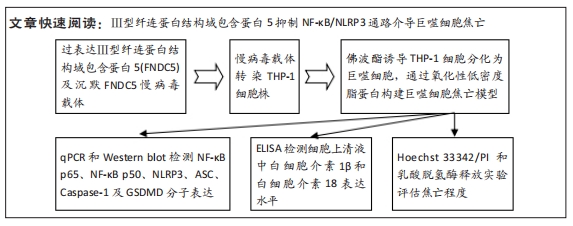
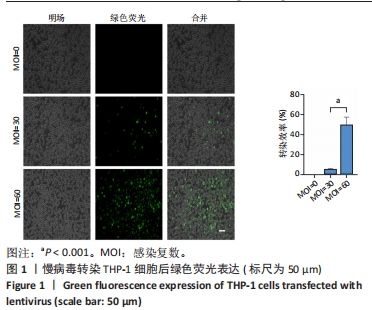
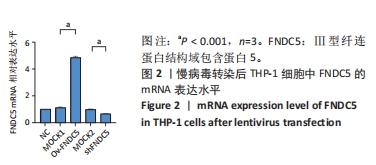
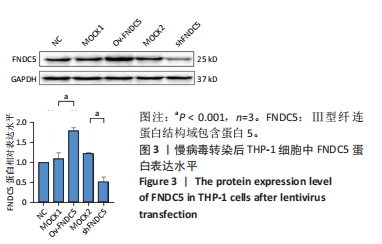
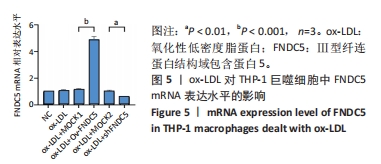
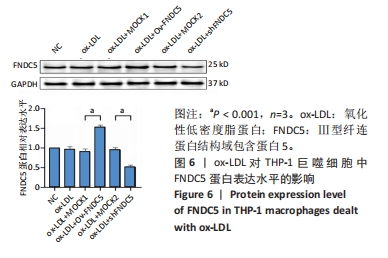
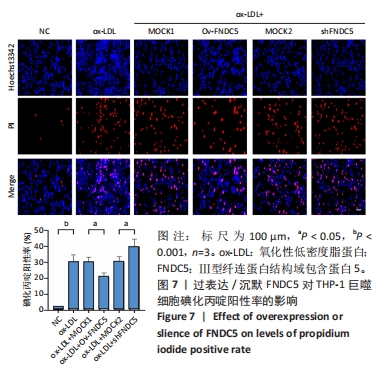
[1] 马丽媛,王增武,樊静,等.《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2021》概要[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2022,30(7):481-496.
[2] BARQUERA S, PEDROZA-TOBÍAS A, MEDINA C, et al. Global Overview of the Epidemiology of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Arch Med Res. 2015;46(5):328-338.
[3] HANSSON GK, HERMANSSON A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. 2011;12(3):204-212.
[4] XU YJ, ZHENG L, HU YW, et al. Pyroptosis and its relationship to atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;476:28-37.
[5] QIAN Z, ZHAO Y, WAN C, et al. Pyroptosis in the Initiation and Progression of Atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:652963.
[6] FENG X, CHEN W, NI X, et al. Metformin, Macrophage Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:682853.
[7] FU J, LI F, TANG Y, et al. The Emerging Role of Irisin in Cardiovascular Diseases. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(20):e022453.
[8] CHENG ZB, HUANG L, XIAO X, et al. Irisin in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2021;522: 158-166.
[9] SONG H, WU F, ZHANG Y, et al. Irisin promotes human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation through the ERK signaling pathway and partly suppresses high glucose-induced apoptosis. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e110273.
[10] ZHANG M, XU Y, JIANG L. Irisin attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein impaired angiogenesis through AKT/mTOR/S6K1/Nrf2 pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):18951-18962.
[11] YE L, XU M, HU M, et al. TRPV4 is involved in irisin-induced endothelium-dependent vasodilation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495(1):41-45.
[12] HUANG J, WANG S, XU F, et al. Exercise training with dietary restriction enhances circulating irisin level associated with increasing endothelial progenitor cell number in obese adults: an intervention study. PeerJ. 2017;5:e3669.
[13] MAZUR-BIALY AI, POCHEĆ E, ZARAWSKI M. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Irisin, Mediator of Physical Activity, Are Connected with TLR4/MyD88 Signaling Pathway Activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4):701.
[14] YIN C, HU W, WANG M, et al. Irisin as a mediator between obesity and vascular inflammation in Chinese children and adolescents. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020; 30(2):320-329.
