中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (12): 1847-1852.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2519
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
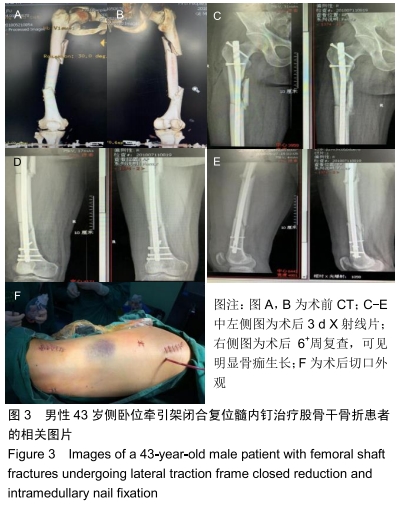
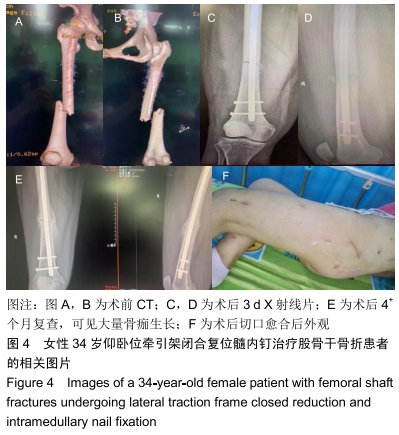
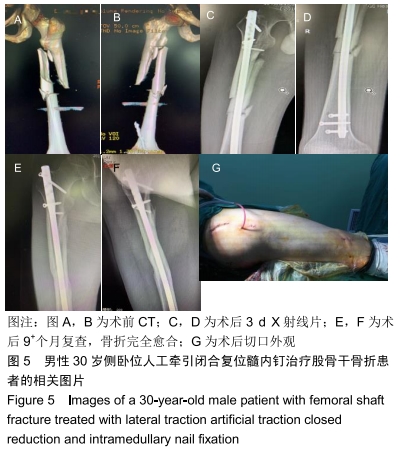
侧卧位牵引架闭合复位髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折
袁 野,黄文良,徐 林,阮世强,王世强
- 遵义医科大学第三附属医院创伤骨科,贵州省遵义市 563000
Treatment of femoral shaft fracture with lateral traction frame closed reduction and intramedullary nail fixation
Yuan Ye, Huang Wenliang, Xu Lin, Ruan Shiqiang, Wang Shiqiang
- Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
闭合复位髓内钉固定:因闭合复位髓内钉术手术创伤小,能间接复位保护骨折端血运,术后伤口并发症较少,生物力学性能优越,已成为长骨干骨折的首选方法。
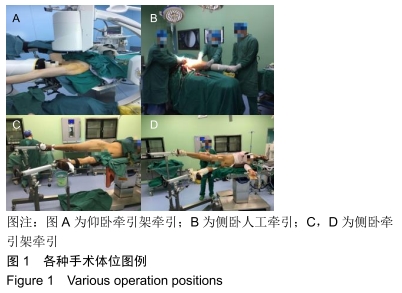
侧卧位与仰卧位牵引架牵引:术中通过充分对抗肌肉对抗力后,仰卧位对骨折端前后移位不好控制或纠正;侧卧位更方便纠正断端移位,且减少髋部软组织对手术操作的干扰。
背景:目前临床上对于股骨干骨折髓内钉治疗的闭合复位方式研究相对较少。
目的:探讨侧卧位应用牵引架闭合复位髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折的效果。
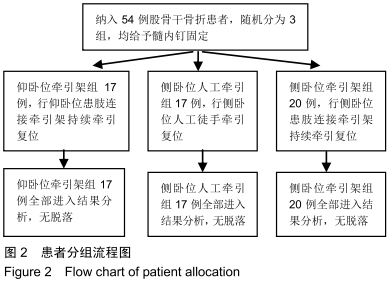
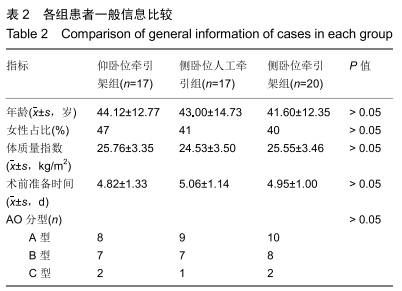
方法:遵义医科大学第三附属医院创伤骨科2015年1月至2018年10月通过髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折54例,随机分为3组,其中仰卧位牵引架组17例,侧卧位人工牵引组17例,侧卧位牵引架组20例。所有患者对治疗方案均知情同意,且得到医院伦理委员会批准。比较3组患者的闭合复位成功率、手术时间、术中出血量、骨折愈合时间及术后 6个月膝关节美国特种外科医院评分。
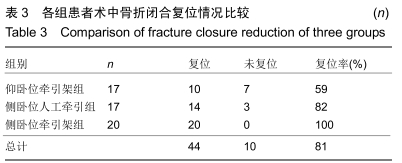
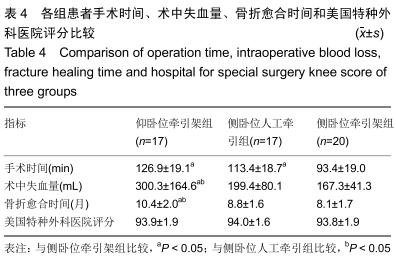
结果与结论:①3组患者获得6-15个月随访;②骨折闭合复位成功率:侧卧位牵引架组100%,侧卧位人工牵引组82%,仰卧位牵引架组59%,仰卧位牵引架组同侧卧位人工牵引组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),侧卧位牵引架组显著高于仰卧位牵引架组(P=0.002),侧卧位牵引架组同侧卧位人工牵引组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③手术时间:仰卧位牵引架组同侧卧位人工牵引组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),侧卧位牵引架组的手术时间显著短于仰卧位牵引架组及侧卧位人工牵引组(P < 0.05);④术中出血量:仰卧位牵引架组的术中失血量显著高于侧卧位人工牵引组(P=0.02)及侧卧位牵引架组(P=0.001),侧卧位人工牵引组同侧卧位牵引架组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑤骨折愈合时间:仰卧位牵引架组骨折愈合时间显著长于侧卧位人工牵引组(P=0.030)及侧卧位牵引架组(P < 0.001),侧卧位人工牵引组同侧卧位牵引架组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑥3组患者术后6个月膝关节美国特种外科医院评分差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑦结果表明,应用侧卧位牵引架闭合复位髓内钉固定治疗股骨干骨折具有复位成功率高、手术时间较短、术中出血更少、骨折愈合快的优点,值得临床推广应用。
ORCID: 0000-0002-4621-2653(袁野)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: