中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (10): 1613-1619.doi: 10.12307/2024.266
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
微弧氧化对金属植入物抗菌和抗炎能力的调节效应
于德浩1,宁凤婷1,杜易朗1,王业元1,白 冰2
- 1中国医科大学口腔医学院,辽宁省沈阳市 110002;2中国医科大学附属口腔医院修复二科,辽宁省口腔医学研究所修复学教研室,辽宁省沈阳市 110001
-
收稿日期:2023-03-10接受日期:2023-04-28出版日期:2024-04-08发布日期:2023-08-21 -
通讯作者:白冰,副教授,副主任医师,中国医科大学附属口腔医院修复二科,辽宁省口腔医学研究所修复学教研室,辽宁省沈阳市 110001 -
作者简介:于德浩,男,2001年生,天津市人,汉族,中国医科大学口腔医学专业本科在读。 宁凤婷,女,2001年生,安徽省合肥市人,汉族,中国医科大学口腔医学专业本科在读。 -
基金资助:东北大学-中国医科大学国家级大学大学生创新项目(220268),项目参与者:白冰
Regulatory effects of micro-arc oxidation on anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties of metal implants
Yu Dehao1, Ning Fengting1, Du Yilang1, Wang Yeyuan1, Bai Bing2
- 1School of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China; 2Second Department of Prosthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, China Medical University; Department of Prosthodontics, Liaoning Institute of Stomatology, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-10Accepted:2023-04-28Online:2024-04-08Published:2023-08-21 -
Contact:Bai Bing, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, Second Department of Prosthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, China Medical University; Department of Prosthodontics, Liaoning Institute of Stomatology, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Yu Dehao, School of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China Ning Fengting, School of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:Northeastern University-China Medical University National College Student Innovation Program, No. 220268 (to BB)
摘要:
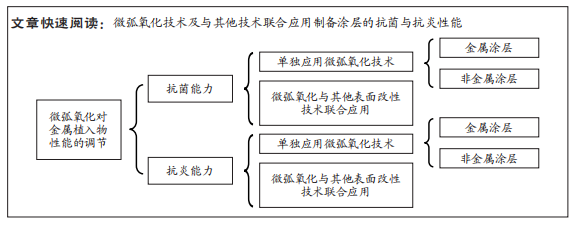
文题释义:
微弧氧化:又称等离子体电解质氧化、阳极火花沉积,是一种通过调节电解液成分和电参数,在电弧放电产生的瞬时高温高压作用下,于铝、镁、钛等阀金属及其合金表面形成致密陶瓷氧化膜的表面改性技术。生物医用材料:是以医疗为目的,用于与组织接触以形成功能的无生命的材料,是用来对生物体进行诊断、治疗、修复或替换其病损组织、器官或增进其功能的一类高技术新材料。
背景:微弧氧化技术能够有效地将生物活性元素掺杂到金属表面,提高生物医用金属材料的抗菌性能和抗炎性能,因此该技术已成为生物医用材料的研究热点之一。
目的:重点介绍微弧氧化技术及其与其他表面改性技术联合应用制备植入物表面涂层的抗菌性能和抗炎性能。方法:以“微弧氧化,抗炎性能,抗菌性能,金属植入物”为中文检索词检索中国知网和万方数据库,以“micro-arc oxidation、antibacterial properties,anti-inflammatory properties,metal implants”为英文检索词检索PubMed数据库,检索时间范围为1996年1月至2022年12月,根据纳入和排除标准初筛后,最后保留89篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:微弧氧化陶瓷层提高了钛、镁等合金的抗菌性能和抗炎性能,联合其他表面改性技术有效解决了孔隙对合金表面性能的影响,进一步提高了氧化膜的生物学性能,在骨科和牙科等领域有着广泛的应用前景。目前研究多局限于金属涂层,而且大部分研究集中在银、铜等具有良好抗菌性能的金属元素,仅有少数研究提到氧化石墨烯、羟基磷灰石和壳聚糖等非金属涂层,未来可以对无机物涂层和高分子涂层进行广泛研究,也可采取更多种不同生物活性元素的组合来提高抗菌性能。目前微弧氧化技术所制备的植入体涂层炎症研究多局限于免疫系统,且集中在巨噬细胞,而其对于中性粒细胞、血小板等的研究稀缺,未来需联合应用多种先进技术手段探究微弧氧化涂层对其他免疫细胞和炎症细胞的具体影响。
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-0619-8832(于德浩);https://orcid.org/0009-0009-5663-8381(宁凤婷)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
于德浩, 宁凤婷, 杜易朗, 王业元, 白 冰. 微弧氧化对金属植入物抗菌和抗炎能力的调节效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(10): 1613-1619.
Yu Dehao, Ning Fengting, Du Yilang, Wang Yeyuan, Bai Bing. Regulatory effects of micro-arc oxidation on anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory properties of metal implants[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1613-1619.