[15] LI K, CHEN J, WANG C, et al. Irisin ameliorates nicotine-mediated atherosclerosis via inhibition of the PI3K pathway. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(9):805.
[16] DONG J, DONG Y, DONG Y, et al. Inhibition of myostatin in mice improves insulin sensitivity via irisin-mediated cross talk between muscle and adipose tissues. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016;40(3):434-442.
[17] XIONG X, LU L, WANG Z, et al. Irisin attenuates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction by attenuating inflammation-induced pyroptosis through a mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase-dependent mechanism. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;152:113199.
[18] LI Q, ZHANG M, ZHAO Y, et al. Irisin Protects Against LPS-Stressed Cardiac Damage Through Inhibiting Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Pyroptosis. Shock. 2021;56(6):1009-1018.
[19] COTO E, REGUERO JR, AVANZAS P, et al. Gene variants in the NF-KB pathway (NFKB1, NFKBIA, NFKBIZ) and risk for early-onset coronary artery disease. Immunol Lett. 2019; 208:39-43.
[20] ZENG W, WU D, SUN Y, et al. The selective NLRP3 inhibitor MCC950 hinders atherosclerosis development by attenuating inflammation and pyroptosis in macrophages. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):19305.
[21] BOSTRÖM P, WU J, JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012;481(7382): 463-468.
[22] ZHANG H, WU X, LIANG J, et al. Irisin, an exercise-induced bioactive peptide beneficial for health promotion during aging process. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;80:101680.
[23] PERAKAKIS N, TRIANTAFYLLOU GA, FERNÁNDEZ-REAL JM, et al. Physiology and role of irisin in glucose homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(6):324-337.
[24] 何青松,刘大男,谭娟.冠心病患者血清鸢尾素水平变化观察[J].山东医药,2020, 60(6):69-71.
[25] 何青松,刘大男,谭娟.鸢尾素对高脂饮食诱导ApoE(-/-)小鼠动脉粥样硬化形成的影响及其机制[J].山东医药,2020,60(22):39-43.
[26] PAN JA, ZHANG H, YU Q, et al. Association of Circulating Irisin Levels and the Characteristics and Prognosis of Coronary Artery Disease. Am J Med Sci. 2021;362(1): 63-71.
[27] ANASTASILAKIS AD, KOULAXIS D, KEFALA N, et al. Circulating irisin levels are lower in patients with either stable coronary artery disease (CAD) or myocardial infarction (MI) versus healthy controls, whereas follistatin and activin A levels are higher and can discriminate MI from CAD with similar to CK-MB accuracy. Metabolism. 2017;73:1-8.
[28] EFE TH, AÇAR B, ERTEM AG, et al. Serum Irisin Level Can Predict the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Stable Angina. Korean Circ J. 2017;47(1):44-49.
[29] ZHANG Y, MU Q, ZHOU Z, et al. Protective Effect of Irisin on Atherosclerosis via Suppressing Oxidized Low Density Lipoprotein Induced Vascular Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0158038.
[30] REMUZGO-MARTÍNEZ S, RUEDA-GOTOR J, PULITO-CUETO V, et al. Irisin as a Novel Biomarker of Subclinical Atherosclerosis, Cardiovascular Risk and Severe Disease in Axial Spondyloarthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:894171.
[31] CARMONA-MAURICI J, ROSA A, AZCONA-GRANADA N, et al. Irisin as a Novel Biomarker of Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Severe Obesity. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):8171.
[32] LU J, XIANG G, LIU M, et al. Irisin protects against endothelial injury and ameliorates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-Null diabetic mice. Atherosclerosis. 2015;243(2):438-448.
[33] WU F, SONG H, ZHANG Y, et al. Irisin Induces Angiogenesis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells In Vitro and in Zebrafish Embryos In Vivo via Activation of the ERK Signaling Pathway. PLoS One. 2015;10(8):e0134662.
[34] ZHU G, WANG J, SONG M, et al. Irisin Increased the Number and Improved the Function of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Diabetes Mellitus Mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2016; 68(1):67-73.
[35] YU P, ZHANG X, LIU N, et al. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):128.
[36] KELLEY N, JELTEMA D, DUAN Y, et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 6;20(13):3328.
[37] VAN OPDENBOSCH N, LAMKANFI M. Caspases in Cell Death, Inflammation, and Disease. Immunity. 2019;50(6):1352-1364.
[38] KOVACS SB, MIAO EA. Gasdermins: Effectors of Pyroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2017;27(9): 673-684.
[39] SEN R, BALTIMORE D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986;46(5):705-716.
[40] SEN R, BALTIMORE D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986;47(6):921-928.
