[1] PEREIRA D, RAMOS E, BRANCO J. Osteoarthritis. Acta Med Port. 2015;28(1): 99-106.
[2] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[3] URBAN H, LITTLE CB. The role of fat and inflammation in the pathogenesis and management of osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(suppl_4): iv10-iv21.
[4] GEYER M, SCHÖNFELD C. Novel Insights into the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):98-107.
[5] 国家统计局.中华人民共和国2019年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[1][N].人民日报,2020-02-29(005).
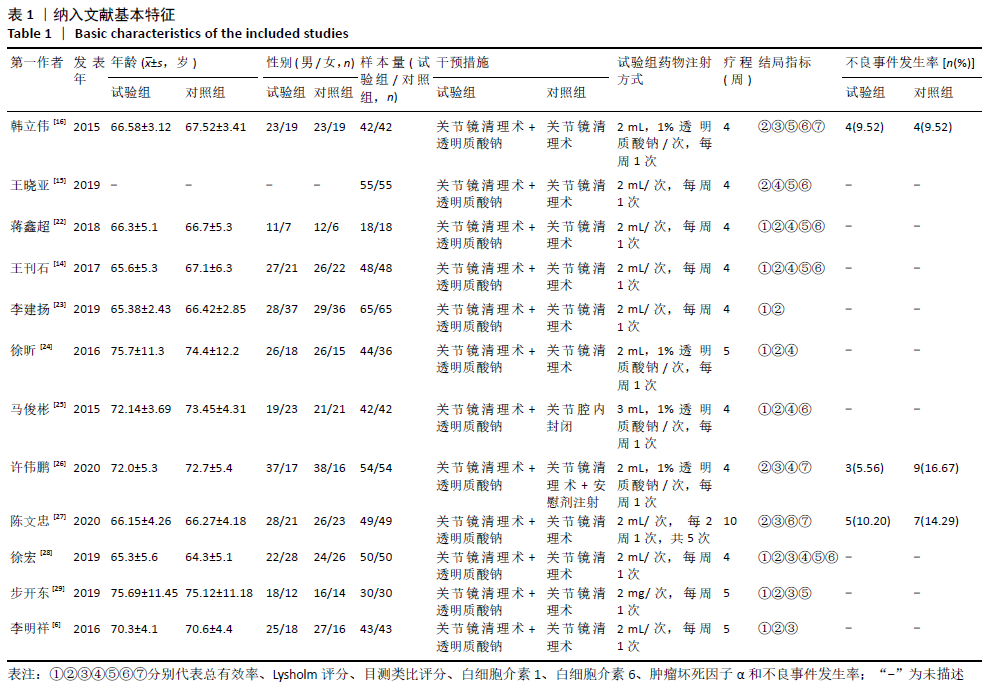
[6] 李明祥,俞维英.老年膝骨性关节炎术后应用玻璃酸钠治疗对减轻其疼痛的作用分析[J].浙江创伤外科,2016,21(4): 722-723.
[7] CHEN P, HUANG L, MA Y, et al. Intra-articular platelet-rich plasma injection for knee osteoarthritis: a summary of meta-analyses. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):385.
[8] BANNURU RR, OSANI MC, VAYSBROT EE, et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(11):1578-1589.
[9] 白朝奇,封鹏,张雪艳,等.关节镜清理联合自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植对膝骨关节炎患者疼痛程度、炎症介质及膝关节功能的影响[J].海南医学,2020, 31(17):2203-2206.
[10] ROSETI L, DESANDO G, CAVALLO C, et al. Articular cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. Cells. 2019;8(11):1305.
[11] YANG X, LIN JH, SUN TS, et al. The efficacy and safety of sodium hyaluronate injection (Adant®) in treating degenerative osteoarthritis: a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, positive-drug parallel-controlled and non-inferiority clinical study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(3):271-278.
[12] 刘爱峰,裴开源,王平,等.玻璃酸钠注射液与生理盐水对照对于膝骨性关节炎临床疗效的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(17):1581-1586.
[13] SHIMIZU M, HIGUCHI H, TAKAGISHI K, et al. Clinical and biochemical characteristics after intra-articular injection for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: prospective randomized study of sodium hyaluronate and corticosteroid. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15(1):51-56.
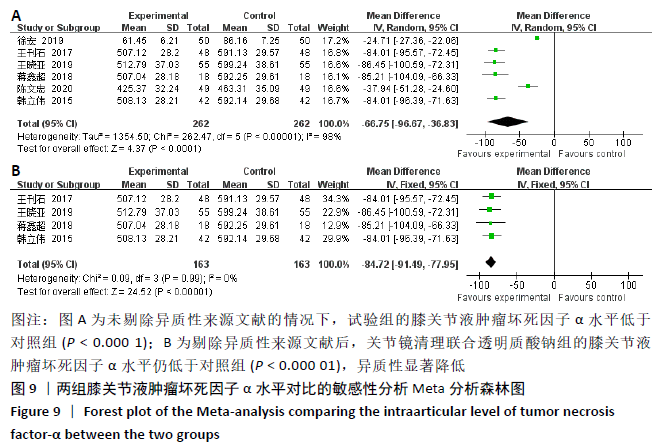
[14] 王刊石,周超,赵磊.关节镜手术联合透明质酸钠对老年膝骨关节炎患者的临床疗效及对关节液内IL-6、IL-1、TNF-α水平的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2017, 37(13):3290-3291.
