|
[1] WOOLF AD, PFLEGER B. Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions.Bull World Health Organ.2003;81(9):646-656.
[2] HAWKER G, CROXFORD R, BIERMAN A, et al. All-cause mortality and serious cardiovascular events in people with hip and knee osteoarthritis: a population based cohort study.PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e91286.
[3] NÜESCH E, DIEPPE P, REICHENBACH S, et al. All cause and disease specific mortality in patients with knee or hip osteoarthritis: population based cohort study.BMJ.2011;342:d1165.
[4] CHRISTENSEN P, HENRIKSEN M, BARTELS E, et al. Long-term weight-loss maintenance in obese patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized trial.Am J Clin Nutr. 2017;106(3): 755-763.
[5] SRIDHAR M, JARRETT C, XEROGEANES J, et al. Obesity and symptomatic osteoarthritis of the knee.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(4):433-440.
[6] LITWIC A, EDWARDS M, DENNISON E, et al. Epidemiology and burden of osteoarthritis. Br Med Bull.2013;105:185-199.
[7] FISHER J, BALLANTYNE P, HAWKER G. Older adults living with osteoarthritis: examining the relationship of age and gender to medicine use.Can J Aging.2012;31(3):323-333.
[8] FILARDO G, KON E, LONGO U, et al. Non-surgical treatments for the management of early osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2016;24(6):1775-1785.
[9] MURPHY L, HELMICK CG. The impact of osteoarthritis in the United States: a population-health perspective.Am J Nurs. 2012; 112(3 Suppl 1):S13-S19.
[10] RICHMOND J, HUNTER D, IRRGANG J, et al. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons clinical practice guideline on the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(4):990-993.
[11] CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION (CDC). Prevalence of doctor-diagnosed arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation--United States, 2010-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.2013;62(44):869-873.
[12] CARR A, ROBERTSSON O, GRAVES S, et al. Knee replacement. Lancet.2012;379(9823):1331-1340.
[13] RAZUMOV AN, PURIGA AO, YUROVA OV. The long-term results of the application of the combined rehabilitative treatment in the patients presenting with knee osteoarthrosis. Vopr Kurortol Fizioter Lech Fiz Kult.2015;92(6):42-44.
[14] JORDAN KM, ARDEN NK, DOHERTY M, et al. EULAR Recommendations 2003: an evidence based approach to the management of knee osteoarthritis: Report of a Task Force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutic Trials (ESCISIT).Ann Rheum Dis.2003;62(12): 1145-1155.
[15] HOCHBERG MC, ALTMAN RD, APRIL KT, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee.Arthritis Care Res.2012;64(4):465-474.
[16] THIEL M. Application of shock waves in medicine.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2001;387:18-21.
[17] HAUPT G. Use of extracorporeal shock waves in the treatment of pseudarthrosis, tendinopathy and other orthopedic diseases.J Urol.1997;158(1:4-11).
[18] 江明,邢更彦,白晓东.体外冲击波疗法在骨科领域的应用[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(16):1099-1101.
[19] SAGGINI R, DI STEFANO A, SAGGINI A, et al.Clinical application of shock wave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders: Part I.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents.2015;29(3):533-545.
[20] TISCHER T, MILZ S, WEILER C, et al. Dose-dependent new bone formation by extracorporeal shock wave application on the intact femur of rabbits.Eur Surg Res.2008;41(1):44-53.
[21] D'AGOSTINO C, ROMEO P, LAVANGA V, et al. Effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in bone marrow edema syndrome of the hip.Rheumatol Int.2014;34(11):1513-1518.
