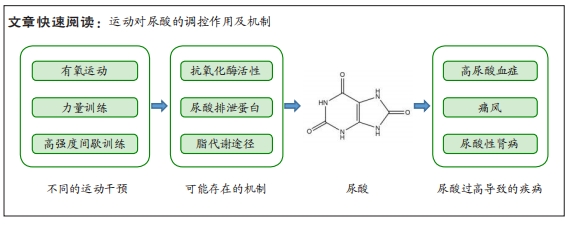
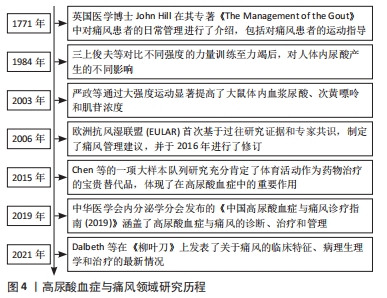
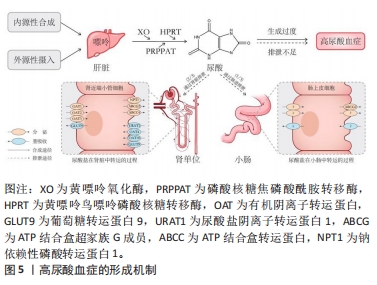
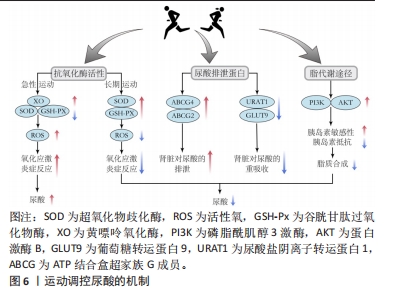
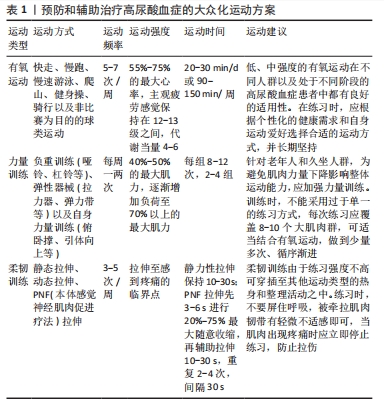
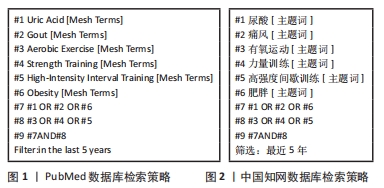
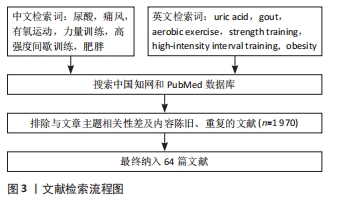
[1] DEHLIN M, JACOBSSON L, RODDY E. Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(7):380-390.
[2] ZHANG T, GU Y, MENG G, et al. Genetic Risk, Adherence to a Healthy Lifestyle, and Hyperuricemia: The TCLSIH Cohort Study. Am J Med. 2023;136(5):476-483.e5.
[3] JOHN H. The Management of the Gout: In Diet, Exercise, and Temperc. R. Baldwin, 1771.
[4] 严政,于文兵,马继政.大强度运动对大鼠嘌呤核苷酸代谢的影响及运动模型研究[J].体育与科学,2003(5):66-68.
[5] 三上俊夫,中山正幸,丹信介,等.运动性高尿酸现象的研究[J].尿酸,1984, 8(2):151-158.
[6] ZHANG W, DOHERTY M, BARDIN T, et al. EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics. EULAR evidence based recommendations for gout. Part II: Management. Report of a task force of the EULAR Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutics (ESCISIT). Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(10):1312-1324.
[7] RICHETTE P, DOHERTY M, PASCUAL E, et al. 2016 updated EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the management of gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(1):29-42.
[8] CHEN JH, WEN CP, WU SB, et al. Attenuating the mortality risk of high serum uric acid: the role of physical activity underused. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(11):2034-2042.
[9] 中华医学会内分泌学分会.中国高尿酸血症与痛风诊疗指南(2019)[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2020,36(1):1-13.
[10] DALBETH N, MERRIMAN TR, STAMP LK. Gout. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2039-2052.
[11] LONG T, LIU L. Research Progress on the Relationship between Dietary Patterns and Hyperuricemia. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2022;2022:5658423.
[12] DALBETH N, GOSLING AL, GAFFO A, et al. Gout. Lancet. 2021;397(10287):1843-1855.
[13] MANDAL AK, MOUNT DB. The molecular physiology of uric acid homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:323-345.
