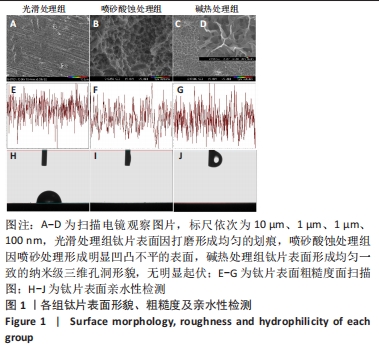
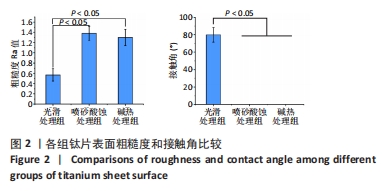
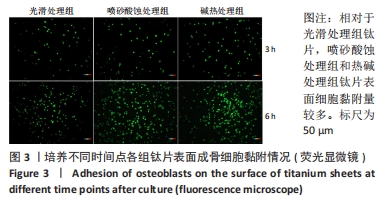
[1] DANIEL B, LARS S, HUGO DB. Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegr- ation: 50 years of progress, current trends and open questions. Periodontol 2000. 2017;73(1):7-21.
[2] 车振家,朱正清,朱礼伟,等.钛植入物表面生物化学改性对骨整合的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(16):2576-2583.
[3] SCULEAN A, GRUBER R, BOSSHARDT DD. Soft tissue wound healing around teeth and dental implants. J Clin Periodontol. 2014;41 Suppl 15:S6-22.
[4] HASEGAWA M, SARUTA J, HIROTA M, et al. A newly created meso-, micro-, and nano-scale rough titanium surface promotes bone-implant integration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):783.
[5] 王旻,姜楠,祝颂松.新型钛表面微纳米共存梯度仿生结构对骨髓间充质细胞黏附、增殖及成骨分化的影响[J].口腔疾病防治,2021,29(4):226-233.
[6] PINTO TS, MARTINS BR, FERREIRA MR, et al. Nanohydroxyapatite-Blasted Bioactive Surface Drives Shear-Stressed Endothelial Cell Growth and Angiogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:1433221.
[7] WANG L, XU C, MENG K, et al. Biomimetic Hydroxyapatite Composite Coatings with a Variable Morphology Mediated by Silk Fibroin and Its Derived Peptides Enhance the Bioactivity on Titanium. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(1):165-181.
[8] LÓPEZ-VALVERDE N, ARAGONESES J, LÓPEZ-VALVERDE A, et al. Effectiveness of biomolecule-based bioactive surfaces, on os-seointegration of titanium dental implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vivo studies. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:986112.
[9] WU J, JIANG S, XIE W, et al. Surface modification of the Ti surface with nanoscale bio-MOF-1 for improving biocompatibility and osteointegration in vitro and in vivo. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(41):8535-8548.
[10] CHEN M, WANG D, LI M, et al. Nanocatalytic Biofunctional MOF Coating on Titanium Implants Promotes Osteoporotic Bone Regeneration through Cooperative Pro-osteoblastogenesis MSC Reprogramming. ACS Nano. 2022;16(9):15397-15412.
[11] LI Y, CHEN G, HE Y, et al. Selenomethionine-Modified Polyethylenimine-Based Nanoparticles Loaded with miR-132-3p Inhibitor-Biofunctionalized Titanium Implants for Improved Osteointegration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(10):4933-4945.
[12] SUN T, HUANG J, ZHANG W, et al. Simvastatin-hydroxyapatite coatings prevent biofilm formation and improve bone formation in implant-associated infections. Bioact Mater. 2022;21:44-56.
[13] ZHU LS, LUO D, LIU Y. Effect of the nano/microscale structure of biomaterial scaffolds on bone regeneration. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):6.
[14] DIOMEDE F, MARCONI GD, FONTICOLI L, et al. Functional relationship between osteogenesis and angiogenesis in tissue regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):3242.
[15] MA L, LI G, LEI J, et al. Nanotopography Sequentially Mediates Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles for Enhancing Osteogenesis. ACS Nano. 2022;16(1):415-430.
[16] XUE Y, ZHANG L, LIU F, et al. Surface Bandgap Engineering of Nanostructured Implants for Rapid Photothermal Ion Therapy of Bone Defects. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(22):e2200998.
[17] KIM HM, MIYAJI F, KOKUBO T, et al. Preparation of bioactive Ti and its alloys via simple chemical surface treatment. J Biomed Mater Res. 1996;32(3):409-417.
[18] Baek HL, YOUNG DK, JI HS, et al. Surface modification by alkali and heat treatments in titanium alloys. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;61(3):466-473.
[19] TADASHI K, SEIJI Y. Groeth of novel ceramic layers on metals via chemical and heat treatments for inducing various biological functions. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015;3:176.
[20] WANG XJ, LI YC, LIN JG, et al. Effect of heat-treatment atmosphere on the bond strength of apatite layer on Ti substrate. Dent Mater. 2008;24(11):1549-1555.
[21] ZHOU Y, WANG YB, ZHANG EW, et al. Alkali-heat treatment of a low modulus biomedical Ti-27NB alloy. Biomed Mater. 2009;4(4):044108.
[22] ZHAO LZ, HU LS, HUO KF, et al. Mechanism of cell repellence on quasi-aligned nanowires arrays on Ti alloy. Biomaterials. 2010;31(32):8341-8349.
[23] DING XL, YANG XQ, ZHOU L, et al. Titanate nanowires scaffolds decorated with anatase nanocrystals show good protein adsorption and low cell adhesion capacity. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:569-579.
