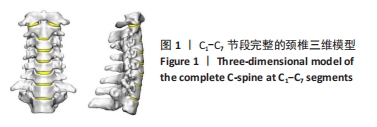
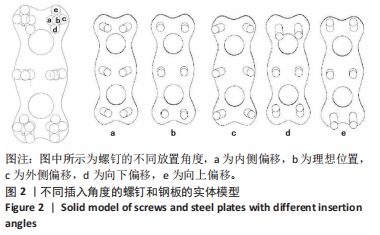
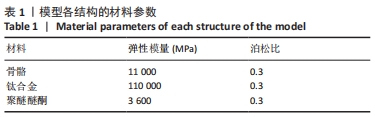
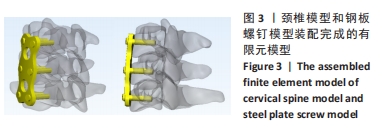
[1] SMITH G, ROBINSON R. The treatment of certain cervical-spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958;(3):607-624.
[2] 胡勇, 董伟鑫, 袁振山,等. 上颈椎结构损伤对C1-C2和C2-C3节段稳定性影响的生物力学研究 [J]. 中华创伤杂志,2015,31(4):360-365.
[3] MOLINARI L, FALCINELLI C, GIZZI A, et al. Biomechanical modeling of metal screw loadings on the human vertebra. Acta Mechanica Sinica. 2021;37:307-320.
[4] WOODARD T, CORTESE B, GUPTA S, et al. Racial Differences in Patients Undergoing Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: A Multi-Site Study. Clin Spine Surg. 2022;35(4):176-180.
[5] LIN M, SHAPIRO S, DOULGERIS J, et al. Cage-screw and anterior plating combination reduces the risk of micromotion and subsidence in multilevel anterior cervical discectomy and fusion-a finite element study. Spine J. 2021;21(5):874-882.
[6] 周盛源,张立岩,王济纬,等.颈前路钛板加钛网固定术后早期稳定性的观察[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2007,13(3):129-131.
[7] CHEUNG Z, GIDUMAL S, WHITE S, et al. Comparison of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion With a Stand-Alone Interbody Cage Versus a Conventional Cage-Plate Technique: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Global Spine J. 2019;9(4):446-455.
[8] FANG G, LIN Y, WU J, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Stand-Alone and Bilateral Pedicle Screw Fixation for Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgery-A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2020;141: e204-e212.
[9] CHIN K, PENCLE F, FRANCIS S, et al. Misaligned Versus Straight Placement of Anterior Cervical Plates: A Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes Study. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(5):389-395.
[10] QI M, CHEN H, XU C, et al. Comparison of three different posterior cervical approaches for treating cervical spine trauma with ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament. Zhonghua wai ke za zhi. 2019;57(3): 176-181.
[11] KARIM SMR, RAHMAN AKMS, SOBHAN SA, et al. Outcome of Long Segment Transpedicular Screw Fixation in Unstable Thoracolumbar Spine Injury with Incomplete Neurological Deficit. J Biosci Med. 2020; 8(3):166-187.
[12] 荣军. 颈椎前路椎间盘切除融合术治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的临床分析[J]. 母婴世界,2021(15):59.
[13] ZHANG W, ZHAO J, JIANG X, et al. Thoracic vertebra fixation with a novel screw-plate system based on computed tomography imaging and finite element method. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;187:104990.
[14] 张美超, 焦培峰. 骨科三维有限元力学仿真的建模[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(1):10-12.
[15] KABEL J, VAN RIETBERGEN B, DALSTRA M, et al. The role of an effective isotropic tissue modulus in the elastic properties of cancellous bone. J Biomech. 1999;32(7):673-680.
[16] WANG X, FENG M, HU Y. Establishment and Finite Element Analysis of a Three-dimensional Dynamic Model of Upper Cervical Spine Instability. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(3):500-509.
[17] RAO R, WANG M, SINGRAKHIA M, et al. Mechanical Evaluation of Posterior Wiring as a Supplement to Anterior Cervical Plate Fixation. Spine. 2004;29:2256-2259.
[18] 赵赫, 俞兴, 唐向盛, 等. 颈椎人工椎间盘置换术与颈椎前路减压融合术治疗双节段颈椎病的Meta分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2016,26(9):791-800.
[19] 祁敏, 陈华江, 徐辰, 等. 三种不同颈后路术式治疗颈椎外伤合并后纵韧带骨化患者的疗效比较[J]. 中华外科杂志,2019,57(3):176-181.
[20] FRAIOLI M, MARCIANI M, UMANA G, et al. Anterior Microsurgical Approach to Ventral Lower Cervical Spine Meningiomas: Indications, Surgical Technique and Long Term Outcome. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2015;14(4):505-510.
[21] HERRMANN A, GEISLER F. Geometric results of anterior cervical plate stabilization in degenerative disease. Spine. 2004;29(11):1226-1234.
[22] NAKASE H, PARK Y, KIMURA H, et al. Complications and long-term follow-up results in titanium mesh cage reconstruction after cervical corpectomy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(5):353-357.
[23] SEEBECK J, GOLDHAHN J, MORLOCK M, et al. Mechanical behavior of screws in normal and osteoporotic bone. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16 Suppl 2:S107-S111.
[24] 王正, 沈国平, 陈伟兵, 等. 椎弓根螺钉内固定稳定性的生物力学测试[J]. 医用生物力学,2002,17(2):80-84.
[25] 蔡风, 廖琦, 唐强, 等. 颈椎前路钢板螺钉系统交叉置钉与平行置钉的生物力学研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(3):223-226.
[26] MA Z, MA X, YANG H, et al. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion versus cervical arthroplasty for the management of cervical spondylosis: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(4):998-1008. |