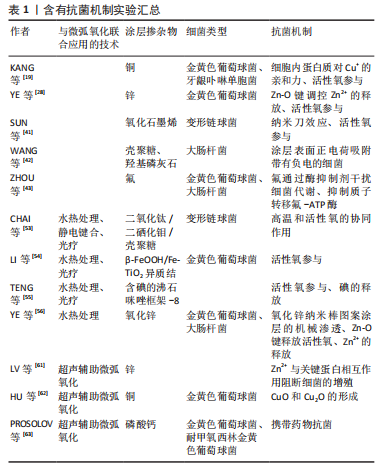
2.1.1 单独应用微弧氧化技术 钛及其合金由于其优异的机械性能和生物相容性而被广泛用于医疗植入装置(人工关节、骨固定器、脊柱固定器、牙科植入物等)[13]。细菌黏附定植于植入物表面后,能够形成细菌微菌落、分泌胞外聚合物并形成生物膜,在生物膜的保护下细菌极易在材料表面增殖,从而导致感染[14–16],这也被认为是口腔科和骨科植入手术失败的主要原因[17]。由于铜、锌和银等金属成分具备良好的抗菌性能,所以研究者经常采用微弧氧化技术将上述元素添加到材料表面涂层中。
(1)应用微弧氧化技术添加铜:铜具有很强的抗菌作用,并已被用于修饰医用钛的表面[18]。KANG等[19]采用微弧氧化在钛表面制备了掺杂不同浓度铜元素的具备火山形微孔表面形貌的二氧化钛涂层,抗菌实验表明,掺杂铜的二氧化钛涂层对金黄色葡萄球菌和牙龈卟啉单胞菌具有良好的抑菌性能,作者认为Cu+的抗菌机制是细胞内蛋白质对Cu+有较强的亲和力,这会使细菌中的重要酶和DNA失活,最终使其复制能力失效;Cu2+的抗菌机制则与活性氧的参与有关[19–21]。SHIMABUKURO等[22]在钛表面成功地制备出掺铜多孔氧化物层,含不同铜离子浓度的氧化层形貌基本相同,抗菌实验表明随着铜含量的增加,涂层表面大肠杆菌与金黄色葡萄球菌的数量显著减少,且对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用强于对大肠杆菌的抑制作用;在生理盐水中浸泡28 d后,该涂层对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌效果得到进一步增强。该作者还采用微弧氧化技术在钛表面制备了掺银/掺铜的多孔二氧化钛层,并使用大肠杆菌评估涂层的抗菌活性,结果显示在生理盐水中培养7 d后,氧化层中银和铜的浓度显著降低,28 d后仍保持少量银和铜的浓度;在生理盐水中培养28 d后,掺银二氧化钛涂层中银的化学状态从Ag2O变为金属银,该涂层的抗菌效果减弱;掺铜二氧化钛涂层中铜的化学状态一直为Cu2O,该涂层的抗菌效果保持不变,该研究表明了在设计掺银/掺铜抗菌涂层时需考虑银与铜的时间瞬变效应[23]。此外,有研究通过微弧氧化技术还可以在Ti-6Al-4V合金表面上制备含铜和磷化合物的多孔特征表面结构,当涂层表面的铜原子浓度在0.54%-0.72%范围时对白色念珠菌和大肠杆菌与基质的黏附明显减小,且涂料中Cu+/Cu2+的含量越高抗菌和杀真菌效果越好,作者认为该涂层抗菌和杀真菌性能符合标准,能够用作植入物和机体组织之间的过渡层[24]。
镁及镁合金由于可吸收、良好的生物相容性和与天然人体骨相似的机械性能等优势,在骨修复材料研发中得到越来越多的青睐。但镁及其合金的抗菌效果较差,为了改善镁合金的抗菌性能,有学者利用微弧氧化将铜掺入到镁合金表面,实验表明不同Cu2+含量的涂层对材料抗菌活性的影响不同,Cu-0.1组的抗菌活性较低,对金黄色葡萄球菌的生长抑制仅仅达到10%;Cu-0.5组和Cu-1组对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制高达50%;时间-杀菌实验曲线显示,Cu-0.5组和Cu-1组在8-24 h内能够显著抑制金黄色葡萄球菌的生长[25]。
(2)应用微弧氧化技术添加锌:锌在DNA合成、核酸代谢、生物矿化等生物功能中发挥着重要的作用,同时锌还具有优异的抗菌性能[26-27]。YE等[28]在钛表面制备了掺杂锌的双层结构镀层,该双层结构的表面层完全由包含钛、氧和锌元素的非晶态组成,其中锌以弱化Zn-O键的形式存在,随着微弧氧化电压的升高,表面非晶态锌的掺杂剂量会增加,弱化的Zn-O键可调控Zn2+的释放和活性氧的产生,作者认为该涂层的抗菌机制为:在适当电压下细胞外活性氧形成增强,导致金黄色葡萄球菌细胞壁和质膜的严重破裂,以及胞内蛋白向外泄漏;同时Zn2+释放增强,细胞外H2O2形成,导致金黄色葡萄球菌细胞内活性氧水平增强,加重了细胞内蛋白质和DNA的损伤以及磷脂和质膜的额外损伤,最终导致细菌死亡。
(3)应用微弧氧化技术添加银:银具有较强的抗菌活性,对哺乳动物的细胞毒性很小,还能够加速伤口的愈合,近年来已被用于各类医疗器械中[29-31]。有学者直接通过一步微弧氧化将银和锶掺入到多孔二氧化钛涂层中,该涂层展现了较强的短期和长期抗菌能力,抗菌实验表明,当银含量为0.58%、锶含量为1.85%时,涂层对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌率在24 h后达到了100%;在磷酸缓冲盐溶液中浸泡30 d后仍保持了相当强的抗菌性能(抗菌率达到77.60%)[32]。SHIMABUKURO等[17]通过两步微弧氧化将银和锌掺入到钛合金表面,发现其能有效杀死大肠杆菌,此涂层在生理盐水中浸泡28 d后也能保持优异的抗菌性能。ZHANG
等[33]分别采用一步法和两步法在钛表面制备了含钙/磷/银的多孔二氧化钛涂层,两种方法制备的含钙/磷/银多孔涂层的表面形貌和元素组成相似,但一步法制备的涂层中银以磷酸银的形式存在,而两步法制备的涂层中银以金属银的形式存在;将大肠杆菌在两种涂层上培养24 h后,抗菌率均在99.9%以上,但一步法制备的表面涂层具有较好的银释放曲线。此外,一步法制备的表面涂层粗糙度和亲水性得到了提高,因此具有较好的生物性能,其临床应用前景更加广阔。
(4)应用微弧氧化技术添加锰:在钛基植入物表层掺入锰被认为是制备生物活性表面的一种有前途的方法。锰既可以提高成骨活性又可以抑制细菌增殖[34],特别是针对革兰阴性大肠杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌[35]。ZHAO等[36]通过微弧氧化在钛表面制备了Mn-TiO2微孔生物涂层,体外实验表明该涂层可造成大肠杆菌收缩、细胞壁穿孔与细胞膜破裂,对大肠杆菌的增殖有抑制作用,并且抗菌能力随锰含量的增加而增加。2020年,有研究者首次在含有乙酸钙、磷酸二氢钠和乙二胺四乙酸锰二钠盐的溶液中使用一步微弧氧化技术制备了掺锰的Ca-P/TiO2复合涂层,抗菌实验表明:未掺锰涂层对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌率约为56.9%,而掺锰涂层的抗菌率(约为69.7%)明显高于未掺锰涂层[37]。
(5)应用微弧氧化技术添加铋:铋化合物不仅已成功用于治疗黏膜和真皮感染,而且被认为是磷酸钙骨水泥中的抗菌添加剂[38-39]。LIN等[40]通过微弧氧化制备了掺杂铋的二氧化钛涂层,结果表明48 h内该涂层上伴放线放线杆菌和耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的菌落数减少率分别为88%和89%,表明该涂层能够抑制伴放线放线杆菌和耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的生长。
(6)应用微弧氧化技术添加非金属:微弧氧化技术还可以将其他非金属材料掺入到涂层内部。氧化石墨烯由带有含氧基团的二维片组成,可以通过纳米刀效应和活性氧来促进抗菌活性。纳米刀效应通过切割细胞膜达到抑制微生物生长的目的。SUN等[41]将不同含量的自组装氧化石墨烯通过微弧氧化技术添加到钛表面,制备出具有诱导牙本质样矿化和预防感染能力的改性钛基牙髓封闭材料,结果表明Ti-MAO-1.0 mg/mL氧化石墨烯涂层对变形链球菌的抗菌率为(90.81±4.02)%。
WANG等[42]采用一步微弧氧化在钛表面制备了羟基磷灰石/二氧化钛复合涂层,然后用浸涂法将壳聚糖负载在羟基磷灰石/二氧化钛表面,抗菌实验表明,大肠杆菌在1CS/MAO-1、1CS/MAO-2和1CS/MAO-3涂层上的减少率分别约为70%,85%和95%,在0.5CS/MAO-3、3CS/MAO-3和4CS/MAO-3涂层上的减少率分别约为90%,99%和100%,这表明涂层的抗菌活性随着壳聚糖负载量的增加而提高。壳聚糖的抗菌机制是壳聚糖在酸性溶液中溶解后形成的正电荷很容易吸附带负电的大肠杆菌,然后在细胞表面形成一层高分子膜来改变细胞膜的通透性,阻止营养物质向细胞的运输和生理代谢废物的排出,导致细菌的代谢紊乱,进而影响细菌的生长和繁殖。
ZHOU等[43]通过微弧氧化在钛上制备了掺杂有不同量氟的二氧化钛/磷酸钙涂层(TiCP-F1、TiCP-F6和TiCP-F9),体外抗菌实验结果显示,在第1天,TiCP-F6和TiCP-F9对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的抗菌率高达约97%;在第28天,TiCP-F6和TiCP-F9仍保持至少94%的高抗菌率;体内抗菌实验显示,在植入感染兔模型8周后,TiCP-F6和TiCP-F9涂层上的细菌数量几乎为0。作者认为氟可以通过酶抑制剂的直接作用有效干扰细菌代谢,并通过形成金属-氟络合物抑制质子移位氟-ATP酶,阻止细菌内ATP的合成和水解。
2.1.2 微弧氧化与其他表面改性技术联合应用 微弧氧化技术中的电压、时间、温度、电解液成分等因素均会影响涂层的表面形貌和成分,从而影响涂层的表面性能[44]。孔隙率高且孔隙直径大的微弧氧化膜疏松层,不仅影响微弧氧化膜的表面质量,还加快了腐蚀介质侵蚀基体的速度[45]。微弧氧化与其他表面改性技术联合应用既可以有效解决孔隙对材料表面性能的影响,还可以赋予涂层良好的抗菌活性、细胞相容性和促成骨活性,抵消元素带来的细胞毒性[44-45]。
微弧氧化与其他表面改性技术的联合应用可分为两种类型[44]:第一种是联合其他表面改性技术向微弧氧化涂层中掺入功能性元素,如水热处理、磁控溅射、浸渍涂覆等;第二种是联合其他表面改性技术改善微弧氧化涂层的物理形貌,如超声辅助微弧氧化、高能喷丸等。
(1)联合其他技术向微弧氧化涂层中掺入功能性元素:光疗包括光热治疗和光动力治疗,被认为是治疗细菌感染的有效方法[46-47]。光热治疗是依靠光热剂在近红外光照射下产生的局部高温达到破坏细菌生物膜结构、蛋白质或酶变性,从而达到杀菌目的的一种技术[48],一般应用水热处理或溶胶-凝胶方法将光热剂引入到合金表面[49]。光动力治疗是依靠光敏剂在有氧条件下吸收特定波长的光源后,可以从基态转变为激发态并能与底物作用形成自由基的能力,通过氧气与自由基结合产生活性氧来破坏细菌的DNA、蛋白质和生物膜的一种杀菌技术[50-51]。光动力治疗的组成包括3种成分:特定波长的光源(包括激光、发光二极管和卤素灯)、光敏剂(包括亚甲基蓝、甲苯胺蓝、卟啉等)和氧气[52]。
CHAI等[53]采用微弧氧化、水热处理和静电键合等复合工艺在钛表面成功制备了二氧化钛/二氧化钼/壳聚糖涂层,二氧化钼的引入显著提高了二氧化钛涂层的光热和光动力能力;通过静电键合将壳聚糖固定在二氧化钼表面,提高了二氧化钼的亲水性和生物相容性;在高温和活性氧的协同作用下,涂层在808 nm近红外光照射15 min后,体内外实验均表现出对变形链球菌的良好抗菌能力。LI 等[54]采用微弧氧化和水热处理技术在钛表面制备了β-FeOOH/Fe-TiO2异质结,异质结是两种不同半导体之间的区域,在异质结处应用光照射10 min后形成的活性氧可以在体外杀死80%的金黄色葡萄球菌。有学者通过结合使用微弧氧化和水热处理技术成功地在钛表面上制备了含碘的沸石咪唑框架-8涂层,在近红外光照射下沸石咪唑框架-8介导的活性氧氧化应激和释放的碘具有抗菌协同作用,增强了此涂层在体外和体内的抗菌功效;此涂层还支持骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化以及在大鼠胫骨髓内模型中加速了植入物表面上的新骨生长,这表明该涂层抗菌功效的改善并不会损害植入物的成骨潜力[55]。
YE等[56]采用微弧氧化和水热处理技术在钛表面制备了一种氧化锌纳米棒图案涂层,该涂层在体内外对黏附的和浮游的金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌均表现出强烈的抗菌活性,该涂层通过机械渗透(即金黄色葡萄球菌分泌的细胞外聚合物诱导细菌黏附氧化锌,驱动纳米棒刺穿细菌细胞壁)和涂层中Zn-O键释放的活性氧达到对黏附细菌的杀菌目的;另一方面,涂层释放的Zn2+对浮游细菌的杀菌作用起决定作用。
FIALHO等[57]采用微弧氧化制备了含有钙和磷的多孔Ta2O5层后,再采用直流磁控溅射的方法将锌纳米颗粒沉积到上述涂层表面,抗菌实验结果显示该涂层对浮游金黄色葡萄球菌有明显的抑制作用,且对金黄色葡萄球菌的定殖也有抑制作用。这两种技术的结合提高了材料的抗菌活性,为防止细菌的初始定殖提供了很好的指导。
AKTUG等[58]采用微弧氧化在金属锆表面包覆生物陶瓷,然后通过浸渍涂覆的方法在生物陶瓷表面覆盖抗菌的壳聚糖层,抗菌实验显示,单纯采用微弧氧化涂层对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌带宽度分别为(5.5±0.7) mm和(4.2±0.3) mm,微弧氧化+壳聚糖涂层对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌带宽度分别为(21.6±1.3) mm和(13.7±0.9) mm;微弧氧化+壳聚糖涂层对大肠杆菌的抗菌活性比微弧氧化表面高74.5%,对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌活性比微弧氧化表面高出69.3%。通过该实验数据可以推断出,微弧氧化+壳聚糖涂层对革兰阴性菌的抑菌效果比革兰阳性菌更有效。
(2)联合其他技术改善微弧氧化涂层的物理形貌:超声波的引入不仅可以提高微弧氧化的涂层厚度、使涂层分布更加均匀,还可以提高涂层与金属的结合强度以及阳离子沉积量,进一步提高了涂层表面的生物活性[59-60]。超声辅助微弧氧化被认为是生产高质量钛基骨科植入物的一种有前途的表面改性方法[61]。
LV等[61]通过超声辅助微弧氧化构建多层锌改性二氧化钛涂层,培养24 h后微弧氧化处理涂层组抗菌率为77.6%,而经超声辅助微弧氧化处理涂层的抗菌率接近90%,实验结果表明超声波能显著提高锌改性二氧化钛涂层的杀菌效果。该作者认为其抗菌机制为Zn2+能够穿透细菌膜与关键蛋白相互作用,损伤细菌的DNA,从而阻断细菌的增殖。HU等[62]利用超声辅助微弧氧化处理Ti-Cu合金增加了涂层粗糙度,改善了亲水性,抗菌实验显示,经超声辅助微弧氧化处理的Ti-Cu合金在生理盐水中浸泡20 d后仍显示出对金黄色葡萄球菌的强抗菌活性(抗菌
率≥99%),作者认为抗菌机制主要是由于CuO和Cu2O的形成。还有使用钛作为沉积基底,利用超声辅助微弧氧化方法来沉积磷酸钙基涂层,再来携带各种类型药物的实验,以万古霉素为例,带有万古霉素的超声辅助微弧氧化沉积的磷酸钙载体提取物在体外可以更有效抑制金黄色葡萄球菌和耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的生长,利用浸泡在万古霉素溶液中的涂层进行抗菌实验,结果显示耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌抑制区在涂层浸泡24 h内呈剂量依赖性增加,随后杀菌活性下降,当涂层浸泡120 h时下降为0[63]。
高能喷丸和微弧氧化技术联合应用可制备出3种多孔涂层(微弧氧化、Si-微弧氧化和Si/Cu-微弧氧化),抑菌实验结果表明,Si-微弧氧化和Si/Cu-微弧氧化涂层对金黄色葡萄球菌[抑菌率(99.1±2.3%)]和变形链球菌[抑菌率(98.7±3.5)%]的抑菌效果均优于微弧氧化涂层组,研究结果表明,Si/Cu-微弧氧化涂层具有优异的综合性能,在牙槽窝感染的即刻种植治疗中具有良好的应用前景[64]。
文章将含有抗菌机制的实验汇总,见表1。
2.2 微弧氧化技术对金属植入物抗炎能力的调节作用 生物材料的表面特性(表面形貌、粗糙度和孔隙率等)能通过影响细胞外基质蛋白的吸附影响蛋白质黏附,形成的蛋白质层可以进一步介导凝血系统、补体系统、血小板和免疫细胞的状态[65],也会影响免疫炎症细胞的进一步募集和黏附[65]。研究者可以通过更改生物材料的表面涂层来修饰支架表面物化性能,以调整促炎级联反应的启动[66],因此生物材料的表面特性在抗炎症和促伤口愈合反应中起着关键作用[65,67]。由此可知,细胞和生物材料之间的界面是决定软组织和硬组织能否成功再生的关键[65]。
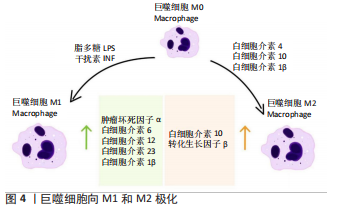
BATOOL等[65]发现生物材料植入时的初始炎症反应有助于组织的修复和再生,但持续的炎症会损害伤口的愈合反应。众多学者研究表明,急性炎症状态是由植入部位的创伤程度决定的,此时免疫炎症细胞以中性粒细胞为主,它能够分泌大量的蛋白水解酶、活性氧、促炎细胞因子和免疫调节因子,进一步激活单核细胞、巨噬细胞、未成熟树突状细胞和淋巴细胞,其中单核细胞和巨噬细胞是参与炎症演化的主要细胞[68-70]。巨噬细胞在早期炎症阶段向M1表型极化,表现为肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素12、白细胞介素23和白细胞介素1β的表达上调,这是伤口愈合过程所必需经历的阶段[71-73]。
在机体损伤后恢复过程的组织重建和功能完善中,巨噬细胞起着重要的作用[74]。巨噬细胞通过吞噬作用和活性自由基消毒伤口、利用胶原酶和弹性酶清除伤口、通过释放细胞因子和生长因子来结束炎症反应,这些是它们对伤口愈合的主要贡献[75-76]。当巨噬细胞极化为M2表型时,M2型特异性表达因子白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β的表达上调[77];此外,巨噬细胞还影响血管生成、纤维增生和细胞外基质合成[75]。巨噬细胞的极化见图4。
下文就微弧氧化技术单独应用和与其他表面改性技术联合应用制备的表面涂层的抗炎性能进行综述。
2.2.1 金属涂层 生物材料诱导的炎症反应是决定植入物体内命运的关键因素之一,因此具有适当抗炎和成骨特性的植入材料可能有望用于骨科应用[78]。当植入物植入体内后,早期持续的免疫反应可导致机体的慢性炎症[79],具有免疫调节作用的植入材料不仅可以降低机体的免疫反应,还能促进植入物与骨组织之间形成理想的骨结合[80]。
LI等[81]在微弧氧化制造的钛表面上引入多孔陶瓷涂层,研究发现微弧氧化修饰的钛表面能使巨噬细胞极化为M1样表型,从而创造适当的炎症微环境,这种炎症微环境可以促进组织培养板上成骨细胞样细胞的胶原蛋白合成和基质矿化。有学者采用微弧氧化技术在钛表面形成含锌的二氧化钛涂层,其中锌主要以氧化锌的形式均匀分布在多孔二氧化钛涂层表面,在与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养时,实验组细胞的肿瘤坏死因子α、CD86和诱导性一氧化氮的mRNA表达下降,碱性磷酸酶蛋白质表达提高[79]。LI等[82]采用微弧氧化技术在钛基体上制备了含镁的二氧化钛涂层,在脂多糖的刺激下,涂层表面生长的巨噬细胞从M1表型转变为M2表型(CD86、CD11c、诱导型一氧化氮合酶、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的基因表达受到抑制,CD163的基因表达被促进);而在无脂多糖的刺激下,涂层表面生长的巨噬细胞的骨形态发生蛋白2、骨形态发生蛋白6和血管内皮生长因子的表达能力得到了显著提高,结果表明镁可以作为抑制炎症和介导成骨的抗炎剂,在与生物材料整合后可以赋予骨生物材料抗炎特性。有学者制备了含铜的微米和纳米形貌生物陶瓷表面(Cu-Hier-Ti)涂层,实验结果表明,直接补充到培养基中的Cu2+或从Cu-Hier-Ti表面释放的Cu2+均可以通过激活巨噬细胞中的铜转运信号(CTR1和ATP7A),使巨噬细胞极化为促炎的M1表型,但Cu-Hier-Ti表面释放的Cu2+引起的炎症反应强度低于直接补充Cu2+引起的炎症反应;Cu-Hier-Ti表面通过调节整合素(integrinα5、αM、β1和β2)和Toll样受体(TLR-3、TLR-4、Myd88和Ticam-1/2)调节细胞的黏附和功能[18]。另有学者发现,在含铜的微弧氧化表面上培养的巨噬细胞可极化为M1表型,上调一氧化氮合酶的表达并下调精氨酸酶的表达,进而增强促炎细胞因子白细胞介素6释放,抑制抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10释放,表明该涂层可以调节成骨细胞样细胞分化的炎症微环境[83]。HUANG等[84]采用粉末冶金策略制备了富钛相和富钽相的合金,采用微弧氧化对Ti-Ta复合材料表面进行改性,结果表明,微弧氧化修饰的Ti-Ta材料表面可以抑制炎症反应并使巨噬细胞极化为抗炎M2表型。
