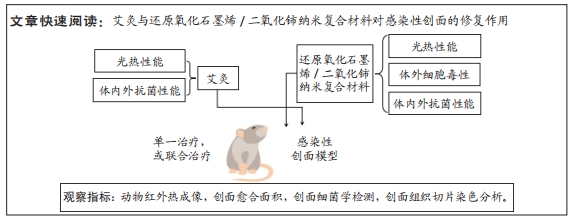
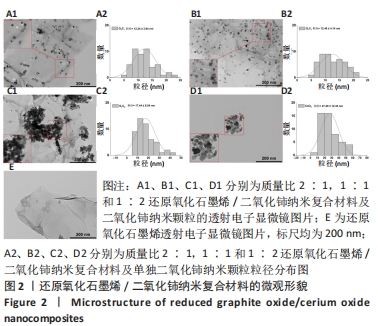
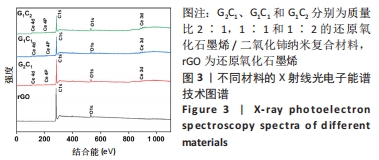
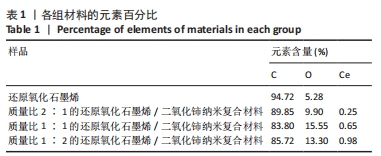
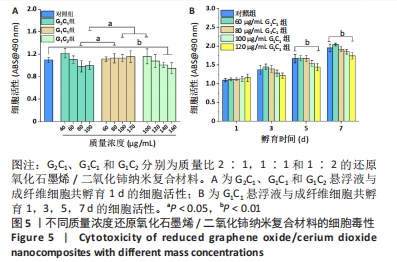
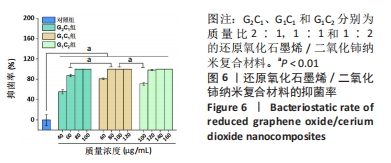
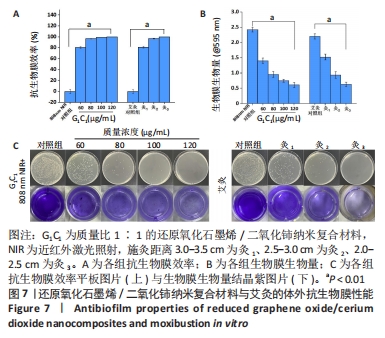
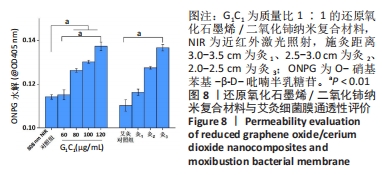
[1] 唐娅妮,崔艺敏,何轶帆,等.艾灸热、光、烟作用机制研究进展[J].中国中医药信息志,2022,29(11):148-151.
[2] 陈日新.热敏灸:中医灸法的传承、创新与发展[J].中国针灸,2023,43(4):483-488.
[3] 黄河,欧阳里知,胡明岸,等.基于生物传热学的艾灸疗法物理学剂量研究[J].世界中医药,2019,14(3):521-526.
[4] WU MC, DEOKAR AR, LIAO JH, et al. Graphene-based photothermal agent for rapid and effective killing of bacteria. ACS Nano. 2013;7(2):1281-1290.
[5] XIA MY, XIE Y, YU CH, et al. Graphene-based nanomaterials: the promising active agents for antibiotics-independent antibacterial applications. J Controll Release. 2019;307:16-31.
[6] TABISH TA, ZHANG S, WINYARD PG. Developing the next generation of graphene-based platforms for cancer therapeutics: The potential role of reactive oxygen species. Redox Biol. 2018;15:34-40.
[7] MATTEINI P, TATINI F, CAVIGLI L, et al. Graphene as a photothermal switch for controlled drug release. Nanoscale. 2014;6(14):7947-7953.
[8] HUI L, AULETTA JT, HUANG Z, et al. Surface disinfection enabled by a layer-by-layer thin film of polyelectrolyte-stabilized reduced graphene oxide upon solar near-infrared irradiation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(19):10511-10517.
[9] LIAO C, LI Y, TJONG SC. Graphene nanomaterials: Synthesis, biocompatibility, and cytotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3564.
[10] VUPPALADADIUM SSR, AGARWAL T, KULANTHAIVEL S, et al. Silanization improves biocompatibility of graphene oxide. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110:110647.
[11] WANG SD, MA Q, WANG K, et al. Improving antibacterial activity and biocompatibility of bioinspired electrospinning silk fibroin nanofibers modified by graphene oxide. ACS Omega. 2018;3(1):406-413.
