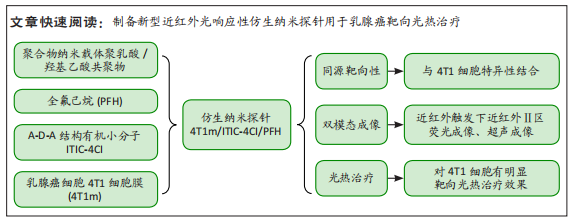
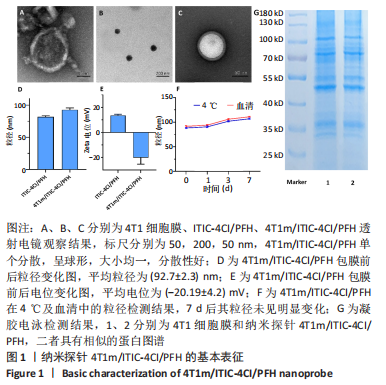
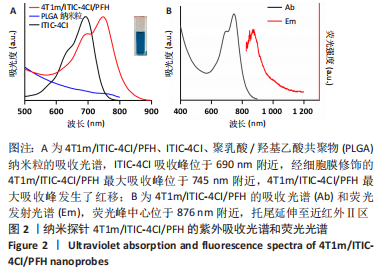
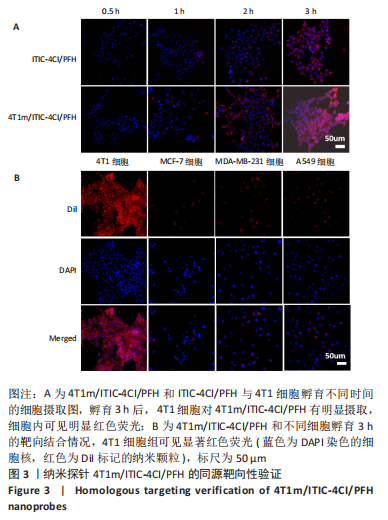
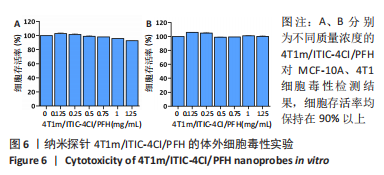
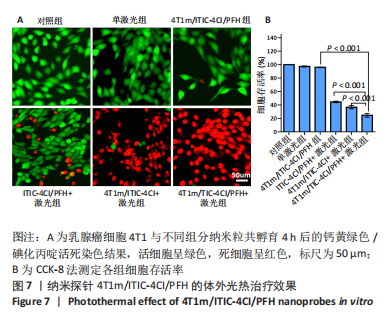
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249.
[2] LIU M, ANDERSON R, LAN X, et al. Recent advances in the development of nanoparticles for multimodality imaging and therapy of cancer. Med Res Rev. 2020;40(3):909-930.
[3] YAN D, WANG M, WU Q, et al. Multimodal imaging‐guided photothermal immunotherapy based on a versatile nir‐ii aggregation‐induced emission luminogen. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2022;61(27):e202202614.
[4] LIU Y, BHATTARAI P, DAI Z, et al. Photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging via nanotheranostics in fighting cancer. Chem Soc Rev. 2019;48(7):2053-2108.
[5] CHANG T, QIU Q, JI A, et al. Organic single molecule based nano-platform for nir-ii imaging and chemo-photothermal synergistic treatment of tumor. Biomaterials. 2022;287:121670.
[6] JI Y, JONES C, BAEK Y, et al. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging in immunotherapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;167:121-134.
[7] LI L, DONG X, LI J, et al. A short review on nir-ii organic small molecule dyes. Dyes Pigments 2020;183:108756.
[8] LI JB, LIU HW, FU T, et al. Recent progress in small-molecule near-ir probes for bioimaging. Spec. Issue Part Two Big Quest Chem. 2019; 1(2):224-234.
[9] 孙阳,王志刚.多功能超声造影剂分子显像与治疗研究进展[J].中国超声医学工程学会,2012,28(1):84-86.
[10] CUI T, YAN Z, QIN H, et al. A sequential target‐responsive nanocarrier with enhanced tumor penetration and neighboring effect in vivo. Small. 2019;15(42):1903323.
[11] DOAN VHM, NGUYEN VT, MONDAL S, et al. Fluorescence/photoacoustic imaging-guided nanomaterials for highly efficient cancer theragnostic agent. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):15943.
[12] PATIL Y, MISRA R. Rational molecular design towards nir absorption: efficient diketopyrrolopyrrole derivatives for organic solar cells and photothermal therapy. J Mater Chem C. 2019;7(42):13020-13031.
[13] JIA S, LI Z, SHAO J, et al. Acceptor regulation of acceptor–donor–acceptor type conjugated oligomer for photothermal combating of resistant bacteria. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2022;4(8):5275-5280.
[14] LI B, GAN Y, YANG K, et al. Acceptor-donor-acceptor structured phototheranostics for near-infrared ii fluorescent and photoacoustic imaging-guided photodynamic and photothermal synergistic therapy. Sci Chin Mater. 2022;66:385-396.
[15] WAN Y, LU G, WEI WC, et al. Stable organic photosensitizer nanoparticles with absorption peak beyond 800 nanometers and high reactive oxygen species yield for multimodality phototheranostics. ACS Nano. 2020;14(8):9917-9928.
[16] ZHANG Y, SHI M, YAN Z, et al. Ultrastable near-infrared nonlinear organic chromophore nanoparticles with intramolecular charge transfer for dually photoinduced tumor ablation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(20):2001042.
[17] HE Z, ZHAO L, ZHANG Q, et al. An acceptor–donor–acceptor structured small molecule for effective nir triggered dual phototherapy of cancer. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(16):1910301.
[18] JUNG HS, VERWILST P, SHARMA A, et al. Organic molecule-based photothermal agents: an expanding photothermal therapy universe. Chem Soc Rev. 2018;47(7):2280-2297.
[19] LI S, DENG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Rational design of conjugated small molecules for superior photothermal theranostics in the nir-ii biowindow. Adv Mater. 2020;32(33):2001146.
[20] LI L, HAN X, WANG M, et al. Recent advances in the development of near-infrared organic photothermal agents. Chem Eng J. 2021;417:128844.
[21] LI H, KIM Y, JUNG H, et al. Near-infrared (nir) fluorescence-emitting small organic molecules for cancer imaging and therapy. Chem Soc Rev. 2022;51(21):8957-9008.
[22] ZHEN X, CHENG P, PU K. Recent advances in cell membrane–camouflaged nanoparticles for cancer phototherapy. Small. 2019;15(1):1804105.
[23] FANG RH, HU CMJ, LUK BT, et al. Cancer cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for anticancer vaccination and drug delivery. Nano Lett. 2014;14(4):2181-2188.
[24] WANG Q, XIA B, XU J, et al. Biocompatible small organic molecule phototheranostics for nir-ii fluorescence/photoacoustic imaging and simultaneous photodynamic/photothermal combination therapy. Mater Chem Front. 2019;3(4):650-655.
[25] OZERSKAYA AV, ZAMAY TN, KOLOVSKAYA OS, et al. 11C-radiolabeled aptamer for imaging of tumors and metastases using positron emission tomography- computed tomography. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;26:1159-1172.
[26] ZIMMER WD, BERQUIST TH, MCLEOD RA, et al. Bone tumors: magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography. Radiology. 1985; 155(3):709-718.
[27] WANG G, SONG L, HOU X, et al. Surface-modified gvs as nanosized contrast agents for molecular ultrasound imaging of tumor. Biomaterials. 2020;236:119803.
[28] ZHANG L, LIU Y, HUANG H, et al. Multifunctional nanotheranostics for near infrared optical imaging-guided treatment of brain tumors. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;190:114536.
[29] PATHAK V, NOLTE T, RAMA E, et al. Molecular magnetic resonance imaging of alpha-v-beta-3 integrin expression in tumors with ultrasound microbubbles. Biomaterials. 2021;275:120896.
[30] 甘甜,王文渊,晏殊瑾,等.携载LXR激动剂近红外光响应性纳米粒的光热协同免疫效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(12):1863-1869.
[31] ZHANG C, LIU J, GUO H, et al. Theranostic nanomedicine carrying l-menthol and near-infrared dye for multimodal imaging-guided photothermal therapy of cancer. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(16):1900409.
[32] LI S, DENG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Rational design of conjugated small molecules for superior photothermal theranostics in the nir-ii biowindow. Adv Mater. 2020;32(33):2001146.
[33] CAI Y, WEI Z, SONG C, et al. Novel acceptor–donor–acceptor structured small molecule-based nanoparticles for highly efficient photothermal therapy. Chem Commun. 2019;55(61):8967-8970.
[34] WAN X, LI C, ZHANG M, et al. Acceptor–donor–acceptor type molecules for high performance organic photovoltaics – chemistry and mechanism. Chem Soc Rev. 2020;49(9):2828-2842.
[35] 黄建波,杨林,阳锐,等.岩藻多糖修饰的相变型造影剂体外超声显像及靶向肝癌的实验研究[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2022, 53(5):752-757.
[36] PEI X, PAN X, XU X, et al. 4T1 cell membrane fragment reunited pamam polymer units disguised as tumor cell clusters for tumor homotypic targeting and anti-metastasis treatment. Biomater. Sci. 2021;9(4):1325-1333.
[37] LI H, LIU Y, HUANG B, et al. Highly efficient gsh-responsive “off–on” nir-ii fluorescent fenton nanocatalyst for multimodal imaging-guided photothermal/chemodynamic synergistic cancer therapy. Anal Chem. 2022;94(29):10470-10478.
[38] ZHU L, ZHONG Y, WU S, et al. Cell membrane camouflaged biomimetic nanoparticles: focusing on tumor theranostics. Mater Today Bio. 2022; 14:100228.
[39] 王红卫,卓忠雄,赵延新,等.超声辐照瘤内注射微泡空化效应的病理学研究[J].中国超声医学杂志,2007(4):256-258.
[40] 周裕卿,彭玉兰,杨林,等.全氟化碳纳米粒在超声分子成像和治疗中的应用[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2022,30(5):514-517. |