中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (17): 2555-2561.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.17.017
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
桥接组合式内固定与金属锁定接骨板钉系统修复股骨干骨折的生物力学比较
吕志强,李兴华,王爱国
- 郑州市骨科医院下肢骨科Ⅰ,河南省郑州市 450000
Repair of femoral shaft fracture with bridging combined internal fixation and locking plate screw system: a biomechanical comparison
Lv Zhi-qiang, Li Xing-hua, Wang Ai-guo
- First Department of Lower Limb Orthopedics, Zhengzhou Orthopedics Hospital, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
金属锁定接骨板钉系统:通过金属锁定接骨板钉固定,可以获得良好的解剖复位效果以及固定效果。在固定过程中,接骨板板上的螺钉加压孔存在一定的倾斜角度,在拧紧螺钉的时候,会出现纵向的滑行现象,导致股骨出现一定的相对板的移动现象。于是,骨折断端间会受到一定的压力,不易于骨折愈合。
桥接组合式内固定系统:是一种新型的内固定系统,包括连接块、连接棒、固定螺钉、锁定螺钉等。桥接组合式内固定具有较好的生物力学特点,通过多棒和转向置钉方式进行三维固定,可减少应力集中等不良情况的出现。在连接块内部设有平行于固定块平面的连接勾,与连接棒滑动配合;垂直于连接块主平面设有螺钉孔,连接槽与螺钉帽局部交叉;固定螺钉或锁定螺钉与螺钉孔配合,螺钉之锥帽紧压于连接棒上。
背景:临床对股骨干骨折进行修复的过程中,可以选择不同内固定方式,包括桥接组合式内固定系统与金属锁定接骨板钉系统。
目的:比较桥接组合式内固定系统与金属锁定接骨板钉系统固定股骨干骨折的生物力学特性。
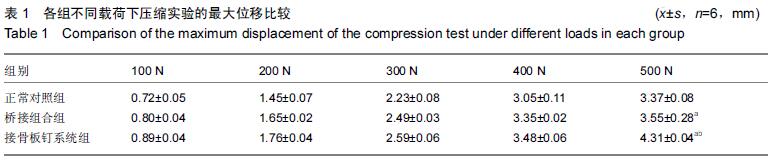
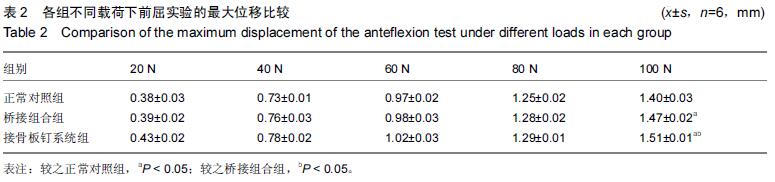
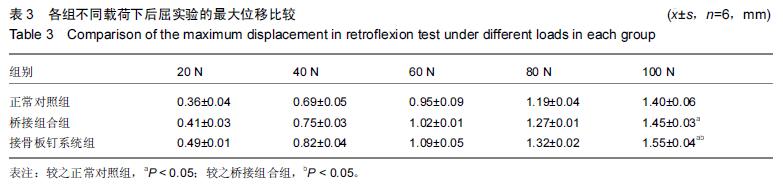
方法:收集18 个股骨标本,随机分为 3 组,每组6个,其中正常对照组不作任何处理,其余两组制备股骨干骨折模型,桥接组合组行桥接组合式内固定,接骨板钉系统组行金属锁定接骨板钉系统内固定。对3组标本进行生物力学测试,通过股骨压缩实验记录3组最大载荷500 N作用下的最大位移;通过股骨前屈实验记录3组最大载荷100 N作用下的最大位移;通过股骨后屈实验记录3组最大载荷 100 N 作用下的最大位移。
结果与结论:①不同载荷下压缩实验:桥接组合组和接骨板钉系统组的最大位移均大于正常对照组,其中在最大载荷500 N下,桥接组合组和接骨板钉系统组的最大位移均显著大于正常对照组(P < 0.05); 且桥接组合组显著小于接骨板钉系统组(P < 0.05);②不同载荷下前屈实验:桥接组合组和接骨板钉系统组的最大位移均大于正常对照组,其中在最大载荷100 N下,桥接组合组和接骨板钉系统组的最大位移均显著大于正常对照组(P < 0.05);且桥接组合组显著小于接骨板钉系统组(P < 0.05);③不同载荷下后屈实验:桥接组合组和接骨板钉系统组的最大位移均大于正常对照组,其中在最大载荷100 N下,桥接组合组和接骨板钉系统组的最大位移均显著大于正常对照组(P < 0.05);且桥接组合组显著小于接骨板钉系统组(P < 0.05);④结果表明,体外模拟股骨干骨折桥接组合式内固定系统与金属锁定接骨板钉系统均能获得一定的固定效果,设计符合生物力学原理,其中桥接组合式内固定在压应力以及前屈、后屈应力作用下,均可以保持较小的位移,提示具有较好的变形抵抗能力。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-6247-5720(吕志强)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)