[24] SticH T, ALAGBOSO F, KŘENEK T, et al. Implant-bone-interface: Reviewing the impact of titanium surface modifications on osteogenic processes in vitro and in vivo. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021;7(1):e10239.
[25] Li S, Ni J, Liu X, et al. Surface characteristics and biocompatibility of sandblasted and acid-etched titanium surface modified by ultraviolet irradiation: an in vitro study. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100(6):1587-1598.
[26] DADFARNIA M, NOVAK P, AHN DC, et al. Recent advances in the study of structural materials compatibility with hydrogen. Adv Mater. 2010;22(10):1128-1135.
[27] HU P, GAO Q, ZHENG H, et al. The Role and Activation Mechanism of TAZ in Hierarchical Microgroove/Nanopore Topography-Mediated Regulation of Stem Cell Differentiation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:1021-1036.
[28] MA L, KE W, LIAO Z, et al. Small extracellular vesicles with nanomorphology memory promote osteogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2022;17:425-438.
[29] YU X, XU R, ZHANG Z. Different Cell and Tissue Behavior of Micro-/Nano-Tubes and Micro-/Nano-Nets Topographies on Selective Laser Melting Titanium to Enhance Osseointegration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:3329-3342.
[30] FUJIBAYASHI S, NAKAMURA T, NISHIGUCHI S, et al. Bioactive titanium: effect of sodium removal on the bone-bonding ability of bioactive titanium prepared by alkali and heat treatment. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;56(4):562-570.
[31] KIM HM, MIYAJI F, KOKUBO T, et al. Graded surface structure of bioactive titanium prepared by chemical treatment. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;45(2):100-107.
[32] BOERCKER JE, ENACHE-POMMER E, AYDIL ES. Growth mechanism of titanium dioxide nanowires for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanotechnology. 2008;19(9): 095604.
[33] WANG F, DAI HX, DENG JG, et al. Manganese oxides with rod-, wire-, tube-, and flower-like morphologies: highly effective catalysts for the removal of toluene. Environ Sci Technol. 2012;46(7):4034-4041.
[34] LIU W, LIANG L, LIU B, et al. The response of macrophages and their osteogenic potential modulated by micro/nano-structured Ti surfaces. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;205:111848.
[35] MASAMOTO K, FUJIBAYASHI S, YAMAGUCHI S, et al. Bioactivity and antibacterial activity of strontium and silver ion releasing titanium. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(2):238-245.
[36] OKUZU Y, FUJIBAYASHI S, YAMAGUCHI S, et al. In vitro study of antibacterial and osteogenic activity of titanium metal releasing strontium and silver ions. J Biomater Appl. 2021;35(6):670-680.
[37] DOYMUS B, KEREM G, YAZGAN KARATAS A, et al. A functional coating to enhance antibacterial and bioactivity properties of titanium implants and its performance in vitro. J Biomater Appl. 2021;35(6):655-669.
[38] JEONG SJ, JEONG MJ. Effect of Thymosin beta4 on the Differentiation and Mineralization of MC3T3-E1 Cell on a Titanium Surface. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016;16(2):1979-1983.
[39] GAO Q, HOU Y, LI Z, et al. mTORC2 regulates hierarchical micro/nano topography-induced osteogenic differentiation via promoting cell adhesion and cytoskeletal polymerization. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(14):6695-6708.
[40] WANG H, XU Q, HU H, et al. The Fabrication and Function of Strontium-modified Hierarchical Micro/Nano Titanium Implant. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:8983-8998.
[41] ALBERTINI M, FERNANDEZ-YAGUE M, LÁZARO P, et al. Advances in surfaces and osseointegration in implantology. Biomimetic surfaces. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2015;20(3):e316-325.
[42] DIAS CORPA TARDELLI J, LIMA DA COSTA VALENTE M, THEODORO DE OLIVEIRA T, et al. Influence of chemical composition on cell viability on titanium surfaces: A systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;125(3):421-425.
[43] LIU J, RUAN J, YIN J, et al. Fabrication of multilevel porous structure networks on Nb-Ta-Ti alloy scaffolds and the effects of surface characteristics on behaviors of MC3T3-E1 cells. Biomed Mater. 2022;17(6). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac9ffd.
[44] SHICHMAN I, OAKLEY C, WILLEMS JH, et al. Novel metaphyseal porous titanium cones allow favorable outcomes in revision total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(3):1537-1547.
[45] ZHANG Y, SUN N, ZHU M, et al. The contribution of pore size and porosity of 3D printed porous titanium scaffolds to osteogenesis. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112651.
[46] DAVIES JE. Understanding peri-implant endosseous healing. J Dent Educ. 2003; 67(8):932-949.
[47] PULEO DA, NANCI A. Understanding and controlling the bone-implant interface. Biomaterials. 1999;20(23-24):2311-2321.
[48] HORI N, UENO T, SUZUKI T, et al. Ultraviolet light treatment for the restoration of age-related degradation of titanium bioactivity. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010;25(1):49-62.
[49] MIYAUCHI T, YAMADA M, YAMAMOTO A, et al. The enhanced characteristics of osteoblast adhesion to photofunctionalized nanoscale TiO2 layers on biomaterials surfaces. Biomaterials. 2010;31(14):3827-3839.
[50] TabUCHI M, HAMAJIMA K, TANAKA M, et al. UV Light-Generated Superhydrophilicity of a Titanium Surface Enhances the Transfer, Diffusion and Adsorption of Osteogenic Factors from a Collagen Sponge. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(13):6811. |