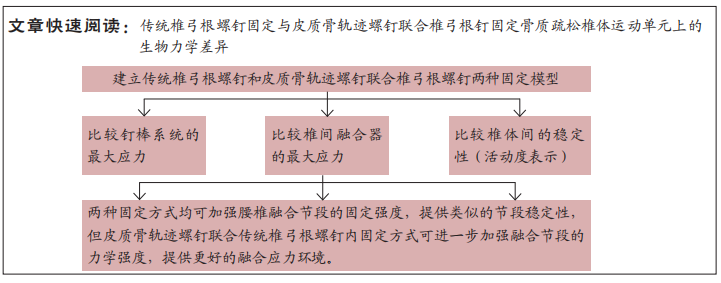
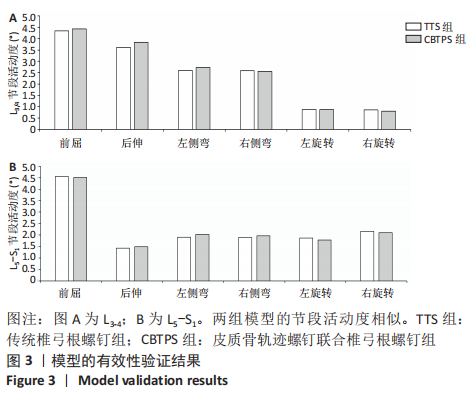
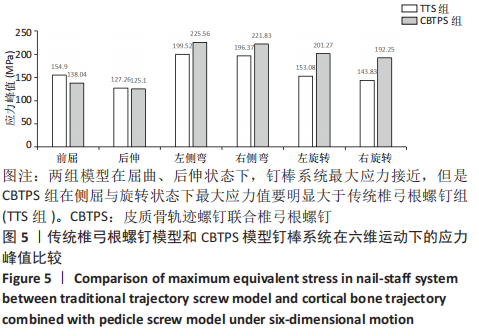
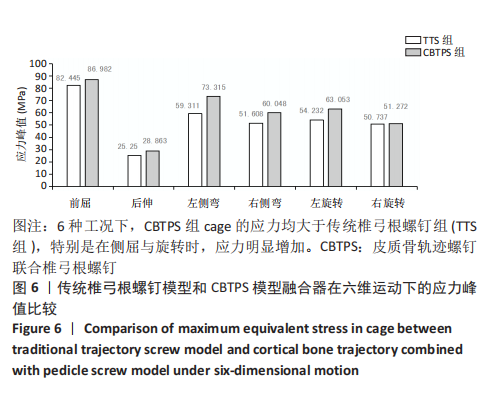
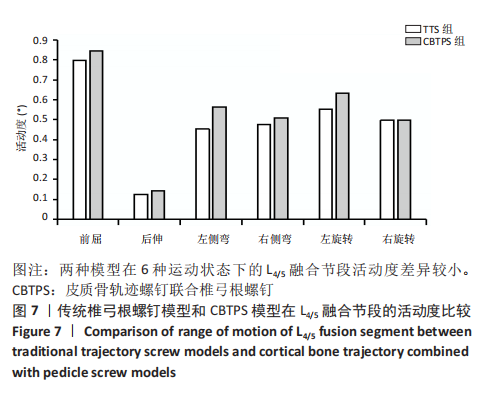
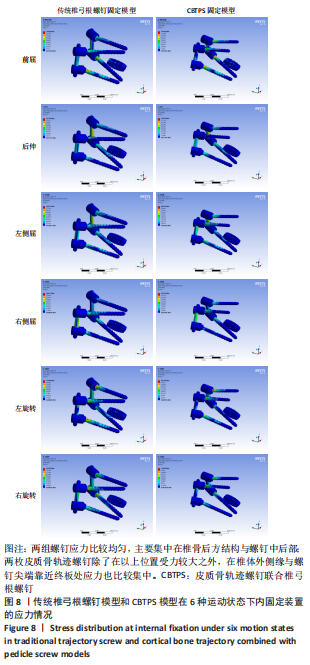
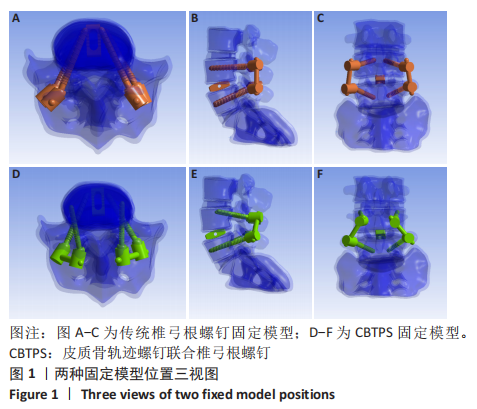
[1] 梁海峰,陆顺一,刘书豪,等.高龄腰椎管狭窄症患者的手术方式选择及疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(8):705-712.
