[1] HENK VERBIEST. A Radicular Syndrome From Developmental Narrowing of the Lumbar Vertebral Canal. SAS Journal. 2009;3(2):77-84.
[2] 何齐芳.老年性腰椎管狭窄的椎间孔镜治疗分析[J].中华全科医学, 2015,13(6):902-905.
[3] MACHADO GC, MAHER CG, FERREIRA PH, et al. Trends, complications, and costs for hospital admission and surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine. 2017;42(22):1737-1743.
[4] BENDITZ A, SPRENGER S, RAUCH L, et al. Increased pain and sensory hyperinnervation of the ligamentum flavum in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(3):737-743.
[5] VIEJO-FUERTES D, LIGUORO D, RIVEL J, et al.Morphologic and histologic study of the ligamentum flavum in the thoraco-lumbar region. Surg Radiol Anat. 1998;20(3):171-176.
[6] KOSAKA H, SAIRYO K, BIYANI A, et al. Pathomechanism of loss of elasticity and hypertrophy of lumbar ligamentum flavum in elderly patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(25):2805-2811.
[7] SCHRÄDER PK, GROB D, RAHN BA, et al. Histology of the ligamentum flavum in patients with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 1999;8(4):323-328.
[8] CHEN HB, CHEN M, PENG HH, et al. Relationship between the benefits of paraspinal mapping and diffusion tensor imaging and the increase of decompression levels determined by conventional magnetic resonance imaging in degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):23.
[9] KIM BJ, HUR JW, PARK JS, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human ligamentum flavum cells treated with tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(3):428-435.
[10] OH IS, HA KY.Matrix metalloproteinase-3 on ligamentum flavum in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(16):E552-E557.
[11] PARK JB, KONG CG, SUHL KH, et al.The increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases associated with elastin degradation and fibrosis of the ligamentum flavum in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis.Clin Orthop Surg. 2009;1(2):81-89.
[12] YABE Y, HAGIWARA Y, ANDO A, et al. Chondrogenic and fibrotic process in the ligamentum flavum of patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis. Spine.2015;40(7):429-435.
[13] LAKEMEIER S, SCHOFER MD, FOLTZ L, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 [alpha], vascular endothelial growth factor, and matrix metalloproteinases 1, 3 and 9 in hypertrophied ligamentum flavum. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(7):400-406.
[14] SAIRYO K, BIYANI A, GOEL VK , et al. Lumbar Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy Is Due to Accumulation of Inflammation-Related Scar Tissue. Spine. 2007;32(11):E340-E347.
[15] NAKAMURA T, OKADA T, ENDO M, et al. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 promotes inflammatory conditions in the ligamentum flavum in the pathogenesis of lumbar spinal canal stenosis by activating interleukin-6 expression. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(9):2001-2009.
[16] CHAO YH, TSUANG YH, SUN JS, et al. Centrifugal force in duces human ligamentum flavum fibroblasts inflammation through activation of JNK and p38 pathways. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(7):382-389.
[17] PARK JO, LEE BH, KANG YM, et al. Inflammatory cytokines induce fibrosis and ossification of human ligamentum flavum cells. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(1):E6-12.
[18] KANG YM, SUK KS, LEE BH, et al. Herniated intervertebral disk induces hypertrophy and ossification of ligamentum flavum. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(7):382-389.
[19] SHAFAQ N, SUZUKI A, TERAI H, et al. Cellularity and cartilage matrix increased in hypertrophied ligamentum flavum: histopathological analysis focusing on the mechanical stress and bone morphogenetic protein signaling. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(2):107-115.
[20] TABATA M, KADOMATSU T, FUKUHARA S, et al. Angiopoietinlike protein 2 promotes chronic adipose tissue inflammation andobesity-related systemic insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009;10(3):178-188.
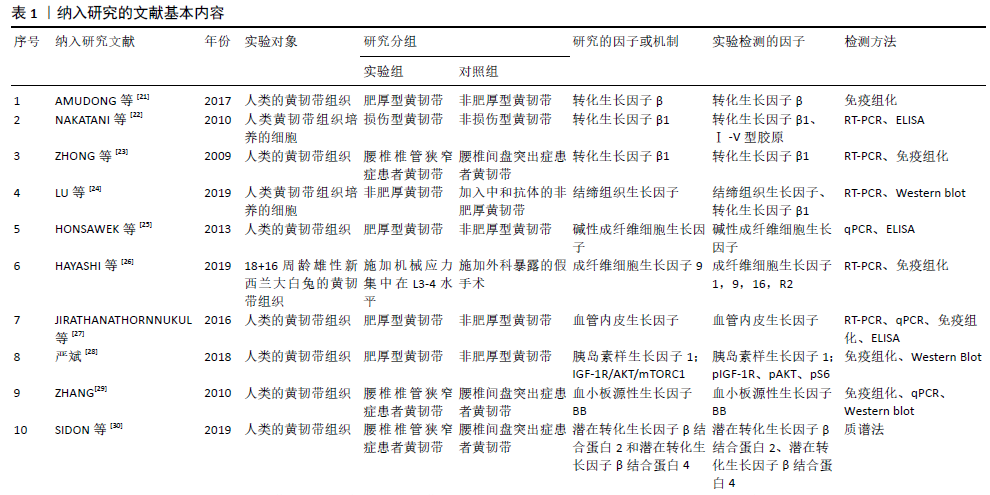
[21] AMUDONG A, MUHEREMU A, ABUDOUREXITI T. Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum and expression of transforming growth factor beta.J Int Med Res. 2017;45(6):2036-2041.
