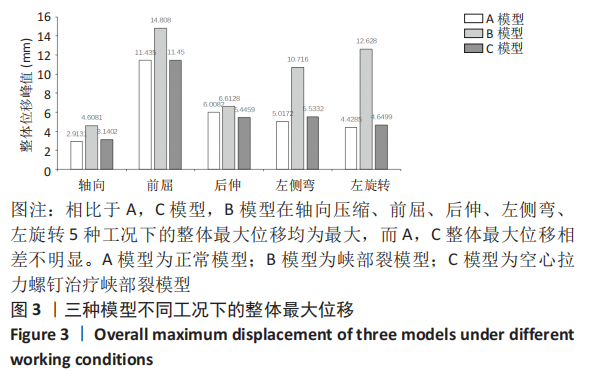
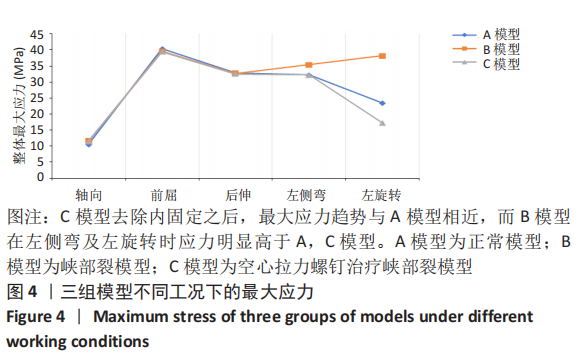
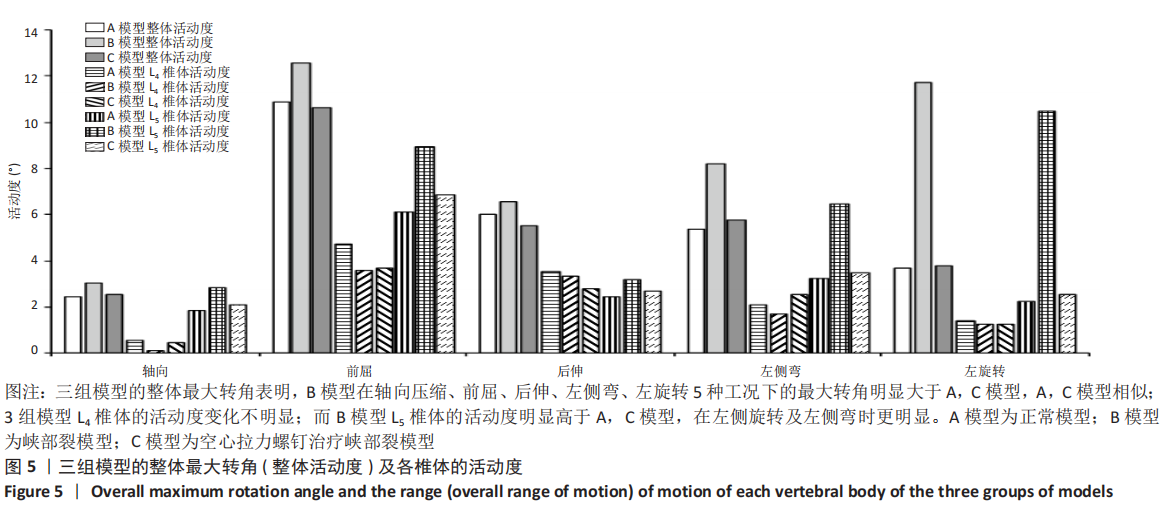
[1] SELHORST M, FISCHER A, MACDONALD J. Prevalence of Spondylolysis in Symptomatic Adolescent Athletes: An Assessment of Sport Risk in Nonelite Athletes. Clin J Sport Med. 2019;29(5):421-425.
[2] OREN S, ITZIK M, CARA O, et al. Overuse Injuries in the IDF’s Combat Training Units: Rates, Types, and Mechanisms of Injury. Mil Med. 2018; (3-4):196-200.
[3] HSU WK, JENKINS TJ. Management of Lumbar Conditions in the Elite Athlete. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(7):489-498.
[4] BERGER R, DOYLE S. Spondylolysis 2019 update. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2019;(1):61-68.
[5] YING L, HRESKO M. Lumbar spine surgery in athletes: outcomes and return-to-play criteria. Clin Sports Med. 2012;(3):487-498.
