中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (34): 5473-5479.doi: 10.12307/2024.721
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
艾灸抑制NLRP3/Caspase-1通路介导的细胞焦亡减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤
于燕艳1,刘 娟2 ,杨 越1,王千慧1,李 姗1,蒋 洁1
- 1新疆医科大学中医学院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2新疆医科大学第四临床医学院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054
Moxibustion inhibits NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway mediated cell pyroptosis and alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
Yu Yanyan1, Liu Juan2, Yang Yue1, Wang Qianhui1, Li Shan1, Jiang Jie1
- 1College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Fourth Clinical Medical College of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
脑缺血再灌注损伤:脑缺血恢复血液供应后,脑组织会产生一系列应激反应进一步加重脑组织损伤。细胞焦亡:又称细胞炎性坏死,是一种程序性细胞死亡,表现为细胞不断膨大直至细胞膜破裂,导致细胞内容物大量释放进而激活强烈的炎症反应。细胞焦亡是机体一种重要的天然免疫反应,在神经系统疾病中发挥重要作用。
背景:研究发现,艾灸能抑制脑缺血/再灌注损伤大鼠血清中的炎症因子,对抗氧化应激,抑制细胞凋亡,有效减轻脑缺血/再灌注损伤。
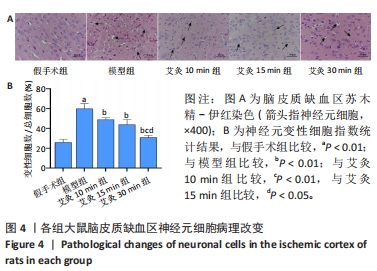
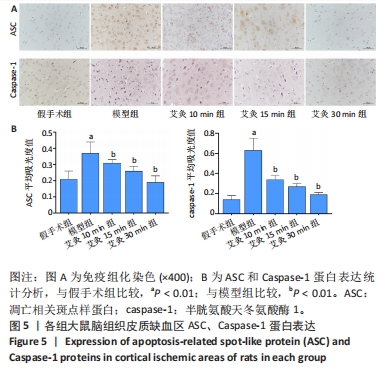
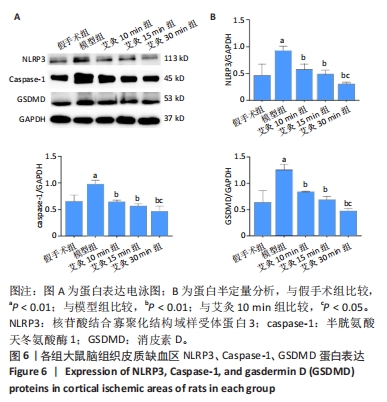
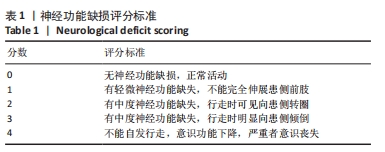
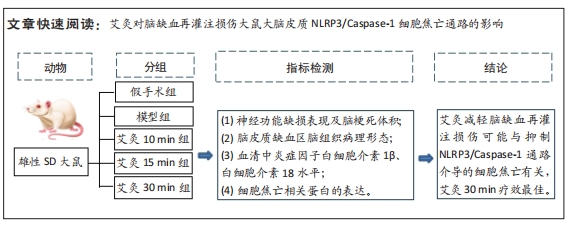
目的:观察艾灸干预不同时间后脑缺血/再灌注损伤模型大鼠核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白3(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3,NLRP3)炎性小体、半胱氨酸天冬氨酸酶1(cysteine aspartase,caspase-1)、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白(ASC)、消皮素D(GSDMD)及白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18表达的变化,并探讨其作用机制。方法:SD大鼠随机分为假手术组9只和造模组36只,造模组制备大脑中动脉栓塞大鼠模型。造模成功后将造模组大鼠进一步分为模型组、艾灸10 min组、艾灸15 min组、艾灸30 min组,每组9只。艾灸10 min、15 min和30 min组大鼠分别给予艾灸悬灸“百会、大椎、足三里”穴,均干预1次/d,共干预7 d。采用LONGA法评估大鼠神经功能缺损情况,TTC法观察脑组织梗死情况,苏木精-伊红染色观察脑组织病理改变,ELISA法检测血清中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18水平,免疫组织化学法和蛋白免疫印迹法测定脑皮质缺血区组织NLRP3、caspase-1、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白、消皮素D蛋白的表达。
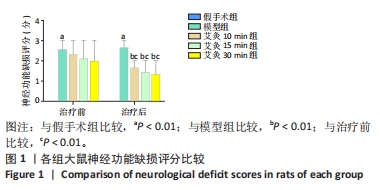
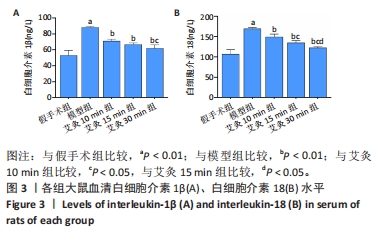
结果与结论:①与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠神经功能缺损评分显著升高(P < 0.01),与模型组比较,艾灸各组大鼠神经功能缺损评分明显降低(P < 0.01);②与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠脑梗死体积明显增大(P < 0.01),与模型组比较,艾灸各组大鼠脑梗死体积明显减少(P < 0.01),艾灸30 min组脑梗死体积最小(P < 0.05);③与模型组比较,艾灸各组大鼠血清白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18水平下降(P < 0.01),与艾灸10 min组比较,艾灸30 min组血清中的炎症因子水平明显下降(P < 0.05);④与模型组比较,艾灸各组大鼠皮质缺血区NLRP3、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白、Caspase-1、消皮素D蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.01),艾灸30 min组蛋白表达明显低于艾灸10 min组和艾灸15 min组(P < 0.05);⑤结论:艾灸百会、大椎、足三里可减轻脑缺血/再灌注损伤,其中艾灸30 min疗效最佳,其机制可能与抑制NLRP3/Caspase-1通路介导的细胞焦亡有关。
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-7160-608X (于燕艳)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: