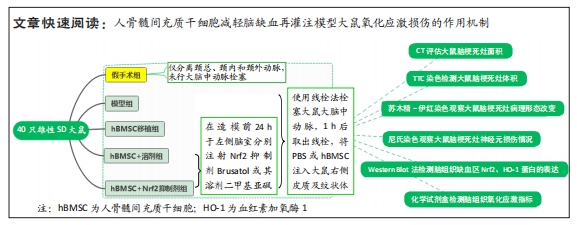
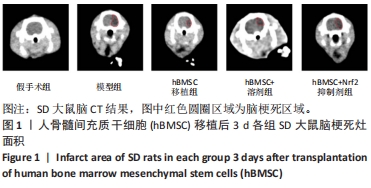
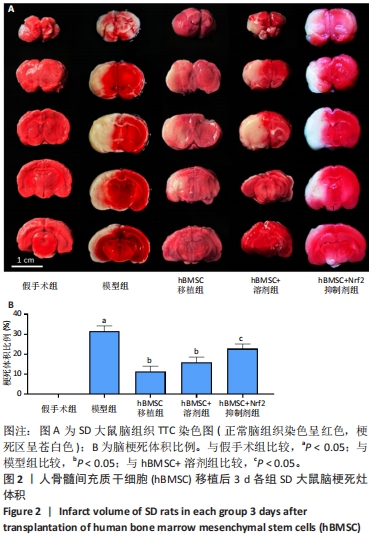
[1] WALTER K. What Is Acute Ischemic Stroke? JAMA. 2022;327(9):885.
[2] SCHIAVONE S, TRABACE L. Small Molecules: Therapeutic Application in Neuropsychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Molecules. 2018;23(2):411.
[3] ORELLANA-URZÚA S, ROJAS I, LÍBANO L, et al. Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke: Role of Oxidative Stress. Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(34):4246-4260.
[4] LIU L, LOCASCIO LM, DORÉ S. Critical Role of Nrf2 in Experimental Ischemic Stroke. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:153.
[5] LI Y, MENG F. Effects of icariside II on brain tissue oxidative stress and Nrf2/HO-1 expression in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury1. Acta Cir Bras. 2019;34(2):e201900208.
[6] XU L, GAO Y, HU M, et al. Edaravone dexborneol protects cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in mice. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2022;36(5):790-800.
[7] DUAN C, WANG H, JIAO D, et al. Curcumin Restrains Oxidative Stress of After Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Rat by Activating the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:889226.
[8] NIE P, BAI X, LOU Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce oxidative damage and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy by activating Nrf2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):450.
[9] ZHAO D, YU W, XIE W, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting oxidative stress in rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022;477(12):2761-2771.
[10] YANG W, YANG Y, YANG JY, et al. Treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with plumbagin alleviates spinal cord injury by affecting oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptotis and the activation of the Nrf2 pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(4):1075-1082.
[11] 李洪亮,薛智慧,龙抗胜,等.线栓法制备MCAO模型大鼠的经验体会[J].中国中医急症,2014,23(12):2216-2219.
[12] 潘杭,朱向情,何洁,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对衰老猕猴胸腺及脾脏结构和功能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(19):2953-2959.
[13] 张小琴,赵优琴,黄莉莉,等.基于Keap-1/Nrf2/ARE信号通路探讨片仔癀改善MCAO大鼠氧化应激损伤的作用[J].中华中医药杂志,2022, 37(11):6466-6470.
[14] MA S, ZHOU X, WANG Y, et al. MG53 protein rejuvenates hUC-MSCs and facilitates their therapeutic effects in AD mice by activating Nrf2 signaling pathway. Redox Biol. 2022;53:102325.
[15] CHEN F, LIU J, LI FQ, et al. β2-Microglobulin exacerbates neuroinflammation, brain damage, and cognitive impairment after stroke in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(3):603-608.
[16] ALLEN CL, BAYRAKTUTAN U. Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2009;4(6):461-470.
[17] SU XT, WANG L, MA SM, et al. Mechanisms of Acupuncture in the Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Treating Ischemic Stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; 2020:7875396.
[18] MIAO R, LI J, MENG C, et al. Diet-Derived Circulating Antioxidants and Risk of Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022; 2022:6457318.
[19] FORRESTER SJ, KIKUCHI DS, HERNANDES MS, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species in Metabolic and Inflammatory Signaling. Circ Res. 2018;122(6):877-902.
[20] SHEHJAR F, MAKTABI B, RAHMAN ZA, et al. Stroke: Molecular mechanisms and therapies: Update on recent developments. Neurochem Int. 2023;162: 105458.
[21] ZHOU L, ZHU H, BAI X, et al. Potential mechanisms and therapeutic targets of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):195.
[22] CHUNG JW, CHANG WH, BANG OY, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Ischemic Stroke. Neurology. 2021;96(7): e1012-e1023.
[23] LEE J, CHANG WH, CHUNG JW, et al. Efficacy of Intravenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Motor Recovery After Ischemic Stroke: A Neuroimaging Study. Stroke. 2022;53(1):20-28.
[24] CHEN H, ZHOU L. Treatment of ischemic stroke with modified mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Med Sci. 2022;19(7):1155-1162.
[25] LEE S, KIM OJ, LEE KO, et al. Enhancing the Therapeutic Potential of CCL2-Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Acute Stroke. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7795.
[26] LIU C, YANG ZX, ZHOU SQ, et al. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor enhances the neuroprotective effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in ischemic stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(6):1286-1292.
[27] GERVOIS P, WOLFS E, RATAJCZAK J, et al. Stem Cell-Based Therapies for Ischemic Stroke: Preclinical Results and the Potential of Imaging-Assisted Evaluation of Donor Cell Fate and Mechanisms of Brain Regeneration. Med Res Rev. 2016;36(6):1080-1126.
[28] ACOSTA SA, TAJIRI N, HOOVER J, et al. Intravenous Bone Marrow Stem Cell Grafts Preferentially Migrate to Spleen and Abrogate Chronic Inflammation in Stroke. Stroke. 2015;46(9):2616-2627.
[29] ZHANG Y, DONG N, HONG H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Therapeutic Mechanisms for Stroke. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2550.
[30] LI J, ZHANG Q, WANG W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for ischemic stroke: A look into treatment mechanism and therapeutic potential. J Neurol. 2021;268(11):4095-4107.
[31] CALIÓ ML, MARINHO DS, KO GM, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells decreases oxidative stress, apoptosis, and hippocampal damage in brain of a spontaneous stroke model. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;70:141-154.
[32] TAKAGI T, KITASHOJI A, IWAWAKI T, et al. Temporal activation of Nrf2 in the penumbra and Nrf2 activator-mediated neuroprotection in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;72:124-133.
|