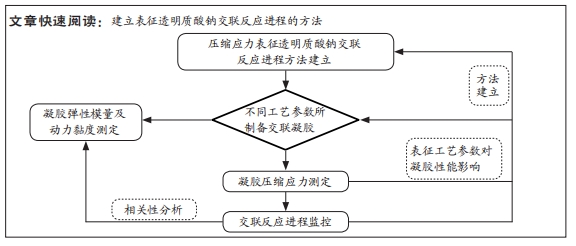
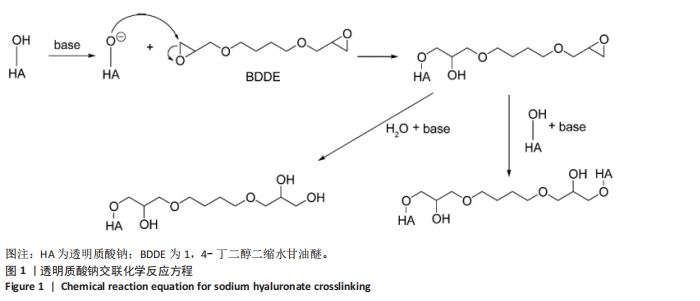
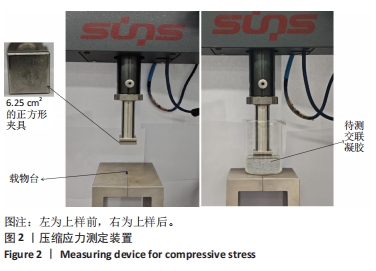
[1] 朱剑锋,徐小慧,施佳丽.交联透明质酸血管栓塞剂的制备及表征[J].高分子通报,2018(9):47-52.
[2] RELLEVE LS, GALLARDO AKR, TECSON MG, et al. Biocompatible hydrogels of carboxymethyl hyaluronic acid prepared by radiation-induced crosslinking. Radiat Phys Chem. 2021;179:109194.
[3] DING YW, WANG ZY, REN ZW, et al. Advances in modified hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels for skin wound healing. Biomater Sci. 2022; 10(13):3393-3409.
[4] LI C, CAO Z, LI W, et al. A review on the wide range applications of hyaluronic acid as a promising rejuvenating biomacromolecule in the treatments of bone related diseases. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;165(Pt A):1264-1275.
[5] TIAN G, SUN X, BAI J, et al. Doxorubicin-loaded dual-functional hyaluronic acid nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and antitumor efficacy in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 2019; 19(1):133-142.
[6] KIM H, JEONG H, HAN S, et al. Hyaluronate and its derivatives for customized biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2017;123:155-171.
[7] 于浩,姜爱莉,李敏,等.《整形手术用交联透明质酸钠凝胶》标准中质量控制方法的研究进展[J].中国美容医学,2020,29(12):185-189.
[8] 李红梅,张素文,郑春玲,等.注射用聚乳酸和交联透明质酸钠凝胶的制备及性能研究[J].生物医学工程研究,2016,35(3):202-204.
[9] SARAVANAKUMAR K, PARK S, SANTOSH SS, et al. Application of hyaluronic acid in tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and nanomedicine: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;222(Pt B):2744-2760.
[10] KATOH S, YOSHIOKA H, SENTHILKUMAR R, et al. Enhanced expression of hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritis-affected knee-cartilage chondrocytes during three-dimensional in vitro culture in a hyaluronic-acid-retaining polymer scaffold. Knee. 2021;29:365-373.
[11] 中国整形美容协会新技术与新材料分会.贝丽姿(R)-注射用交联透明质酸钠凝胶专家共识(2018)[J].中国美容医学,2019,28(6):73-77.
[12] WENDE FJ, XUE Y, NESTOR G, et al. Relaxation and diffusion of water protons in BDDE cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogels investigated by NMR spectroscopy-Comparison with physicochemical properties. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;248(29):365-373.
[13] FAIVRE J, PIGWEH AI, IEHL J, et al. Crosslinking hyaluronic acid soft-tissue fillers: current status and perspectives from an industrial point of view. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2021;18(12):1175-1187.
[14] HINSENKAMP A, ÉZSIÁS B, PÁL É, et al. Crosslinked Hyaluronic Acid Gels with Blood-Derived Protein Components for Soft Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(11-12):806-820.
[15] GIUBERTONI G, PÉREZ DE ALBA ORTÍZ A, BANO F, et al. Strong Reduction of the Chain Rigidity of Hyaluronan by Selective Binding of Ca2+ Ions. Macromolecules. 2021;54(3):1137-1146.
[16] KHUNMANEE S, JEONG Y, PARK H. Crosslinking method of hyaluronic-based hydrogel for biomedical applications. J Tissue Eng. 2017;8(2):204173141772646.
[17] IACONISI GN, LUNETTI P, GALLO N, et al. Hyaluronic Acid: A Powerful Biomolecule with Wide-Ranging Applications-A Comprehensive Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(12):10296.
[18] 王珏,胡丽,武美芹,等.NMR技术测定PVPP交联度及其粉体可压缩性研究[J].药学学报,2022,57(2):474-479.
[19] 李利,黄光速.部分交联聚丙烯酰胺凝胶化反应中交联剂的影响[J].塑料工业,2013,41(3):35-39,71.
[20] 张雪慧,王艳芹,郑强.仿生各向异性结构复合水凝胶及其流变学行为研究[J].高分子学报,2024-05-07.doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2023.23275
[21] 沈煜年,覃宗喜.一种测定水凝胶软材料内部应力-应变场的方法:CN202210177194.7[P].CN202210177194.7[2024-04-12].
[22] 张泳柔.单轴荷载下PVA水凝胶力学行为的实验表征与模型研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2024.
[23] FIGUEIREDO T, JING J, JEACOMINE I, et al. Injectable Self-Healing Hydrogels Based on Boronate Ester Formation between Hyaluronic Acid Partners Modified with Benzoxaborin Derivatives and Saccharides. Biomacromolecules. 2020;21(1):230-239.
[24] 陈倩倩,刘杰,张建强,等.交联玻璃酸钠凝胶的制备及流变学研究[J].中国药学杂志,2017,52(15):1342-1346.
[25] 任秀,白继超,王亚萍,等. 6种克罗诺杆菌精准鉴定及标准物质的制备研究[J].食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(17):6817-6825.
[26] 陈钧,刘国荣,曾博,等.t检验和方差分析识别EMC测量系统间性能偏离[J].环境技术,2023,41(7):80-83.
[27] 方忠俊,季蔚青,张婧娴,等.痛风性关节炎患者HLA-B*5801基因型携带率及相关实验室指标分析[J].检验医学,2021,36(9):896-900.
[28] 康婕,陈鸿剑,李媛.羊乳制品中高氯酸盐污染来源分析[J].中国乳品工业,2024,52(4):45-49.
[29] LUO Y, TAN J, ZHOU Y, et al. From crosslinking strategies to biomedical applications of hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;231:123308.
[30] WENDE FJ, GOHIL S, NORD LI, et al. Insights on the reactivity of chondroitin and hyaluronan toward 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;131:812-820.
[31] 张萍,刘月明.注射用透明质酸钠在面部轮廓修饰及年轻化中的应用[J].中国美容医学,2018,27(8):65-69.
[32] HIROSE R, WATANABE N, NAITO Y, et al. Comparison of sodium alginate-based and sodium hyaluronate-based submucosal injection materials based on rheological analysis. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;124:104816.
[33] 张慧君,俞冰,牛峰,等.注射用透明质酸钠在面部美容外科中的应用观察[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2017,52(3):194-197.
|