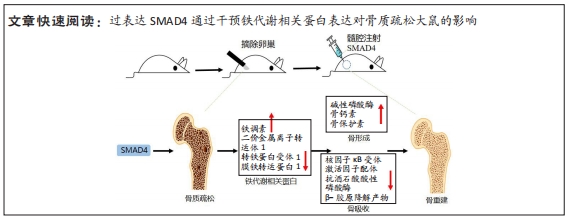
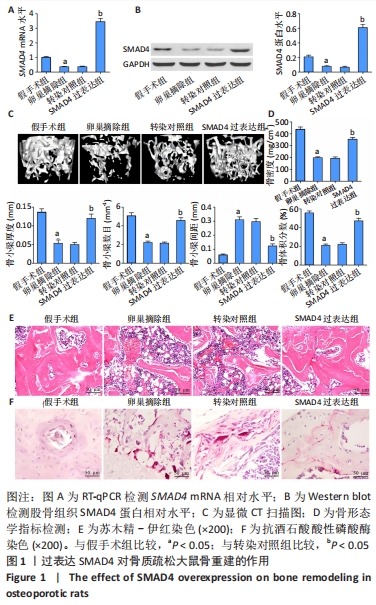
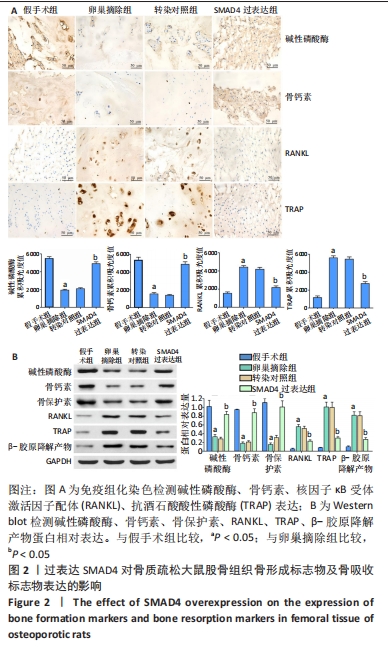
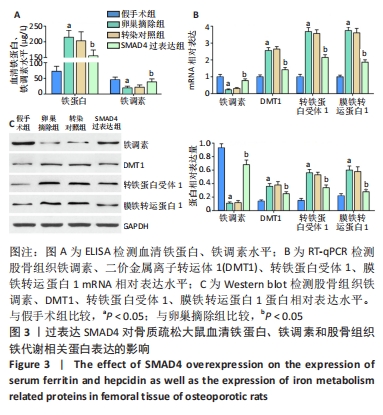
[1] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;123:14-21.
[2] GUO DJ, ZHAO MG, XU W, et al. Dietary interventions for better management of osteoporosis: An overview. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(1):125-144.
[3] 孙文星, 黄万新, 刘传慧, 等. 黄芪多糖通过PI3K/AKT/mTOR促进激素性骨质疏松大鼠成骨细胞增殖[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(1):35-40.
[4] CAI H, ZHANG HM, HE WT, et al. Iron accumulation and its impact on osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2023;24(4):301-311.
[5] SZYMCZAK A, ZALEWSKA M, RYMER W, et al. Asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection with high CD4+ T cell count does not alter iron metabolism or hepcidin levels: The pilot study. Infect Dis Ther. 2022;11(1): 265-275.
[6] WIJEKOON S, SUNAGA T, WANG Y, et al. Pentosan polysulfate regulates hepcidin 1-facilitated formation and function of osteoclast derived from canine bone marrow. PLoS One. 2022;17(3):e0265596.
[7] MEZZANOTTE M, AMMIRATA G, BOIDO M, et al. Activation of the hepcidin-Ferroportin1 pathway in the brain and astrocytic-neuronal crosstalk to counteract iron dyshomeostasis during aging. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11724.
[8] MEHTA KJ, BUSBRIDGE M, PATEL VB, et al. hepcidin secretion was not directly proportional to intracellular iron-loading in recombinant-TfR1 HepG2 cells: short communication. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020;468(1-2):121-128.
[9] FERRAO K, ALI N, MEHTA KJ. Iron and iron-related proteins in alcohol consumers: cellular and clinical aspects. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022;100(12):1673-1689.
[10] 倪硕, 袁音, 邝言斌, 等. 破骨细胞中铁代谢的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(5):701-705.
[11] LIU HR, WANG XH. Epidermal growth factor-like domain protein 6 recombinant protein facilitates osteogenic differentiation in adipose stem cells via bone morphogenetic protein 2/recombinant mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 signaling pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):6558-6566.
[12] 肖锐, 周芳丽, 万春虎, 等. miR-214通过对BMP-2和Smad4的靶向调控作用对骨质疏松的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(10):1413-1418.
[13] 白登彦, 王冠, 张海军, 等. TGF-β1/Smad4信号通路对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨髓微环境的影响及针刺干预机制[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2021, 27(8):1140-1146.
[14] 张紫嫣. 温肾益髓生血方对肾性贫血大鼠肝组织BMP/SMAD-hepcidin影响的实验研究[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学,2018.
[15] 曲申, 邹晓峰, 刘英伟. 山菠菜多糖对长时间大强度运动大鼠铁代谢的影响及分子机制研究[J]. 沈阳体育学院学报,2016,35(5):63-67.
[16] JIANG ZX, WANG H, QI GB, et al. Iron overload-induced ferroptosis of osteoblasts inhibits osteogenesis and promotes osteoporosis: An in vitro and in vivo study. IUBMB Life. 2022;74(11):1052-1069.
[17] ZHANG H, WANG AF, SHEN GS, et al. Hepcidin-induced reduction in iron content and PGC-1β expression negatively regulates osteoclast differentiation to play a protective role in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(8):11296-11314.
[18] MA JW, WANG AF, ZHANG Z, et al. Iron overload induced osteocytes apoptosis and led to bone loss in Hepcidin-/- mice through increasing sclerostin and RANKL/OPG. Bone. 2022;164:116511.
[19] WANG Z, CHEN Q, YANG ZH, et al. MiR-125b aggregates osteoporosis in postmenopausal rats via targeting Smad4. Minerva Surg. 2022;77(5):511-512.
[20] XU YX, JIN YC, HONG FL, et al. MiR-664-3p suppresses osteoblast differentiation and impairs bone formation via targeting Smad4 and Osterix. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(11):5025-5037.
[21] SILVESTRI L, NAI A, DULJA A, et al. Hepcidin and the BMP-SMAD pathway: An unexpected liaison. Vitam Horm. 2019;110:71-99.
[22] WU DJ, WEN XW, XU LL, et al. Iron chelation effect of curcumin and baicalein on aplastic anemia mouse model with iron overload. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019;22(6):660-668.
[23] JENEY V. Clinical impact and cellular mechanisms of iron overload-associated bone loss. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:77.
[24] POGGI M, SORRENTINO F, PUGLIESE P, et al. Longitudinal changes of endocrine and bone disease in adults with β-thalassemia major receiving different iron chelators over 5 years. Ann Hematol. 2016;95(5):757-763.
[25] MIN HK, SUNG SA, OH YK, et al. Hepcidin, iron indices and bone mineral metabolism in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020;35(1):147-154.
[26] ZHAO Y, WANG CQ, YANG TY, et al. Chlorogenic acid alleviates chronic stress-induced duodenal ferroptosis via the inhibition of the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70(14):4353-4361.
[27] ZHENG J, WANG JJ, MA HM, et al. Norcantharidin down-regulates iron contents in the liver and spleen of lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. Redox Rep. 2022;27(1):119-127.
[28] HUANG YJ, ZHANG XM, ZHAN JD, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-206 promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in osteoarthritis by reducing Elf3. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(16): 7734-7745.
[29] ATILANO-MIGUEL S, BARBOSA-CORTÉS L, ORTIZ-MUÑIZ R. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: RANK/RANKL/OPG (receptor activator of nuclear factor-kB/RANK ligand/osteoprotegerin) system and glucocorticoids. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 2022;79(5):275-283.
[30] 刘秀娟. 血清铁调素、铁代谢水平与老年骨质疏松女性骨密度及发生骨折的相关性分析[J]. 中国医学创新,2021,18(32):123-126.
[31] 张辉, 王爱飞, 吴加东, 等. 铁调素过表达对雌性去势小鼠铁代谢和骨代谢指标的影响[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2018,11(4):375-379.
[32] 孙丽. Hepcidin基因敲除对小鼠骨代谢的影响及相关机制研究[D]. 济南:济南大学,2014.
[33] 张在竹, 余卫. 铁过载测量在骨质疏松症评估中的应用[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(4):400-405.
|