[14] ICHIDA K, MATSUO H, TAKADA T, et al. Decreased extra-renal urate excretion is a common cause of hyperuricemia. Nat Commun. 2012;3:764.
[15] XU X, LI C, ZHOU P, et al. Uric acid transporters hiding in the intestine. Pharm Biol. 2016;54(12):3151-3155.
[16] TIN A, MARTEN J, HALPERIN KUHNS V L, et al. Target genes, variants, tissues and transcriptional pathways influencing human serum urate levels. Nat Genet. 2019;51(10):1459-1474.
[17] 薛政昊,陈德明.运动防治肥胖合并高尿酸血症患者研究现状与展望[J].哈尔滨体育学院学报,2022,40(5):82-90.
[18] 李抒,曹甍,邹昱,等.高强度间歇训练对肥胖儿童内脏脂肪和心肺适能的影响[J].体育学刊,2023,30(3):138-144.
[19] 谢舟煜,何艾舟,李婷,等.有氧运动对肥胖大鼠内皮功能障碍和内脂素的影响[J].中国实验动物学报,2022,30(4):533-539.
[20] 曲静,林小晶,王业玲,等.4周结合饮食控制的有氧运动降低肥胖青年血清炎症因子chemerin水平及其应用价值[J].中国体育科技,2022,58(7):76-82.
[21] 潘丽英,马春莲,谷涌泉.6周有氧运动改善不同程度肥胖青少年体质健康的研究[J].武汉体育学院学报,2022,56(7):76-83.
[22] 安亚琼,傅松波,汤旭磊,等.兰州市居民高尿酸血症现状及相关因素分析[J].中国预防医学杂志,2020,21(8):841-845.
[23] 黄秀兰,于金芝,李春霞.有氧运动对老年慢性病患者健康管理效果分析[J].中国卫生标准管理,2022,13(8):60-62.
[24] 刘振华,严鹏飞,刘陪沛,等.高龄老人有氧运动与血脂及尿酸关系的研究[J].人民军医,2014,57(8):840-841.
[25] HOU Y, MA R, GAO S, et al. The Effect of Low and Moderate Exercise on Hyperuricemia: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:716802.
[26] 辛东岭,刘淑文,戴剑松.不同剂量运动对高尿酸血症影响的试验研究[J].科技资讯,2020,18(13):204-206.
[27] VILLEGAS R, XIANG YB, CAI Q, et al. Prevalence and determinants of hyperuricemia in middleaged,urban Chinese men. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2010;8(3):263-270.
[28] CHEN N, HAN T, LIU H, et al. Muscle Fat Content Is Strongly Associated With Hyperuricemia: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chinese Adults. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:935445.
[29] LUSTGARTEN MS, FIELDING RA. Metabolites related to renal function, immune activation, and carbamylation are associated with muscle composition in older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2017;100:1-10.
[30] HUANG C, NIU K, KOBAYASHI Y, et al. An inverted J-shaped association of serum uric acid with muscle strength among Japanese adult men: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:258.
[31] 成晓翠,孙明艳,孙巧云,等.有氧运动和抗阻运动在痛风患者延续管理中的应用效果比较[J].山东医药,2021,61(35):72-75.
[32] KRAEMER WJ, RATAMESS NA, VOLEK JS, et al. The effects of amino acid supplementation on hormonal responses to resistance training overreaching. Metabolism. 2006;55(3):282-291.
[33] FAELLI E, BISIO A, CODELLA R, et al. Acute and Chronic Catabolic Responses to CrossFit((R)) and Resistance Training in Young Males. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(19):71-72.
[34] 苗晶晶.高强度间歇训练对青年高尿酸血症痛风患者血清尿酸水平和痛风发作频次的影响[J].中国疗养医学,2021,30(1):78-80.
[35] 史锦伟.有氧运动结合高强度间歇性力量训练对单纯性肥胖青少年的减肥效果研究[D].上海:上海体育学院,2020.
[36] HAYES LD, HERBERT P, SCULTHORPE N, et al. High intensity interval training (HIIT) produces small improvements in fasting glucose, insulin, and insulin resistance in sedentary older men but not masters athletes. Exp Gerontol. 2020;140:111074.
[37] 苏志燕,刘薇,史婷婷.老年2型糖尿病患者血尿酸浓度与代谢综合征的相关性分析[J].首都医科大学学报,2023,44(1):137-142.
[38] WANG F, ZHAO X, SU X, et al. Isorhamnetin, the xanthine oxidase inhibitor from Sophora japonica, ameliorates uric acid levels and renal function in hyperuricemic mice. Food Funct. 2021;12(24):12503-12512.
[39] 谢文杰,周刚,谢金美,等.一次性力竭运动模型大鼠心肌氧化损伤的作用途径[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(2):247-252.
