中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 2036-2041.doi: 10.12307/2024.141
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
过表达miR-378a促进巨噬细胞向M2极化且抑制巨噬细胞向M1极化
杨 泉1,2,何惠宇2,3,王思凡2,3,吕尚毅2,3,周琦琪2,3,韩祥祯2,3
- 新疆医科大学第一附属医院(附属口腔医院),1口腔急诊综合科,3口腔修复科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2新疆维吾尔自治区口腔医学研究所,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054
Overexpression of miR-378a promotes macrophage M2 polarization and inhibits M1 polarization
Yang Quan1, 2, He Huiyu2, 3, Wang Sifan2, 3, Lyu Shangyi2, 3, Zhou Qiqi2, 3, Han Xiangzhen2, 3
- 1Department of Oral Emergency Medicine,3Department of Prosthodontics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Xinjiang Institute of Stomatology, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:

文题释义:
巨噬细胞极化:巨噬细胞首先被极化为促炎M1表型,M1巨噬细胞通过增强吞噬作用以及增加促炎细胞因子的产生和释放,促进先天免疫,以清除损伤部位产生的组织碎片以及来自体外的病原微生物。随后,巨噬细胞表型改变,形成以抗炎反应为主的M2表型并促进组织重塑和修复。慢病毒:由于慢病毒载体具有许多吸引人的特点,已成为基因治疗中体外转基因传递的首选工具之一。慢病毒载体基因组一旦融入宿主细胞基因组,就可以实现长期稳定的转基因表达,并且慢病毒载体的遗传毒性更低,已成为转基因传递的首选载体。
背景:M2型巨噬细胞具有降低炎症因子及促进组织愈合的功能,因此,如何调节巨噬细胞M2极化是近年来研究的热点,研究发现部分miRNAs具有此功能。
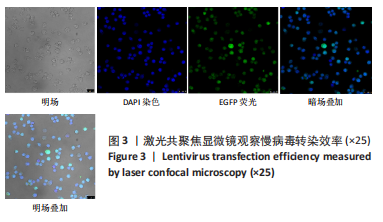
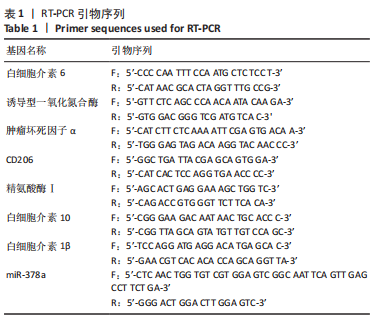
目的:探讨miR-378a对Raw264.7巨噬细胞系极化的影响。方法:首先使用脂多糖和干扰素γ协同诱导巨噬细胞M1极化,使用白细胞介素4诱导巨噬细胞M2极化,qRT-PCR检测各型细胞中内源性miR-378a的表达,验证miR-378a是否参与巨噬细胞的极化。通过慢病毒载体将miR-378a转染至巨噬细胞,筛选出miR-378a稳定表达的细胞系,使用脂多糖和干扰素γ协同诱导巨噬细胞M1极化,使用白细胞介素4诱导巨噬细胞M2极化,ELISA检测巨噬细胞培养基上清液中M1/M2极化相关细胞因子水平,qRT-PCR检测M1/M2型巨噬细胞极化特征及相关细胞因子的mRNA表达。
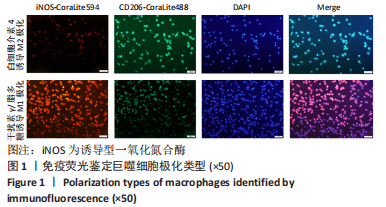
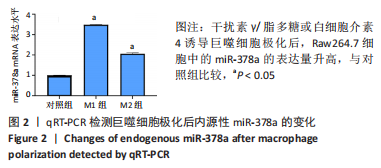
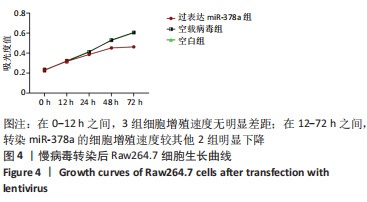
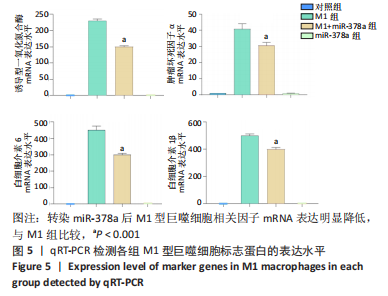
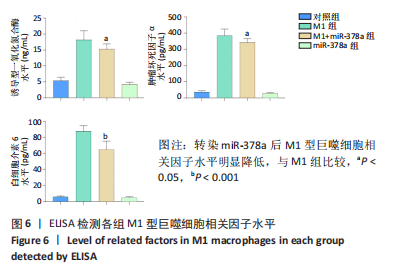
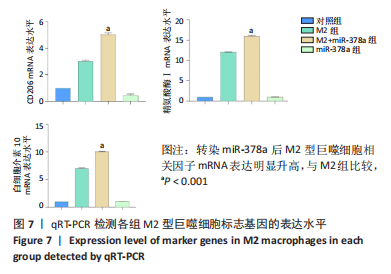
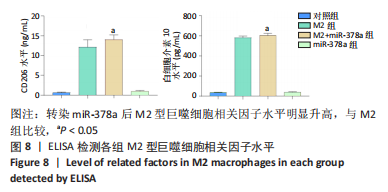
结果与结论:①诱导巨噬细胞极化后,各组Raw264.7细胞中内源性miR-378a的表达量均升高;②与未转染组比较,转染miR-378a组诱导巨噬细胞M1极化后促炎性细胞因子诱导型一氧化氮合酶、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β表达显著降低(P < 0.05),细胞上清液中诱导型一氧化氮合酶、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6水平也明显降低(P < 0.05);③与未转染组比较,转染miR-378a组诱导巨噬细胞M2极化后CD206、白细胞介素10、精氨酸酶Ⅰ的表达显著升高(P < 0.05),细胞上清液中CD206、白细胞介素10水平也明显升高(P < 0.05);④结果表明:过表达miR-378a促进巨噬细胞向M2极化且抑制巨噬细胞向M1极化。
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-5367-1725 (杨泉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: