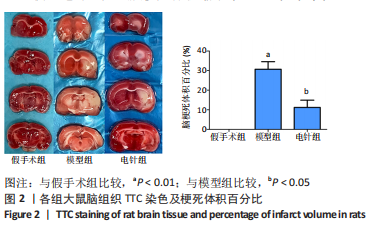
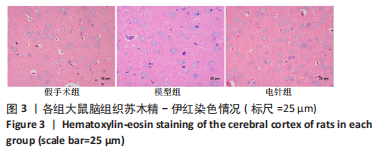
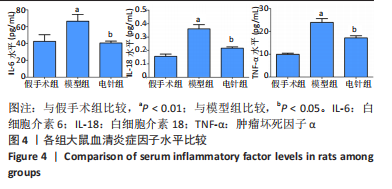
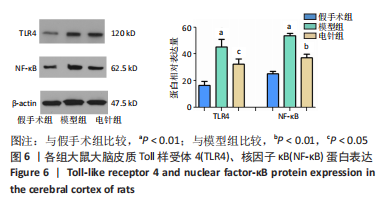
[1] 李侍显,张梅奎,李敏,等.活血利水方对MCAO大鼠模型海马组织EGFR和AKT表达的影响[J].解放军医学院学报,2019,40(11):1068-1073,1078.
[2] DATTA A, SARMAH D, MOUNICA L, et al. Cell Death Pathways in Ischemic Stroke and Targeted Pharmacotherapy. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11(6):1185-1202.
[3] 赵亚伟,傅天,张彦利.中医药治疗脑卒中的研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2017,26(24):2733-2736.
[4] 梁繁荣.针灸学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2006:189-190.
[5] 闫冬.《备急千金要方》《千金翼方》中任督二脉腧穴的文献研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2018.
[6] 王琪,李澎,许军峰.针刺水沟穴治疗缺血性脑损伤机制研究进展[J].针灸临床杂志,2021,37(7):88-91.
[7] 唐红,汪红娟,江姗姗,等.针刺“百会”“水沟”“大椎”穴对脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠海马区差异circRNAs表达的影响[J].中医杂志,2022,64(5): 512-517.
[8] 钟晓勇,阮甦,王芳,等.电针通过调节内源性褪黑素分泌减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的机制研究[J].针刺研究,2021,47(1):39-45.
[9] JIANG T, WU M, ZHANG Z, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuated cerebral ischemic injury and neuroinflammation through α7nAChR-mediated inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome in stroke rats. Mol Med. 2019;25(1):22.
[10] 孙光华,周君,周桂娟,等.580例脑卒中运动障碍患者针刺配合物理治疗的回顾性研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2019,46(10):2039-2042.
[11] 王宇.基于“络脑调神”探讨眼针治疗急性脑梗死的临床观察及作用机制[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2020.
[12] 杨海永,王东岩.电针结合屈伸肌交替刺激法改善脑卒中患者下肢功能障碍临床研究[J].针灸临床杂志,2021,37(1):30-34.
[13] YAO L, LIANG W, DU X, et al. Effect of acupuncture on long-term outcomes in patients with post-stroke dysphagia. NeuroRehabilitation. 2022;51(3):433-441.
[14] 胡晓娟,李帅,王明杰.浮针疗法联合加味黄芪桂枝五物汤辅治脑卒中后痉挛性偏瘫临床观察[J].实用中医药杂志,2022,38(7):1198-1200.
[15] 刘莉,王念宏,张群,等.微小核糖核酸参与电针治疗缺血性脑卒中研究概况[J].针刺研究,2019,44(9):686-692.
[16] 丁娜,袁阳,王明山,等.电针预处理对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠皮质神经细胞线粒体融合蛋白2表达的影响[J].精准医学杂志,2022,37(6):550-553.
[17] ZHANG W, HAN L, WEN Y, et al. Electroacupuncture reverses endothelial cell death and promotes angiogenesis through the VEGF/Notch signaling pathway after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Behav. 2023;13(3):e2912.
[18] 冯刚,封蔚彬,青云,等.电针预处理通过抑制AMPK-Beclin1/Vps34通路介导的细胞自噬减轻脑缺血再灌注损伤[J].重庆医科大学学报,2020,45(12): 1762-1769.
[19] 刘丹妮,周君,黄夏荣,等.电针“水沟”“百会”穴对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠海马神经元自噬的影响[J].针刺研究,2022,47(6):491-496.
[20] 刘丹妮,孙光华,周桂娟,等.电针水沟、百会穴对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠大脑皮质神经元凋亡的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(35):5620-5625.
[21] 罗敷,封蔚彬,刘丹妮,等.电针“百会“”人中”对脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠脑脊液炎症因子及皮质缺血区脑组织GSDMD表达的影响[J].中医杂志, 2022,63(2):164-168.
[22] TANG J, XU L, ZENG Y, et al. Effect of gut microbiota on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;91:107272.
[23] AOKI T, NISHIMURA M, MATSUOKA T, et al. PGE(2) -EP(2) signalling in endothelium is activated by haemodynamic stress and induces cerebral aneurysm through an amplifying loop via NF-κB. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163(6):1237-1249.
[24] ISLAM MA, HUQ ATANU MS, SIRAJ MA, et al. Supplementation of syringic acid-rich Phrynium pubinerve leaves imparts protection against allergic inflammatory responses by downregulating iNOS, COX-2, and NF-κB expressions. Heliyon. 2023;9(2):e13343.
[25] HUANG D, ZHOU J, LI W, et al. Casticin protected against neuronal injury and inhibited the TLR4/NF-κB pathway after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021;9(2):e00752.
[26] 马贤德,孙宏伟,柴纪严,等.线栓法制备大鼠脑缺血再灌注模型的方法研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2009,27(6):1200-1201.
[27] 张露芬.实验针灸学[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2010:91-93.
[28] WICHA P, TOCHARUS J, JANYOU A, et al. Hexahydrocurcumin alleviated blood-brain barrier dysfunction in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. Pharmacol Rep. 2020;72(3):659-671.
[29] HAN VX, JONES HF, PATEL S, et al. Emerging evidence of Toll-like receptors as a putative pathway linking maternal inflammation and neurodevelopmental disorders in human offspring: A systematic review. Brain Behav Immun. 2022; 99:91-105.
[30] PAWLUK H, WOŹNIAK A, GRZEŚK G, et al. The Role of Selected Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Pathogenesis of Ischemic Stroke. Clin Interv Aging. 2020;15:469-484.
[31] ZINDEL J, KUBES P. DAMPs, PAMPs, and LAMPs in Immunity and Sterile Inflammation. Annu Rev Pathol. 2020;15:493-518.
[32] FITZGERALD KA, KAGAN JC. Toll-like Receptors and the Control of Immunity. Cell. 2020;180(6):1044-1066.
[33] TI D, HAO H, TONG C, et al. LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J Transl Med. 2015;13:308.
[34] CAO M, YAN H, HAN X, et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles alter macrophage polarization to inhibit melanoma growth. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):326.
[35] FENG K, CHEN Z, PENGCHENG L, et al. Quercetin attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via SIRT1/AMPK-mediated inhibition of ER stress in rat chondrocytes and prevents the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(10):18192-18205.
|