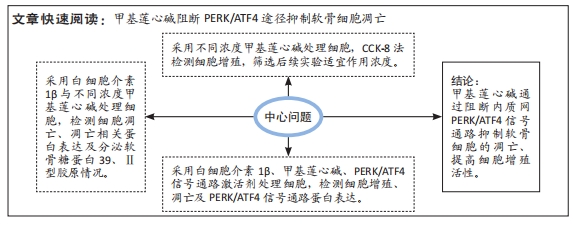
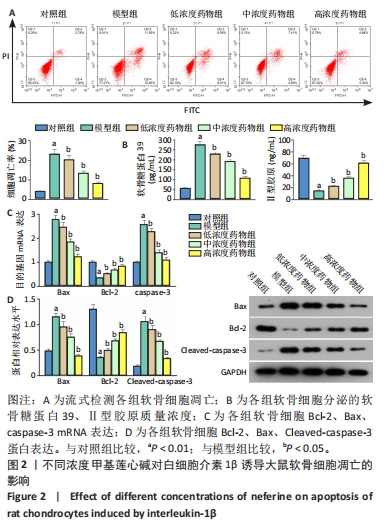
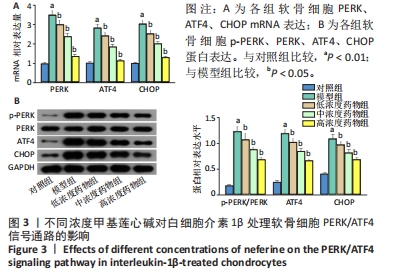
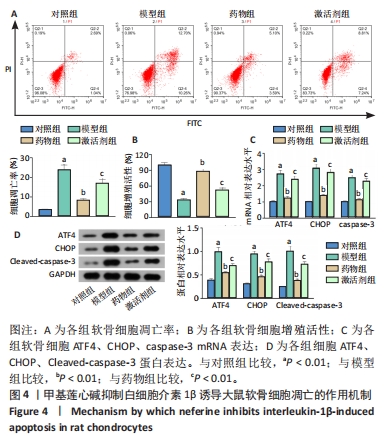
[1] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6): 568-578.
[2] 孟纬.膝骨关节炎的个体化治疗[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32): 5216-5220.
[3] 袁芳,何晓瑾,邱亦江,等.骨关节炎的软骨细胞凋亡机制[J].实用医学杂志,2015,31(4):666-668.
[4] TENG C, WU J, ZHANG Z, et al. Fucoxanthin ameliorates endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibits apoptosis and alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats by upregulating Sirt1. Phytother Res. 2023. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8057.
[5] LIU Q, GUO S, HUANG Y, et al. Inhibition of TRPA1 Ameliorates Periodontitis by Reducing Periodontal Ligament Cell Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via PERK/eIF2α/ATF-4/CHOP Signal Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022: 4107915.doi: 10.1155/2022/4107915.
[6] FAN P, JORDAN VC. PERK, Beyond an Unfolded Protein Response Sensor in Estrogen-Induced Apoptosis in Endocrine-Resistant Breast Cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2022;20(2):193-201.
[7] 胡斌.塞来昔布联合富血小板血浆对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨组织形态学的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(14):2017-2020.
[8] YANG CC, HUNG YL, KO WC, et al. Effect of neferine on DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis in HaCaT cells and BALB/c mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15): 8237.
[9] LI S, ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Neferine exerts ferroptosis-inducing effect and antitumor effect on thyroid cancer through Nrf2/HO-1/NQO1 inhibition. J Oncol. 2022;2022:7933775.
[10] QI Z, WANG R, LIAO R, et al. Neferine ameliorates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction through anti-apoptotic and antioxidative effects by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:706251.
[11] JAHAN N, CHOWDHURY A, LI T, et al. Neferine improves oxidative stress and apoptosis in benign prostate hyperplasia via Nrf2-ARE pathway. Redox Rep. 2021;26(1):1-9.
[12] WU XL, DENG MZ, GAO ZJ, et al. Neferine alleviates memory and cognitive dysfunction in diabetic mice through modulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and alleviation of endoplasmic-reticulum stress. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106559.
