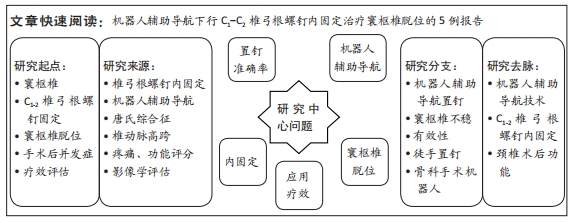
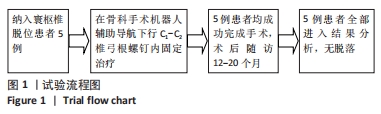
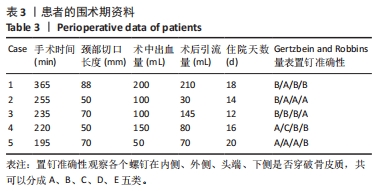
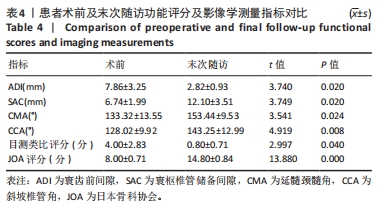
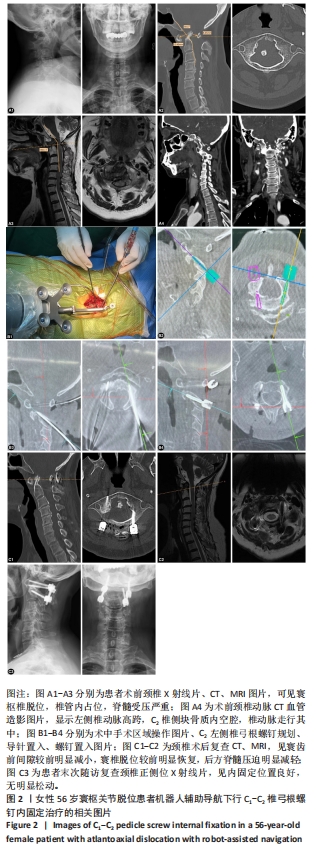
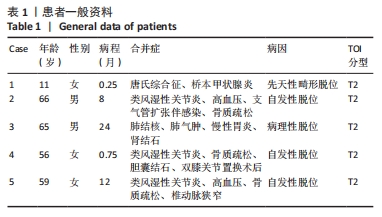
[1] 李俊宏, 廖晖. 寰枢椎脱位的分型与外科治疗[J]. 骨科,2022,13(3): 279-284.
[2] XIONGSHENG C, YIFAN T. Diagnosis and treatment of atlantoaxial dislocation. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2023;43(7):471.
[3] 欧阳北平, 马向阳, 罗春山, 等. 不同横连模式后路寰枢椎椎弓根钉棒固定术治疗寰枢椎脱位的临床疗效[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2022,32(12):1112-1119.
[4] 谭明生. 寰枢椎脱位的中西医治疗[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022, 30(21):1921-1924.
[5] 移平, 谭明生. 寰椎椎弓根螺钉固定的解剖学基础及置钉技术[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017,27(1):89-94.
[6] 刘仲源, 魏传付, 李念虎. 手术治疗寰枢关节不稳或脱位的研究进展[J]. 中国现代手术学杂志,2023,27(2):150-154.
[7] CACCIOLA F, PHALKE U, GOEL A. Vertebral artery in relationship to C1-C2 vertebrae: An anatomical study. Neurology India. 2004;52(2):178-184.
[8] KANEYAMA S, SUGAWARA T, SUMI M, et al. A novel screw guiding method with a screw guide template system for posterior C-2 fixation: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(2):231-238.
[9] 田伟, 范明星, 张琦, 等. 中国骨科手术机器人的发展[J]. 应用力学学报,2023,40(1):1-6.
[10] 谭明生, 张光铂, 王文军, 等. 寰枢椎脱位的外科分型及其处理对策[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2007,17(2):111-115.
[11] TIAN C, LV Y, LI S, et al. Factors related to improved American Spinal Injury Association grade of acute traumatic spinal cord injury. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8(20):4807-4815.