[6] CRAWFORD C, LEDONIO C, BESS R, et al. Current Evidence Regarding the Etiology, Prevalence, Natural History, and Prognosis of Pediatric Lumbar Spondylolysis: A Report from the Scoliosis Research Society Evidence-Based Medicine Committee. Spine Deform. 2015;(1):12-29.
[7] RITA G, RENATO A, FILIPE L, et al. Return to play after conservative and surgical treatment in athletes with spondylolysis: A systematic review. Phys Ther Sport. 2019;37:34-43.
[8] BUCK J. Direct repair of the defect in spondylolisthesis. Preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970;52(3):432-437.
[9] 张涛, 屈涛, 刘华, 等. Wiltse入路椎弓根钉-椎板钩内固定联合自体髂骨移植修复单节段腰椎峡部裂疗效分析[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2020,7(45):761-766.
[10] GILLET P, PETIT M. Direct repair of spondylolysis without spondylolisthesis, using a rod-screw construct and bone grafting of the pars defect. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999;24(12):1252-1256.
[11] GHISELLI G, WANG JC, BHATIA NN, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration in the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86(7): 1497-1503.
[12] LU T, LU Y. Comparison of Biomechanical Performance Among Posterolateral Fusion and Transforaminal, Extreme, and Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019;129:e890-e899.
[13] XU H, JU W, XU N, et al. Biomechanical comparison of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with 1 or 2 cages by finite-element analysis. Neurosurgery. 2013;73(2 Suppl Operative):ons198-205; discussion ons205.
[14] EDELSON JG, NATHAN H. Nerve root compression in spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68(4):596-599.
[15] DENOZIERE G, KU DN. Biomechanical comparison between fusion of two vertebrae and implantation of an artificial intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 2006;39(4):766-775.
[16] MO Z, ZHAO Y, DU C, et al. Does location of rotation center in artificial disc affect cervical biomechanics? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(8): E469-E475.
[17] KIM TY, KANG KT, YOON DH, et al. Effects of lumbar arthrodesis on adjacent segments: differences between surgical techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(17):1456-1462.
[18] AMBATI DV, WRIGHT EJ, LEHMAN RJ, et al. Bilateral pedicle screw fixation provides superior biomechanical stability in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a finite element study. Spine J. 2015;15(8): 1812-1822.
[19] TENCER AF, AHMED AM, BURKE DL. Some static mechanical properties of the lumbar intervertebral joint, intact and injured. J Biomech Eng. 1982;104(3):193-201.
[20] MARKOLF KL. Deformation of the thoracolumbar intervertebral joints in response to external loads: a biomechanical study using autopsy material. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1972;54(3):511-533.
[21] DUNN B. Lumbar spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. JAAPA. 2019; 32(12):50-51.
[22] MICHELI LJ, WOOD R. Back pain in young athletes. Significant differences from adults in causes and patterns. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1995;149(1):15-18.
[23] 杨大龙, 申勇, 张英泽, 等. 成人峡部裂性腰椎滑脱合并椎间盘突出的手术治疗[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(6):485-486.
[24] BELYTSCHKO T, KULAK RF, SCHULTZ AB, et al. Finite element stress analysis of an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 1974;7(3):277-285.
[25] 聂文忠, 李晓萱, 曾嘉艺, 等. 腰椎病变融合器注入骨水泥后不同置入及固定方法的生物力学变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(10):1505-1509.
[26] 于博. 腰椎弹性内固定系统的设计与力学研究[D]. 广州:南方医科大学,2009.
[27] 朱立新, 王健, 曹延林, 等. 腰椎峡部裂机翼型记忆合金固定装置的有限元分析[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2012,30(3):333-336.
[28] 周初松, 肖文德, 张效三, 等. 腰椎峡部裂翼状记忆合金节段内固定器的研制[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2006,4(1):33-37.
[29] 顾晓民, 贾连顺, 陈雄生, 等. 单椎节与单节段内固定治疗腰椎椎弓峡部裂的有限元分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2011,26(1):63-68.
[30] 朱磊, 许鹏, 王冬冬, 等. 青少年腰椎峡部裂单椎体内固定研究进展[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2019,17(3):211-215.
[31] KURD MF, PATEL D, NORTON R, et al. Nonoperative treatment of symptomatic spondylolysis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007;20(8):560-564. |