2.2.2 非金属涂层 有学者研究了在不同电压下通过微弧氧化沉积在钛上的磷酸钙涂层的理化性能和生物学性能,用抗CD2/CD3/CD28抗体激活肿瘤来源的Jurkat T细胞与该涂层的共培养,在14 d时该涂层维持了活化Jurkat T细胞的促炎能力,活化Jurkat T细胞的促炎趋化因子(巨噬细胞炎症蛋白1-α和巨噬细胞炎症蛋白1-β)的分泌增加;激活Jurkat T细胞的促炎细胞因子分泌增强了CD4+亚群的体外生存[85]。
另有学者描述了一种用羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒装饰的微孔二氧化钛涂层,该涂层是通过微弧氧化作用于钛并随后退火产生的。通过改变微弧氧化的退火温度可以调整涂层的表面形貌、润湿性和化学性能。体外实验表明,退火温度为650 ℃的微弧氧化涂层不仅支持成骨细胞和内皮细胞的增殖和分化,还可抑制巨噬细胞的炎症反应(显著下调白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达)[86]。
2.2.3 微弧氧化与其他表面改性技术的联合应用 有学者用微弧氧化和水热处理技术生产了含羟基磷灰石纳米结构的钛涂层[87-88],在该涂层表面的巨噬细胞能够抑制炎症反应(下调白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素18、肿瘤坏死因子α的表达;上调M2型巨噬细胞相关细胞因子的表达),并促进样本表面自噬标志物LC3A、LC3B、ATG5的表达,从而调节免疫环境[87-88]。另有学者采用微弧氧化和水热处理的混合工艺在钛表面上制备了β-FeOOH/TiO2涂层,该涂层在大鼠皮下软组织感染模型中植入4 d后,通过下调白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达减轻炎症反应[89]。

| [1] 董亮,何星.生物医用材料的研究进展及发展前景[J].世界复合医学, 2015,1(4):340-342. [2] 赵艳.口腔钛合金种植体的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(42):7943-7946. [3] ERBEL R, DI MARIO C, BARTUNEK J, et al. Temporary scaffolding of coronary arteries with bioabsorbable magnesium stents: a prospective, non-randomised multicentre trial. Lancet. 2007;369(9576):1869-1875. [4] YANG H, JIA B, ZHANG Z, et al. Alloying design of biodegradable zinc as promising bone implants for load-bearing applications. Nat Commun. 2020; 11(1):401. [5] 雷姗,王梦.介入用金属材料及其表面改性方法研究进展[J].中国金属通报,2022(5):88-90. [6] 贺晓静. 纯钛硬植入体表面抗菌微/纳米仿生涂层的构建及其生物学行为[D].太原:太原理工大学,2018. [7] 王淇.钛合金植入物表面仿生水凝胶涂层的制备[D].长春:吉林大学, 2022. [8] 范竞一,马迅,李伟,等.医用钛合金表面改性技术研究进展[J].功能材料,2022,53(7):7027-7039. [9] LI LH, KONG YM, KIM HW, et al. Improved biological performance of Ti implants due to surface modification by micro-arc oxidation. Biomaterials. 2004;25(14):2867-2875. [10] 孙志华,刘明,国大鹏,等.微弧氧化技术的发展现状和存在问题分析[J].装备环境工程,2009,6(6):46-49+55. [11] 张勇,张虹,陈跃良.微弧氧化技术在航空领域的应用前景及存在的问题[J].材料保护,2008(9):43-45+86. [12] 梁鹏晨,李路易,常庆,等.微弧氧化技术在骨科钛植入体生物功能改性中的应用进展[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2019,36(11):1335-1341. [13] HANAWA T. Titanium-Tissue Interface Reaction and Its Control With Surface Treatment. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:170. [14] ZHANG E, ZHAO X, HU J, et al. Antibacterial metals and alloys for potential biomedical implants. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(8):2569-2612. [15] FERRARIS S, SPRIANO S. Antibacterial titanium surfaces for medical implants. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;61:965-978. [16] MACKINTOSH EE, PATEL JD, MARCHANT RE, et al. Effects of biomaterial surface chemistry on the adhesion and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;78(4):836-842. [17] SHIMABUKURO M, TSUTSUMI H, TSUTSUMI Y, et al. Enhancement of antibacterial property of titanium by two-step micro arc oxidation treatment. Dent Mater J. 2021;40(3):592-598. [18] HUANG Q, OUYANG Z, TAN Y, et al. Activating macrophages for enhanced osteogenic and bactericidal performance by Cu ion release from micro/nano-topographical coating on a titanium substrate. Acta Biomater. 2019; 100:415-426. [19] KANG B, LAN D, YAO C, et al. Evaluation of antibacterial property and biocompatibility of Cu doped TiO2 coated implant prepared by micro-arc oxidation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:941109. [20] VAN HENGEL IAJ, TIEROLF MW AM, VALERIO VPM, et al. Self-defending additively manufactured bone implants bearing silver and copper nanoparticles. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(8):1589-1602. [21] MEGHANA S, KABRA P, CHAKRABORTY S, et al. Understanding the pathway of antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015;5(16): 12293-12299. [22] SHIMABUKURO M, TSUTSUMI Y, NOZAKI K, et al. Investigation of antibacterial effect of copper introduced titanium surface by electrochemical treatment against facultative anaerobic bacteria. Dent Mater J. 2020;39(4): 639-647. [23] SHIMABUKURO M, HIJI A, MANAKA T, et al. Time-Transient Effects of Silver and Copper in the Porous Titanium Dioxide Layer on Antibacterial Properties. J Funct Biomater. 2020;11(2):E44. [24] ROKOSZ K, HRYNIEWICZ T, KACALAK W, et al. Porous Coatings Containing Copper and Phosphorus Obtained by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of Titanium. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(4):E828. [25] LIANG DY, LIANG PC, YI QQ, et al. Copper coating formed by micro-arc oxidation on pure Mg improved antibacterial activity, osteogenesis, and angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Biomed Microdevices. 2021;23(3):39. [26] ZHAO Q, CHENG L, LIU Z, et al. Surface characteristics of Zinc–TiO 2 coatings prepared via micro-arc oxidation. Compos Interfaces. 2014;21(6):585-593. [27] STORRIE H, STUPP SI. Cellular response to zinc-containing organoapatite: an in vitro study of proliferation, alkaline phosphatase activity and biomineralization. Biomaterials. 2005;26(27):5492-5499. [28] YE J, LI B, LI M, et al. ROS induced bactericidal activity of amorphous Zn-doped titanium oxide coatings and enhanced osseointegration in bacteria-infected rat tibias. Acta Biomater. 2020;107:313-324. [29] SAMANI S, HOSSAINALIPOUR SM, TAMIZIFAR M, et al. In vitro antibacterial evaluation of sol-gel-derived Zn-, Ag-, and (Zn + Ag)-doped hydroxyapatite coatings against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(1):222-230. [30] GINALSKA G, KOWALCZUK D, OSIŃSKA M. A chemical method of gentamicin bonding to gelatine-sealed prosthetic vascular grafts. Int J Pharm. 2005; 288(1):131-140. [31] HARDES J, AHRENS H, GEBERT C, et al. Lack of toxicological side-effects in silver-coated megaprostheses in humans. Biomaterials. 2007;28(18):2869-2875. [32] ZHANG YY, ZHU Y, LU DZ, et al. Evaluation of osteogenic and antibacterial properties of strontium/silver-containing porous TiO2 coatings prepared by micro-arc oxidation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(4): 505-516. [33] ZHANG L, LI B, ZHANG X, et al. Biological and antibacterial properties of TiO2 coatings containing Ca/P/Ag by one-step and two-step methods. Biomed Microdevices. 2020;22(2):24. [34] YU L, QIAN S, QIAO Y, et al. Multifunctional Mn-containing titania coatings with enhanced corrosion resistance, osteogenesis and antibacterial activity. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(33):5397-5408. [35] YU L, TIAN Y, QIAO Y, et al. Corrigendum to “Mn-containing titanium surface with favorable osteogenic and antimicrobial functions synthesized by PIII&D” [Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 152 (2017) 376-384]. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;191:110970. [36] ZHAO QM, SUN YY, WU CS, et al. Enhanced osteogenic activity and antibacterial ability of manganese-titanium dioxide microporous coating on titanium surfaces. Nanotoxicology. 2020;14(3):289-309. [37] ZHANG X, LV Y, FU S, et al. Synthesis, microstructure, anti-corrosion property and biological performances of Mn-incorporated Ca-P/TiO2 composite coating fabricated via micro-arc oxidation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;117:111321. [38] TIEKINK ERT. Antimony and bismuth compounds in oncology. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2002;42(3):217-224. [39] CHEN F, LIU C, MAO Y. Bismuth-doped injectable calcium phosphate cement with improved radiopacity and potent antimicrobial activity for root canal filling. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(8):3199-3207. [40] LIN DJ, TSAI MT, SHIEH TM, et al. In vitro antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility of bismuth doped micro-arc oxidized titanium. J Biomater Appl. 2013;27(5):553-563. [41] SUN N, YIN S, LU Y, et al. Graphene oxide-coated porous titanium for pulp sealing: an antibacterial and dentino-inductive restorative material. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(26):5606-5619. [42] WANG X, LI B, ZHANG C. Preparation of BMP-2/chitosan/hydroxyapatite antibacterial bio-composite coatings on titanium surfaces for bone tissue engineering. Biomed Microdevices. 