[13] NI B, HUANG X, XI Y, et al. Neferine Inhibits Expression of Inflammatory Mediators and Matrix Degrading Enzymes in IL-1β-Treated Rat Chondrocytes via Suppressing MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Inflammation. 2020; 43(4):1209-1221.
[14] STOCKWELL SR, PLATT G, BARRIE SE, et al. Mechanism-based screen for G1/S checkpoint activators identifies a selective activator of EIF2AK3/PERK signalling. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e28568.
[15] WHITTAKER JL, TRUONG LK, DHIMAN K, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2020: rehabilitation and outcomes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(2): 190-207.
[16] 梅轶芳.中国骨关节炎流行病学研究现状及规范[J].中国实用内科杂志, 2019,39(8): 663-665.
[17] MOLNAR V, MATIŠIĆ V, KODVANJ I, et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9208.
[18] ZHENG L, ZHANG Z, SHENG P, et al. The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66: 101249.
[19] MAO L, WU W, WANG M, et al. Targeted treatment for osteoarthritis: drugs and delivery system. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):1861-1876.
[20] SENGKING J, OKA C, YAWOOT N, et al. Protective Effect of Neferine in Permanent Cerebral Ischemic Rats via Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Apoptotic Mechanisms. Neurotox Res. 2022;40(5):1348-1359.
[21] NI B, HUANG X, XI Y, et al. Neferine inhibits expression of inflammatory mediators and matrix degrading enzymes in IL-1β-treated rat chondrocytes via suppressing MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Inflammation. 2020; 43(4):1209-1221.
[22] LEE HR, JEONG YJ, LEE JW, et al. Tannic acid, an IL-1β-direct binding compound, ameliorates IL-1β-induced inflammation and cartilage degradation by hindering IL-1β-IL-1R1 interaction. PLoS One. 2023;18(4):e0281834.
[23] 戴宇祥,姜宏,俞鹏飞.中药复方介导p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路在腰椎间盘突出症中作用的研究现状[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2020,36(2): 213-216.
[24] 王为,汤翔宇,易智谦,等.骨关节炎诱导软骨细胞凋亡和细胞外基质降解的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(20): 3133-3140.
[25] LIU XJ, WANG YQ, SHANG SQ, et al. TMT induces apoptosis and necroptosis in mouse kidneys through oxidative stress-induced activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022;230:113167.
[26] ZHANG Y, LIU W, LIU Z, et al. Daurisoline attenuates H2O2-induced chondrocyte autophagy by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):248.
[27] 郭秀珍,高斌礼,郭文,等.LncRNA FGD5-AS1靶向miR-103a-3p对IL-1β诱导的关节软骨细胞凋亡的机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(6): 832-837.
[28] CONNOR JR, DODDS RA, EMERY JG, et al. Human cartilage glycoprotein 39 (HC gp-39) mRNA expression in adult and fetal chondrocytes, osteoblasts and osteocytes by in-situ hybridization. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2000;8(2):87-95.
[29] FAN A, WU G, WANG J, et al. Inhibition of fibroblast activation protein ameliorates cartilage matrix degradation and osteoarthritis progression. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):3.
[30] MA X, ZHANG Z, SHEN M, et al. Changes of type II collagenase biomarkers on IL-1β-induced rat articular chondrocytes. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(6):582.
[31] YU H, LIU Y, YANG X, et al. The anti-inflammation effect of strontium ranelate on rat chondrocytes with or without IL-1β in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 2022;23(3):208.
[32] WISEMAN RL, MESGARZADEH JS, HENDERSHOT LM. Reshaping endoplasmic reticulum quality control through the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell. 2022;82(8):1477-1491.
[33] MERIGHI A, LOSSI L. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling and Neuronal Cell Death. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(23):15186.
[34] SHI M, CHAI Y, ZHANG J, et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Associated Neuronal Death and Innate Immune Response in Neurological Diseases. Front Immunol. 2022;12:794580.
[35] PARK KM, PARK JY, PYO J, et al. Induction of DR5-Dependent Apoptosis by PGA2 through ATF4-CHOP Pathway. Molecules. 2022;27(12):3804.
[36] RONG K, XIA QQ, WU XH, et al. Articular Cartilage Stem Cells Influence the Postoperative Repair of Hip Replacement by Regulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Chondrocytes via PERK Pathway. Orthop Surg. 2020; 12(2):609-616.
|