[1] JAZAYERI SB, MAROUFI SF, MOHAMMADI E, et al. Incidence of traumatic spinal cord injury worldwide: A systematic review, data integration, and update. World Neurosurg X. 2023;18:100171.
[2] 李丰,周文华,陈大勇,等.迷迭香酸对大鼠急性脊髓损伤的神经保护作用及其机制[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023,31(2):1-5.
[3] ELI I, LERNER DP, GHOGAWALA Z. Acute Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Neurol Clin. 2021;39(2):471-488.
[4] ZIPSER CM, CRAGG JJ, GUEST JD, et al. Cell-based and stem-cell-based treatments for spinal cord injury: evidence from clinical trials. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(7):659-670.
[5] CHEN C, QIAO X, LIU W, et al. Epidemiology of spinal cord injury in China: A systematic review of the chinese and english literature. Spinal Cord. 2022;60(12):1050-1061.
[6] ZHAO Q, LIU F, ZHOU B, et al. Ferroptosis: A Novel Therapeutic Direction of Spinal Cord Injury. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022;2022:7906218.
[7] URSINI F, MAIORINO M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152:175-185.
[8] LANE D, AYTON S, BUSH AI. Iron and Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update on Emerging Mechanisms. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;64(s1):S379-S395.
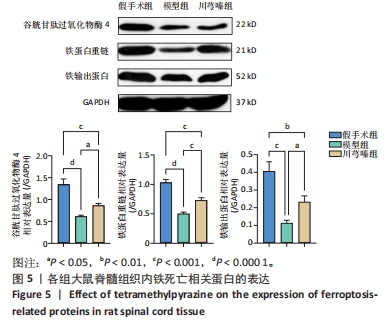
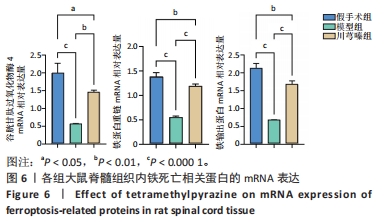
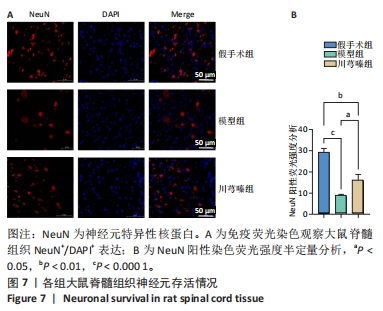
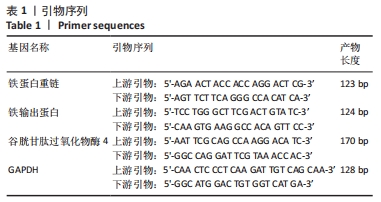
[9] 范筱,陶经纬,蒋昇源,等.川芎嗪对大鼠脊髓损伤后铁代谢的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(22):3561-3566.
[10] YAO X, ZHANG Y, HAO J, et al. Deferoxamine promotes recovery of traumatic spinal cord injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(3):532-541.
[11] XU T, DING W, JI X, et al. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(8):4900-4912.
[12] ZHENG YQ, ZENG JX, LIN JX, et al. [Herbal textual research on Chuanxiong Rhizoma in Chinese classical prescriptions]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021; 46(16):4293-4299.
[13] LIN J, WANG Q, ZHOU S, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine: A review on its mechanisms and functions. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;150:113005.
[14] 袁蓉,李梓涵,黄美雯,等.川芎-赤芍药对干预心肌梗死合并动脉粥样硬化复合模型的circRNA/lncRNA表达谱研究[J].中国中药杂志,2023,48(14): 3890-3903.
[15] CHEN J, TIAN J, GE H, et al. Effects of tetramethylpyrazine from Chinese black vinegar on antioxidant and hypolipidemia activities in HepG2 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017;109(Pt 2):930-940.
[16] LIN J, HAO C, GONG Y, et al. Effect of Tetramethylpyrazine on Neuroplasticity after Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion in Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:1587241.
[17] HU J, CAO Y, WU T, et al. Micro-CT as a Tool to Investigate the Efficacy of Tetramethylpyrazine in a Rat Spinal Cord Injury Model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(16):1272-1278.
[18] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(3):486-541.
[19] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072.
[20] CLIFFORD T, FINKEL Z, RODRIGUEZ B, et al. Current Advancements in Spinal Cord Injury Research—Glial Scar Formation and Neural Regeneration. Cells. 2023;12(6):853.
[21] 陶经纬,范筱,蒋昇源,等.可注射水凝胶在脊髓损伤中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(16):2548-2555.
[22] CHEN Y, LIU S, LI J, et al. The Latest View on the Mechanism of Ferroptosis and Its Research Progress in Spinal Cord Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020: 6375938.
[23] MENG Z, CHEN H, MENG S. The Roles of Tetramethylpyrazine During Neurodegenerative Disease. NNeurotox Res. 2021;39(5):1665-1677.
[24] HUANG J, CAO Y, ZENG L, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine enhances functional recovery after contusion spinal cord injury by modulation of MicroRNA-21, FasL, PDCD4 and PTEN expression. Brain Res. 2016;1648(Pt A):35-45.
[25] DANG R, WANG M, LI X, et al. Edaravone ameliorates depressive and anxiety-like behaviors via Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1/Gpx4 pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 2022; 19(1):41.
[26] ZHANG Y, SWANDA RV, NIE L, et al. mTORC1 couples cyst(e)ine availability with GPX4 protein synthesis and ferroptosis regulation. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):1589.
[27] LUO Y, GAO X, ZOU L, et al. Bavachin Induces Ferroptosis through the STAT3/P53/SLC7A11 Axis in Osteosarcoma Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:1783485.
[28] ZHOU H, YIN C, ZHANG Z, et al. Proanthocyanidin promotes functional recovery of spinal cord injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. J Chem Neuroanat. 2020;107:101807.
[29] KIM DH, KIM WD, KIM SK, et al. TGF-beta1-mediated repression of SLC7A11 drives vulnerability to GPX4 inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(5):406.
[30] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125.
[31] GONG F, GE T, LIU J, et al. Trehalose inhibits ferroptosis via NRF2/HO-1 pathway and promotes functional recovery in mice with spinal cord injury. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(7):3216-3232.
[32] GE H, XUE X, XIAN J, et al. Ferrostatin-1 Alleviates White Matter Injury Via Decreasing Ferroptosis Following Spinal Cord Injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(1): 161-176. |