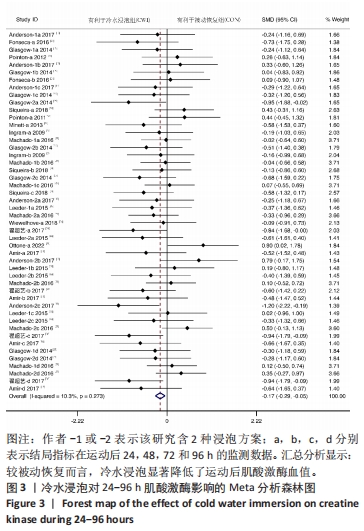
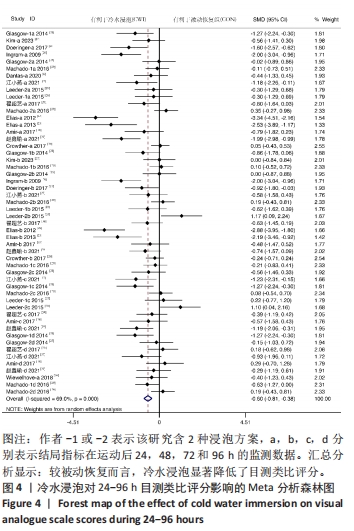
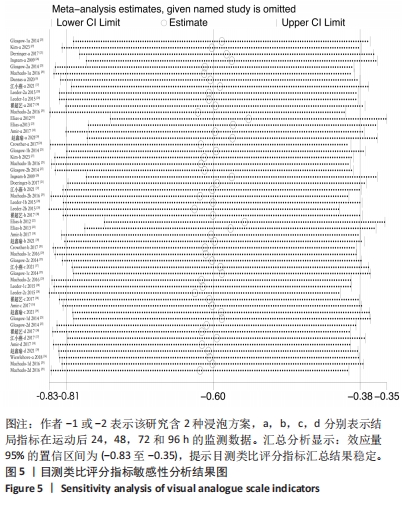
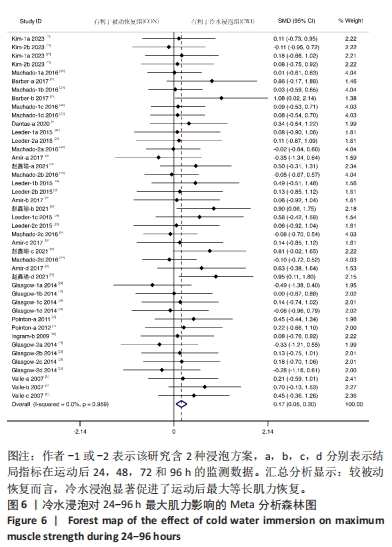
[1] ALLAN R, MALONE J, ALEXANDER J, et al. Cold for centuries: a brief history of cryotherapies to improve health, injury and post-exercise recovery. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022;122(5):1153-1162.
[2] CESAR EP, JUNIOR CSR, FRANCISCO RN. Effects of 2 intersection strategies for physical recovery in Jiu-Jitsu athletes. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2021;16(4):585-590.
[3] LI F, SONG Y, CEN X, et al. Comparative efficacy of vibration foam rolling and cold water immersion in amateur basketball players after a simulated load of basketball game. Healthcare (Basel). 2023;11(15):2178.
[4] FARKHARI BABAK M, MOSAFERI ZIAALDINI M, HOSEINI SEYYED REZA A. Experience of cold-water immersion on recovery efficiency after soccer match. Tunis Med. 2021; 99(2):252-258.
[5] CHAUVINEAU M, PASQUIER F, GUYOT V, et al. Effect of the depth of cold water immersion on sleep architecture and recovery among well-trained male endurance runners. Front Sports Act Living. 2021;3:659990.
[6] DANTAS G, BARROS A, SILVA B, et al. Cold-water immersion does not accelerate performance recovery after 10-km street run: randomized controlled clinical trial. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2020;91(2):228-238.
[7] WILSON LJ, COCKBURN E, PAICE K, et al. Recovery following a marathon: a comparison of cold water immersion, whole body cryotherapy and a placebo control. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018;118(1):153-163.
[8] POPPENDIECK W, WEGMANN M, HECKSTEDEN A, et al. Does cold-water immersion after strength training attenuate training adaptation? Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2021;16(2): 304-310.
[9] 王泽文,王润极,李海鹏,等.冷水浸泡和局部身体冷冻对足球运动员在高温高湿环境下运动后恢复的影响[J].体育科学,2022,42(5):58-67.