[40] FEOLI AM, MACAGNAN FE, PIOVESAN CH, et al. Xanthine oxidase activity is associated with risk factors for cardiovascular disease and inflammatory and oxidative status markers in metabolic syndrome: effects of a single exercise session. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:587083.
[41] 刘晓晨,王改凤,张社峰.有氧运动可改善糖尿病肾病模型小鼠肾脏的氧化应激损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(17):2712-2717.
[42] 周中源,史媛媛,王梦,等.有氧运动抑制NLRP3炎性小体活化减轻2型糖尿病小鼠肾脏损伤[J].中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(12):962-969.
[43] 朱凤林,闫会萍,陆一帆,等.运动和2,3,7,8-四氯二苯并二噁英(TCDD)持续暴露对大鼠肾脏氧化应激指标的影响[J].生态毒理学报,2023,18(2):366-372.
[44] PADILHA CS, RIBEIRO AS, FLECK SJ, et al. Effect of resistance training with different frequencies and detraining on muscular strength and oxidative stress biomarkers in older women. Age. 2015;37(5):104.
[45] ADOMAKO EA, MOE OW. Uric acid transport, transporters, and their pharmacological targeting. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2023;238(2):e13980.
[46] CARNEY EF. Prevention: Intensive exercise associated with reduced risk of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11(4):198.
[47] REYNA SM, TANTIWONG P, CERSOSIMO E, et al. Short-term exercise training improves insulin sensitivity but does not inhibit inflammatory pathways in immune cells from insulin-resistant subjects. J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:107805.
[48] 何标,梁艳,徐波,等.跑台运动对TgAPP/PS1小鼠海马Aβ转运清除的影响[J].体育学刊,2018,25(4):134-139.
[49] ERALY SA, VALLON V, RIEG T, et al. Multiple organic anion transporters contribute to net renal excretion of uric acid. Physiol Genomics. 2008;33(2):180-192.
[50] LIU S, YUAN Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Phloretin attenuates hyperuricemia-induced endothelial dysfunction through co-inhibiting inflammation and GLUT9-mediated uric acid uptake. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(10):2553-2562.
[51] MANOLESCU AR, AUGUSTIN R, MOLEY K, et al. A highly conserved hydrophobic motif in the exofacial vestibule of fructose transporting SLC2A proteins acts as a critical determinant of their substrate selectivity. Mol Membr Biol. 2007;24(5-6): 455-463.
[52] JIANG Z, CAO J, SU H, et al. Exercise serum regulates uric acid transporters in normal rat kidney cells. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):18086.
[53] MA Z, WANG Y, XU C, et al. Obesity-Related Genetic Variants and Hyperuricemia Risk in Chinese Men. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne). 2019;10:230.
[54] LI Q, LI X, WANG J, et al. Diagnosis and treatment for hyperuricemia and gout: a systematic review of clinical practice guidelines and consensus statements. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e026677.
[55] BEN-DOV IZ, Bursztyn M. Associations of arterial stiffness indices with measures of insulin resistance and renal sodium reabsorption. Am J Hypertens. 2019;32(9): 810-812.
[56] KOESTER AM, GEISER A, BOWMAN PRT, et al. GLUT4 translocation and dispersal operate in multiple cell types and are negatively correlated with cell size in adipocytes. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):20535.
[57] FLORES-OPAZO M, RAAJENDIRAN A, WATT MJ, et al. Exercise serum increases GLUT4 in human adipocytes. Exp Physiol. 2019;104(5):630-634.
[58] WANG N, KONG R, LUO H, et al. Peroxisome proliferator- activated receptors associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. PPAR Res. 2017;2017:6561701.
[59] TANG H, ZENG Q, TANG T, et al. Kaempferide improves glycolipid metabolism disorder by activating PPARgamma in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Life Sci. 2021;270: 119133.
[60] 宋燕娟,马春莲,肖笑.中等强度有氧运动调节PPARγ/PI3K/AKT通路改善2型糖尿病大鼠肝脏糖脂代谢紊乱及炎症[J].中国运动医学杂志,2023,42(1): 48-56.
[61] MCGEE SL, HARGREAVES M. Exercise adaptations: molecular mechanisms and potential targets for therapeutic benefit. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(9):495-505.
[62] 祝锴烨,吴秋雪,罗海静,等.紫云英苷对急性力竭运动小鼠肝脏组织中miR-155表达的影响[J].动物营养学报,2021,33(12):7062-7069.
[63] BELLAR A, WELCH N, DASARATHY S. Exercise and physical activity in cirrhosis: opportunities or perils. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020;128(6):1547-1567.
[64] 美国运动医学学会.ACSM运动测试与运动处方指南(第十版)[M].王正珍,译.北京:北京体育大学出版社,2019. |