2019;21(4):89. [43] ZHOU J, LI B, HAN Y. F-doped TiO2 microporous coating on titanium with enhanced antibacterial and osteogenic activities. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17858. [44] 王欢,刘洋,戚孟春,等.微弧氧化技术制备钛基种植体表面涂层的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2020,47(4):439-444. [45] 杨华山,包晔峰,蒋永锋,等.微弧氧化陶瓷层的后处理技术研究现状及展望[C].第八届全国表面工程学术会议暨第三届青年表面工程学术论坛论文集(五),2010:62-67. [46] ZHANG X, ZHANG G, CHAI M, et al. Synergistic antibacterial activity of physical-chemical multi-mechanism by TiO2 nanorod arrays for safe biofilm eradication on implant. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):12-25. [47] LI J, LI Z, LIU X, et al. Interfacial engineering of Bi2S3/Ti3C2Tx MXene based on work function for rapid photo-excited bacteria-killing. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1224. [48] DENG Y, GAO X, SHI XL, et al. Graphene Oxide and Adiponectin-Functionalized Sulfonated Poly(etheretherketone) with Effective Osteogenicity and Remotely Repeatable Photodisinfection. Chem Mater. 2020;32(5):2180-2193. [49] LI T, ZHAO Y, CHEN M. Study on Enhancing the Corrosion Resistance and Photo-Thermal Antibacterial Properties of the Micro-Arc Oxidation Coating Fabricated on Medical Magnesium Alloy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10708. [50] 曹飞,刘童斌,张晓明.光动力疗法在口腔种植体周围炎治疗中的研究进展[J].中国医学创新,2021,18(27):177-181. [51] XIE X, MAO C, LIU X, et al. Tuning the Bandgap of Photo-Sensitive Polydopamine/Ag3 PO4 /Graphene Oxide Coating for Rapid, Noninvasive Disinfection of Implants. ACS Cent Sci. 2018;4(6):724-738. [52] 郝昶,林江.光动力疗法对口腔疾病免疫调控作用的研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2021,50(10):151-154. [53] CHAI M, AN M, ZHANG X. Construction of a TiO2/MoSe2/CHI coating on dental implants for combating Streptococcus mutans infection. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;129:112416. [54] LI K, XUE Y, ZHANG L, et al. β-FeOOH/Fe-TiO2 heterojunctions on Ti for bacteria inactivation under light irradiation and biosealing. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(21):6004-6016. [55] TENG W, ZHANG Z, WANG Y, et al. Iodine Immobilized Metal-Organic Framework for NIR-Triggered Antibacterial Therapy on Orthopedic Implants. Small. 2021;17(35):e2102315. [56] YE J, LI B, LI M, et al. Formation of a ZnO nanorods-patterned coating with strong bactericidal capability and quantitative evaluation of the contribution of nanorods-derived puncture and ROS-derived killing. Bioact Mater. 2022; 11:181-191. [57] FIALHO L, GRENHO L, FERNANDES MH, et al. Porous tantalum oxide with osteoconductive elements and antibacterial core-shell nanoparticles: A new generation of materials for dental implants. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;120:111761. [58] AKTUG SL, DURDU S, KALKAN S, et al. In vitro biological and antimicrobial properties of chitosan-based bioceramic coatings on zirconium. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):15104. [59] PENG S, LI M, WANG J, et al. Corrosion behavior and biological activity of micro-arc oxidation coating with puerarin on pure magnesium surface. Results Phys. 2019;12:1481-1489. [60] HE D, LI G, SHEN D, et al. Effect mechanism of ultrasound on growth of micro-arc oxidation coatings on A96061 aluminum alloy. Vacuum. 2014; 107:99-102. [61] LV Y, SUN S, ZHANG X, et al. Construction of multi-layered Zn-modified TiO2 coating by ultrasound-auxiliary micro-arc oxidation: Microstructure and biological property. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;131:112487. [62] HU J, LI H, WANG X, et al. Effect of ultrasonic micro-arc oxidation on the antibacterial properties and cell biocompatibility of Ti-Cu alloy for biomedical application. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;115:110921. [63] PROSOLOV KA, KOMAROVA EG, KAZANTSEVA EA, et al. UMAOH Calcium Phosphate Coatings Designed for Drug Delivery: Vancomycin, 5-Fluorouracil, Interferon α-2b Case. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(13):4643. [64] SHEN X, HU W, PING L, et al. Antibacterial and Osteogenic Functionalization of Titanium With Silicon/Copper-Doped High-Energy Shot Peening-Assisted Micro-Arc Oxidation Technique. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:573464. [65] BATOOL F, ÖZÇELIK H, STUTZ C, et al. Modulation of immune-inflammatory responses through surface modifications of biomaterials to promote bone healing and regeneration. J Tissue Eng. 2021;12:20417314211041428. [66] ANDERSSON J, EKDAHL KN, LARSSON R, et al. C3 adsorbed to a polymer surface can form an initiating alternative pathway convertase. J Immunol. 2002;168(11):5786-5791. [67] JENNEY CR, ANDERSON JM. Adsorbed serum proteins responsible for surface dependent human macrophage behavior. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;49(4):435-447. [68] ANDERSON JM, RODRIGUEZ A, CHANG DT. Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin Immunol. 2008;20(2):86-100. [69] MARRAZZO P, O’LEARY C. Repositioning Natural Antioxidants for Therapeutic Applications in Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering. 2020;7(3):104. [70] PARK CJ, GABRIELSON NP, PACK DW, et al. The effect of chitosan on the migration of neutrophil-like HL60 cells, mediated by IL-8. Biomaterials. 2009;30(4):436-444. [71] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [72] LEE J, BYUN H, MADHURAKKAT PERIKAMANA SK, et al. Current Advances in Immunomodulatory Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(4):e1801106. [73] LOI F, CÓRDOVA LA, PAJARINEN J, et al. Inflammation, fracture and bone repair. Bone. 2016;86:119-130. [74] FRANZ S, RAMMELT S, SCHARNWEBER D, et al. Immune responses to implants - a review of the implications for the design of immunomodulatory biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2011;32(28):6692-6709. [75] BROUGHTON G, JANIS JE, ATTINGER CE. The basic science of wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(7 Suppl):12S-34S. [76] WITTE MB, BARBUL A. General principles of wound healing. Surg Clin North Am. 1997;77(3):509-528. [77] CHAMPAGNE CM, TAKEBE J, OFFENBACHER S, et al. Macrophage cell lines produce osteoinductive signals that include bone morphogenetic protein-2. Bone. 2002;30(1):26-31. [78] MAVROGENIS AF, DIMITRIOU R, PARVIZI J, et al. Biology of implant osseointegration. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2009;9(2):61-71. [79] SUN H, YANG Y, YU L, et al. Inhibition of Inflammatory Response and Promotion of Osteogenic Activity of Zinc-Doped Micro-Arc Titanium Oxide Coatings. ACS Omega. 2022;7(17):14920-14932. [80] HOTCHKISS KM, REDDY GB, HYZY SL, et al. Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:425-434. [81] LI X, HUANG Q, HU X, et al. Evaluating the osteoimmunomodulatory properties of micro-arc oxidized titanium surface at two different biological stages using an optimized in vitro cell culture strategy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110:110722. [82] LI X, HUANG Q, LIU L, et al. Reduced inflammatory response by incorporating magnesium into porous TiO2 coating on titanium substrate. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;171:276-284. [83] HUANG Q, LI X, ELKHOOLY TA, et al. The Cu-containing TiO2 coatings with modulatory effects on macrophage polarization and bactericidal capacity prepared by micro-arc oxidation on titanium substrates. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;170:242-250. [84] HUANG Q, LI X, ELKHOOLY TA, et al. The osteogenic, inflammatory and osteo-immunomodulatory performances of biomedical Ti-Ta metal-metal composite with Ca- and Si-containing bioceramic coatings. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;169:49-59. [85] SHARKEEV YP, KOMAROVA EG, CHEBODAEVA VV, et al. Amorphous-Crystalline Calcium Phosphate Coating Promotes In Vitro Growth of Tumor-Derived Jurkat T Cells Activated by Anti-CD2/CD3/CD28 Antibodies. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(13):3693. [86] BAI L, DU Z, DU J, et al. A multifaceted coating on titanium dictates osteoimmunomodulation and osteo/angio-genesis towards ameliorative osseointegration. Biomaterials. 2018;162:154-169. [87] BAI L, LIU Y, DU Z, et al. Differential effect of hydroxyapatite nano-particle versus nano-rod decorated titanium micro-surface on osseointegration. Acta Biomater. 2018;76:344-358. [88] WANG X, MEI L, JIANG X, et al. Hydroxyapatite-Coated Titanium by Micro-Arc Oxidation and Steam-Hydrothermal Treatment Promotes Osseointegration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:625877. [89] XUE Y, CHEN J, DING T, et al. Building biointegration of Fe2O3-FeOOH coated titanium implant by regulating NIR irradiation in an infected model. Bioact Mater. 2022;8:1-11 |