[41] OECKINGHAUS A, GHOSH S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009;1(4):a000034.
[42] HAYDEN MS, GHOSH S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008;132(3):344-362.
[43] RITCHIE ME. Nuclear factor-kappaB is selectively and markedly activated in humans with unstable angina pectoris. Circulation. 1998;98(17):1707-1713.
[44] WILSON SH, BEST PJ, EDWARDS WD, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB immunoreactivity is present in human coronary plaque and enhanced in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Atherosclerosis. 2002;160(1):147-153.
[45] HAJRA L, EVANS AI, CHEN M, et al. The NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway in aortic endothelial cells is primed for activation in regions predisposed to atherosclerotic lesion formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(16):9052-9057.
[46] TANG YL, JIANG JH, WANG S, et al. TLR4/NF-κB signaling contributes to chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. PLoS One. 2015;10(4): e0123685.
[47] CHEN M, LI W, ZHANG Y, et al. MicroRNA-20a protects human aortic endothelial cells from Ox-LDL-induced inflammation through targeting TLR4 and TXNIP signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:191-197.
[48] ZANG YH, CHEN D, ZHOU B, et al. FNDC5 inhibits foam cell formation and monocyte adhesion in vascular smooth muscle cells via suppressing NFκB-mediated NLRP3 upregulation. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019;121:106579.
[49] XING Y, YAO X, LI H, et al. Cutting Edge: TRAF6 Mediates TLR/IL-1R Signaling-Induced Nontranscriptional Priming of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. J Immunol. 2017;199(5):1561-1566.
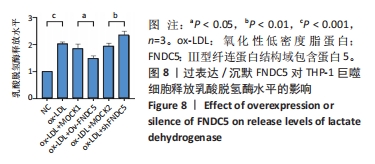
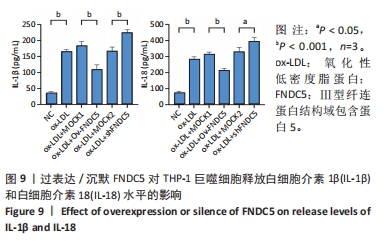
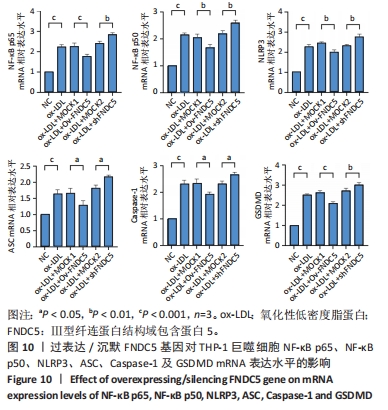
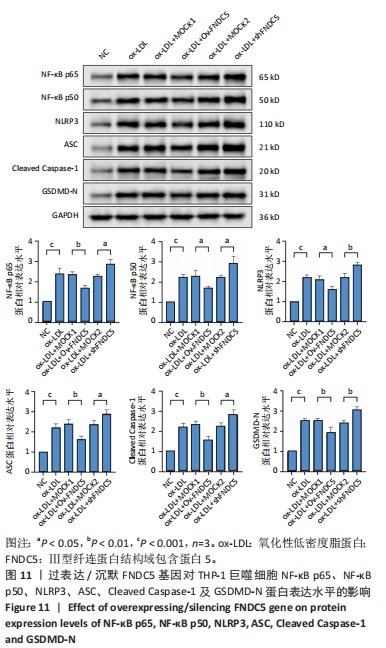
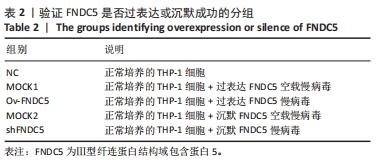
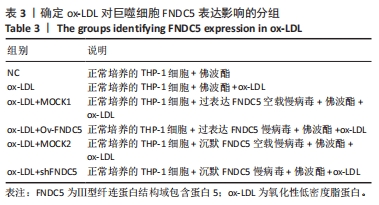
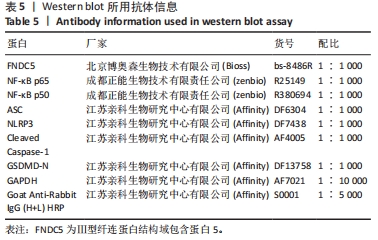
[50] 王尧.FNDC5基因过表达或沉默对动脉粥样硬化斑块形成中焦亡功能因子的影响及机制研究[D].贵阳:贵州医科大学,2022.
[51] MAZUR-BIALY AI. Irisin acts as a regulator of macrophages host defense. Life Sci. 2017; 176:21-25.
|