[15] 王晓亚,任猛,王浩,等.关节镜手术联合透明质酸钠在老年膝骨关节炎治疗的效果及炎性因子的影响[J].河北医药, 2019,41(8):1235-1237.
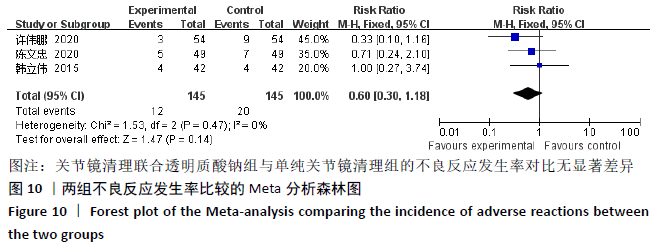
[16] 韩立伟.关节镜下清理术联合透明质酸钠对老年膝骨关节炎疼痛及IL-6、TNF-α的影响[J].广西医科大学学报,2015,32(5): 778-780.
[17] 中华医学会骨科学分会.骨关节炎诊治指南(2007年版)[J].中国临床医生,2008, 36(1):28-30.
[18] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[19] HIGGINS JP, ALTMAN DG, GØTZSCHE PC, et al. Cochrane Bias Methods Group; Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;10(18):343:d5928.
[20] CUMPSTON M, LI T, PAGE MJ, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;10:ED000142.
[21] HIGGINS JP, GREEN S. Cochrane Handbook For Systematic Reviews Of Interventions Version 5.0.0. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv für experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie. 2008;5(2):S38.
[22] 蒋鑫超.关节镜手术联合透明质酸钠在老年膝骨关节炎治疗的效果及炎性因子的影响评价[J]. 国际感染杂志(电子版), 2018,7(3):76-77.
[23] 李建扬,杨先腾,罗锐,等.关节镜手术联合透明质酸钠治疗老年膝骨关节炎的疗效观察[J].双足与保健,2019,28(19):156-157.
[24] 徐昕,董耘,徐华,等.关节镜清理联合透明质酸钠腔内注射治疗80例高龄膝关节骨性关节炎患者临床分析[J].中华全科医学,2016,14(9):1463-1465.
[25] 马俊彬,朱传银,鲁兵.透明质酸钠联合膝关节镜治疗老年膝关节骨性关节炎的疗效分析[J].中国医药指南,2015,13(15): 184-185.
[26] 许伟鹏,徐志强,吴峰,等.关节镜清理联合透明质酸钠治疗膝骨关节炎的短期疗效[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2020,14(3):370-374.
[27] 陈文忠,侯颖周,李科伟,等.关节镜清理联合玻璃酸钠注射治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床观察[J].中国老年保健医学, 2020,18(2):47-49.
[28] 徐宏.关节镜与玻璃酸钠联合治疗膝骨关节炎的效果[J].中国合理用药探索,2019, 16(2):73-76.
[29] 步开东,范顺武,翁科迪.关节镜微创手术联合玻璃酸钠治疗对老年膝关节骨性关节炎患者生活质量及血清IL-6、IL-10的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2019,39(7): 1637-1639.
[30] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311.
[31] NEES TA, ROSSHIRT N, REINER T, et al. Inflammation and osteoarthritis-related pain. Schmerz. 2019;33(1):4-12.
[32] WANG T, HE C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: the link between obeaqsity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018;44:38-50.
[33] WOJDASIEWICZ P, PONIATOWSKI A, SZUKIEWICZ D, et al. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014; 2014:561459.
[34] ALTMAN RD, MANJOO A, FIERLINGER A, et al. The mechanism of action for hyaluronic acid treatment in the osteoarthritic knee: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:321
[35] 廖瑛,张兴,周君,等.透明质酸对膝关节骨性关节炎相关细胞因子及生物标志物的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2019, 29(4):33-38.
[36] 王波,余楠生.膝骨关节炎阶梯治疗专家共识(2018年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(1):124-130.
[37] HENROTIN Y, RAMAN R, RICHETTE P, et al. Consensus statement on viscosupplementation with hyaluronic acid for the management of osteoarthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2015;45(2):140-149.
[38] BRONSTONE A, NEARY JT, LAMBERT TH, et al. Supartz (sodium hyaluronate) for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a review of efficacy and safety. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;12:1179544119835221.
[39] LI ZM, LI M. Improvement in orthopedic outcome score and reduction in IL-1β, CXCL13, and TNF-α in synovial fluid of osteoarthritis patients following arthroscopic knee surgery. Genet Mol Res. 2017. doi: 10.4238/gmr16039487.
|