| [1] Litwic A, Edwards MH, Dennison EM, et al. Epidemiology and burden of osteoarthritis. Br MedBull. 2013;105:185-199.[2] Busija L, Bridgett L, Williams SR, et al. Osteoarthritis. Best Pract ResClin Rheumatol. 2010;24(6):757-768.[3] Mishra SK, Pramanik R, Das P, et al. Role of intra-articular ozone in osteo-arthritis of knee for functional and symptomatic improvement. Ind J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;22(2):65-69.[4] Raeissadat SA,Rayegani SM,Forogh B,et al.Intra-articular ozone or hyaluronic acid injection: Which one is superior in patients with knee osteoarthritis? A 6-month randomized clinical trial.J Pain Res 2018;11:111-117.[5] 刘爱峰,裴开源,王平,等.玻璃酸钠注射液与生理盐水对照对于膝骨性关节炎临床疗效的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016, 24(17):1581-1586.[6] Kang S,Gao F,Han J,et al.Extracorporeal shock wave treatment can normalize painful bone marrow edema in knee osteoarthritis: A comparative historical cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore) 2018;97:e9796.[7] Lizis P,Kobza W.Extracorporeal shockwave therapy vs. kinesiotherapy for osteoarthritis of the knee: A pilot randomized controlled trial.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 2017;30:1121-1128.[8] 视觉模拟评分法 (Visual analogue scale, VAS) [J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2013,12(23):1925. [9] 陆斌,李建武,杨艳,等.臭氧联合玻璃酸钠对膝关节骨性关节炎患者膝关节功能及疼痛症状的改善效果观察[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2018,17(11):1186-1189.[10] 潘勇,祝健,卢华斌.白细胞介素-6、白细胞介素-17、白细胞介素-23与膝骨关节炎患者病情活动的相关性研究[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2018,28(11):1395-1396+1400.[11] Jackson BD, Wluka AE, Teichtahl AJ,et al. Reviewing knee osteoarthritis-a biomechanical perspective. J Sci Med Sport. 2004;7(3): 347.[12] Wu CW, Kalunian KC. New developments in osteoarthritis. Clin Geriatr Med. 2005; 21(3): 589.[13] Gracitelli GC, Moraes VY, Franciozi CE,et al. Surgical interventions (microfracture, drilling, mosaicplasty, and allograft transplantation) for treating isolated cartilage defects of the knee in adults. Cochrane Database SystRev. 2016; 3(9): CD010675.[14] Raeissadat SA, Babaee M, Rayegani SM, et al. An overview of platelet products (PRP, PRGF, PRF, etc.) in the Iranian studies. Futur Sci OA.2017;3(4):FSO231.[15] Kanchanatawan W, Arirachakaran A, Chaijenkij K, et al. Short-term outcomes of platelet-rich plasma injection for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(5):1665-1677.[16] Raeissadat SA, Rayegani SM, Hassanabadi H, et al. Knee osteoarthritis injection choices: platelet-rich plasma (PRP) versus hyaluronic acid (a one year randomized clinical trial). Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;8:1-8.[17] Adams ME, Atkinson MH, Lussier AJ, et al. The role of viscosupplementation with hylan G-F 20 in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee:a Canadian multicenter trial comparing hylan G-F 20 alone, hylan G-F 20 with non-steroidal anti-in?ammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and NSAIDs alone. Osteoarthr Cartil. 1995;3(4):213-225[18] Rodriguez-Merchan EC. Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid and other drugs in the knee joint. HSS J. 2013;9(2): 180-182[19] Nguyen C, Lefevre-Colau MM, Poiraudeau S, et al. Evidence and recommendations for use of intraarticular injections for knee osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 2016;59:184-9[20] Richette P, Chevalier X, Ea HK, et al. Hyaluronan for knee osteoarthritis: an updated meta-analysis of trials with low risk of bias.RMD Open 2015;1:e000071.[21] Altman RD, Manjoo A, Fierlinger A, et al. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee: a systematic review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2015;16:321.[22] Muratovic D,Findlay DM,Cicuttini FM,et al.Bone matrix microdamage and vascular changes characterize bone marrow lesions in the subchondral bone of knee osteoarthritis. Bone 2018;108:193-201.[23] Wang CJ, Hsu SL, Weng LH, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows a number of treatment related chondroprotective effect in osteoarthritis of the knee in rats. BMC Musculoskelet Disord2013;14:44.[24] Wang CJ, Sun YC, Wong T, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows timedependent chondroprotective effects in osteoarthritis of the knee in rats. J Surg Res 2012;178: 196-205.[25] Zhao Z, Ji H, Jing R, et al. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy reduces progression of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits by reducing nitric oxide level and chondrocyte apoptosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2012;132:1547-53[26] Ochiai N,Ohtori S,Sasho T,et al.Ex tracorporeal shock wave therapy improves motor dysfunction and pain originating from knee osteoarthritis in rats.Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2007;15: 1093-1096.[27] Moretti B, Iannone F, Notarnicola A, et al. Extracorporeal shock waves down-regulate the expression of interleukin-10 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2008.31(9):16.[28] 刘洪柏,区丽明.体外冲击波对骨关节炎作用的研究进展[J].现代医院,2012,12(01):13-15.[29] Lee JH,Lee S,Choi S,et al.The effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on the pain and function of patients with degenerative knee arthritis.J Phys Ther Sci 2017;29:536-538.