[10] MACHADO AF, FERREIRA PH, MICHELETTI JK, et al. Can water temperature and immersion time influence the effect of cold water immersion on muscle soreness? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2016;46(4):503-514.
[11] MOSELEY AM, ELKINS MR, VAN DER WEES PJ, et al. Using research to guide practice: the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro). Braz J Phys Ther. 2020;24(5):384-391.
[12] HOPKINS WG, MARSHALL SW, BATTERHAM AM, et al. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41(1):3-13.
[13] ANDERSON D, NUNN J, TYLER CJ. Effect of cold (14 degrees C) vs. ice (5 degrees C) water immersion on recovery from intermittent running exercise. J Strength Cond Res. 2018; 32(3):764-771.
[14] 任绪艳.不同模式水浴疗法对大学生功率自行车运动后疲劳恢复的效果研究[D].北京:首都体育学院,2020.
[15] WANG J, GUAN H, HOSTRUP M, et al. The road to the beijing winter olympics and beyond: opinions and perspectives on physiology and innovation in winter sport. J Sci Sport Exerc. 2021;3(4):321-331.
[16] 邓通,汪洋,黄笛.临床实践指南制订方法——GRADE方法理论篇[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2018,10(12):1441-1445, 1449.
[17] 黄笛,黄瑞秀,郭晨煜.临床实践指南制定方法——证据分级与推荐强度[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2018, 10(7):769-776.
[18] AMIR NH, HASHIM HA, SAHA S. The effect of single bout of 15 minutes of 15-degree celsius cold water immersion on delayed-onset muscle soreness indicators. 3rd Int Conf Movement, Hlth Exerc. 2017;45-51.
[19] BARBER S, PATTISON J, BROWN F, et al. Efficacy of repeated cold water immersion on recovery after a simulated rugby union protocol. J Strength Cond Res. 2020;34(12):3523-3529.
[20] CROWTHER F, SEALEY R, CROWE M, et al. Influence of recovery strategies upon performance and perceptions following fatiguing exercise: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2017;9:25.
[21] DOERINGER JR, COLAS M, PEACOCK C, et al. The effects of postexercise cooling on muscle performance and soreness perception. Int J Athl Ther Train. 2018;23(2):73-76.
[22] ELIAS GP, VARLEY MC, WYCKELSMA VL, et al. Effects of water immersion on posttraining recovery in Australian footballers. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2012;7(4):357-366.
[23] ELIAS GP, WYCKELSMA VL, VARLEY MC, et al. Effectiveness of water immersion on postmatch recovery in elite professional footballers. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2013;8(3):243-253.
[24] FONSECA LB, BRITO CJ, SILVA RJ, et al. Use of cold-water immersion to reduce muscle damage and delayed-onset muscle soreness and preserve muscle power in Jiu-Jitsu athletes. J Athl Train. 2016;51(7):540-549.
[25] GLASGOW PD, FERRIS R, BLEAKLEY CM. Cold water immersion in the management of delayed-onset muscle soreness: is dose important? A randomised controlled trial. Phys Ther Sport. 2014;15(4):228-233.
[26] INGRAM J, DAWSON B, GOODMAN C, et al. Effect of water immersion methods on post-exercise recovery from simulated team sport exercise. J Sci Med Sport. 2009;12(3):417-421.
[27] KIM HW, JOO CH. Effects of cold water immersion and protein intake combined recovery after eccentric exercise on exercise performance in elite soccer players. J Exerc Rehabil. 2023;19(2):126-133.
[28] LEEDER JD, VAN SOMEREN KA, BELL PG, et al. Effects of seated and standing cold water immersion on recovery from repeated sprinting. J Sports Sci. 2015;33(15):1544-1552.
[29] MACHADO AF, ALMEIDA AC, MICHELETTI JK, et al. Dosages of cold-water immersion post exercise on functional and clinical responses: a randomized controlled trial. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2017;27(11):1356-1363.
[30] MINETT GM, DUFFIELD R, BILLAUT F, et al. Cold-water immersion decreases cerebral oxygenation but improves recovery after intermittent-sprint exercise in the heat. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014;24(4):656-666.
[31] OTTONE VO, DE PAULA F, BROZINGA PFA, et al. Modulation of leukocyte subsets mobilization in response to exercise by water immersion recovery. Front Physiol. 2022;13:867362.
[32] POINTON M, DUFFIELD R. Cold water immersion recovery after simulated collision sport exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(2):206-216.
[33] POINTON M, DUFFIELD R, CANNON J, et al. Cold water immersion recovery following intermittent-sprint exercise in the heat. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(7):2483-2494.
[34] SIQUEIRA A F, VIEIRA A, BOTTARO M, et al. Multiple cold-water immersions attenuate muscle damage but not alter systemic inflammation and muscle function recovery: a parallel randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10961.
[35] VAILE J, HALSON S, GILL N, et al. Effect of hydrotherapy on the signs and symptoms of delayed onset muscle soreness. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008;102(4):447-455.
[36] WIEWELHOVE T, SCHNEIDER C, DOWELING A, et al. Effects of different recovery strategies following a half-marathon on fatigue markers in recreational runners. PLoS One. 2018; 13(11):e0207313.
[37] 江小燕,朱海飞,蔺海旗,等.冷疗干预延迟性肌肉酸痛的自限性恢复[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(23):3609-3613.
[38] 瞿超艺.不同冷疗方式对中长跑运动员运动性肌肉微损伤时序性恢复的影响[D].上海:上海体育学院,2017.
[39] 赵鑫瑜.冷水浴对短跑运动员离心运动后DOMS症状的干预效果研究[J].辽宁体育科技,2021,43(1):63-68, 87.
[40] MISSAU E, TEIXEIRA ADO, FRANCO OS, et al. Cold water immersion and inflammatory response after resistance exercises. revista brasileira med esporte. 2018;24(5):372-376.
[41] HIGGINS TR, GREENE DA, BAKER MK. Effects of cold water immersion and contrast water therapy for recovery from team sport: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(5):1443-1460.
[42] GREENHAM G, BUCKLEY JD, GARRETT J, et al. Biomarkers of physiological responses to periods of intensified, non-resistance-based exercise training in well-trained male athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2018;48(11):2517-2548.
[43] XIAO F, KABACHKOVA A V, JIAO L, et al. Effects of cold water immersion after exercise on fatigue recovery and exercise performance--meta analysis. Front Physiol. 2023;14: 1006512.
[44] NASSER N, ZORGATI H, CHTOUROU H, et al. Cold water immersion after a soccer match: Does the placebo effect occur? Front Physiol. 2023;14:12.
[45] NUNES RFH, DUFFIELD R, NAKAMURA FY, et al. Recovery following Rugby Union matches: effects of cold water immersion on markers of fatigue and damage. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2019;44(5):546-556.
[46] SECO-CALVO J, MIELGO-AYUSO J, CALVO-LOBO C, et al. Cold water immersion as a strategy for muscle recovery in professional basketball players during the competitive season. J Sport Rehabil. 2020;29(3):301-309.
[47] EIMONTE M, EIMANTAS N, DANIUSEVICIUTE L, et al. Recovering body temperature from acute cold stress is associated with delayed proinflammatory cytokine production in vivo. Cytokine. 2021;143:155510.
[48] PAWLOWSKA M, MILA-KIERZENKOWSKA C, BORACZYNSKI T, et al. The influence of ambient temperature changes on the indicators of inflammation and oxidative damage in blood after submaximal exercise. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(12):2445.
[49] BARTLEY JM, STEARNS RL, MUNOZ CX, et al. Effects of cold water immersion on circulating inflammatory markers at the Kona Ironman World Championship. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2021;46(7):719-726.
[50] WESOLOWSKI R, MILA-KIERZENKOWSKA C, PAWLOWSKA M, et al. The influence of winter swimming on oxidative stress indicators in the blood of healthy males. Metabolites. 2023;13(2):143.
[51] POPPENDIECK W, FAUDE O, WEGMANN M, et al. Cooling and performance recovery of trained athletes: a meta-analytical review. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2013;8(3):227-242.
[52] MAWHINNEY C, HEINONEN I, LOW DA, et al. Changes in quadriceps femoris muscle perfusion following different degrees of cold-water immersion. J Appl Physiol. 2020; 128(5):1392-1401.
[53] BLEAKLEY C, MCDONOUGH S, GARDNER E, et al. Cold-water immersion (cryotherapy) for preventing and treating muscle soreness after exercise. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;2012(2):CD008262.
[54] SINGH H, MOORE BA, RATHORE R, et al. Skeletal effects of eccentric strengthening exercise: a scoping review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):611.
[55] FREITAG L, CLIJSEN R, DEFLORIN C, et al. Intramuscular temperature changes in the quadriceps femoris muscle after post-exercise cold-water immersion (10 degrees c for 10 min): a systematic review with meta-analysis. Front Sports Act Living. 2021;3:660092.