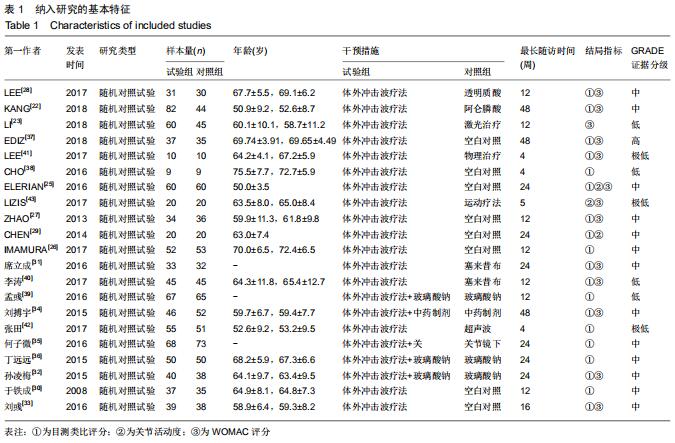
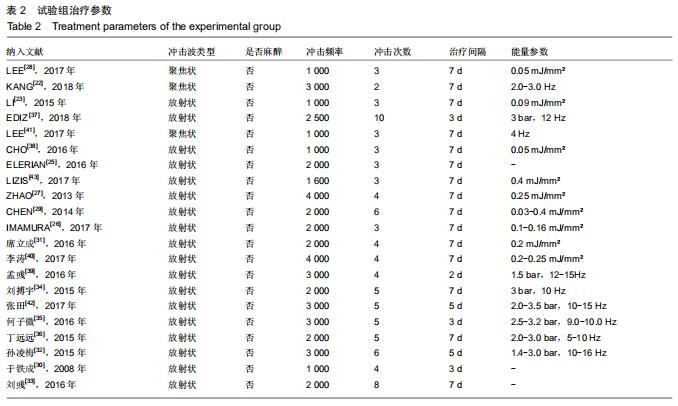
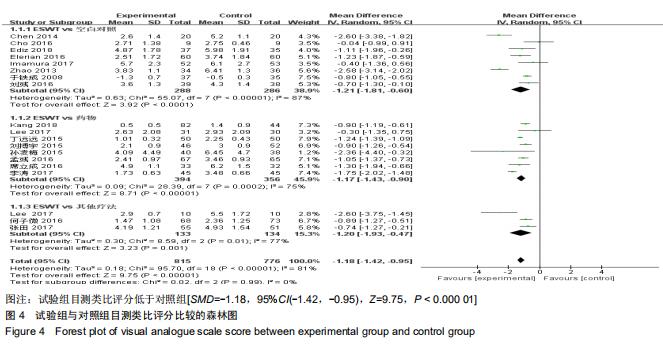
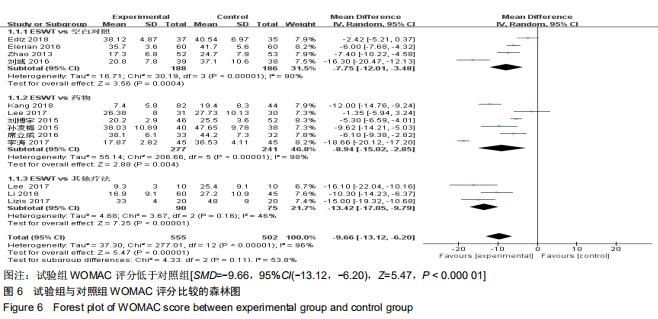
[22] KANG S, GAO F, HAN J, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave treatment can normalize painful bone marrow edema in knee osteoarthritis: A comparative historical cohort study.Medicine. 2018;97(5): e9796.
[23] LI W, PAN Y, YANG Q, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: A retrospective study. Medicine.2018;97(27):e11418.
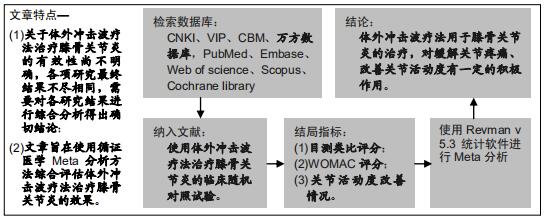
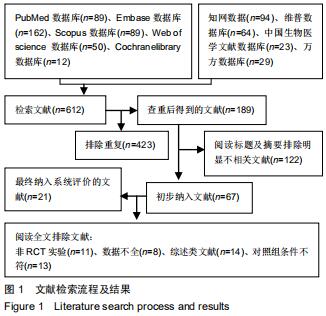
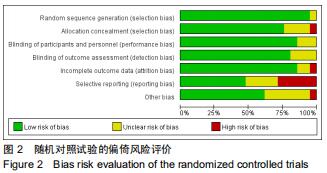
[24] MOHER D, SHAMSEER L, CLARKE M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement.Syst Rev.2015;4:1.
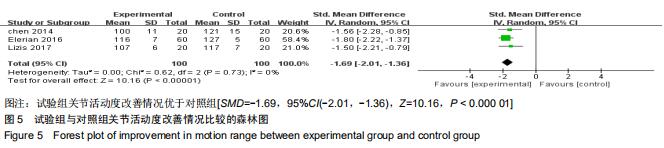
[25] ELERIAN AE, EWIDEA TMA, ALI N. Effect Of Shock Wave Therapy Versus Corticosteroid Injection In Management Of Knee Osteoarthritis.J Physiothe.2016;3(2):246-251.
[26] IMAMURA M, ALAMINO S, HSING WT, et al. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy for disabling pain due to severe primary knee osteoarthritis.J Rehabil Med.2017;49(1): 54-62.
[27] ZHAO Z, JING R, SHI Z, et al. Efficacy of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. J Surg Res.2013;185(2):661-666.
[28] LEE JK, LEE BY, SHIN WY, et al. Effect of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy Versus Intra-articular Injections of Hyaluronic Acid for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis.Ann Rehabil Med. 2017;41(5):828-835.
[29] CHEN TW, LIN CW, LEE CL, et al. The efficacy of shock wave therapy in patients with knee osteoarthritis and popliteal cyamella. Kaohsiung J Med Sci.2014;30(7):362-370.
[30] 于铁成,陈小英,董世娜,等.冲击波治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的单盲平行模拟对照临床研究[J].中国老年学杂志, 2008,28(13):1301-1303.
[31] 席立成,李宏宇,赵子星,等.体外冲击波治疗早中期膝关节骨性关节炎效果观察及其机制[J].山东医药,2016,56(48):60-62.
[32] 孙凌梅,吕客,朱贺,等.放散式冲击波联合玻璃酸钠关节腔内注射治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效观察[J].淮海医药, 2015,33(6):548-549.
[33] 刘彧.体外冲击波疗法对绝经后女性早中期膝骨关节炎的疗效观察[D].石家庄:河北医科大学, 2016.
[34] 刘搏宇,李宏宇,金先跃,等.独活寄生汤联合体外冲击波治疗膝关节骨关节炎的效果[J].广东医学,2015,36(23):3709-3711.
[35] 何子微,赵维彪.关节镜下膝关节清理术联合体外冲击波治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效分析[J].沈阳医学院学报, 2016,18(5):347-349.
[36] 丁远远,姚鹏.气压弹道式体外冲击波联合玻璃酸钠治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效观察 [J].实用药物与临床, 2015,18(7):799-803.
[37] EDIZ L, ÖZGÖKÇE M. Effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy to treat primary medial knee osteoarthritis with and without bone marrow edema in elderly patients. Turk Geriatri Derg. 2018;21(3):394-401.
[38] CHO SJ, YANG JR, YANG HS, et al. Effects of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy in Chronic Stroke Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study.Ann Rehabil Med. 2016;40(5): 862-870.
[39] 孟彧,吴嫚,王宏沛,等.冲击波联合关节腔内注射在膝骨关节炎治疗中的应用[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2016,22(8):638-639.
[40] 李涛,宋奇志,裴建祥,等.体外冲击波治疗早中期膝关节骨关节炎的近期临床疗效观察[J].重庆医学,2017,46(3):338-340.
[41] LEE JH, LEE S, CHOI S, et al. The effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on the pain and function of patients with degenerative knee arthritis.J Phys Ther Sci. 2017;29(3):536-538.
[42] 张田,刘文波,李华,等.放射状冲击波治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J].中国医学创新, 2017,14(30):36-40.
[43] LIZIS P, KOBZA W, MANKO G. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy vs. kinesiotherapy for osteoarthritis of the knee: A pilot randomized controlled trial.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil.2017; 30(5):1121-1128.
[44] LANE N, NEVITT M. Osteoarthritis, bone mass, and fractures: how are they related?.Arthritis Rheum.2002;46(1):1-4.
[45] DYMAREK R, BIDZIŃSKA G, ZWIERZCHOWSKI K, et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in selected musculoskeletal system disorders of the inflammatory etiology--a critical review of the literature.Wiad Lek.2015;68(2):183-192.
[46] WANG C. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders.J Orthop Surg Res.2012;7:11.
[47] FRISBIE D, KAWCAK C, MCILWRAITH C. Evaluation of the effect of extracorporeal shock wave treatment on experimentally induced osteoarthritis in middle carpal joints of horses.Am J Vet Res.2009;70(4):449-454.
[48] ZHAO Z, JI H, JING R, et al. Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy reduces progression of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits by reducing nitric oxide level and chondrocyte apoptosis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2012;132(11):1547-1553.
[49] WANG C, WENG L, KO J, et al. Extracorporeal shockwave shows regression of osteoarthritis of the knee in rats.J Surg Res. 2011; 171(2):601-608.
[50] KIM JH, KIM JY, CHOI CM, et al. The Dose-Related Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Knee Osteoarthritis. Ann Rehabil Med.2015;39(4):616-623.
|