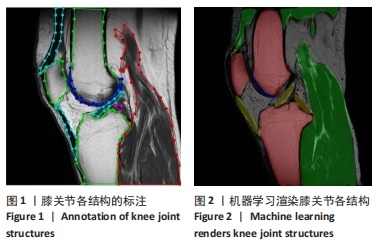
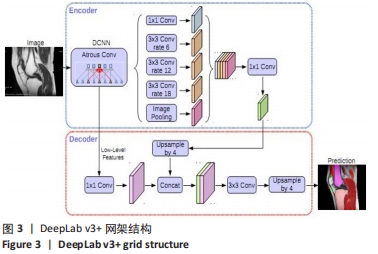
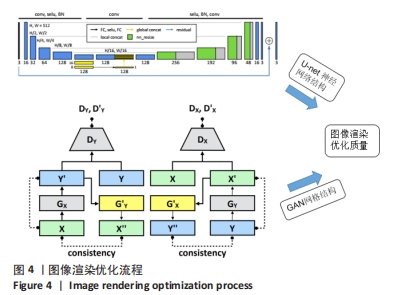
[1] 孙若凡,张唯唯. 基于3D U-Net实现人体耳软骨MRI图像的解剖结构分割[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报,2021,40(5):531-539.
[2] PETERFY CG, GOLD G, ECKSTEIN F, et al. MRI protocols for whole-organ assessment of the knee in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14 Suppl A:A95-111.
[3] ROEMER FW, CREMA MD, TRATTNIG S, et al. Advances in imaging of osteoarthritis and cartilage. Radiology. 2011;260(2):332-354.
[4] PEDOIA V, MAJUMDAR S, LINK TM. Segmentation of joint and musculoskeletal tissue in the study of arthritis. MAGMA. 2016;29(2):207-221.
[5] ZARYCHTA P. Atlas-Based Segmentation in Extraction of Knee Joint Bone Structures from CT and MR. Sensors (Basel). 2022;22(22):8960.
[6] LEE JG, GUMUS S, MOON CH, et al. Fully automated segmentation of cartilage from the MR images of knee using a multi-atlas and local structural analysis method. Med Phys. 2014;41(9):092303.
[7] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521:436-444.
[8] 胜照友. 基于深度学习的膝关节MRI图像半月板撕裂识别与检测方法研究[D].武汉:武汉科技大学,2022
[9] 于宁波,刘嘉男,高丽,等.基于深度学习的膝关节MR图像自动分割方法[J].仪器仪表学报,2020,41(6):140-149.
[10] SMITH SE, BAHOUTH SM, DURYEA J. Quantitative bone marrow lesion, meniscus, and synovitis measurement: current status. Skeletal Radiol. 2023;52(11):2123-2135.
[11] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, PAIEMENT P, PELLETIER JP. Magnetic resonance imaging assessments for knee segmentation and their use in combination with machine/deep learning as predictors of early osteoarthritis diagnosis and prognosis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2023;15:1759720X231165560.
[12] KESSLER DA, MACKAY JW, CROWE VA, et al. The optimisation of deep neural networks for segmenting multiple knee joint tissues from MRIs. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2020;86:101793.
[13] GAJ S, YANG M, NAKAMURA K, et al. Automated cartilage and meniscus segmentation of knee MRI with conditional generative adversarial networks. Magn Reson Med. 2020;84(1):437-449.
[14] ALMAJALID R, ZHANG M, SHAN J. Fully Automatic Knee Bone Detection and Segmentation on Three-Dimensional MRI. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(1):123.
[15] LIU F, ZHOU Z, SAMSONOV A, et al. Deep learning approach for evaluating knee MR images: achieving high diagnostic performance for cartilage lesion detection. Radiology. 2018;289(1):160-169.
[16] PEDOIA V, NORMAN B, MEHANY SN, et al. 3D convolutional neural networks for detection and severity staging of meniscus and PFJ cartilage morphological degenerative changes in osteoarthritis and anterior cruciate ligament subjects. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019;49(2):400-410.
[17] BIEN N, RAJPURKAR P, BALL RL, et al. Deep-learning-assisted diagnosis for knee magnetic resonance imaging: Development and retrospective validation of MRNet. PLoS Med. 2018;15(11):e1002699.