[56] ABAIDIA AE, LAMBLIN J, DELECROIX B, et al. Recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage: cold-water immersion versus whole-body cryotherapy. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2017;12(3):402-409.
[57] PESENTI FB, DA SILVA RA, MONTEIRO DC, et al. The effect of cold water immersion on pain, muscle recruitment and postural control in athletes. Revista Brasileira De Medicina Do Esporte. 2020;26(4):323-327.
[58] TAKAGI R, FUJITA N, ARAKAWA T, et al. Influence of icing on muscle regeneration after crush injury to skeletal muscles in rats. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011;110(2):382-388.
[59] HERRERA E, SANDOVAL MC, CAMARGO DM, et al. Motor and sensory nerve conduction are affected differently by ice pack, ice massage, and cold water immersion. Phys Ther. 2010;90(4):581-591.
[60] EIMONTE M, PAULAUSKAS H, DANIUSEVICIUTE L, et al. Residual effects of short-term whole-body cold-water immersion on the cytokine profile, white blood cell count, and blood markers of stress. Int J Hyperthermia. 2021;38(1): 696-707.
[61] MURRAY A, CARDINALE M. Cold applications for recovery in adolescent athletes: a systematic review and meta analysis. Extrem Physiol Med. 2015;4:17.
[62] FAKHRO M A, ALAMEEN F, FAYAD R. Comparison of total cold-water immersion’s effects to ice massage on recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage. J Exp Orthop. 2022;9(1):59.
[63] MOORE E, FULLER JT, BUCKLEY JD, et al. Impact of cold-water immersion compared with passive recovery following a single bout of strenuous exercise on athletic performance in physically active participants: a systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression. Sports Med. 2022;52(7):1667-1688.
[64] BOUZID MA, GHATTASSI K, DAAB W, et al. Faster physical performance recovery with cold water immersion is not related to lower muscle damage level in professional soccer players. J Therm Biol. 2018;78:184-191.
[65] 隋瀚.间歇冷疗对短跑运动员无氧运动能力恢复的影响研究[D].北京:首都体育学院,2018.
[66] GASPAR-JUNIOR JJ, DELLAGRANA RA, BARBOSA FSS, et al. Efficacy of different cold-water immersion temperatures on neuromotor performance in young athletes. Life (Basel). 2022;12(5):683.
[67] SECO-CALVO J, MIELGO-AYUSO J, CALVO-LOBO C, et al. Cold water immersion as a strategy for muscle recovery in professional basketball players during the competitive season. J Sport Rehabil. 2020;29(3):301-309.
[68] BOUCHIBA M, BRAGAZZI NL, ZARZISSI S, et al. Cold water immersion improves the recovery of both central and peripheral fatigue following simulated soccer match-play. Front Physiol. 2022;13:860709.
[69] WILSON LJ, DIMITRIOU L, HILLS FA, et al. Whole body cryotherapy, cold water immersion, or a placebo following resistance exercise: a case of mind over matter? Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019;119(1):135-147.
[70] 李钊,李庆,曹春梅.耐力项目运动员运动后冷水浴的作用机制与实践应用[J].山东体育学院学报,2017,33(3):79-86.
[71] 刘强,赵相轩,潘诗农,等.骨骼肌细胞损伤致延迟性肌肉酸痛:如何有效提高损伤肌肉恢复的速度和质量[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(38):6189-6193.
[72] 殷彰冶.冲刺性间歇训练生理学特点及能量代谢特征的研究[D].武汉:武汉体育学院,2023.
[73] BOUCHIBA M, BRAGAZZI N L, ZARZISSI S, et al. Cold water immersion improves the recovery of both central and peripheral fatigue following simulated soccer match-play. Front Physiol. 2022;13:9.
[74] SIEGLER JC, MARSHALL P. The effect of metabolic alkalosis on central and peripheral mechanisms associated with exercise-induced muscle fatigue in humans. Exp Physiol. 2015;100(5): 519-530.
[75] GIMENES SV, MAROCOLO M, PAVIN LN, et al. Compression stockings used during two soccer matches improve perceived muscle soreness and high-intensity performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2021;35(7):2010-2017.
[76] 李刃.不同放松方法对腘绳肌离心训练后肌肉疲劳消除的效果研究[D].石家庄:河北师范大学,2022.
[77] STEPHENS JM, HALSON S, MILLER J, et al. Cold-water immersion for athletic recovery: one size does not fit all. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2017;12(1):2-9.
[78] 白峥嵘,孙羽,张振显,等.延迟性肌肉酸痛与运动性骨骼肌记忆[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(11):1762-1766.
|