[12] MA S, LU Y, ZHU X, et al. Efficient Modulation of Electron Pathways by Constructing a MnO2–x@ CeO2 Interface toward Advanced Lithium–Oxygen Batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(19):22104-22113.
[13] CHENG X, ZHANG X, SU D, et al. NO reduction by CO over copper catalyst supported on mixed CeO2 and Fe2O3: Catalyst design and activity test. Appl Catal B-Environ. 2018;239:485-501.
[14] EMA T, CHOI PG, TAKAMI S, et al. Facet-Controlled Synthesis of CeO2 Nanoparticles for High-Performance CeO2 Nanoparticle/SnO2 Nanosheet Hybrid Gas Sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(51):56998-57007.
[15] WANG Y, HUANG Y, FU Y, et al. Reductive damage induced autophagy inhibition for tumor therapy. Nano Res. 2023;16(4):5226-5236.
[16] ZHENG H, WANG S, CHENG F, et al. Bioactive anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, conductive multifunctional scaffold based on MXene@ CeO2 nanocomposites for infection-impaired skin multimodal therapy. Chem EngJ. 2021;424:130148.
[17] ALSHARIF NB, SAMU GF, SÁRINGER S, et al. Antioxidant colloids via heteroaggregation of cerium oxide nanoparticles and latex beads. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;216: 112531.
[18] SHIN SR, AGHAEI-GHAREH-BOLAGH B, DANG TT, et al. Cell-laden microengineered and mechanically tunable hybrid hydrogels of gelatin and graphene oxide. Adv Mater. 2013; 25(44):6385-6391.
[19] SRIVASTAVA M, DAS AK, KHANRA P, et al. Characterizations of in situ grown ceria nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide as a catalyst for the electrooxidation of hydrazine. J Mater Chem A Mater. 2013;1(34):9792-9801.
[20] ZHAO H, HUANG J, LI Y, et al. ROS-scavenging hydrogel to promote healing of bacteria infected diabetic wounds. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120286.
[21] TAO B, SHEN X, YUAN Z, et al. N-halamine-based multilayers on titanium substrates for antibacterial application. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;170:382-392.
[22] 成鸿群,刘宜成,徐金鹏,等.温和灸和雀啄灸温度场分布特点的实验研究[J].中国针灸,2021,41(10):1113-1117.
[23] 李松梅,赵彦春,赵娟,等.不同艾灸灸距和时长对糖尿病周围神经病变的疗效与安全性研究[J].北京中医药,2023,42(2):143-145.
[24] 毛珍,江润,段骏,等.不同灸量热敏灸治疗膝骨关节炎临床研究[J].针灸临床杂志,2022,38(10):52-56.
[25] 朱兵 . 关于灸材和灸温的思考 [J]. 针刺研究 ,2018,43(2):63-67.
[26] SONG Y, WANG Y, ZHU Y, et al. Biomodal tumor‐targeted and redox‐responsive Bi2Se3 hollow nanocubes for MSOT/CT imaging guided synergistic low‐temperature photothermal radiotherapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(16):1900250.
[27] 刘磊,王敏君,吴立斌,等.不同艾条直径和施灸距离对大鼠穴区皮肤表面温度的影响[J].针刺研究,2020,45(5):396-401.
[28] LIAO C, LI Y, TJONG SC. Graphene nanomaterials: Synthesis, biocompatibility, and cytotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11): 3564.
[29] 王永灵,蒉纲.艾灸疗法治疗外科创面的研究进展[J].湖北中医药大学学报,2012, 14(1):73-74.
[30] 张雪琳,高崚,陈新旺,等.艾烟的化学成分及药理活性研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(8):4560-4564.
[31] 张帆,吴立斌,刘磊,等.艾灸烟热效应促进大鼠外伤创面愈合及组织修复的研究[J].针刺研究,2021,46(7):575-579+585.
[32] XU C, PU K. Second near-infrared photothermal materials for combinational nanotheranostics. Chem Soc Rev. 2021;50(2):1111-1137.
[33] MEI L, ZHU S, YIN W, et al. Two-dimensional nanomaterials beyond graphene for antibacterial applications: current progress and future perspectives. Theranostics. 2020;10(2):757.
[34] WANG Y, LI J, LI X, et al. Graphene-based nanomaterials for cancer therapy and anti-infections. Bioact Mater. 2022;14:335-349.
[35] XIA MY, XIE Y, YU CH, et al. Graphene-based nanomaterials: the promising active agents for antibiotics-independent antibacterial applications. J Controll Release. 2019;307:16-31.
[36] LUO M, SHAITAN K, QU X, et al. Bioactive rare earth-based inorganic-organic hybrid biomaterials for wound healing and repair. Appl Mater Today. 2022;26:101304.
|