[30] 赵喆,史展,闫君,等.体外冲击波治疗早中期膝骨关节炎的效果[J].中国康复理论与实践,2014,20(1):76-78.[31] Lee JK,Lee BY,Shin WY,et al.Effect of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Versus Intra-articular Injections of Hyaluronic Acid for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis.Ann Rehabil Med 2017;41:828-835.[32] Imamura M,Alamino S,Hsing WT,et al.Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy for disabling pain due to severe primary knee osteoarthritis.J Rehabil Med 2017;49:54-62.[33] Kim JH, Kim JY, Choi CM,et al. The Dose-Related Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Knee Osteoarthritis. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015;39(4):616. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
体外冲击波:由于能量的突然释放而产生的高能量压力波,具有压力瞬间增高和高速传导的特性,冲击波在穿越人体组织时,直达深部组织。冲击波作用于人体后,通过力-化学信号转导产生生物学效应(代谢效应、空化效应等),促进生长因子释放,引起微血管新生及组织再生与修复。
透明质酸钠:透明质酸是人体内一种固有的成分,是一种葡聚糖醛酸,为关节腔滑液的主要成分,为软骨基质的成分之一,在关节起到润滑作用,减少组织间的摩擦,关节腔内注入后可明显改善滑液组织的炎症反应,增强关节液的黏稠性和润滑功能,保护关节软骨,促进关节软骨的愈合与再生,缓解疼痛,增加关节的活动度。
文题释义:
体外冲击波:由于能量的突然释放而产生的高能量压力波,具有压力瞬间增高和高速传导的特性,冲击波在穿越人体组织时,直达深部组织。冲击波作用于人体后,通过力-化学信号转导产生生物学效应(代谢效应、空化效应等),促进生长因子释放,引起微血管新生及组织再生与修复。
透明质酸钠:透明质酸是人体内一种固有的成分,是一种葡聚糖醛酸,为关节腔滑液的主要成分,为软骨基质的成分之一,在关节起到润滑作用,减少组织间的摩擦,关节腔内注入后可明显改善滑液组织的炎症反应,增强关节液的黏稠性和润滑功能,保护关节软骨,促进关节软骨的愈合与再生,缓解疼痛,增加关节的活动度。.jpg) 文题释义:
体外冲击波:由于能量的突然释放而产生的高能量压力波,具有压力瞬间增高和高速传导的特性,冲击波在穿越人体组织时,直达深部组织。冲击波作用于人体后,通过力-化学信号转导产生生物学效应(代谢效应、空化效应等),促进生长因子释放,引起微血管新生及组织再生与修复。
透明质酸钠:透明质酸是人体内一种固有的成分,是一种葡聚糖醛酸,为关节腔滑液的主要成分,为软骨基质的成分之一,在关节起到润滑作用,减少组织间的摩擦,关节腔内注入后可明显改善滑液组织的炎症反应,增强关节液的黏稠性和润滑功能,保护关节软骨,促进关节软骨的愈合与再生,缓解疼痛,增加关节的活动度。
文题释义:
体外冲击波:由于能量的突然释放而产生的高能量压力波,具有压力瞬间增高和高速传导的特性,冲击波在穿越人体组织时,直达深部组织。冲击波作用于人体后,通过力-化学信号转导产生生物学效应(代谢效应、空化效应等),促进生长因子释放,引起微血管新生及组织再生与修复。
透明质酸钠:透明质酸是人体内一种固有的成分,是一种葡聚糖醛酸,为关节腔滑液的主要成分,为软骨基质的成分之一,在关节起到润滑作用,减少组织间的摩擦,关节腔内注入后可明显改善滑液组织的炎症反应,增强关节液的黏稠性和润滑功能,保护关节软骨,促进关节软骨的愈合与再生,缓解疼痛,增加关节的活动度。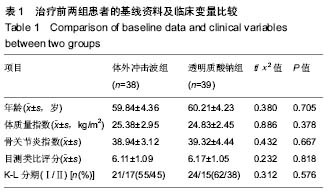
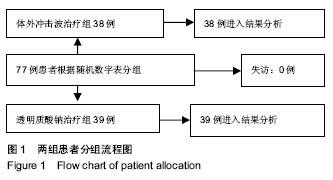
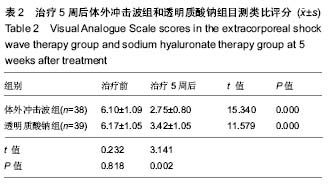
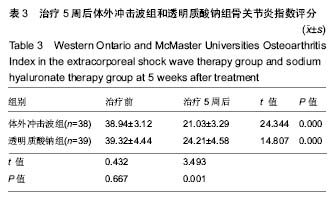
.jpg) 文题释义:
体外冲击波:由于能量的突然释放而产生的高能量压力波,具有压力瞬间增高和高速传导的特性,冲击波在穿越人体组织时,直达深部组织。冲击波作用于人体后,通过力-化学信号转导产生生物学效应(代谢效应、空化效应等),促进生长因子释放,引起微血管新生及组织再生与修复。
透明质酸钠:透明质酸是人体内一种固有的成分,是一种葡聚糖醛酸,为关节腔滑液的主要成分,为软骨基质的成分之一,在关节起到润滑作用,减少组织间的摩擦,关节腔内注入后可明显改善滑液组织的炎症反应,增强关节液的黏稠性和润滑功能,保护关节软骨,促进关节软骨的愈合与再生,缓解疼痛,增加关节的活动度。
文题释义:
体外冲击波:由于能量的突然释放而产生的高能量压力波,具有压力瞬间增高和高速传导的特性,冲击波在穿越人体组织时,直达深部组织。冲击波作用于人体后,通过力-化学信号转导产生生物学效应(代谢效应、空化效应等),促进生长因子释放,引起微血管新生及组织再生与修复。
透明质酸钠:透明质酸是人体内一种固有的成分,是一种葡聚糖醛酸,为关节腔滑液的主要成分,为软骨基质的成分之一,在关节起到润滑作用,减少组织间的摩擦,关节腔内注入后可明显改善滑液组织的炎症反应,增强关节液的黏稠性和润滑功能,保护关节软骨,促进关节软骨的愈合与再生,缓解疼痛,增加关节的活动度。