[2] 王坤,梅伟.腰椎管狭窄症的治疗进展[J].骨科,2019,10(3):248-252+ 256.
[3] JIA L, YU Y, KHAN K, et al. Superior Facet Joint Violations during Single Level Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Preliminary Retrospective Clinical Study. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:6152769.
[4] 丁红涛,海涌,刘玉增,等.腰椎后路融合术应用皮质骨轨迹螺钉内固定对邻近节段退变的影响[J].中华医学杂,2020,100(43):3437-3442.
[5] SANTONI BG, HYNES RA, MCGILVRAY KC, et al. Cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screws. Spine. 2009;9(5):366-373.
[6] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, HYNES RA, et al. Cortical bone trajectory for thoracic pedicle screws: a technical note. ClinSpine Surg. 2017;30(5): E497-504.
[7] 席焱海, 王洋, 余将明, 等.应用皮质骨轨迹螺钉联合椎弓根螺钉内固定技术治疗老年骨质疏松腰椎退变性疾病的临床疗效[J].第二军医大学学报,2016;37(7):879-883.
[8] CHIU PY, CHI JE, KAO FC, et al. Minimally Invasive Surgery Combining Cortical Bone Trajectory Screws and Pedicle Screws to Treat Spondylodiskitis: Technical Notes and Preliminary Results. World Neurosurg. 2020;135:e333-e338.
[9] XU H, JU W, XU N, et al. Biomechanical comparison of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with 1 or 2 cages by finite-element analysis. Neurosurgery. 2013;73(2 Suppl Operative):ons198-205;discussion ons205.
[10] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, NEMOTO O, et al. Morphometric measurement of cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screw insertion using computed tomography. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(6):E248-253.
[11] GUO LX, FAN W. The Effect of Single-Level Disc Degeneration on Dynamic Response of the Whole Lumbar Spine to Vertical Vibration. World Neurosurg. 2017;105:510-518.
[12] 陆声,徐永清,张美超,等.骨质疏松椎体增强后对相邻椎体生物力学影响的有限元研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(9):864-867.
[13] HUANG YP, DU CF, CHENG CK, et al. Preserving Posterior Complex Can Prevent Adjacent Segment Disease following Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgeries: A Finite Element Analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11(11):e0166452.
[14] SHIM CS, PARK SW, LEE SH, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an interspinous stabilizing device, Locker. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33(22):E820-827.
[15] 魏源标,郭惠智,张顺聪.皮质骨轨迹螺钉固定对相邻节段影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(18):2799-2804.
[16] SHEN H, FOGEL GR, ZHU J, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of Different Lumbar Interspinous Process Devices: A Finite Element Study. World Neurosurg. 2019;127:e1112-e1119.
[17] BALUCH DA, PATEL AA, LULLO B, et al. Effect of physiological loads on cortical and traditional pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(22):E1297-1302.
[18] WRAY S, MIMRAN R, VADAPALLI S, et al. Pedicle screw placement in the lumbar spine: effect of trajectory and screw design on acute biomechanical purchase. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(5):503-510.
[19] 潘爱星,刘玉增,海涌,等. 腰椎皮质骨螺钉联合椎弓根螺钉固定对融合节段应力影响的有限元分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2022,32(1):67-74.
[20] James JY.脊柱功能重建外科学:高级理论和技巧[M].邹德威,杨慧林,金大地,等译.北京:人民军医出版社,2008.
[21] 吴晓宇,王哲,甘浩然,等.皮质骨轨迹螺钉技术应用于骨质疏松患者腰椎固定的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(12): 1126-1131.
[22] 刘光普,刘磊,宋飞霏,等.后路减压椎间融合联合皮质骨轨迹螺钉内固定治疗腰椎融合术后邻近节段退行性病变疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2020,35(3):278-280.
[23] 中国康复医学会脊柱脊髓专业委员会腰椎研究学组.腰椎后路经皮质骨轨迹螺钉内固定技术应用中国专家共识[J].中华医学杂志, 2022,102(13):908-913.
[24] LEE GW, SHIN JH. Comparative Study of Two Surgical Techniques for Proximal Adjacent Segment Pathology after Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Pedicle Screws: Fusion Extension using Conventional Pedicle Screw vs Cortical Bone Trajectory-Pedicle Screw (Cortical Screw). World Neurosurg. 2018;117:e154-e161.
[25] BRUZZO M, SEVERI P, BACIGALUPPI S. Midline lumbar fusion with cortical bone trajectory as first line treatment in a selected series of patients with lumbar instability. J Neurosurg Sci. 2020;64(3):238-242.
[26] ZHANG L, TIAN N, YANG J, et al. Risk of pedicle and spinous process violation during cortical bone trajectory screw placement in the lumbar spine. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):536.
[27] SAKAURA H, MIWA T, YAMASHITA T, et al. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cortical bone trajectory screw fixation versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion using traditional pedicle screw fixation for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: a comparative study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25(5):591-595.
|