[22] NAKATANI T, MARUI T T, DOITA M, et al. Mechanical stretching force promotes collagen synthesis by cultured cells from human ligamentum flavum via transforming growth factor-beta1.J Orthop Res. 2002;20(6):1380-1386.
[23] ZHONG ZM, CHEN JT. Overexpression of transforming growth factor-beta1 in degenerative ligamentum flavum. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009;29(2):316-318.
[24] LU C, LIU Z, ZHANG H, et al. Proliferation effect of ligamentum flavum cells induced by transforming growth factor β1 and its effect on connective tissue growth factor.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019;33(7):883-888.
[25] HONSAWEK S, POONPUKDEE J, CHALERMPANPIPAT C, et al.Hypertrophy of the ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis is associated with increased bFGF expression. Int Orthop. 2013;37(7):1387-1392.
[26] HAYASHI K, SUZUKI A, TERAI H, et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 Is Upregulated Upon Intervertebral Mechanical Stress-Induced Ligamentum Flavum Hypertrophy in a Rabbit Model.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(20):E1172-E1180.
[27] JIRATHANATHORNNUKUL N, LIMTHONGKUL W, YINGSAKMONGKOL W, et al. Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with hypertrophic ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis.J Investig Med. 2016;64(4):882-887.
[28] 严斌. IGF-1通过激活IGF-1R/AKT/mTORC1信号通路促进黄韧带增生肥厚[D].广州:南方医科大学,2018.
[29] ZHANG Y, CHEN J, ZHONG ZM, et al. Is Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB Expression Proportional to Fibrosis in the Hypertrophied Lumber Ligamentum Flavum?. Spine.2010;35(25):E1479-E1486.
[30] SIDON E, SHEMESH SS, MOR-YOSSEF MOLDOVAN L, et al. Molecular profile of ultrastructure changes of the ligamentum flavum related to lumbar spinal canal stenosis. J Cell Biochem. 2019 Mar 1.doi: 10.1002/jcb.28451.
[31] 曹延林. p38 MAPK通路介导TGF-β1/CTGF调控人黄韧带肥厚增生的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2015.
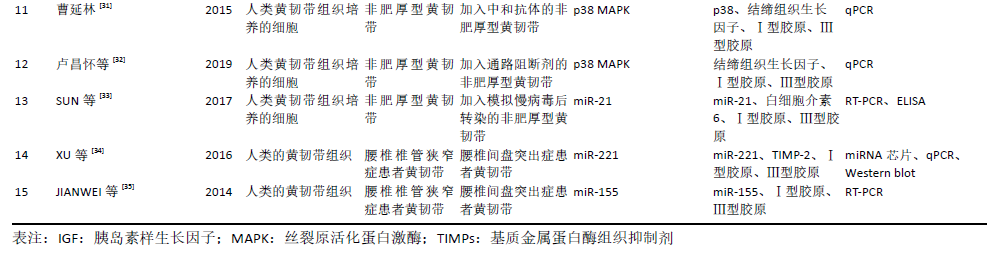
[32] 卢昌怀,刘志军,张宏波,等.p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路介导TGF-β1/结缔组织生长因子调控人腰椎黄韧带增生肥厚的机制研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(6):730-735.
[33] SUN C, TIAN J, LIU X, et al. MiR-21 promotes fibrosis and hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar spinal canal stenosis by activating IL-6 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490(3):1106-1111.
[34] XU YQ, ZHANG ZH, ZHENG YF, et al. MicroRNA-221 Regulates Hypertrophy of Ligamentum Flavum in Lumbar Spinal Stenosis by Targeting TIMP-2.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(4):275-282.
[35] JIANWEI C, ZUDE L, GUIBIN Z, et al. Hypertrophy of Ligamentum Flavum in Lumbar Spine Stenosis Is Associated with Increased miR-155 Level. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:786543.
[36] HAN JJ, TAN HF, FENG C, et al. Data on cell spread area and directional contraction in human umbilicalvein endothelial cells on fibronectin and on collagen type I-coated micro-posts. Data Brief. 2016;6:803-810.
[37] POORMASJEDI‐MEIBOD MS, SALIMI ELIZEI S, LEUNG V, et al.Kynurenine Modulates MMP‐1 and Type‐I Collagen Expression Via Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation in Dermal Fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(12):2749-2760.
[38] FABIAN M R, SONENBERG N, FILIPOWICZ W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79: 351-379.
|