.
[30] GORONZY JJ, ZETTL A, WEYAND CM. T cell receptor repertoire in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Rev Immunol. 1998;17(5-6):339-363.
[31] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2): 905.
[32] RAO DA, GURISH MF, MARSHALL JL, et al. Pathologically expanded peripheral T helper cell subset drives B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2017;542(7639):110-114.
[33] GAO Y, CAI W, ZHOU Y, et al. Immunosenescence of T cells: a key player in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res. 2022; 71(12):1449-1462.
[34] KOTSCHENREUTHER K, YAN S, KOFLER DM. Migration and homeostasis of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:947636.
[35] DELGADO-ARÉVALO C, CALVET-MIRABENT M, TRIGUERO-MARTINEZ A, et al. POS0367 NLRC4 and FC-γ-R crosstalk on cd1c+ dendritic cells differentially contributes to rheumatoid arthritis immunopathology. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:413.
[36] WANG Z, ZHANG J, AN F, et al. The mechanism of dendritic cell-T cell crosstalk in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):193.
[37] TAI Y, WANG Q, KORNER H, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of T Cells Activation by Dendritic Cells in Autoimmune Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:642.
[38] YU MB, LANGRIDGE WHR. The function of myeloid dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37(7): 1043-1051.
[39] SINGH A, BEHL T, SEHGAL A, et al. Mechanistic insights into the role of B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;99:108078.
[40] WU F, GAO J, KANG J, et al. B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Treatment Prospects. Front Immunol. 2021;12:750753.
[41] KARMAKAR U, VERMEREN S. Crosstalk between B cells and neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunology. 2021; 164(4):689-700.
[42] XIE Y, DING J, GAO J, et al. Triptolide reduces PD-L1 through the EGFR and IFN-γ/IRF1 dual signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;118:109993.
|