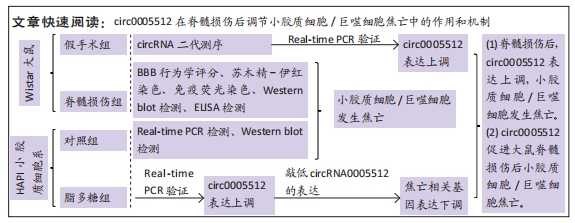
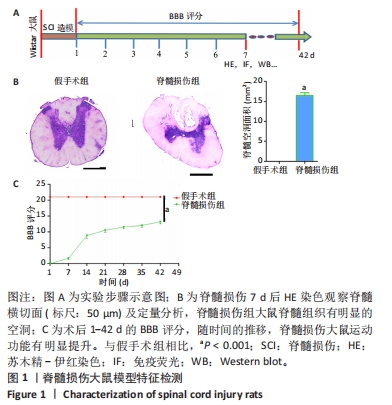
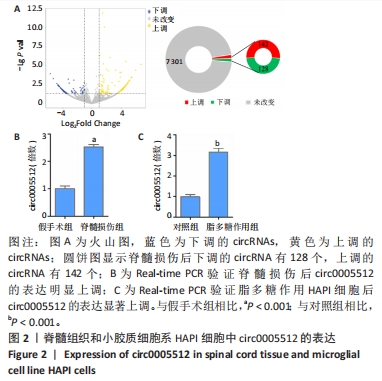
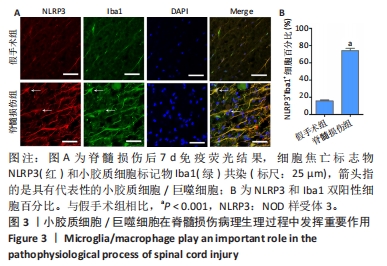
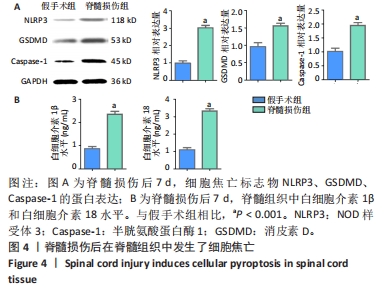
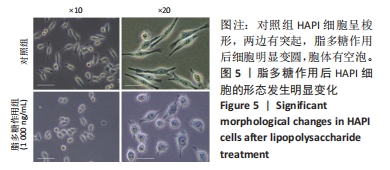
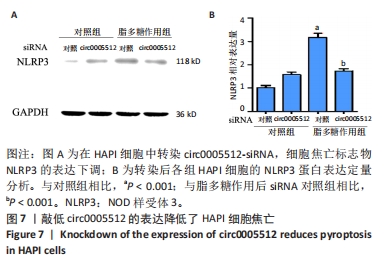
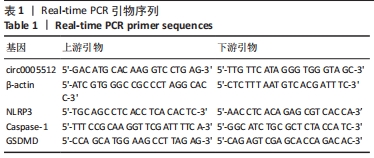
[1] LAGU T, SCHROTH SL, HAYWOOD C, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Risk in Individuals With Spinal Cord Injury: A Narrative Review. Circulation. 2023;148(3):268-277.
[2] 戴家峰,王丽昭,韩齐,等.脊髓损伤重塑皮质脊髓运动神经元突触输入的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(25):4054-4059.
[3] 尚文雅,任亚锋,李冰,等.脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡调控机制及治疗策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(11):1772-1779.
[4] CRAGG JJ, TONG B, JUTZELER CR, et al. A Longitudinal Study of the Neurologic Safety of Acute Baclofen Use After Spinal Cord Injury. Neurotherapeutics. 2019;16(3):858-867.
[5] HU X, XU W, REN Y, et al. Spinal cord injury: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):245.
[6] COLL RC, SCHRODER K, PELEGRÍN P. NLRP3 and pyroptosis blockers for treating inflammatory diseases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022;43(8):653-668.
[7] MA Q. Pharmacological Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome: Structure, Molecular Activation, and Inhibitor-NLRP3 Interaction. Pharmacol Rev. 2023;75(3):487-520.
[8] KAGAN JC. Excess lipids on endosomes dictates NLRP3 localization and inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol. 2023;24(1):3-4.
[9] AL MAMUN A, WU Y, MONALISA I, et al. Role of pyroptosis in spinal cord injury and its therapeutic implications. J Adv Res. 2020;28:97-109.
[10] LIU Z, YAO X, JIANG W, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products induce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):90.
[11] MOONEN S, KOPER MJ, VAN SCHOOR E, et al. Pyroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease: cell type-specific activation in microglia, astrocytes and neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 2023;145(2):175-195.
[12] VAN SCHOOR E, OSPITALIERI S, MOONEN S, et al. Increased pyroptosis activation in white matter microglia is associated with neuronal loss in ALS motor cortex. Acta Neuropathol. 2022;144(3):393-411.
[13] KAMEDA S, OHNO H, SAITO H. Synthetic circular RNA switches and circuits that control protein expression in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(4):e24.
[14] DONG Y, GAO Q, CHEN Y, et al. Identification of CircRNA signature associated with tumor immune infiltration to predict therapeutic efficacy of immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):2540.
[15] YANG L, WILUSZ JE, CHEN LL. Biogenesis and Regulatory Roles of Circular RNAs. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2022;38:263-289.
[16] CONN VM, GABRYELSKA M, TOUBIA J, et al. Circular RNAs drive oncogenic chromosomal translocations within the MLL recombinome in leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2023;41(7):1309-1326.e10.
[17] CHEN M, LAI X, WANG X, et al. Long Non-coding RNAs and Circular RNAs: Insights Into Microglia and Astrocyte Mediated Neurological Diseases. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:745066.
[18] DU M, WU C, YU R, et al. A novel circular RNA, circIgfbp2, links neural plasticity and anxiety through targeting mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress-induced synapse dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27(11):4575-4589.
[19] ZHANG Y, LIU Z, ZHANG W, et al. Melatonin improves functional recovery in female rats after acute spinal cord injury by modulating polarization of spinal microglial/macrophages. J Neurosci Res. 2019; 97(7):733-743.
[20] BASSO DM, BEATTIE MS, BRESNAHAN JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1):1-21.
[21] WU Q, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Riluzole improves functional recovery after acute spinal cord injury in rats and may be associated with changes in spinal microglia/macrophages polarization. Neurosci Lett. 2020;723:134829.
[22] LIVAK KJ, SCHMITTGEN TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408.
[23] GUÍZAR-SAHAGÚN G, GRIJALVA I, FRANCO-BOURLAND RE, et al. Aging with spinal cord injury: A narrative review of consequences and challenges. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;90:102020.
[24] WANG H, LIN F, WU Y, et al. Carrier-Free Nanodrug Based on Co-Assembly of Methylprednisolone Dimer and Rutin for Combined Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. ACS Nano. 2023;17(13):12176-12187.
[25] LAURITSEN J, ROMERO-RAMOS M. The systemic immune response in Parkinson’s disease: focus on the peripheral immune component. Trends Neurosci. 2023;46(10):863-878.
[26] KAYA T, MATTUGINI N, LIU L, et al. CD8+ T cells induce interferon-responsive oligodendrocytes and microglia in white matter aging. Nat Neurosci. 2022;25(11):1446-1457.
[27] YIN N, ZHAO Y, LIU C, et al. Engineered Nanoerythrocytes Alleviate Central Nervous System Inflammation by Regulating the Polarization of Inflammatory Microglia. Adv Mater. 2022;34(27):e2201322.
[28] ZHOU Y, WEN LL, LI YF, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect the injured spinal cord by inhibiting pericyte pyroptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):194-202.
[29] 刘涛,张文凯,马子谦,等.利鲁唑干预脊髓损伤大鼠小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎性小体的活化[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(7): 1036-1042.
[30] YANG Z, HUANG C, WEN X, et al. Circular RNA circ-FoxO3 attenuates blood-brain barrier damage by inducing autophagy during ischemia/reperfusion. Mol Ther. 2022;30(3):1275-1287.
[31] JIANG Q, SU DY, WANG ZZ, et al. Retina as a window to cerebral dysfunction following studies with circRNA signature during neurodegeneration. Theranostics. 2021;11(4):1814-1827.
[32] ZHANG Y, YUN HJ, JI Y, et al. Advancements in our understanding of circular and long non-coding RNAs in spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(11):2399-2403.
[33] ZHANG Y, DU L, BAI Y, et al. CircDYM ameliorates depressive-like behavior by targeting miR-9 to regulate microglial activation via HSP90 ubiquitination. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(6):1175-1190.
[34] YANG L, HAN B, ZHANG Z, et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Delivery of Circular RNA SCMH1 Promotes Functional Recovery in Rodent and Nonhuman Primate Ischemic Stroke Models. Circulation. 2020;142(6):556-574.
[35] WANG K, SU X, SONG Q, et al. The circ_006573/miR-376b-3p Axis Advances Spinal Cord Functional Recovery after Injury by Modulating Vascular Regeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(9): 4983-4999.
[36] LI X, KANG J, LV H, et al. CircPrkcsh, a circular RNA, contributes to the polarization of microglia towards the M1 phenotype induced by spinal cord injury and acts via the JNK/p38 MAPK pathway. FASEB J. 2021;35(12):e22014.
[37] CHEN JN, ZHANG YN, TIAN LG, et al. Down-regulating Circular RNA Prkcsh suppresses the inflammatory response after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):144-151.
|