| [1] | 王伟庆, 周 越. 慢性炎症调控脂肪组织的纤维化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [2] | 曾凡卓, 李雨欣, 孙嘉晨, 谷欣阳, 文 山, 田 鹤, 梅晰凡. 脊髓损伤模型小胶质细胞的高效移植替换策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1007-1014. |
| [3] | 王业元, 杜易朗, 于德浩, 宁凤婷, 白 冰. 微弧氧化处理对医用金属生物活性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 771-776. |
| [4] | 刘安宏, 蔡萌萌, 韩 笑, 王战会. 医用镁合金元素选择的研究现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 777-782. |
| [5] | 兰伟伟, 于耀东, 黄 棣, 陈维毅. Mg-Zn-Ca合金的体外降解行为[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 717-723. |
| [6] | 杨雨晴, 陈志宇. 早期短暂M1巨噬细胞在骨组织工程中的作用及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [7] | 孟志成, 乔卫平, 赵 阳, 刘洪飞, 李凯杰, 马 博. 免疫细胞及相关细胞因子在骨关节炎发病及治疗中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 280-287. |
| [8] | 张晨辉, 付婷婷, 吴阳林, 张 钦, 刘 昂, 杨惠林, 林 俊. 褪黑素抑制NLRP3炎症小体激活缓解钴铬钼颗粒引起的骨溶解[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(10): 1484-1489. |
| [9] | 邓 劲, 李廷华, 朱 海, 杨 晓, 曹 俊, 朱向东. 不同构型精氨酸改性壳聚糖水凝胶促皮肤创面的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(10): 1497-1504. |
| [10] | 贝 颖, 李文靖, 李美运, 苏 梦, 张 津, 黄 玉, 朱彦兆, 李嘉丽, 武 艳. 普鲁士蓝纳米颗粒促进糖尿病皮肤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(10): 1526-1532. |
| [11] | 邓 锐, 黄科铭, 罗 建 , 陈 功, 冯 健 , 黄维义, 魏 刚. 血红素氧合酶1介导阿托伐他汀在巨噬细胞极化和胆固醇蓄积中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 62-67. |
| [12] | 王彦金, 周英杰, 柴旭斌, 禚汉杰. 3D打印多孔钛合金椎间融合器在颈椎前路椎间盘切除植骨融合中应用效果与安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1434-1440. |
| [13] | 杨芷姗, 唐正龙. Hippo信号通路中的核心因子YAP/TAZ参与骨形成的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [14] | 高 煜, 韩佳慧, 葛 新. 脊髓缺血再灌注损伤后的免疫炎性微环境[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [15] | 王书祥, 伍 权, 周小淞, 况现桃. 钛合金全冠选择性激光熔化成形工艺及变形实验[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1012-1016. |
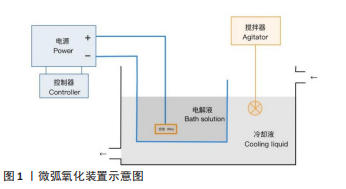
微弧氧化又称等离子体电解质氧化、阳极火花沉积,是一种通过调节电解液成分和电参数,在电弧放电产生的瞬时高温高压作用下于铝、镁、钛等阀金属及合金表面形成致密陶瓷氧化膜的表面改性技术[9],见图1。由于微弧氧化膜层具有高硬度、低磨损、耐蚀性好、耐热性好等优点,可用于零件的表面处理与防腐处理,还能提高一些零件的使用性能和寿命,目前微弧氧化技术已被广泛应用于航空航天、汽车、纺织、化工等工业领域[10-11]。
 植入材料的感染问题与手术的成败有很大关系,因此研发出具有抗菌性能和抗炎性能的植入体材料十分必要。微弧氧化可以将生物活性元素加入到电解液中,从而嵌入到氧化膜涂层上,进而改善金属表面的生物相容性和抗菌性能[12]。该文就单独应用微弧氧化技术及联合应用其他表面改性技术制备表面涂层的抗菌性能和抗炎性能进行综述。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
植入材料的感染问题与手术的成败有很大关系,因此研发出具有抗菌性能和抗炎性能的植入体材料十分必要。微弧氧化可以将生物活性元素加入到电解液中,从而嵌入到氧化膜涂层上,进而改善金属表面的生物相容性和抗菌性能[12]。该文就单独应用微弧氧化技术及联合应用其他表面改性技术制备表面涂层的抗菌性能和抗炎性能进行综述。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2022年12月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 1996年1月至2022年12月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、中国知网、万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索途径 主题词、关键词检索。
1.1.5 检索词 微弧氧化,抗菌性能,抗炎性能,金属植入物,micro-arc oxidation,antibacterial,anti-inflammatory,metal implants。
1.1.6 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述。
1.1.7 手工检索情况 无。
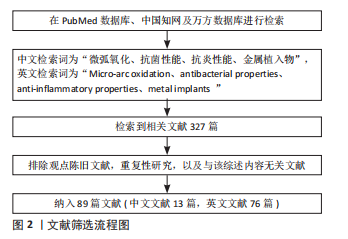
1.1.8 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图2。

1.2 入选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与微弧氧化高度相关的文献;②与微弧氧化涂层材料抗菌性能和抗炎性能高度相关的文献;③可信度高的文献(引用量较高,期刊影响因子较高,分区靠前,中文核心期刊,作者权威)。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与该综述研究内容不符的文献;②观点陈旧及重复性的研究。
1.3 质量评估数据的提取 初检文献327篇,根据纳入与排除标准,最终纳入符合标准的89篇文献,其中中文文献13篇、英文文献76篇,见图3。
总之,微弧氧化与各种表面改性技术联合应用可以增强植入物表面的抗菌性能和抗炎性能,为临床研究提供了重要参考。后阶段还要多方面研究它的抗菌和抗炎机制,提高植入体的抗菌、抗炎、生物活性、促成骨等综合性能。相信在不久的将来,微弧氧化与其他表面改性技术会更加完善,弥补现阶段的不足。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
微弧氧化:又称等离子体电解质氧化、阳极火花沉积,是一种通过调节电解液成分和电参数,在电弧放电产生的瞬时高温高压作用下,于铝、镁、钛等阀金属及其合金表面形成致密陶瓷氧化膜的表面改性技术。生物医用材料:是以医疗为目的,用于与组织接触以形成功能的无生命的材料,是用来对生物体进行诊断、治疗、修复或替换其病损组织、器官或增进其功能的一类高技术新材料。
医用植入材料的感染问题与手术的成败关系密切,研发出兼有抗菌和抗炎性能的植入体材料十分重要。微弧氧化技术能够在金属基体上制备可以改善植入物抗菌和抗炎性能的表面涂层,而以往的文献大多关注于材料的抗腐蚀性能和成骨性能,较少综述其抗菌和抗炎性能,涉及其机制的报道更是少之又少。该文重点总结比较微弧氧化技术单独应用、与其他表面改性技术联合应用两种条件下制备的表面涂层的抗菌性能、抗炎性能和机制,指出现阶段微弧氧化技术在抗菌和抗炎性能方面的不足,展望微弧氧化技术的未来发展趋势,旨在为后续临床研究提供参考。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||