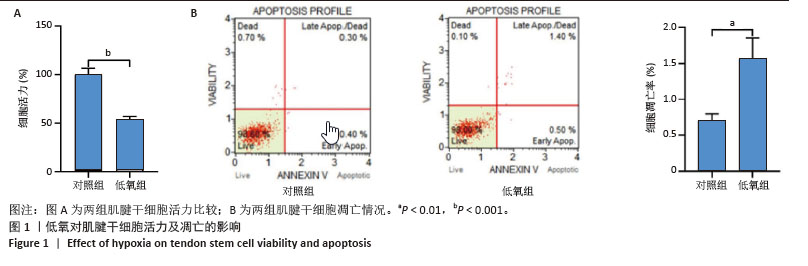
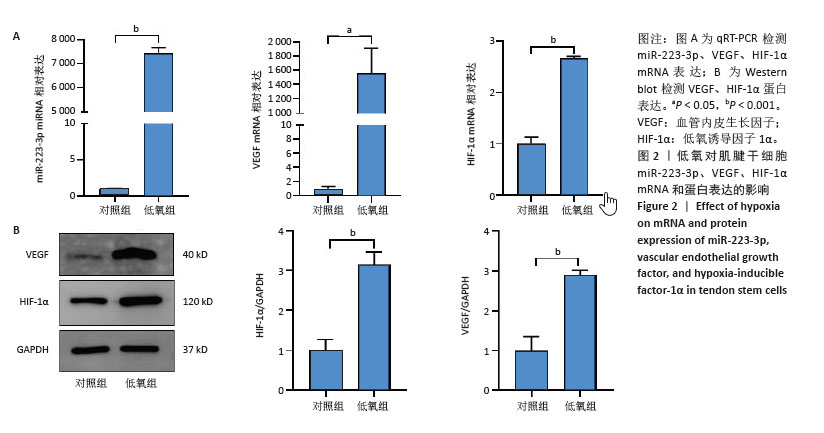
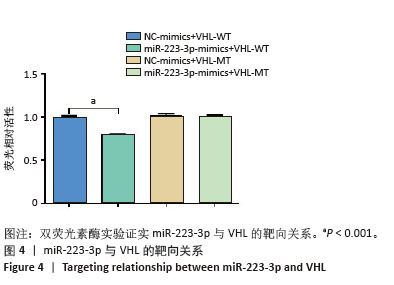
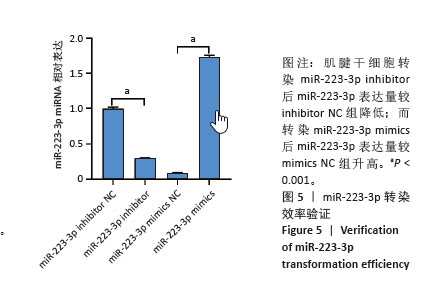
[1] TANG C, WANG Z, XIE Y, et al. Classification of distinct tendinopathy subtypes for precision therapeutics. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):9460.
[2] PRAKASH N, KIM J, JEON J, et al. Progress and emerging techniques for biomaterial-based derivation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs). Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):31.
[3] HE Y, LU S, CHEN W, et al. Exosomes derived from tendon stem/progenitor cells enhance tendon-bone interface healing after rotator cuff repair in a rat model. Bioact Mater. 2024;40:484-502.
[4] 逯静薇,吕可馨,蒋莉,等.影响肌腱干细胞分化的因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(13):2098-2104.
[5] CAI Z, XIN Z, WANG H, et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Contained Thrombospondin 1 Retards Age-Related Degenerative Tendinopathy by Rejuvenating Tendon Stem/Progenitor Cell Senescence. Small. 2024;20(38):e2400598.
[6] DIENER C, KELLER A, MEESE E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022;38(6):613-626.
[7] BAO H, PENG Z, CHENG X, et al. GABA induced by sleep deprivation promotes the proliferation and migration of colon tumors through miR-223-3p endogenous pathway and exosome pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023;42(1):344.
[8] LIU X, JIN S, LIU J, et al. MiR-223-3p overexpressed adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote wound healing via targeting MAPK10. Acta Histochem. 2023;125(8):152102.
[9] KRYLOVA SV, FENG D. The Machinery of Exosomes: Biogenesis, Release, and Uptake. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1337.
[10] ZHANG Z, WANG P, ZHENG Y, et al. Exosomal microRNA-223 from neutrophil-like cells inhibits osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs through the cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. J Periodontal Res. 2023; 58(6):1315-1325.
[11] ZHANG MW, SHEN YJ, SHI J, et al. MiR-223-3p in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;7:610561.
[12] BARBAGALLO D, PONTI D, BASSANI B, et al. MiR-223-3p in Cancer Development and Cancer Drug Resistance: Same Coin, Different Faces. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(15):8191.
[13] GAO H, GAO R, ZHANG L, et al. Esrrb plays important roles in maintaining self-renewal of trophoblast stem cells (TSCs) and reprogramming somatic cells to induced TSCs. J Mol Cell Biol. 2019; 11(6):463-473.
[14] PRINGELS L, COOK JL, WITVROUW E, et al. Exploring the role of intratendinous pressure in the pathogenesis of tendon pathology: a narrative review and conceptual framework. Br J Sports Med. 2023;57(16):1042-1048.
[15] 陆加霖,高尧,李涵,等.富血小板血浆治疗肌腱病的影响因素与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(12):1944-1953.
[16] ZENG CY, WANG XF, HUA FZ. HIF-1α in Osteoarthritis: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 927126.
[17] CHEN W, WU P, YU F, et al. HIF-1α Regulates Bone Homeostasis and Angiogenesis, Participating in the Occurrence of Bone Metabolic Diseases. Cells. 2022;11(22):3552.
[18] YANG W, MA J, ZHOU W, et al. Reciprocal regulations between miRNAs and HIF-1α in human cancers. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(3):453-471.
[19] SONG S, ZHANG G, CHEN X, et al. HIF-1α increases the osteogenic capacity of ADSCs by coupling angiogenesis and osteogenesis via the HIF-1α/VEGF/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):257.
[20] LU X, LI L, LIN J, et al. PAARH promotes M2 macrophage polarization and immune evasion of liver cancer cells through VEGF protein. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;281(Pt 4):136580.
[21] YU Y, LIN L, ZHOU Y, et al. Effect of Hypoxia on Self-Renewal Capacity and Differentiation in Human Tendon-Derived Stem Cells. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:1334-1339.
[22] LI D, JIU J, LIU H, et al. Tissue-engineered mesenchymal stem cell constructs alleviate tendinopathy by suppressing vascularization. Bioact Mater. 2024;36:474-489.
[23] JIANG L, LIU T, LYU K, et al. Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy. Open Life Sci. 2023;18(1):20220729.
[24] SHI J, YAO H, CHONG H, et al. Tissue-engineered collagen matrix loaded with rat adipose-derived stem cells/human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells for rotator cuff tendon-bone repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;282(Pt 4):137144.
[25] ZHANG M, DAI GC, ZHANG YW, et al. Enhancing osteogenic differentiation of diabetic tendon stem/progenitor cells through hyperoxia: Unveiling ROS/HIF-1α signalling axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2024; 28(20):e70127.
[26] ZHANG W, YAO C, WEI Z, et al. miR-128 promoted adipogenic differentiation and inhibited osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by suppression of VEGF pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2017;37(3):217-223.
[27] LI X, YANG N. Exosome miR-223-3p in the bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviates the inflammation and airway remodeling through NLRP3-induced ASC/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;123:110746.
[28] LONG C, CEN S, ZHONG Z, et al. FOXO3 is targeted by miR-223-3p and promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing autophagy. Hum Cell. 2021;34(1):14-27.
[29] YFANTIS A, MYLONIS I, CHACHAMI G, et al. Transcriptional Response to Hypoxia: The Role of HIF-1-Associated Co-Regulators. Cells. 2023; 12(5):798.
[30] LI X, LONG J, ZONG L, et al. ZNF561-AS1 Regulates Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Myocardial Infarction Through miR-223-3p/NLRP3 Axis. Cell Transplant. 2022;31:9636897221077928.
[31] ZHI Y, ZHANG W, WU Z, et al. miR-223-3p Targets KIF4A and Promotes the Oxidative Stress-Mediated Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2025. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2024.0102.
[32] DIEHL CJ, CIULLI A. Discovery of small molecule ligands for the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) E3 ligase and their use as inhibitors and PROTAC degraders. Chem Soc Rev. 2022;51(19):8216-8257.
[33] SEMENZA GL. Involvement of oxygen-sensing pathways in physiologic and pathologic erythropoiesis. Blood. 2009;114(10):2015-2019.
[34] PÉREZ-GUTIÉRREZ L, FERRARA N. Biology and therapeutic targeting of vascular endothelial growth factor A. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023; 24(11):816-834.
[35] APTE RS, CHEN DS, FERRARA N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell. 2019;176(6):1248-1264.
[36] CÉBE SUAREZ S, PIEREN M, CARIOLATO L, et al. A VEGF-A splice variant defective for heparan sulfate and neuropilin-1 binding shows attenuated signaling through VEGFR-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63(17): 2067-2077.
[37] CHEN C, SONG C, LIU B, et al. Activation of BMP4/SMAD pathway by HIF-1α in hypoxic environment promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and leads to ectopic bone formation. Tissue Cell. 2024;88: 102376.
[38] CHENG X, YUN X, WEI Y, et al. Hypoxia-Mimicking Microenvironment Scaffold for Enhanced Tendon Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025;17(6):8937-8948.
[39] MABETA P, STEENKAMP V. The VEGF/VEGFR Axis Revisited: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15585.
[40] ASAKIYA C, ZHU L, YUHAN J, et al. Current progress of miRNA-derivative nucleotide drugs: modifications, delivery systems, applications. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2022;19(4):435-450. |