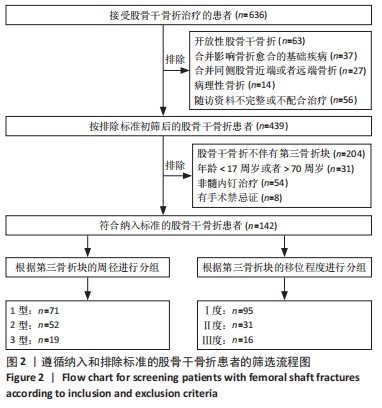
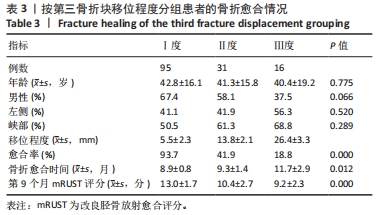
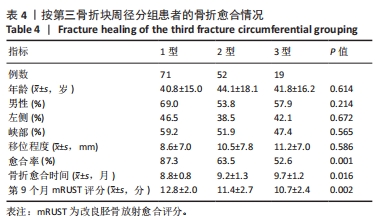
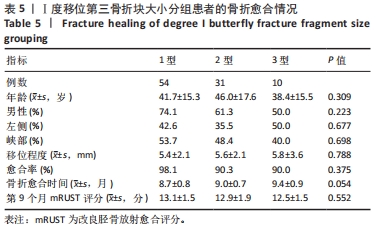
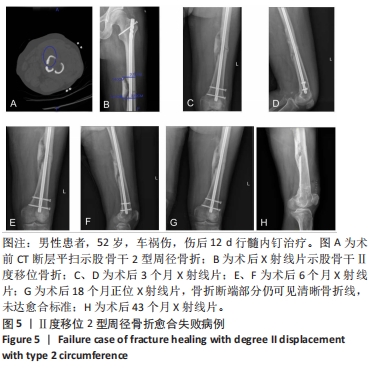
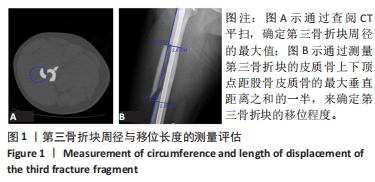
[1] LEE JR, KIM HJ, LEE KB. Effects of third fragment size and displacement on non-union of femoral shaft fractures after locking for intramedullary nailing. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016;102(2):175-181.
[2] LAYON D, MORRELL AT, LEE C. The flipped third fragment in femoral shaft fractures: A reason for open reduction? Injury. 2021;52(3):589-593.
[3] PIHLAJAMAKI HK, SALMINEN ST, BOSTMAN OM. The treatment of nonunions following intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractuSres. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16(6):394-402.
[4] SALMINEN ST, PIHLAJAMAKI HK, AVIKAINEN VJ, et al. Population based epidemiologic and morphologic study of femoral shaft fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(372):241-249.
[5] BURC H, ATAY T, DEMIRCI D, et al. The Intramedullary Nailing of Adult Femoral Shaft Fracture by the Way of Open Reduction is a Disadvantage or Not? Indian J Surg. 2015;77(Suppl 2):583-588.
[6] PERSIANI P, NOIA G, DE CRISTO C, et al. A study of 44 patients with subtrochanteric fractures treated using long nail and cerclage cables. Musculoskelet Surg. 2015;99(3):225-230.
[7] APIVATTHAKAKUL T, PHALIPHOT J, LEUVITOONVECHKIT S. Percutaneous cerclage wiring, does it disrupt femoral blood supply? a cadaveric injection study. Injury. 2013;44(2):168-174.
[8] SANTOLINI E, WEST RM, GIANNOUDIS PV. Leeds-Genoa Non-Union Index: a clinical tool for asessing the need for early intervention after long bone fracture fixation. Int Orthop. 2020;44(1):161-172.
[9] LIN SJ, CHEN CL, PENG KT, et al. Effect of fragmentary displacement and morphology in the treatment of comminuted femoral shaft fractures with an intramedullary nail. Injury. 2014;45(4):752-756.
[10] VICENTI G, CARROZZO M, CAIAFFA V, et al. The impact of the third fragment features on the healing of femoral shaft fractures managed with intramedullary nailing: a radiological study. Int Orthop. 2019;43(1):193-200.