[12] 徐宏光, 张敏, 王弘, 等. QLS-DSD与JOA评分量表在脊柱退行性疾病患者评分应用中的比较[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2013,6(6): 482-486.
[13] BOTELHO RV, FERREIRA ED. Angular craniometry in craniocervical junction malformation. Neurosurg Rev. 2013;36(4):603-610,610.
[14] VARDIMAN AB, WALLACE DJ, CRAWFORD NR, et al. Pedicle screw accuracy in clinical utilization of minimally invasive navigated robot-assisted spine surgery. J Robot Surg. 2020;14(3):409-413.
[15] 刘虎, 李承鑫. 唐氏综合征患儿寰枢椎不稳定颈后路内固定术的疗效[J]. 武警医学,2021,32(8):691-694.
[16] 谭明生, ATUL GOEL, KUNIYOSHI ABUMI, 等. 寰枢椎脱位中西医结合诊治指南(2019)[J]. 中国骨伤,2020,33(1):27-38.
[17] 李文浩, 张刘波, 何昆, 等. 寰椎椎弓根螺钉技术治疗寰枢椎脱位的Meta分析[J]. 中日友好医院学报,2021,35(1):35-37.
[18] BULL MJ. Down Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(24): 2344-2352.
[19] CAIRD MS, WILLS BP, DORMANS JP. Down syndrome in children: the role of the orthopaedic surgeon. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2006;14(11): 610-619.
[20] LI C, TIAN Y, REN Q, et al. Treatment of Atlantoaxial Dislocation in Children with Down Syndrome Using Posterior Atlantoaxial Screw Fixation. Front Surg. 2022;9:877929.
[21] PUESCHEL SM, SCOLA FH, PEZZULLO JC. A longitudinal study of atlanto-dens relationships in asymptomatic individuals with Down syndrome. Pediatrics. 1992;89(6 Pt 2):1194-1198.
[22] KLEPINOWSKI T, ZYLKA N, PALA B, et al. Prevalence of high-riding vertebral arteries and narrow C2 pedicles among Central-European population: a computed tomography-based study. Neurosurg Rev. 2021;44(6):3277-3282.
[23] 黄学良, 朱双芳, 林雨聪, 等. 三维重建CT血管造影在C1-2水平椎动脉变异诊断中的价值[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(4):315-319.
[24] JEANNERET B, MAGERL F. Primary posterior fusion C1/2 in odontoid fractures: indications, technique, and results of transarticular screw fixation. J Spinal Disord. 1992;5(4):464-475.
[25] HARMS J, MELCHER RP. Posterior C1-C2 fusion with polyaxial screw and rod fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(22):2467-2471.
[26] 吴冬灵, 谢亮文, 刘瑞仁, 等. 标杆型3D打印导板在寰枢椎脱位治疗中的应用疗效及准确性研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020, 13(2):138-142.
[27] ZHAN J, XU W, LIN J, et al. Accuracy and Safety of Robot-Assisted versus Fluoroscopy-Guided Posterior C1 Lateral Mass and C2 Pedicle Screw Internal Fixation for Atlantoaxial Dislocation: A Preliminary Study. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:8508113.
[28] 徐子航, 龙浩, 何祖波, 等. 机器人辅助皮质骨轨迹螺钉内固定术治疗腰椎退行性疾病的置钉准确率及学习曲线分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022,32(4):305-312.
[29] 刘毅, 赵志刚, 王昕, 等. 机器人辅助椎弓根钉固定治疗颈椎骨折脱位[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(21):1941-1946.
[30] HU Y, DONG W, SPIKER WR, et al. An anatomic study to determine the optimal entry point, medial angles, and effective length for safe fixation using posterior C1 lateral mass screws. Spine. 2015;40(4):E191-E198.
[31] 褚开伟, 洪宾, 石岩, 等. 机器人引导技术与计算机辅助导航胸腰椎椎弓根螺钉置钉准确性的荟萃分析[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2023,44(3): 349-352.
[32] 贾红伟, 马文海, 龙玉斌, 等. 机器人导航辅助经皮椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效观察[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2023,44(3):445-447. |