[18] COUTEAUX V, SI-MOHAMED S, NEMPONT O, et al. Automatic knee meniscus tear detection and orientation classification with Mask-RCNN. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019;100(4):235-242.
[19] ROBLOT V, GIRET Y, ANTOUN MB, et al. Artificial intelligence to diagnose meniscus tears on MRI. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019;100(4):243-249.
[20] CHANG PD, WONG TT, RASIEJ MJ. Deep Learning for Detection of Complete Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear. J Digit Imaging. 2019;32(6):980-986.
[21] GERMANN C, MARBACH G, CIVARDI F, et al. Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: Performance Comparison of Homogenous Versus Heterogeneous Knee MRI Cohorts With Different Pulse Sequence Protocols and 1.5-T and 3-T Magnetic Field Strengths. Invest Radiol. 2020;55(8):499-506.
[22] NORMAN B, PEDOIA V, MAJUMDAR S. Use of 2D U-Net Convolutional Neural Networks for Automated Cartilage and Meniscus Segmentation of Knee MR Imaging Data to Determine Relaxometry and Morphometry. Radiology. 2018; 288(1):177-185.
[23] TIULPIN A, THEVENOT J, RAHTU E, et al. Automatic knee osteoarthritis diagnosis from plain radiographs: a deep learning-based approach. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1-10.
[24] 马明昌,李永杰,徐国胜,等. KOAX线辅助诊断模型建立的临床应用初探[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(2):152-158.
[25] GUAN B, LIU F, HAJ-MIRZAIAN A, et al. Deep learning risk assessment models for predicting progression of radiographic medial joint space loss over a 48-MONTH follow-up period. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(4):428-437.
[26] 王昕,刘爽,周长才. 基于深度学习和磁共振图像的KOA分类[J].长春工业大学学报,2023,44(1):45-51.
[27] 司莉萍,宣锴,姚伟武.基于膝关节软骨磁共振半定量评分的自动分割与分类评价[J].磁共振成像,2018,9(12):928-935.
[28] LIU F, ZHOU Z, JANG H, et al. Deep convolutional neural network and 3D deformabl approach for tissue segmentation in musculoskeletal magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2018;79(4):2379-2391.
[29] COOTES TF, TAYLOR CJ, COOPER DH, et al. Active shape models-their training and application. Computer Vision Image Understand. 1995;61:38-59.
[30] KAUFFMANN C, GRAVEL P, GODBOUT B, et al. Computer-aided method for quantification of cartilage thickness and volume changes using MRI: validation study using a synthetic model. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2003;50(8):978-988.
[31] DURYEA J, NEUMANN G, BREM MH, et al. Novel fast semi-automated software to segment cartilage for knee MR acquisitions. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007; 15(5):487-492.
[32] TAMEZ-PENA JG, BARBU-MCINNIS M, TOTTERMAN S. Knee cartilage extraction and bone cartilage interface analysis from 3D MRI data sets. In: Fitzpatrick JM and Sonka M (eds.) SPIE Proceedings Medical Imaging: Image Processing. Washington, D. C.: SPIE, 2004:1774-1785.
[33] STAMMBERGER T, ECKSTEIN F, MICHAELIS M, et al. Interobserver reproducibility of quantitative cartilage measurements: comparison of B-spline snakes and manual segmentation. Magn Reson Imaging. 1999;17(7):1033-1042.
[34] SHIM H, LEE S, KIM B, et al. 3-D segmentation of articular cartilages by graph cuts using knee MR images from osteoarthritis initiative. In: Reinhart JM and Pluim JPW (eds.) Medical Imaging: Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA: SPIE Digital Library, 2008:691448.
[35] WARFIELD SK, KAUS M, JOLESZ FA, et al. Adaptive, template moderated, spatially varying statistical classification. Med Image Anal. 2000;4(1):43-55
[36] STAMMBERGER T, ECKSTEIN F, ENGLMEIER KH, et al. Determination of 3D cartilage thickness data from MR imaging: computational method and reproducibility in the living. Magn Reson Med. 1999;41(3):529-536.
[37] WIRTH W, ECKSTEIN F. A technique for regional analysis of femorotibial cartilage thickness based on quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2008;27(6):737-744.