[11] YANG S, YANG Y, HUO Y, et al. Effect of the degree of displacement of the third fragment on healing of femoral shaft fracture treated by intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):380.
[12] BOSTMAN O, VARJONEN L, VAINIONPAA S, et al. Incidence of local complications after intramedullary nailing and after plate fixation of femoral shaft fractures. J Trauma. 1989;29(5):639-645.
[13] 常凤,李彦龙. 不同慢性病中老年女性骨折风险及低骨量切点预测分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(14):2140-2144.
[14] 刘洋. 交锁髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折的体会[J]. 中国医药指南,2009, 7(8):90.
[15] LITRENTA J, TORNETTA PR, MEHTAS, et al. Determination of Radiographic Healing: An Assessment of Consistency Using RUST and Modified RUST in Metadiaphyseal Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(11):516-520.
[16] PLUMAROM Y, WILKINSON BG, WILLEY MC, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of modified RUST score using clinical and radiographic findings as a gold standard. Bone Jt Open. 2021;2(10):796-805.
[17] MISRI A, YILDIZ KI, KIZKAPAN TB, et al. Reliability of RUST and modified RUST scores for evaluation of union in pediatric and adult femoral shaft fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021;55(2):127-133.
[18] KIZKAPAN TB, MISIR A, OGUZKAYA S, et al. Reliability of radiographic union scale in tibial fractures and modified radiographic union scale in tibial fractures scores in the evaluation of pediatric forearm fracture union. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2021;32(1):185-191.
[19] NAKAMURA A, AKAHANE M, SHIGEMATSU H, et al. Cell sheet transplantation of cultured mesenchymal stem cells enhances bone formation in a rat nonunion model. Bone. 2010;46(2):418-424.
[20] 梁志勇,李华壮,赵光宗,等. 髓内钉内固定治疗股骨干多段骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(4):375-377.
[21] 黄培镇,董航,蔡群斌,等. 顺行和逆行髓内钉治疗不同部位股骨干骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(6):868-872.
[22] BHANDARI M, GUYATT GH, SWIONTKOWSKI MF, et al. A lack of consensus in the assessment of fracture healing among orthopaedic surgeons. J Orthop Trauma. 2002;16(8):562-566.
[23] WHELAN DB, BHANDARI M, MCKEE MD, et al. Interobserver and intraobserver variation in the assessment of the healing of tibial fractures after intramedullary fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002,84(1):15-18.
[24] CLAES L, ECKERT-HUBNER K, AUGAT P. The effect of mechanical stability on local vascularization and tissue differentiation in callus healing. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(5):1099-1105.
[25] LIENAU J, SCHELL H, DUDA GN, et al. Initial vascularization and tissue differentiation are influenced by fixation stability. J Orthop Res. 2005; 23(3):639-645.
[26] HAMAHASHI K, UCHIYAMA Y, KOBAYASHI Y, et al. Clinical outcomes of intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures with third fragments: a retrospective analysis of risk factors for delayed union. Trauma Surg Acute Care Open. 2019;4(1):e203.
[27] YOON YC, SONG HK, HAN JS, et al. Antegrade nailing in femoral shaft fracture patients - comparison of outcomes of isolated fractures, multiple fractures and severely injured patients. Injury. 2021;52(10):3068-3074.
[28] 杨楷文,何思远,罗亮,等. 侧方钢板联合植骨治疗股骨干骨折髓内钉固定术后不愈合17例[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2022,30(7):65-69.
[29] AGARWALA S, MENON A, CHAUDHARI S. Cerclage Wiring as an Adjunct for the Treatment of Femur Fractures: Series of 11 Cases. J Orthop Case Rep. 2017;7(4):39-43.
[30] APIVATTHAKAKUL T, PHORNPHUTKUL C. Percutaneous cerclage wiring for reduction of periprosthetic and difficult femoral fractures: a technical note. Injury. 2012;43(6):966-971.
[31] EHLINGER M, NIGLIS L, FAVREAU H, et al. Vascular complication after percutaneous femoral cerclage wire. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018; 104(3):377-381.
[32] DEVENDEA A, AVINASH M, CHIDAMBARAM D, et al. Vascular injuries due to cerclage passer: Relevant anatomy and note of caution. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26(1):614422904.
|