[38] RAYNAULD JP, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BERTHIAUME MJ, et al. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of knee osteoarthritis progression over two years and correlation with clinical symptoms and radiologic changes. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(2):476-487.
[39] IRANPOUR-BOROUJENI T, WATANABE A, BASHTAR R, et al. Quantification of cartilage loss in local regions of knee joints using semi-automated segmentation software: analysis of longitudinal data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(3):309-314.
[40] LEE JG, GUMUS S, MOON CH, et al. Fully automated segmentation of cartilage from the MR images of knee using a multi-atlas and local structural analysis method. Med Phys. 2014;41(9):092303.
[41] DAM EB, LILLHOLM M, MARQUES J, et al. Automatic segmentation of high- and low-field knee MRIs using knee image quantification with data from the osteoarthritis initiative. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2015;2(2):024001.
[42] KUBICEK J, AUGUSTYNEK M, PENHAKER M, et al. Multiregional fuzzy thresholding segmentation completed by spatial median aggregation: modeling and segmentation of early pathological findings of articular cartilage. EMBEC NBC. 2017;65:876-879.
[43] FOLKESSON J, DAM E, OLSEN OF, et al. Automatic segmentation of the articular cartilage in knee MRI using a hierarchical multi-class classification scheme. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2005;8(Pt 1):327-334.
[44] PRASOON A, PETERSEN K, IGEL C, et al. Deep feature learning for knee cartilage segmentation using a triplanar convolutional neural network. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2013;16(Pt 2):246-253.
[45] WALLACE KG, PFEIFFER SJ, PIETROSIMONE LS, et al. Changes in Infrapatellar Fat Pad Volume 6 to 12 Months After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction and Associations With Patient-Reported Knee Function. J Athl Train. 2021;56(11):1173-1179.
[46] BONAKDARI H, TARDIF G, ABRAM F, et al. Serum adipokines/related inflammatory factors and ratios as predictors of infrapatellar fat pad volume in osteoarthritis: Applying comprehensive machine learning approaches. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):9993.
[47] LI W, ABRAM F, PELLETIER JP, et al. Fully automated system for the quantification of human osteoarthritic knee joint effusion volume using magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(5):R173. |
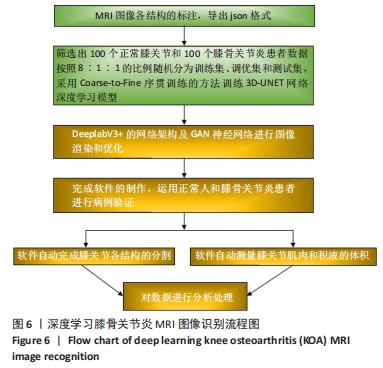
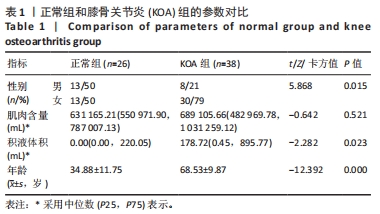
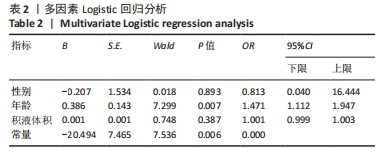
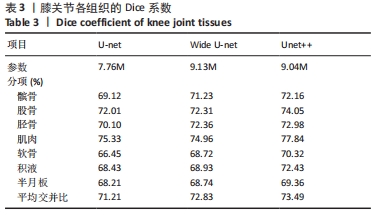
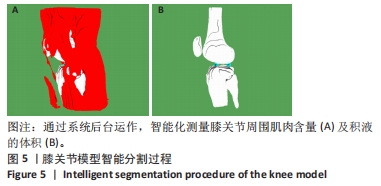
 其中pred为预测值的集合,true为真实值的集合,分子为pred和true之间的交集,乘以2是因为分母存在重复计算pred和true之间的共同元素的原因,分母为pred和true的并集。见表3。
其中pred为预测值的集合,true为真实值的集合,分子为pred和true之间的交集,乘以2是因为分母存在重复计算pred和true之间的共同元素的原因,分母为pred和true的并集。见表3。